Содержание
- 2. Ionization Energy The amount of energy required to completely remove an electron from a gaseous atom.
- 3. Ionization Energy The second and third ionization energies can be represented as follows: X+ (g) +
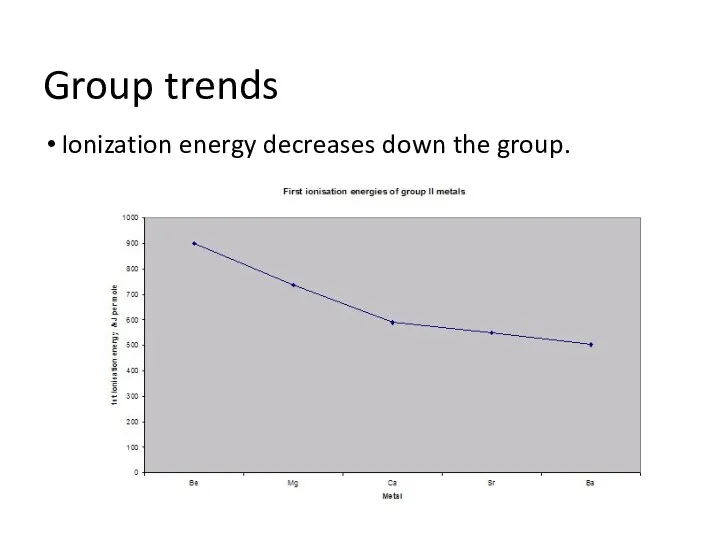
- 4. Group trends Ionization energy decreases down the group.
- 5. Going from Be to Mg, IE decreases because: Mg outer electron is in the 3s sub-shell
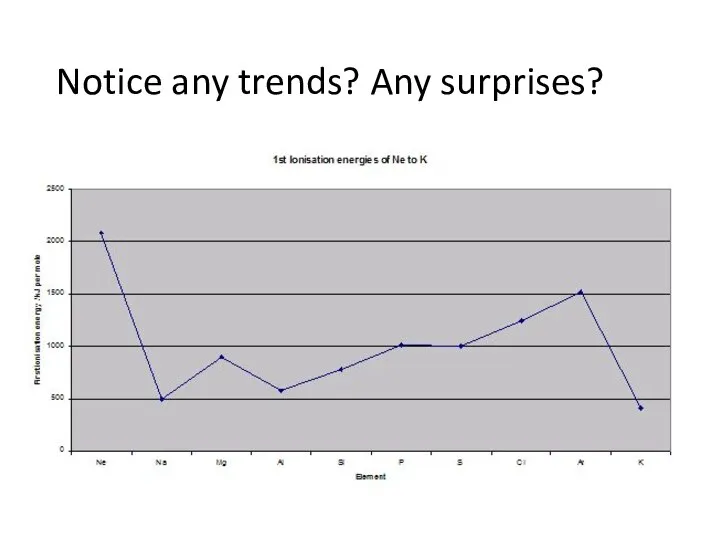
- 6. Notice any trends? Any surprises?
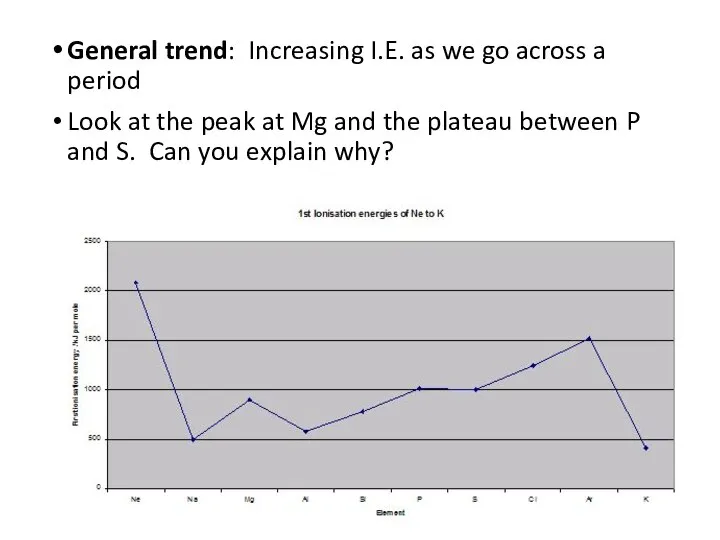
- 7. General trend: Increasing I.E. as we go across a period Look at the peak at Mg
- 8. Why is there a fall from Mg to Al? Al has configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
- 9. Why is there a fall from P to S? This can be explained in terms of
- 10. Driving Force Full Energy Levels are very low energy. Noble Gases have full energy levels. Atoms
- 11. 2nd Ionization Energy For elements that reach a filled or half filled sublevel by removing 2
- 13. Скачать презентацию







 Производство азотной кислоты
Производство азотной кислоты Обмен липидов. Часть 2
Обмен липидов. Часть 2 «Оксиды на службе у человека».
