Содержание
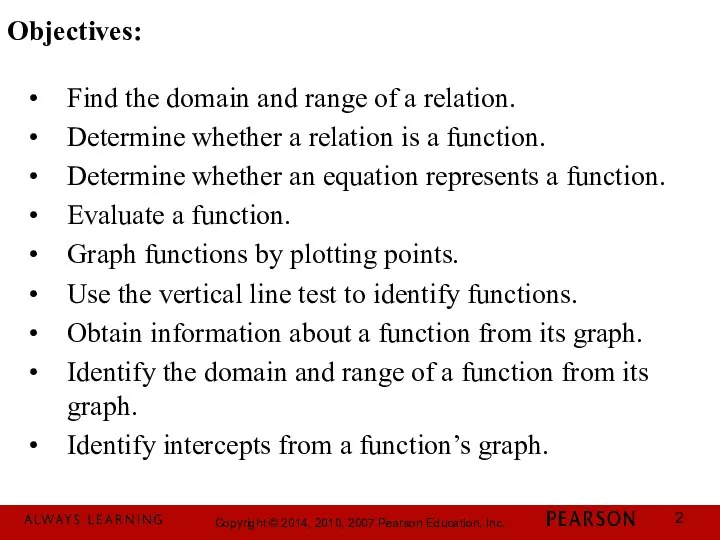
- 2. Find the domain and range of a relation. Determine whether a relation is a function. Determine
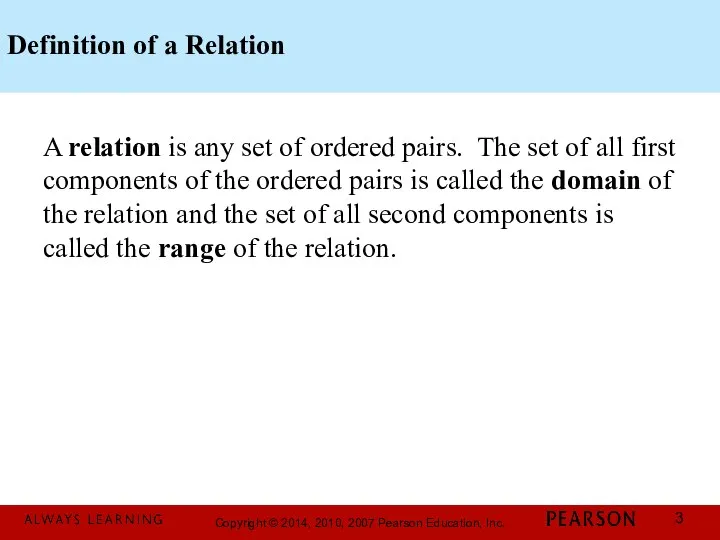
- 3. Definition of a Relation A relation is any set of ordered pairs. The set of all
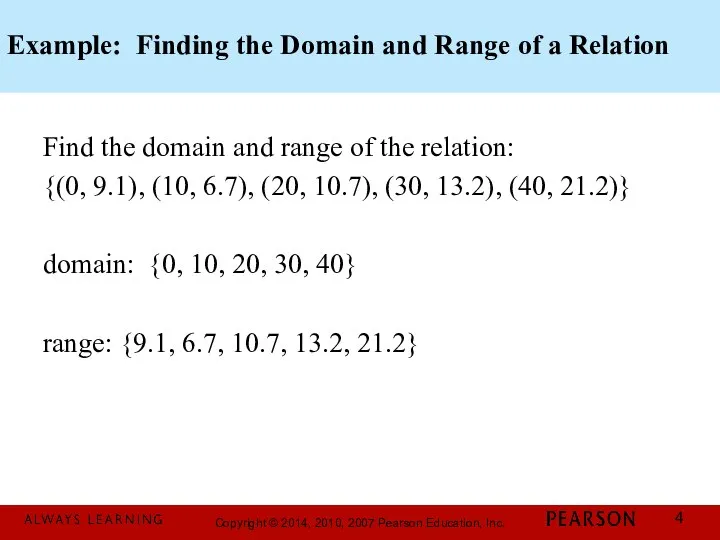
- 4. Example: Finding the Domain and Range of a Relation Find the domain and range of the
- 5. Definition of a Function A function is a correspondence from a first set, called the domain,
- 6. Example: Determining Whether a Relation is a Function Determine whether the relation is a function: {(1,
