Содержание
- 2. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chapter Topics Why a manager needs
- 3. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chapter Topics Why data are needed
- 4. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Why a Manager Needs to Know
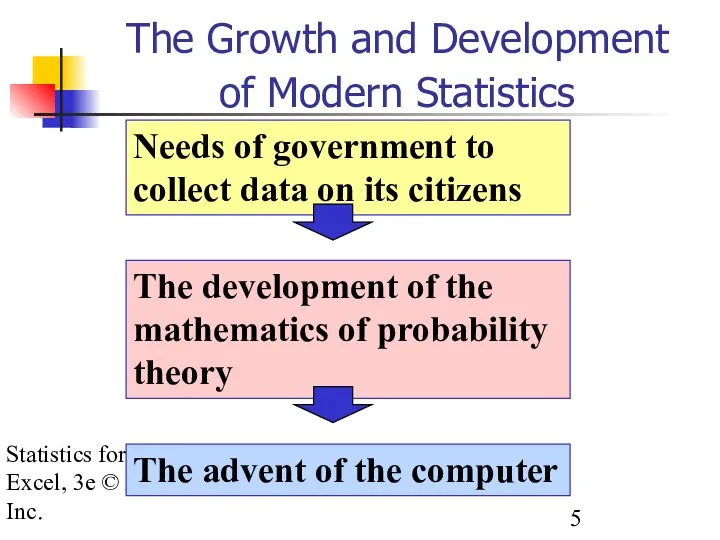
- 5. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. The Growth and Development of Modern
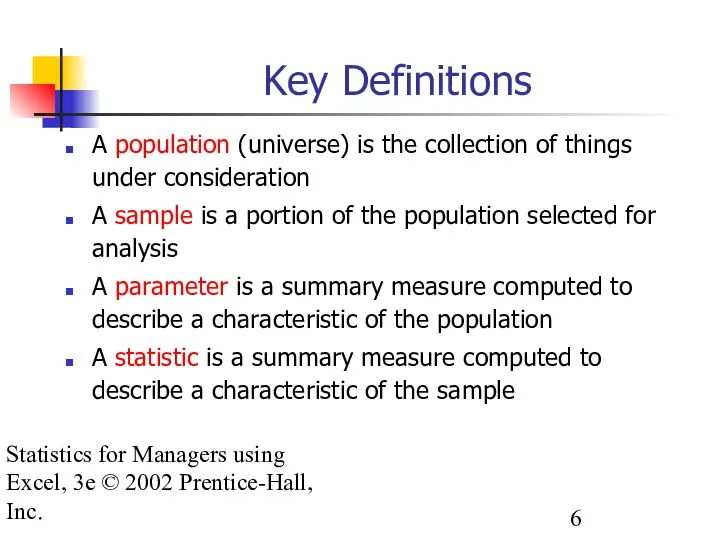
- 6. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Key Definitions A population (universe) is
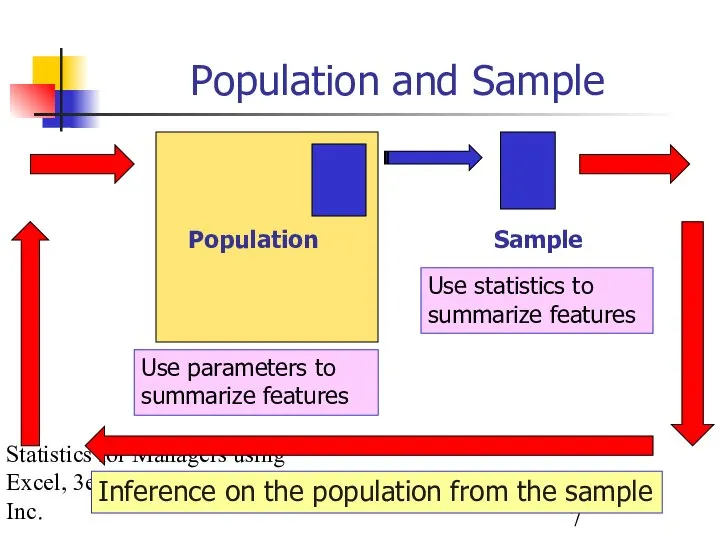
- 7. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Population and Sample Population Sample Use
- 8. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Statistical Methods Descriptive statistics Collecting and
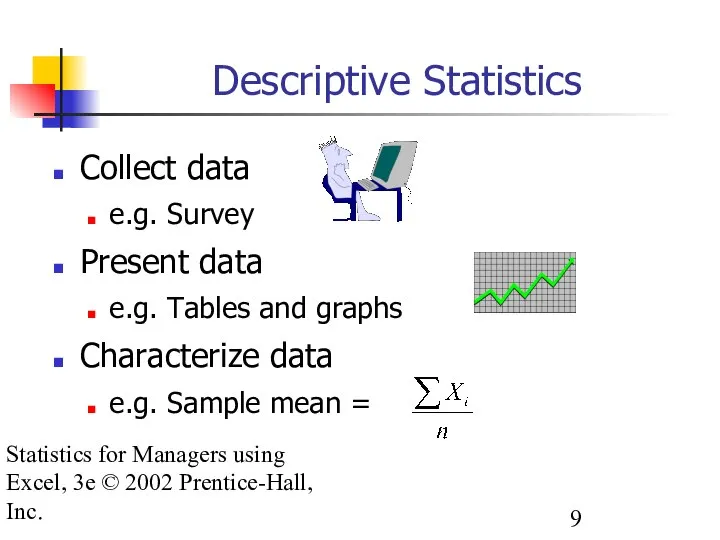
- 9. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Descriptive Statistics Collect data e.g. Survey
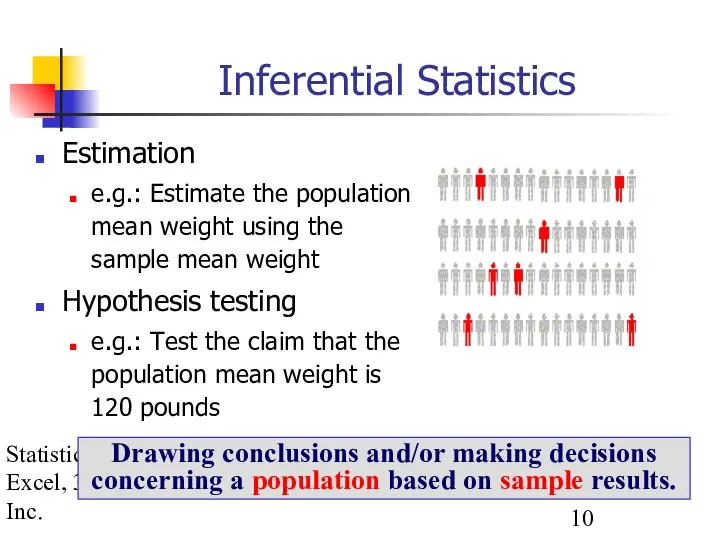
- 10. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Inferential Statistics Estimation e.g.: Estimate the
