Содержание
- 2. PROMOTION Promotion describes the methods used by a business to inform, persuade a target market about
- 3. Promotion The communication Process Promotional mix Developing Ad program Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relation Developing
- 4. Promotion
- 5. Promotion Promotion represents the fourth element in the marketing mix (4 p’s) Promotional is a mix
- 6. Promotion objectives Advertising objectives can be classified by primary purpose: Inform Introducing new products Persuade Becomes
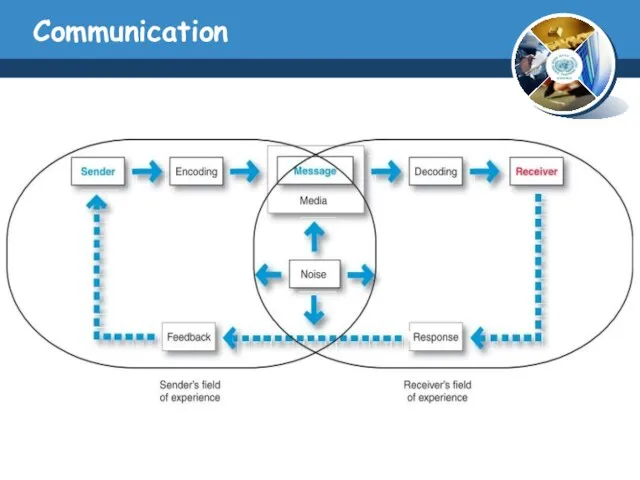
- 7. Communication Communication: is the sharing of meaning and requires five elements a source, a massage, a
- 8. Communication
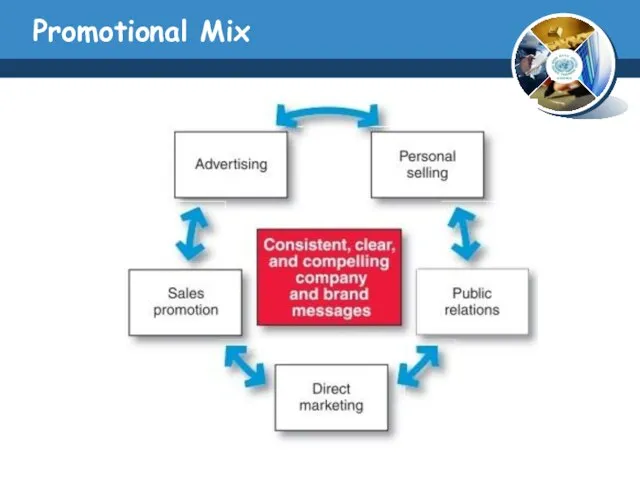
- 9. Promotional Mix
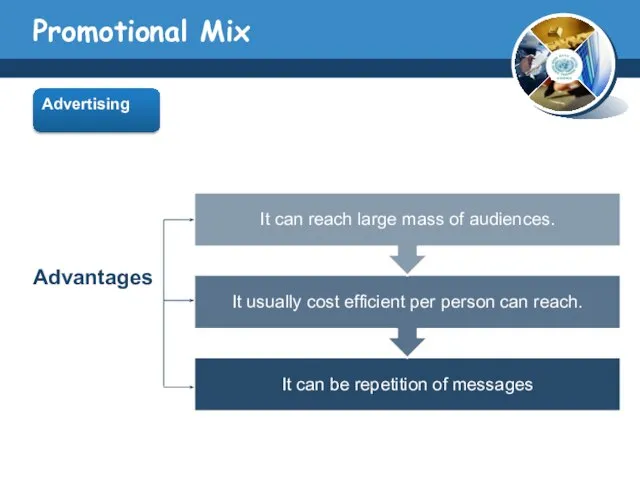
- 10. Promotional Mix Advertising ADVERTISING paid, impersonal communication regarding goods, services, organizations, people, places, and ideas that
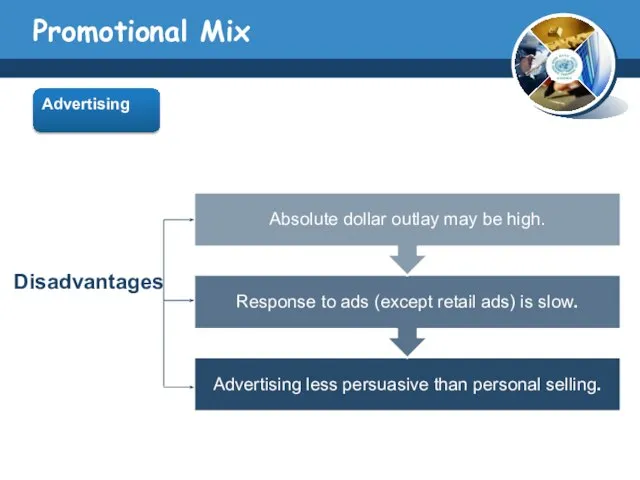
- 11. Promotional Mix Advertising
- 12. Promotional Mix Advertising
- 13. Promotional Mix Personal Selling Face to face communication is buyers to inform and persuade them to
- 14. Promotional Mix Personal Selling PERSONAL selling: involves oral communication with one or more prospective buyers by
- 15. Promotional Mix Sales Promotion Sales promotion activities are important to build traffic, attract attention, generate increased
- 16. Promotional Mix Public Relation Publicity is no personal public relations that is transmitted Public relations includes