- 7. Functions as Equations If an equation is solved for y and more than one value of
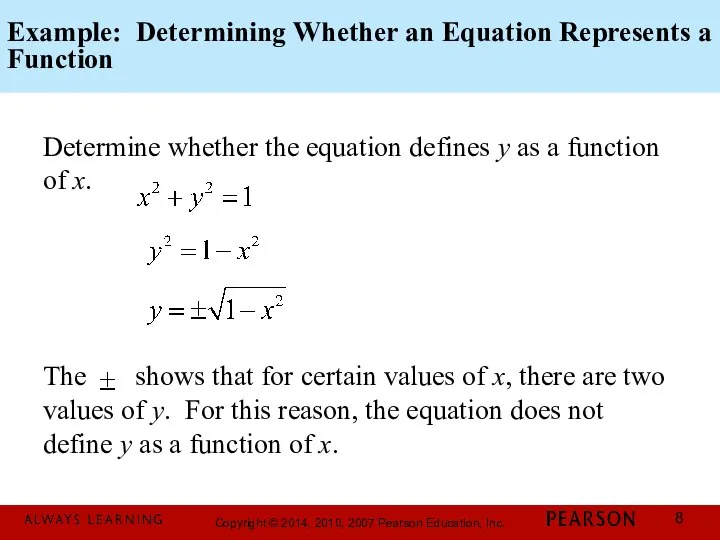
- 8. Example: Determining Whether an Equation Represents a Function Determine whether the equation defines y as a
- 9. Function Notation The special notation f(x), read “f of x” or “f at x”, represents the
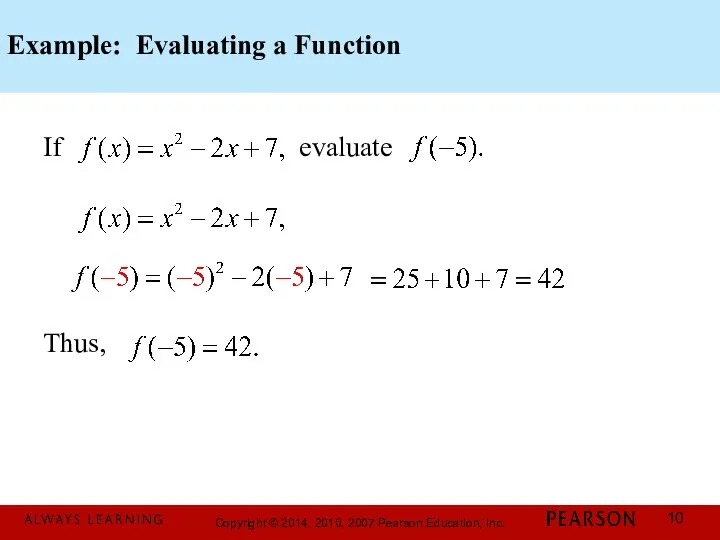
- 10. Example: Evaluating a Function If evaluate Thus,
- 11. Graphs of Functions The graph of a function is the graph of its ordered pairs.
