Содержание
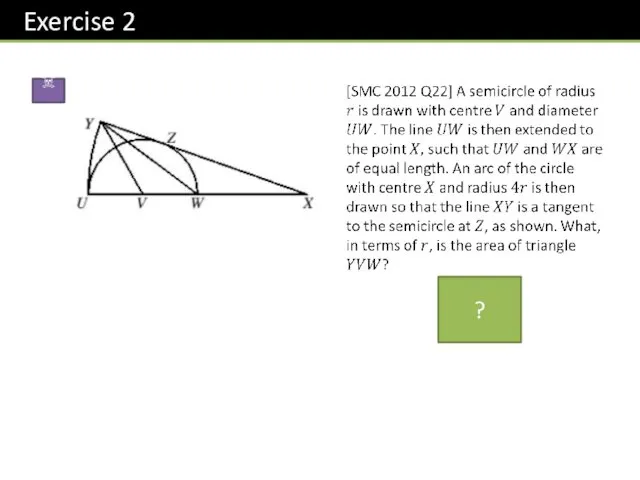
- 2. Sector (Minor) Segment Diameter Radius Tangent Chord (Minor) Arc Circumference ? ? ? ? ? ?
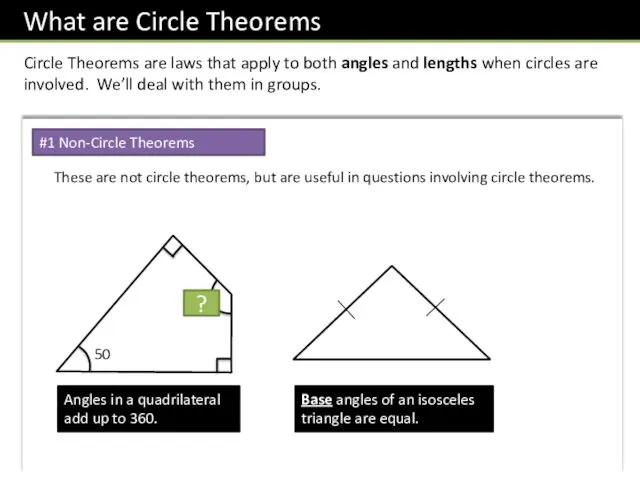
- 3. Circle Theorems are laws that apply to both angles and lengths when circles are involved. We’ll
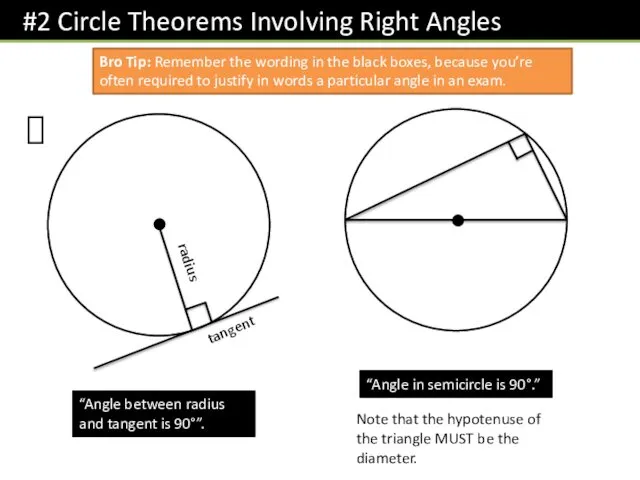
- 4. ? radius tangent “Angle between radius and tangent is 90°”. “Angle in semicircle is 90°.” Note