- 17. Promotional Mix Public Relation It may be personal or impersonal, paid or unpaid, and sponsor controlled
- 18. Developing And Managing An Advertising Program
- 19. Developing & Managing An Advertising Program Advertising is any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion
- 20. Developing & Managing An Advertising Program In developing an advertising program, marketing managers must always start
- 21. Objectives of Advertising An advertising goal (or objective) is a specific communications task and achievement level
- 22. Advertising Budget Specific Factors To Consider When Setting The Advertising Budget. Stage in the product life
- 23. Advertising Budget Specific Factors To Consider When Setting The Advertising Budget. Competition and clutter- In a
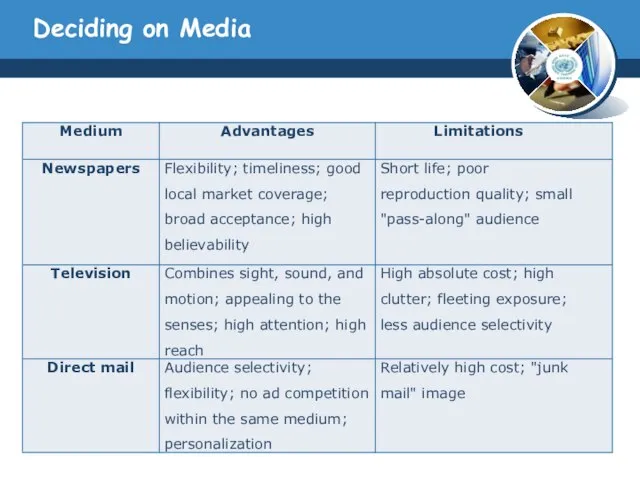
- 24. Deciding on Media Deciding on Reach, Frequency, and Impact Media selection is finding the most cost-effective
- 25. Deciding on Media Choosing Among Major Media Types The media planner has to know the capacity
- 26. Deciding on Media
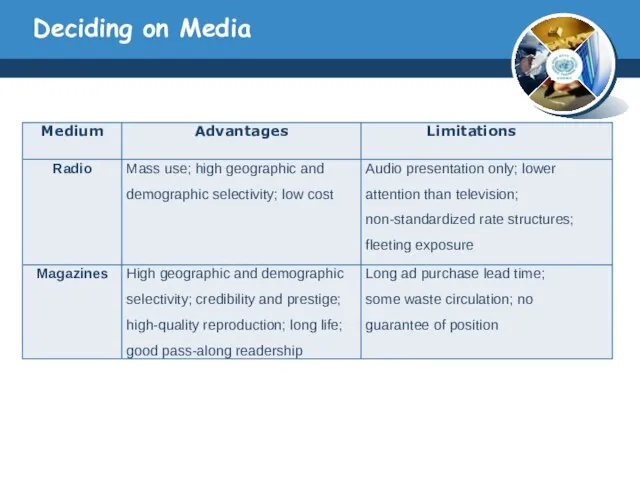
- 27. Deciding on Media
- 28. Deciding on Media
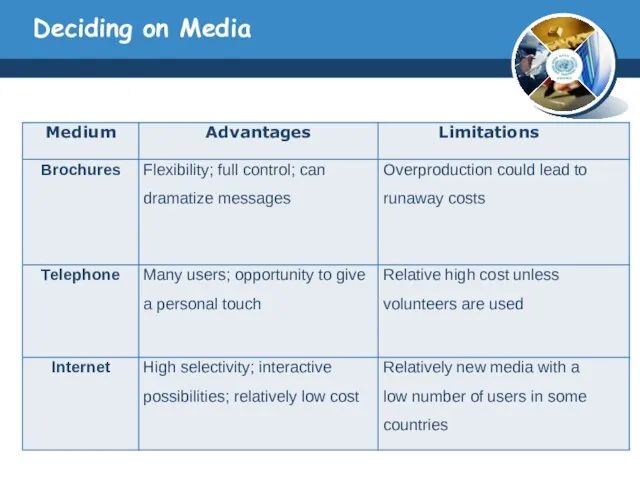
- 29. Deciding on Media
- 30. Deciding on Media Media planners make their choices by considering the following variables: Target audience media
- 31. Deciding on Media Media planners make their choices by considering the following variables: Message characteristics. A
- 32. Deciding on Media Media planners make their choices by considering the following variables: Cost Television is
- 33. Deciding on Media Evaluating Advertising Effectiveness Good planning and control of advertising depend on measures of