- 12. Example: Graphing Functions Graph the functions f(x) = 2x and g(x) = 2x – 3 in
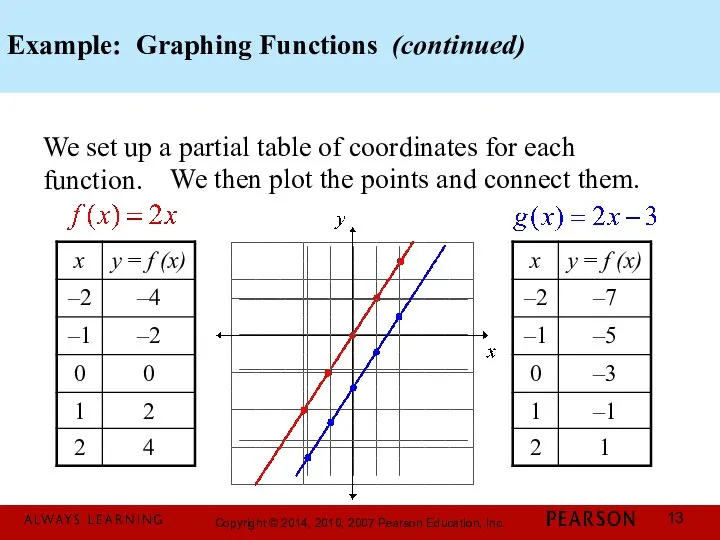
- 13. Example: Graphing Functions (continued) We set up a partial table of coordinates for each function. We
- 14. The Vertical Line Test for Functions If any vertical line intersects a graph in more than
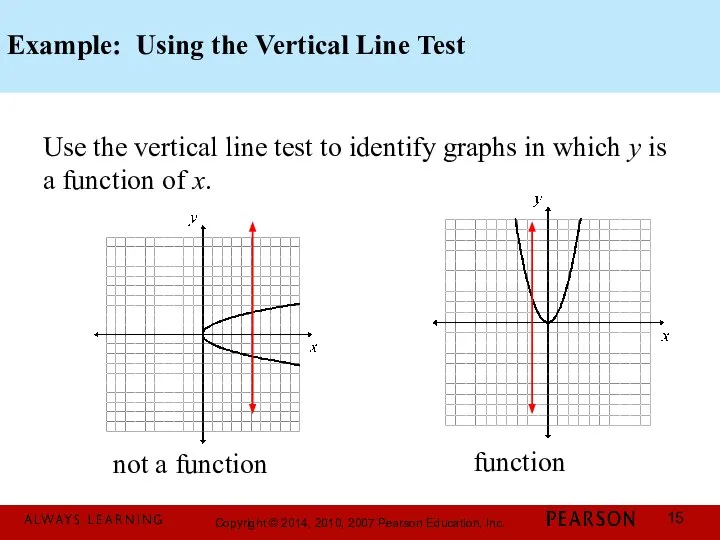
- 15. Example: Using the Vertical Line Test Use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which
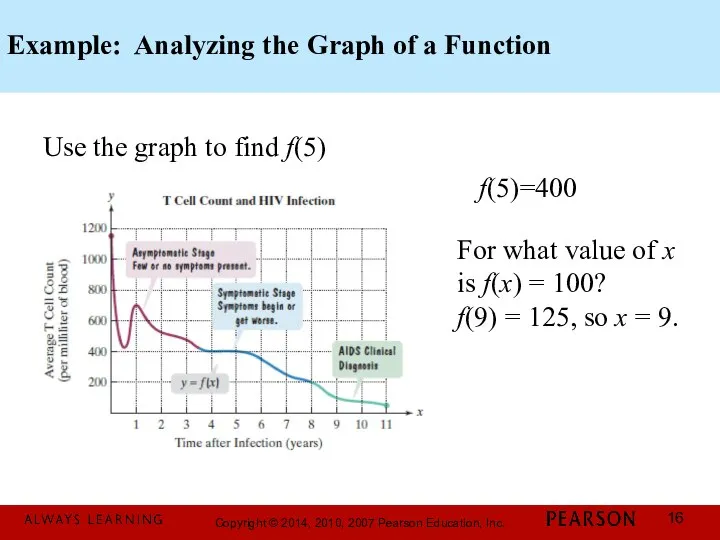
- 16. Example: Analyzing the Graph of a Function Use the graph to find f(5) For what value
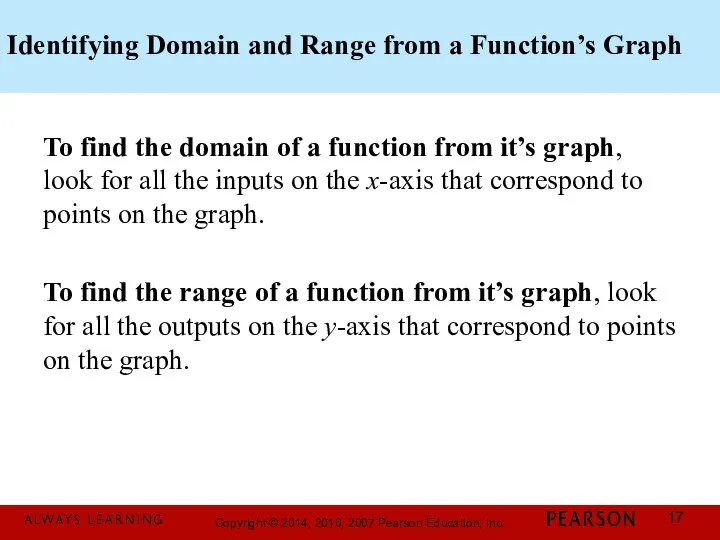
- 17. Identifying Domain and Range from a Function’s Graph To find the domain of a function from
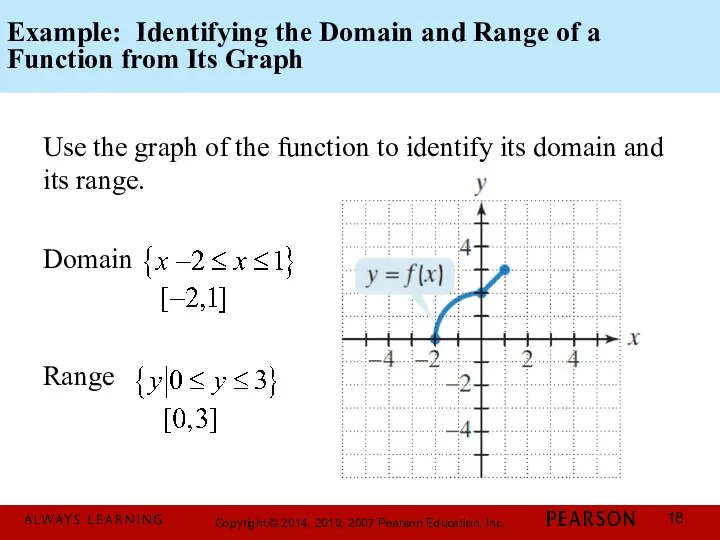
- 18. Example: Identifying the Domain and Range of a Function from Its Graph Use the graph of
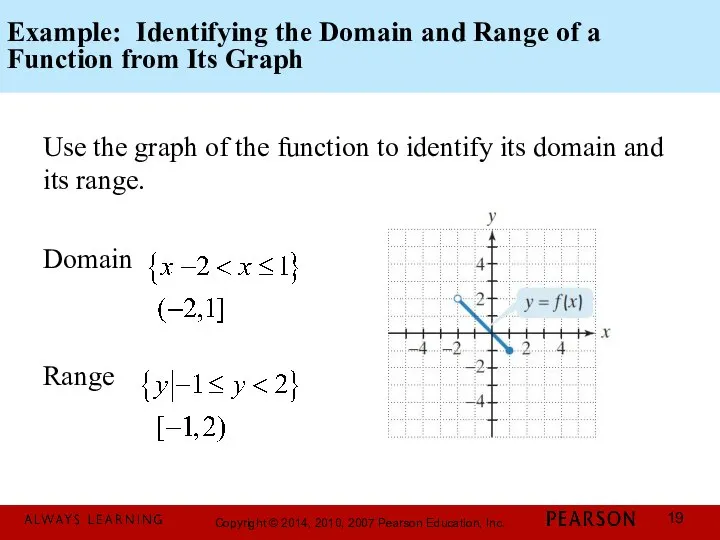
- 19. Example: Identifying the Domain and Range of a Function from Its Graph Use the graph of
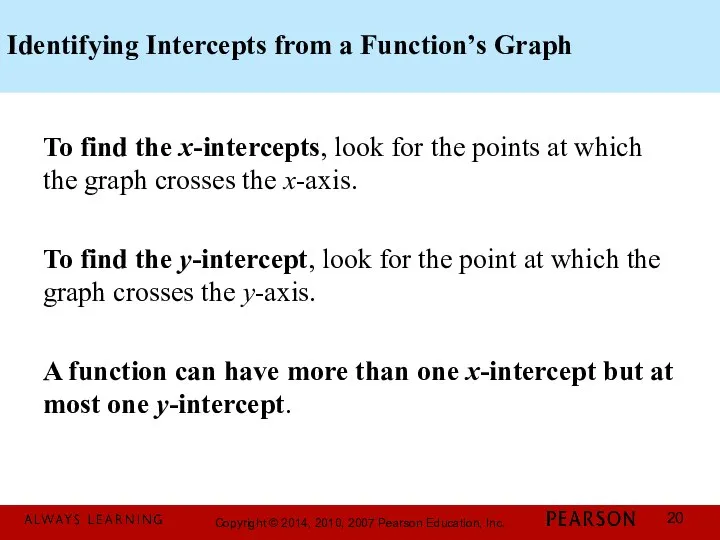
- 20. Identifying Intercepts from a Function’s Graph To find the x-intercepts, look for the points at which