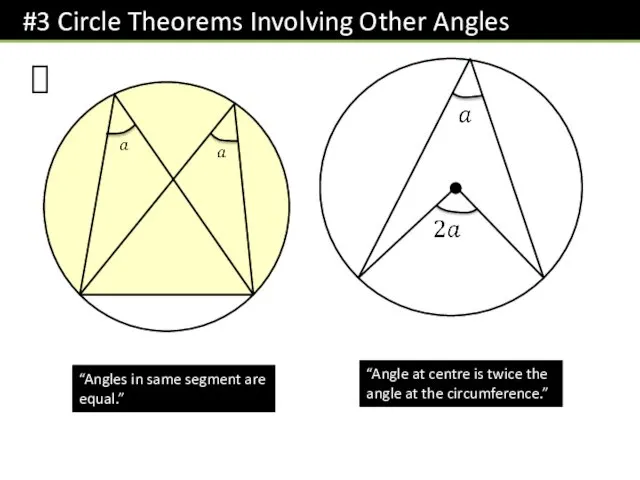
- 5. ? “Angles in same segment are equal.” “Angle at centre is twice the angle at the
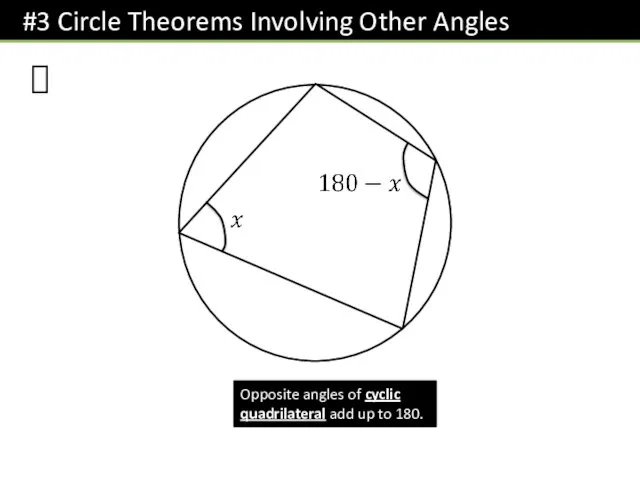
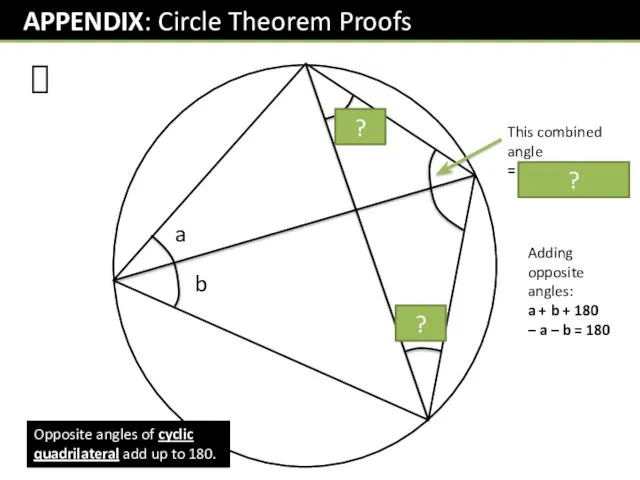
- 6. ? Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180.
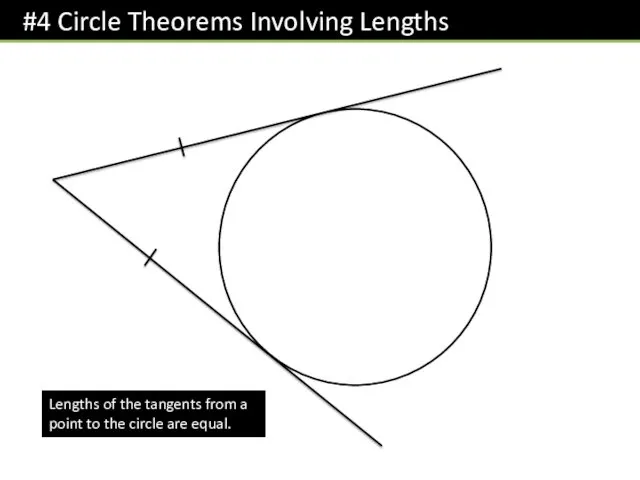
- 7. Lengths of the tangents from a point to the circle are equal.