«Оксиды на службе у человека». Физиология микроорганизмов. (Лекция 7)
Физиология микроорганизмов. (Лекция 7) Пятичленные гетероциклические соединения. Профильный уровень
Пятичленные гетероциклические соединения. Профильный уровень Алюминий. Строение
Алюминий. Строение Газоподібна і тверда фаза грунту. Методи аналізу зернового складу
Газоподібна і тверда фаза грунту. Методи аналізу зернового складу Презентация по Химии "Вещества, входящие в состав живых организмов" - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Вещества, входящие в состав живых организмов" - скачать смотреть бесплатно Галогены. Физические свойства галогенов
Галогены. Физические свойства галогенов Задача на химическое равновесие
Задача на химическое равновесие Кремний и его соединения
Кремний и его соединения Барометр – анероид. Атмосферное давление на различных высотах. Манометры
Барометр – анероид. Атмосферное давление на различных высотах. Манометры Основные постулаты квантовой механики
Основные постулаты квантовой механики Факторы влияющие на скорость химической реакции
Факторы влияющие на скорость химической реакции Вода - уникальнейшая структура жизни. Способы ее очистки
Вода - уникальнейшая структура жизни. Способы ее очистки Азот
Азот Органическая химия. История развития
Органическая химия. История развития Э.М. Спиридонов. Эволюция минералов олова в зоне гипергенеза
Э.М. Спиридонов. Эволюция минералов олова в зоне гипергенеза Бактериалық жасушаның химиялық құрамы
Бактериалық жасушаның химиялық құрамы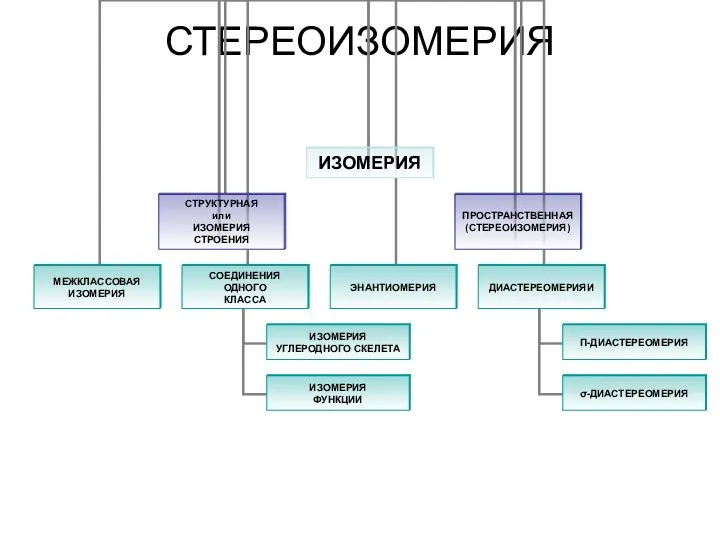 Стереоизомерия. Изомерия. Пространственная (стереоизомерия) углеродного скелета
Стереоизомерия. Изомерия. Пространственная (стереоизомерия) углеродного скелета Неметаллы. Положение неметаллов в ПСХЭ Д.И. Менделеева. Галогены
Неметаллы. Положение неметаллов в ПСХЭ Д.И. Менделеева. Галогены Биохимия нервной и мышечной ткани
Биохимия нервной и мышечной ткани Азотсодержащие органические соединения
Азотсодержащие органические соединения Текстовые задачи в ЕГЭ Задачи на проценты В12
Текстовые задачи в ЕГЭ Задачи на проценты В12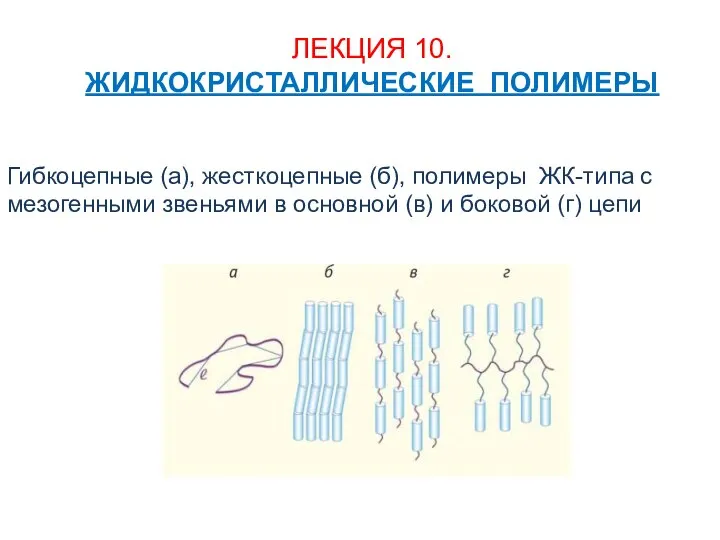 Жидкокристаллические полимеры
Жидкокристаллические полимеры Полиэтилен высокого давления
Полиэтилен высокого давления Вуглеводи
Вуглеводи Silicon. Silicate minerals. Weathering
Silicon. Silicate minerals. Weathering