- 11. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Why We Need Data To provide
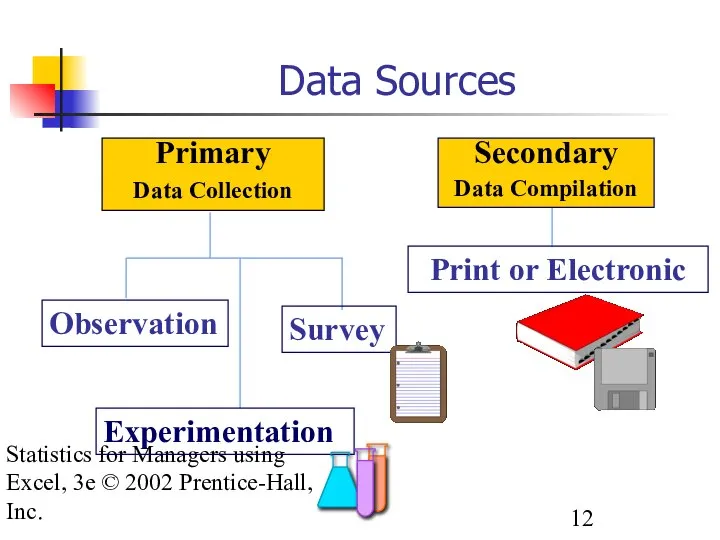
- 12. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Data Sources Primary Data Collection Secondary
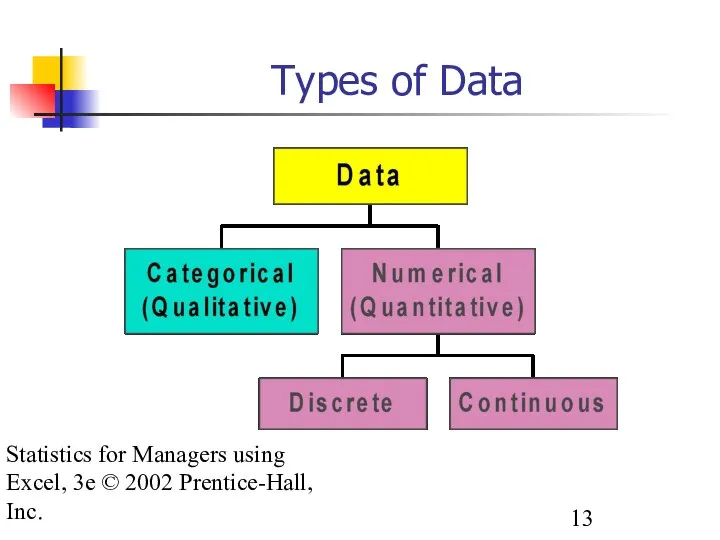
- 13. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Types of Data
- 14. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Design of Survey Research Choose an
- 15. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Design of Survey Research Identify broad
- 16. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Design of Survey Research Write a
- 17. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Reasons for Drawing a Sample Less
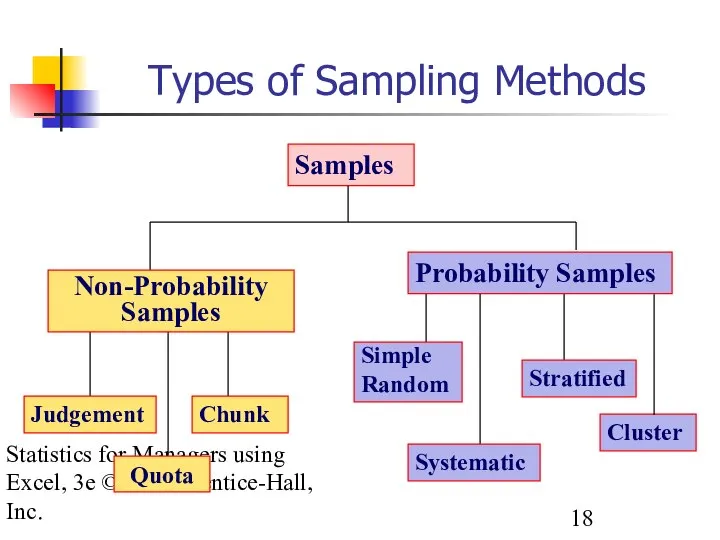
- 18. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Types of Sampling Methods Quota Samples
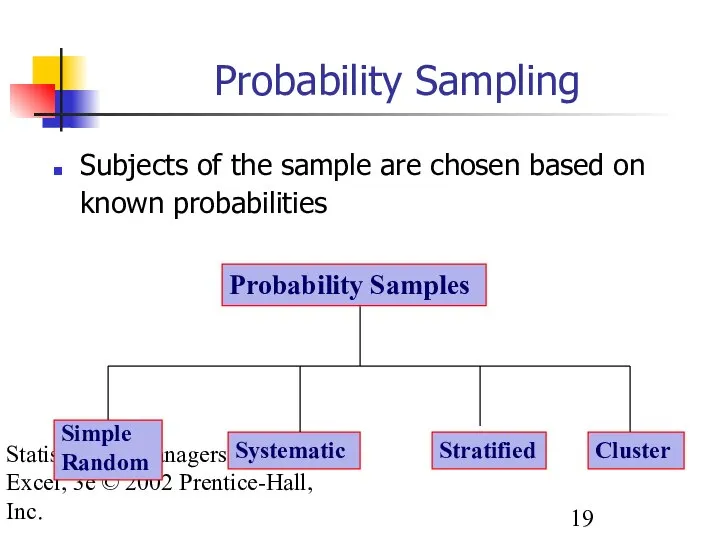
- 19. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Probability Sampling Subjects of the sample
- 20. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Simple Random Samples Every individual or