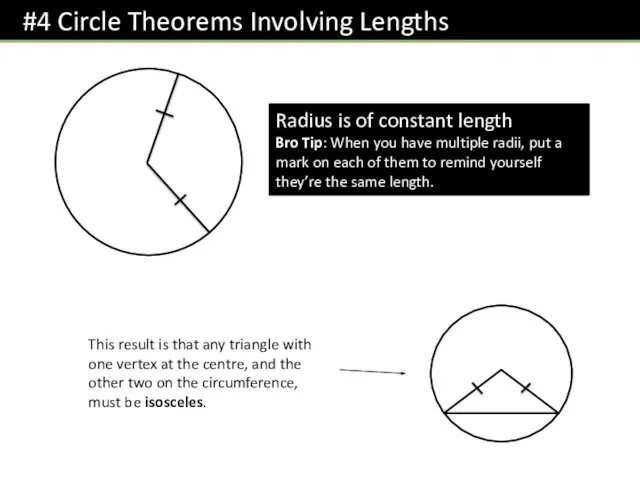
- 8. Radius is of constant length Bro Tip: When you have multiple radii, put a mark on
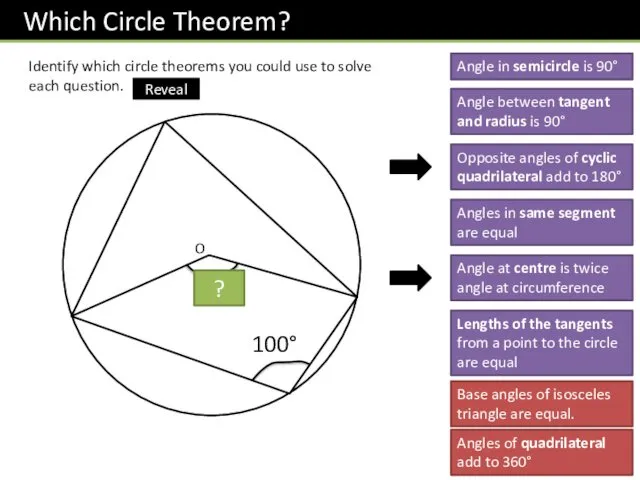
- 9. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. O 160° 100° ? Angle
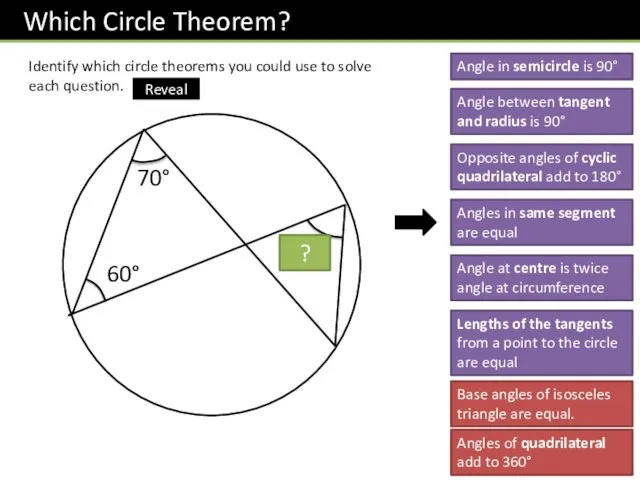
- 10. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. 70° 60° 70° ? Angle
- 11. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. 115° ? Angle in semicircle
