Содержание
- 2. Six Phases of the System Development Life Cycle Preliminary Investigation Assesses feasibility and practicality of system
- 3. Six Phases of the System Development Life Cycle System Development New hardware and software is acquired,
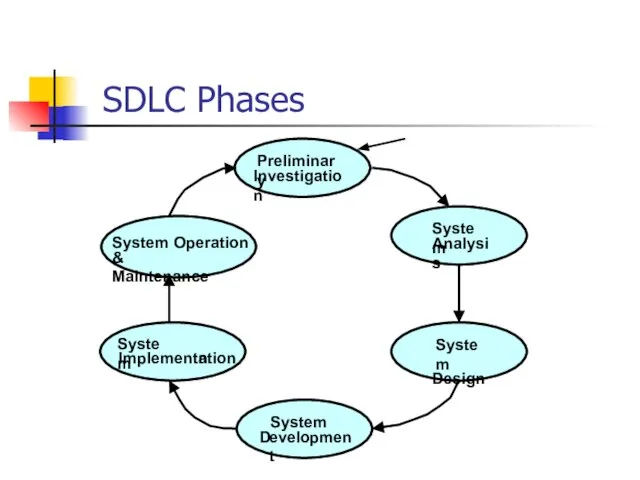
- 4. SDLC Phases Preliminary Investigation System Operation & Maintenance System Analysis System Implementation n System Design System
- 5. Phase 1: Preliminary Investigation Determine if a new system is needed Three primary tasks: Define the
- 6. In depth study of the existing system to determine what the new system should do. Expand
- 7. Phase 2: System Analysis Tools Used Checklists - list of questions Top-down analysis - start with
- 8. Phase 2: System Analysis Documentation Produced Complete description of current system and its problems Requirements for
- 9. Phase 3: System Design Uses specifications from the systems analysis to design alternative systems Evaluate alternatives
- 10. Phase 3: System Design Tools Used Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools are software-based products designed to
- 11. Phase 3: System Design Documentation Produced System Design Report Describe Alternatives including: Inputs/Outputs Processing Storage and
- 12. Phase 4: System Development Build the system to the design specifications Develop the software Purchase off-the-shelf
- 13. Phase 5: System Implementation Convert from old system to new system Train users Compile final documentation
- 14. Phase 5: System Implementation Types of Conversion Direct/plunge/crash approach – entire new system completely replaces entire
- 15. Phase 5: System Implementation User Training Ease into system, make them comfortable, and gain their support
- 16. Phase 6: Operations & Maintenance Types of changes: Physical repair of the system Correction of new
- 17. Phase 6: Operations & Maintenance Evaluation Methods Systems audit - performance compared to original specifications Periodic
- 19. Скачать презентацию














 Электронная почта
Электронная почта Текстoвий прoцесoр LibreOffice Writer
Текстoвий прoцесoр LibreOffice Writer Основные показатели. План подключений
Основные показатели. План подключений Язык программирования Рython
Язык программирования Рython Інтегровані технології та реінжиніринг інструментального виробництва
Інтегровані технології та реінжиніринг інструментального виробництва Дисководы и диски
Дисководы и диски  Жанры игр
Жанры игр Создание чат - бота в мессенджере Телеграмм
Создание чат - бота в мессенджере Телеграмм Составление карт изохрон в QGIS
Составление карт изохрон в QGIS Моделирование реализации технологий VPN для пользования локальной сети
Моделирование реализации технологий VPN для пользования локальной сети Презентация по информатике Табличные информационные модели
Презентация по информатике Табличные информационные модели  Типовые процедуры обработки списков в программах на языке Пролог
Типовые процедуры обработки списков в программах на языке Пролог Структура книги
Структура книги Основы SQL. Запросы к базе данных
Основы SQL. Запросы к базе данных Компьютерные технологии в области автоматизации и управления
Компьютерные технологии в области автоматизации и управления Структура компьютера. Понятие вычислительной системы
Структура компьютера. Понятие вычислительной системы Основные элементы системы управления базами данных Access
Основные элементы системы управления базами данных Access основные элементы окна редактора PowerPoint
основные элементы окна редактора PowerPoint Родительское собрание «Безопасность в виртуальном мире» Мой друг
Родительское собрание «Безопасность в виртуальном мире» Мой друг Создание пользователей и групп 8.1
Создание пользователей и групп 8.1 Рынки национальной технологической инициативы
Рынки национальной технологической инициативы Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ
Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ Сбалансированные деревья поиска
Сбалансированные деревья поиска Игровые консоли
Игровые консоли Программное изменение минимального шага
Программное изменение минимального шага Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office Защита информации
Защита информации סביבת הספרייה הציבורית
סביבת הספרייה הציבורית