- 34. Deciding on Media Evaluating Advertising Effectiveness Communication-effect research seeks to determine whether an ad is communicating
- 35. Deciding on Media Evaluating Advertising Effectiveness Portfolio tests Ask consumers to view or listen to a
- 36. Deciding on Media Evaluating Advertising Effectiveness Laboratory Tests: Use equipment to measure physiological reactions—heartbeat, blood pressure,
- 37. Sales Promotion
- 38. Sales Promotion Sales promotion, a key ingredient in marketing campaigns, consists of a collection of incentive
- 39. Sales promotion includes tools Consumer promotion (samples, coupons, cash refund offers, prices off, premiums, prizes, patronage
- 40. Sales promotion includes tools Trade promotion (prices off, advertising and display allowances, and free goods). Business
- 41. Purpose of sales promotion Attract new triers or brand switchers Reward loyal customers Increase repurchase rates
- 43. Скачать презентацию

































 Сеть кафе “Вилки Нет”
Сеть кафе “Вилки Нет” Языковые особенности рекламных слоганов
Языковые особенности рекламных слоганов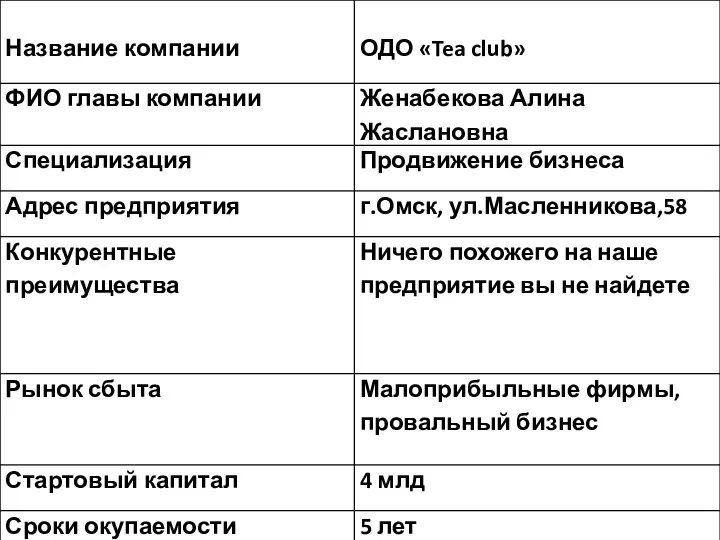 Компания ОДО Tea club. Продвижение бизнеса
Компания ОДО Tea club. Продвижение бизнеса Подходы к оценке эффективности информационного моделирования
Подходы к оценке эффективности информационного моделирования Актуальная версия приложения
Актуальная версия приложения Ателье Булавочка
Ателье Булавочка Позиционирование товара на рынке
Позиционирование товара на рынке Южный вкус Pulpy-Milk
