Содержание
- 2. Class – why? Classes split application code to parts (from sophisticated to simple) Very often class
- 3. Class Description class name { // field declarations // method declarations } * Infopulse Training Center
- 4. Class Fields Class fields should be declared inside class out of all class methods Fields can
- 5. Defining Methods return_type method_name (parameter_list){ // method body } Example: int getFinalData(int a, int r){ int
- 6. Return Type The return type describes the value that comes back from the method A method
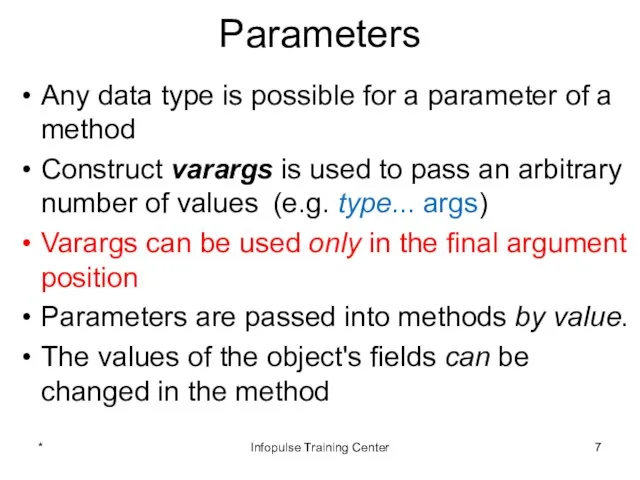
- 7. Parameters Any data type is possible for a parameter of a method Construct varargs is used
- 8. Constructors Constructor name should be the same as class name Constructor has no return type The
- 9. Objects Creating Object: class_name object_variable = new construtor_call; Declaring a Variable to Refer to an Object:
- 10. Using the this Keyword this is a reference to the current object The most common example:
- 11. Complex Numbers (1 of 4) Is it always possible to solve square equation within real numbers
- 12. Complex Numbers (2 of 4) Is it always possible to solve square equation within real numbers
- 13. Complex Numbers (3 of 4) Number of a + b * i type where a and
- 14. Complex Numbers (4 of 4) To add complex numbers use formula To multiply complex numbers use
- 15. Exercise 2.4.1. Create a class for saving and manipulating complex numbers. * Infopulse Training Center
- 16. Home Exercise 2.4.2 (1 of 2) 3D Vector is ordered sequence of 3 numbers (vector’s coordinates):
- 18. Скачать презентацию














 Основні категорії теорії баз даних і типи зв’язків між ними
Основні категорії теорії баз даних і типи зв’язків між ними Управление компьютером с помощью меню
Управление компьютером с помощью меню Техническое задание. Система голосования v3. Регистрация. Страница регистрации на сайте
Техническое задание. Система голосования v3. Регистрация. Страница регистрации на сайте Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц
Решение логических задач с помощью нескольких таблиц Домеханические и механические счетные машины
Домеханические и механические счетные машины Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office Презентация "Апробация электронных учебников в общеобразовательных учреждениях" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Апробация электронных учебников в общеобразовательных учреждениях" - скачать презентации по Информатике Схемотехника комбинационных узлов
Схемотехника комбинационных узлов Работа на клавиатуре. Назначение клавиш
Работа на клавиатуре. Назначение клавиш Информационные технологии
Информационные технологии Набор Lego Mindstorms EV3 Education
Набор Lego Mindstorms EV3 Education САОД (stl)
САОД (stl) Методолия моделирования социально-экономических процессов
Методолия моделирования социально-экономических процессов Патерни проектування
Патерни проектування Continuous integration
Continuous integration Сказка о том, откуда возникла наука Информатика
Сказка о том, откуда возникла наука Информатика Презентация "Путешествие на остров Информация" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Путешествие на остров Информация" - скачать презентации по Информатике Web - каталоги. Принципы организации и применения поисковых машин. Стратегии поиска информации
Web - каталоги. Принципы организации и применения поисковых машин. Стратегии поиска информации Середовище описання і виконання алгоритмів
Середовище описання і виконання алгоритмів HTML. Язык описания Web-страниц
HTML. Язык описания Web-страниц Двоичная система счисления
Двоичная система счисления Технологии разработки ПО. Основные понятия и определения
Технологии разработки ПО. Основные понятия и определения Операционная система(ОС)
Операционная система(ОС) Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL
Решение расчётной задачи в среде электронной таблицы EXCEL Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа дополнительного образования Мир программирования Scratch
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа дополнительного образования Мир программирования Scratch Презентация "Накопители на гибких магнитных дисках (НГМД)" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Накопители на гибких магнитных дисках (НГМД)" - скачать презентации по Информатике Мой любимый Интернет. Библиотечный урок по информационной культуре для среднего школьного возраста
Мой любимый Интернет. Библиотечный урок по информационной культуре для среднего школьного возраста Отчет о практической работе
Отчет о практической работе