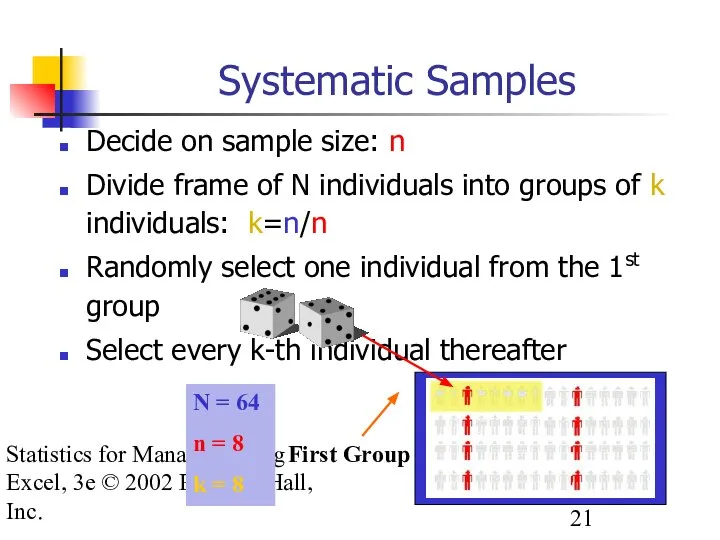
- 21. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Decide on sample size: n Divide
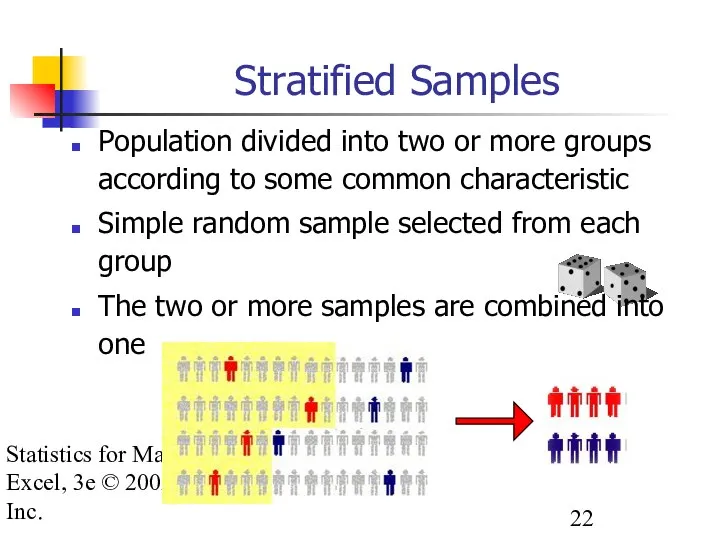
- 22. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Stratified Samples Population divided into two
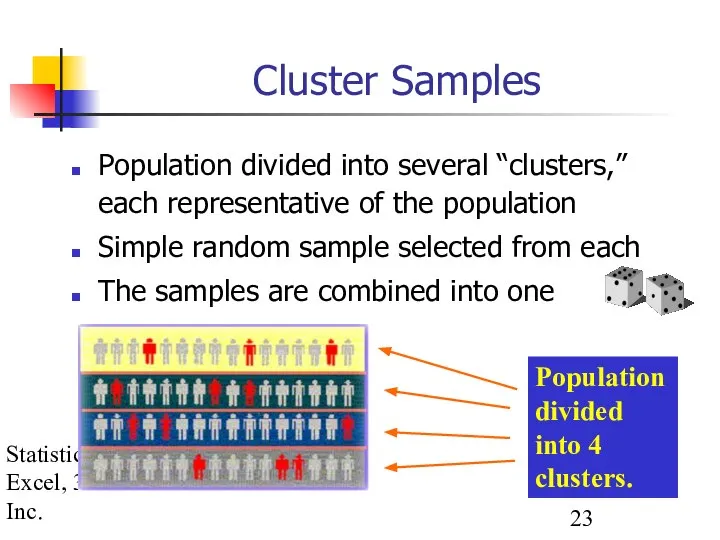
- 23. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Cluster Samples Population divided into several
- 24. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Advantages and Disadvantages Simple random sample
- 25. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Evaluating Survey Worthiness What is the
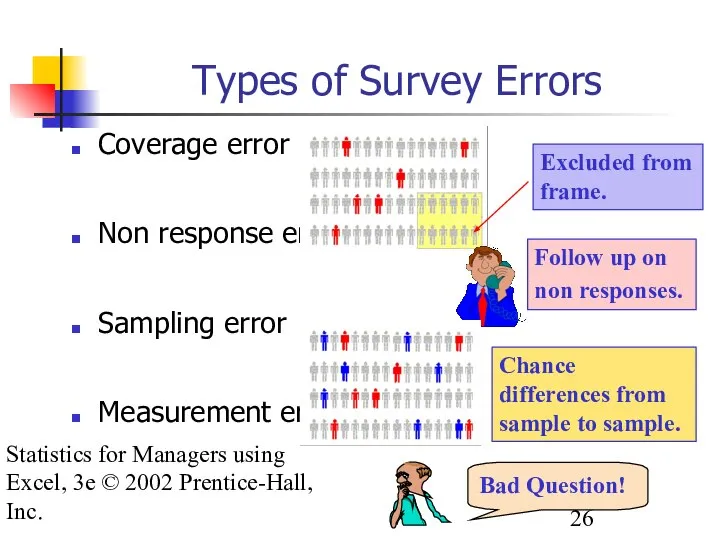
- 26. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Types of Survey Errors Coverage error
- 27. Statistics for Managers using Excel, 3e © 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chapter Summary Addressed why a manager
- 29. Скачать презентацию












 Модуль экспертной системы построения функции принадлежности нечетких множеств
