Содержание
- 2. You are a scientist in the field of ecology and you were given the task to
- 3. Data collection and analysis Methods of mathematical statistics The application of these methods makes it possible
- 4. Types of statistical test T-test (Student’s T-test) Use to test the equality of the average values
- 5. T-test 2 test groups Determining the differences between the two groups One or more samples per
- 6. Example of research question Which species of pine (Scotch or Kulunda) are more common in Kazakhstan?
- 7. Examples of Hypotheses Research Hypotheses In Kazakhstan the Kulunda pine is more common Statistical hypotheses Null
- 8. Methods of ecological research Laboratory method Experimental and experimental method Field method The objects of field
- 9. Objectives of field researches Determine (определить) the distribution (распространение), abundance (численность) and quality of the species,
- 10. Methods of field research Lay out and describe a sample area (закладка и описание пробных площадей
- 12. Example Question: Which part of the school garden has more dandelions? Research hypothesis: Null hypothesis: Alternate
- 13. Method of research (squares method or key sites) метод квадратов или ключевых участков Select the sample
- 14. Data collection Number of dandelions on the school garden
- 15. Step 1 Calculate the mean value
- 17. Step 2 Calculate the deviation from mean by subtracting the mean from the value of X
- 19. Step 3 Square the deviation from the mean for both the samples
- 21. Step 4 Calculate the sum of the squares
- 23. Step 5 Calculate the variance for both the samples
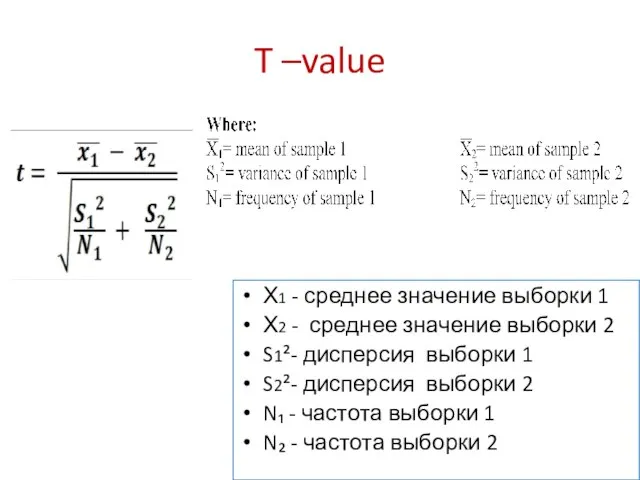
- 25. Step 6 calculate the value of T using the formula provided in the Table
- 26. T –value Х1 - среднее значение выборки 1 Х2 - среднее значение выборки 2 S1²- дисперсия
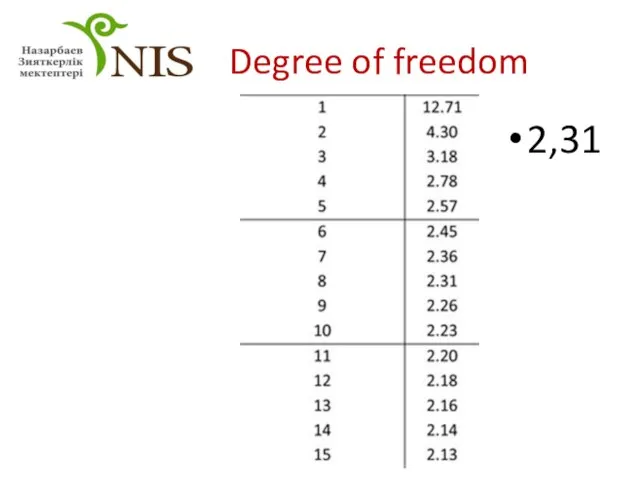
- 27. Answer 2,14
- 28. Step 7 Calculate the degree of freedom Рассчитать степень свободы df = (N1+ N2) – 2=
- 29. Step 8 Find the critical value using the t- table
- 30. Degree of freedom 2,31
- 31. Data analysis If the T-value is less than the critical value, then accept the null hypothesis
- 32. Analysis of results If the null hypothesis is accepted, then there was NO significant difference in
- 34. Скачать презентацию




























 Связь между сложением и вычитанием. Выше, ниже
Связь между сложением и вычитанием. Выше, ниже Свойства параллельных прямых
Свойства параллельных прямых Урок 6. Перколяционные процессы
Урок 6. Перколяционные процессы Сложение и вычитание положительных и отрицательных чисел. 6 класс
Сложение и вычитание положительных и отрицательных чисел. 6 класс Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Решение задач
Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Решение задач Основные геометрические приложения определенного интеграла
Основные геометрические приложения определенного интеграла Теорема Пифагора. Теорема в стихах
Теорема Пифагора. Теорема в стихах Метод анализа иерархий. Методика метода МАИ
Метод анализа иерархий. Методика метода МАИ Сфера и шар
Сфера и шар Построение графиков функции y = sinx и y = cosx
Построение графиков функции y = sinx и y = cosx Делитель. Делимое
Делитель. Делимое Сложение и вычитание
Сложение и вычитание Математический закон красоты мира Выполнила ученица 10 класса Сметанина Юлия
Математический закон красоты мира Выполнила ученица 10 класса Сметанина Юлия Складання та виконання алгоритмів із розгалуженням
Складання та виконання алгоритмів із розгалуженням Деревья. Построение дерева двоичного поиска
Деревья. Построение дерева двоичного поиска Презентация по математике Вычитание натуральных чисел
Презентация по математике Вычитание натуральных чисел  Элементы комбинаторики
Элементы комбинаторики Удивительный мир Симметрии
Удивительный мир Симметрии Шатровская Светлана Николаевна Г.Казань РТ МБОУ «СОШ№99»
Шатровская Светлана Николаевна Г.Казань РТ МБОУ «СОШ№99»  Тангенс и котангенс
Тангенс и котангенс Построение и анализ частотных характеристик СУ
Построение и анализ частотных характеристик СУ РЕШЕНИЕ ТРИГОНОМЕТРИЧЕСКИХ УРАВНЕНИЙ НА ИНТЕРВАЛЕ. Урок № 18
РЕШЕНИЕ ТРИГОНОМЕТРИЧЕСКИХ УРАВНЕНИЙ НА ИНТЕРВАЛЕ. Урок № 18  Прямые
Прямые Игра для учащихся «Математический активизатор»
Игра для учащихся «Математический активизатор» Логика и алгебра высказываний
Логика и алгебра высказываний Презентация к открытому уроку математики в 1 классе Тема: «Сложение и вычитание. Прибавить и вычесть 1».
Презентация к открытому уроку математики в 1 классе Тема: «Сложение и вычитание. Прибавить и вычесть 1».  Сечение тетраэдра
Сечение тетраэдра Площади геометрических фигур
Площади геометрических фигур