Южный вкус Pulpy-Milk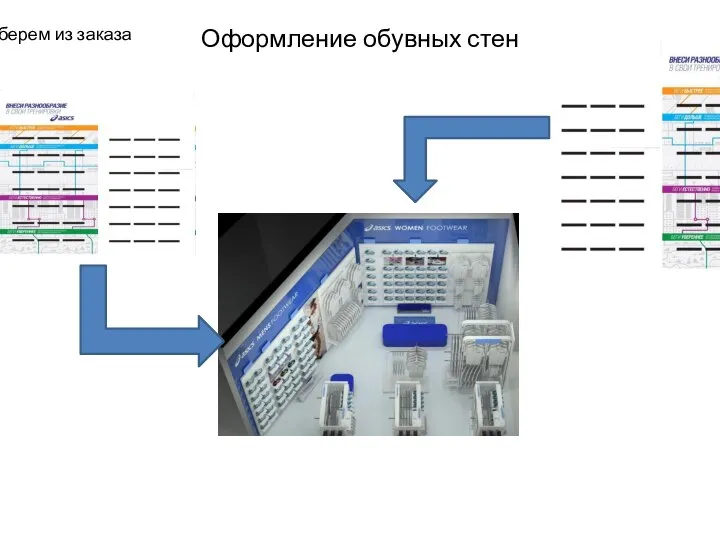 Оформление обувных стен
Оформление обувных стен Тандыр. Осетинские пироги
Тандыр. Осетинские пироги Этапы продаж
Этапы продаж Опыт компании Солво по внедрению WMS на рынках России и СНГ
Опыт компании Солво по внедрению WMS на рынках России и СНГ Виды рекламных объявлений
Виды рекламных объявлений Ойынның шарттары. Біздің Технодом
Ойынның шарттары. Біздің Технодом Что такое Маскоты компаний
Что такое Маскоты компаний Маркетинговое исследование. Ювелирные изделия Thomas Sabo
Маркетинговое исследование. Ювелирные изделия Thomas Sabo Реклама в СССР
Реклама в СССР Фармацевтический маркетинг
Фармацевтический маркетинг WiMAX. Бизнес модель
WiMAX. Бизнес модель РЭП Ижевский канал ТТ (промежуточные итоги ноября)
РЭП Ижевский канал ТТ (промежуточные итоги ноября) Coral Detox и Coral Detox Plus
Coral Detox и Coral Detox Plus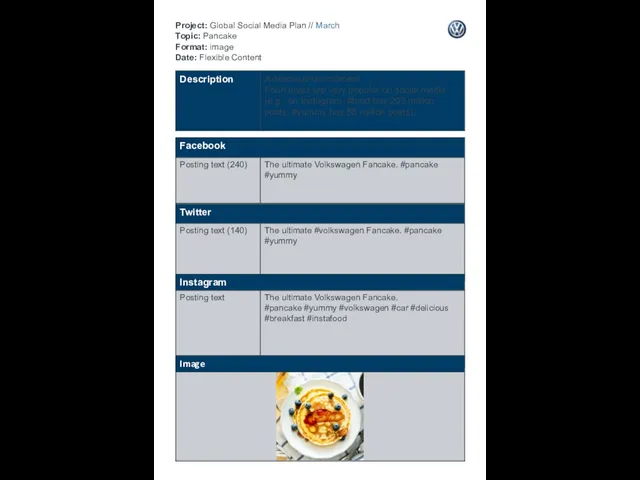 Project: Global Social Media Plan // March Topic: Pancake Format: image Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // March Topic: Pancake Format: image Date: Flexible Content First National Group
First National Group Акция Карамельная зима
Акция Карамельная зима Компания Revent. Производство ротационных печей
Компания Revent. Производство ротационных печей Nicol Professional Cosmetics. Каталог продукции
Nicol Professional Cosmetics. Каталог продукции Проведение мероприятий на стадионе ЮНОСТЬ 18.05.2021 г
Проведение мероприятий на стадионе ЮНОСТЬ 18.05.2021 г Pizza Papa John`s. 01 march – 13 march
Pizza Papa John`s. 01 march – 13 march