- 22. Скачать презентацию





 Тела вращения
Тела вращения Прямоугольный параллелепипед
Прямоугольный параллелепипед Цели урока: показать, как работать с памятью калькулятора
Цели урока: показать, как работать с памятью калькулятора Частотная таблица
Частотная таблица Параллельные прямые в пространстве
Параллельные прямые в пространстве Случайные величины
Случайные величины Координатная плоскость
Координатная плоскость Математика - 6. Домашнее задание
Математика - 6. Домашнее задание Математические модели числа
Математические модели числа Презентация по математике "Литр" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Литр" - скачать бесплатно Окружность. Формулы окружности
Окружность. Формулы окружности Способы решения уравнений высших степеней
Способы решения уравнений высших степеней Биссектриса угла
Биссектриса угла Средние величины
Средние величины Жүрек . Жүрек қан тамырлары
Жүрек . Жүрек қан тамырлары Конечные автоматы. Абстрактные и структурные автоматы. Синтез конечных автоматов и МПА
Конечные автоматы. Абстрактные и структурные автоматы. Синтез конечных автоматов и МПА Дифференциальное исчисление функций одной переменной
Дифференциальное исчисление функций одной переменной Понятие процента
Понятие процента Логарифмические уравнения и приложен видеоурок
Логарифмические уравнения и приложен видеоурок Матрицы. Виды и действия над матрицами
Матрицы. Виды и действия над матрицами Процент. Знать и уметь находить
Процент. Знать и уметь находить Вейвлет-преобразование и его использование в рамках процедур обработки данных
Вейвлет-преобразование и его использование в рамках процедур обработки данных Признаки делимости на 3 и 9 (записываем № вопроса и выбранное число или слово)
Признаки делимости на 3 и 9 (записываем № вопроса и выбранное число или слово) Оптимизация последовательности обработки деталей на двух станках
Оптимизация последовательности обработки деталей на двух станках Длина окружности и площадь круга
Длина окружности и площадь круга Деление дробей
Деление дробей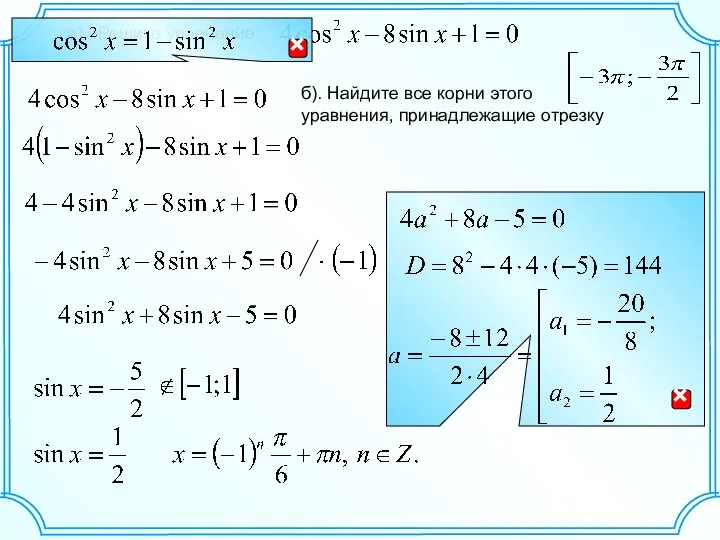 C1 20. Решить уравнение
C1 20. Решить уравнение Умножение десятичных дробей. Устный счёт
Умножение десятичных дробей. Устный счёт