- Главная
- Математика
- Determinants, their properties. Minors and cofactors. Lecture 2

Содержание
- 2. Example:
- 3. The minor М of the element a of a square matrix A(n; n) is the determinant
- 4. Example: Find and for the determinant of the third order The cofactor А of the element
- 5. Property 2. If we replace any two neighbouring rows (columns) then the determinant will change a
- 6. Corollary 2. A determinant at which elements of two arbitrary rows (columns) are proportional respectively is
- 8. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Example:
Example:
Слайд 3
The minor М of the element a of a square matrix
The minor М of the element a of a square matrix
A(n; n) is the determinant obtained from the given one by deletion of the i-th row and the j-th column.
For a determinant of the second order
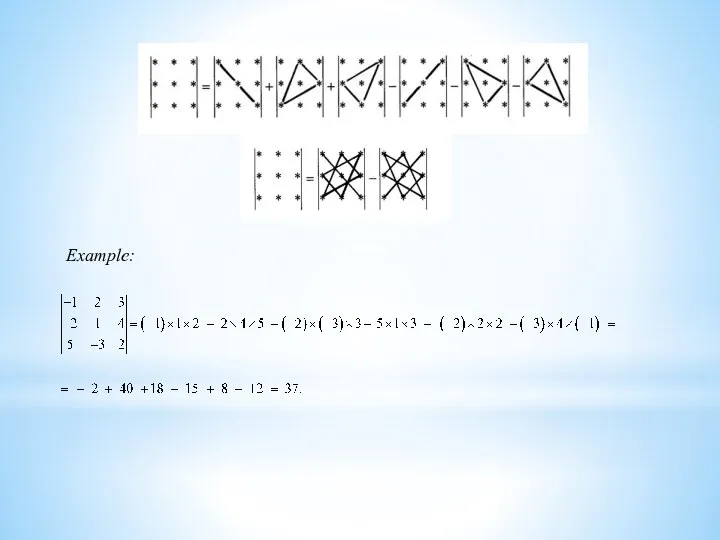
Example: Δ=
For a determinant of the third order
and etc.
For a determinant of the second order
Example: Δ=
For a determinant of the third order
and etc.
Слайд 4
Example: Find and for the determinant of the third order
The
Example: Find and for the determinant of the third order
The
cofactor А of the element а of a square matrix А(n; n) is the minor multiplied on the number , i.e.
Properties of determinants
Property 1. The value of a determinant doesn’t change if we replace all its rows by the corresponding columns and vice versa.
Properties of determinants
Property 1. The value of a determinant doesn’t change if we replace all its rows by the corresponding columns and vice versa.
Слайд 5
Property 2. If we replace any two neighbouring rows (columns) then
Property 2. If we replace any two neighbouring rows (columns) then
the determinant will change a sign.
Property 3. If all the elements of a row (column) of a determinant are multiplied on the same non-zero number «m» then the determinant value increases (decreases) in «m» times.
Example:
Corollary 1. If all the elements of a row (column) of a determinant have a non-zero common multiplier, it can be taken out the determinant sign.
Property 3. If all the elements of a row (column) of a determinant are multiplied on the same non-zero number «m» then the determinant value increases (decreases) in «m» times.
Example:
Corollary 1. If all the elements of a row (column) of a determinant have a non-zero common multiplier, it can be taken out the determinant sign.
Слайд 6
Corollary 2. A determinant at which elements of two arbitrary rows
Corollary 2. A determinant at which elements of two arbitrary rows
(columns) are proportional respectively is equal to zero.
Property 4. Let each element of an arbitrary row (column) be the sum of two addends. Then the determinant is equal to the sum of two determinants such that the corresponding row (column) of the first determinant consists of the first addends, and the corresponding row (column) of the second determinant consists of the second addends.
Example: For example, let the first column of the determinant be the sum of two addends. Then
Property 4. Let each element of an arbitrary row (column) be the sum of two addends. Then the determinant is equal to the sum of two determinants such that the corresponding row (column) of the first determinant consists of the first addends, and the corresponding row (column) of the second determinant consists of the second addends.
Example: For example, let the first column of the determinant be the sum of two addends. Then




 Системы линейных неравенств с одним неизвестным. 9 класс
Системы линейных неравенств с одним неизвестным. 9 класс Формирование навыков УУД при изучении темы «Решение задач на построение графиков алгебраических функций» (на примере линейной фу
Формирование навыков УУД при изучении темы «Решение задач на построение графиков алгебраических функций» (на примере линейной фу Площадь трапеции
Площадь трапеции Симметрия (9 класс) - презентация_
Симметрия (9 класс) - презентация_ Системы счисления
Системы счисления  Правильные и неправильные дроби. Смешанные числа. 5 класс
Правильные и неправильные дроби. Смешанные числа. 5 класс Численные методы решения систем уравнений
Численные методы решения систем уравнений Тема урока: Применение различных способов разложения на множители многочлена Презентацию выполнила Шурыгина И.В.
Тема урока: Применение различных способов разложения на множители многочлена Презентацию выполнила Шурыгина И.В.  Дробные выражения
Дробные выражения 20160624_pifagor._materialy_k_uroku_istorii_i_obshchestvoznaniya
20160624_pifagor._materialy_k_uroku_istorii_i_obshchestvoznaniya Линейные ДУ второго порядка
Линейные ДУ второго порядка Десятичные дроби
Десятичные дроби Логарифмические уравнения. Способы решения
Логарифмические уравнения. Способы решения Методические аспекты использования координатно – векторного метода при решении стереометрических задач
Методические аспекты использования координатно – векторного метода при решении стереометрических задач Признак перпендикулярности
Признак перпендикулярности Трехзначные логики и их расширения: использование в информатике и искусственном интеллекте
Трехзначные логики и их расширения: использование в информатике и искусственном интеллекте Практическое применение интегралов в различных областях
Практическое применение интегралов в различных областях Урок математики. 1 класс. Повторение по теме «Число и цифра 8»
Урок математики. 1 класс. Повторение по теме «Число и цифра 8» Решение дифференциальных уравнений методом ломаных Эйлера с использованием электронных таблиц MS Excel
Решение дифференциальных уравнений методом ломаных Эйлера с использованием электронных таблиц MS Excel Использование компьютерных технологий для реализации решений систем линейных уравнений
Использование компьютерных технологий для реализации решений систем линейных уравнений Численное решение нелинейных уравнений
Численное решение нелинейных уравнений Неопределённый интеграл
Неопределённый интеграл Числа и вычисления. Задание №1
Числа и вычисления. Задание №1 Симметрия в пространстве
Симметрия в пространстве Прямые измерения, косвенные, совокупные и совместные
Прямые измерения, косвенные, совокупные и совместные Луч и угол. (7 класс)
Луч и угол. (7 класс) Презентация по математике "СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ МНОГОЧЛЕНОВ" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "СЛОЖЕНИЕ И ВЫЧИТАНИЕ МНОГОЧЛЕНОВ" - скачать бесплатно Занимательная математика
Занимательная математика