Модуль экспертной системы построения функции принадлежности нечетких множеств Социальные сети
Социальные сети Барни Калхун из игры Halflife 2
Барни Калхун из игры Halflife 2 Фреймы
Фреймы 1С:Музей и 1С:Музейный каталог
1С:Музей и 1С:Музейный каталог Логика. Основные понятия
Логика. Основные понятия Электронная почта и другие серверы компьютерных сетей
Электронная почта и другие серверы компьютерных сетей Инфографика
Инфографика Презентация "10 вариантов одной логической задачи" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "10 вариантов одной логической задачи" - скачать презентации по Информатике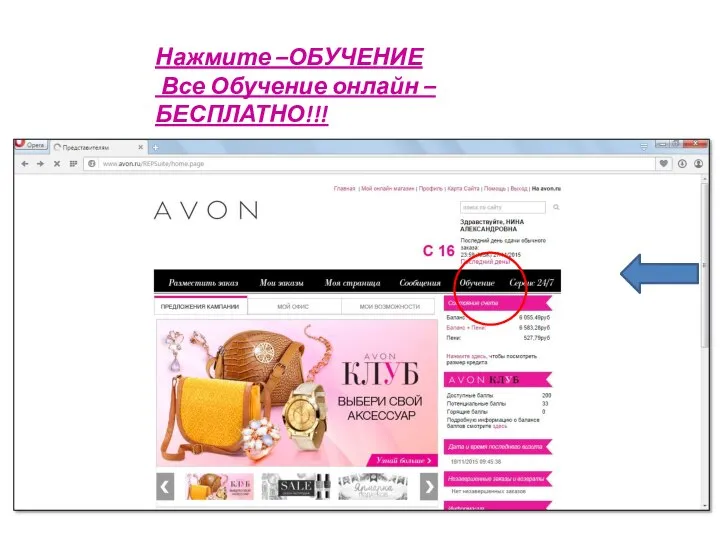 Как пройти онлайн-обучение в Avon
Как пройти онлайн-обучение в Avon Виды и форматы оптических дисков
Виды и форматы оптических дисков Формы записи алгоритмов
Формы записи алгоритмов Проектирование связей между таблицами баз данных
Проектирование связей между таблицами баз данных Виртуальная мобильная АТС
Виртуальная мобильная АТС Использование программ в среде ГРИС "Стрелочка"
Использование программ в среде ГРИС "Стрелочка" Операционные системы
Операционные системы ВМСиС Слайды лек 07
ВМСиС Слайды лек 07 Инструкция по работе с онлайн-трансляциями лекций по дисциплине Налоговое право
Инструкция по работе с онлайн-трансляциями лекций по дисциплине Налоговое право Виды компьютерной графики
Виды компьютерной графики Решение задач по теме: перевод чисел из одной системы счисления в другую
Решение задач по теме: перевод чисел из одной системы счисления в другую Делаем слайды для презентации. Типичные ошибки на плохих слайдах
Делаем слайды для презентации. Типичные ошибки на плохих слайдах Повышение безопасности и улучшение условий труда путем внедрения системы с числовым программным управлением
Повышение безопасности и улучшение условий труда путем внедрения системы с числовым программным управлением Требования к разработке ПО
Требования к разработке ПО Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Unix/Linux
Unix/Linux Модели данных. Реляционная модель
Модели данных. Реляционная модель Хмарні технології (віддалена обробка та зберігання даних)
Хмарні технології (віддалена обробка та зберігання даних) Java course
Java course