- 12. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. 70° ? Angle in semicircle
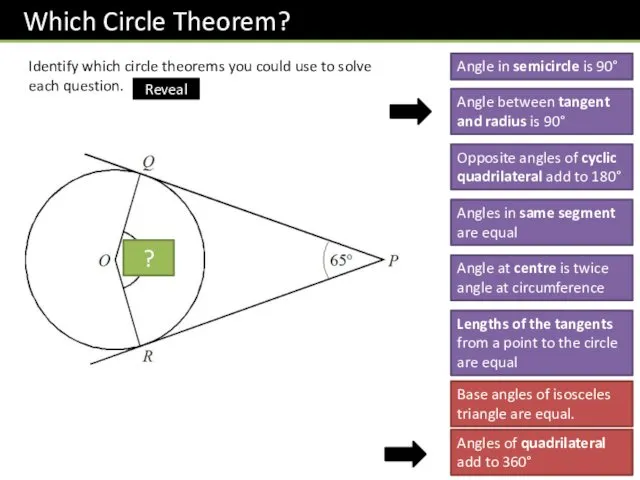
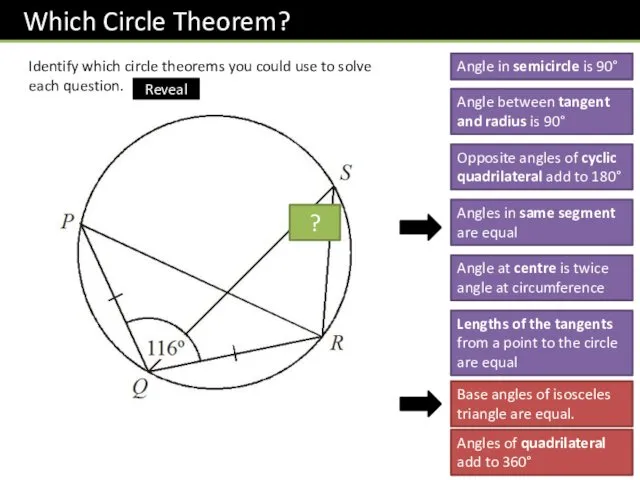
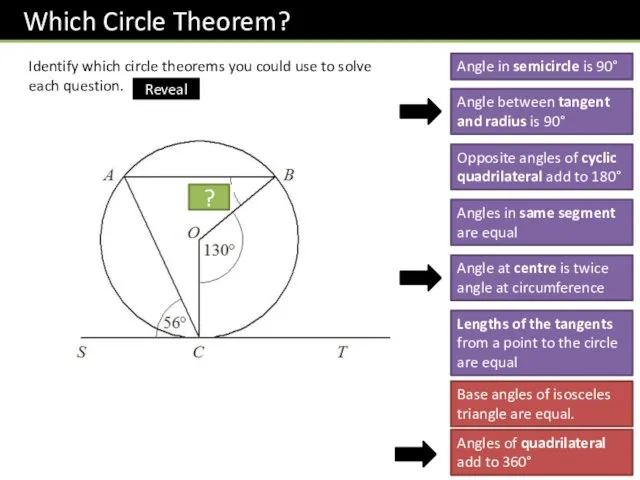
- 13. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. Angle in semicircle is 90°
- 14. Identify which circle theorems you could use to solve each question. Angle in semicircle is 90°
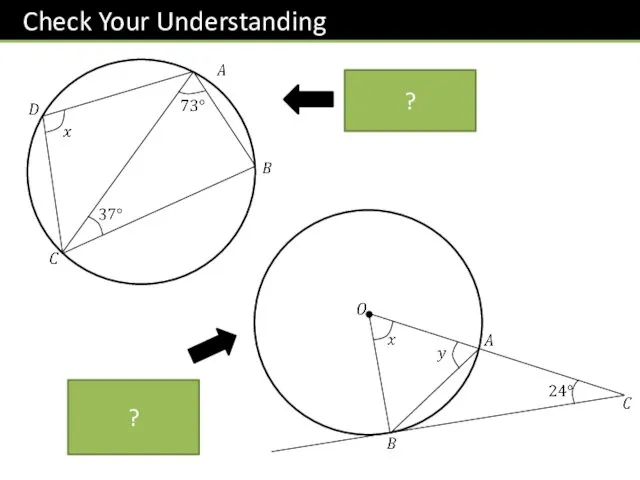
- 15. ? ?
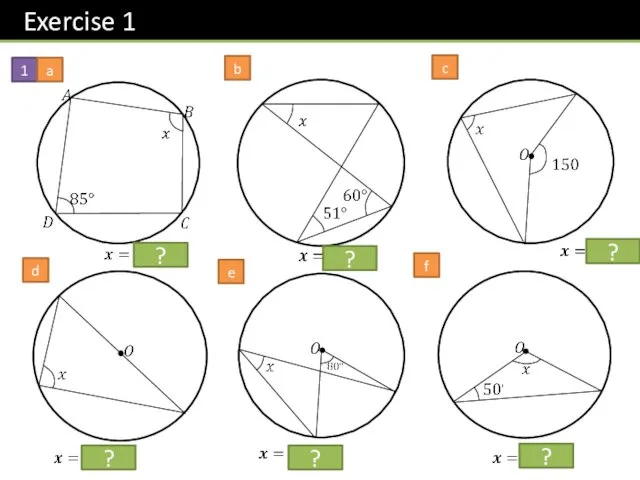
- 16. 1 b c a d e f ? ? ? ? ? ?
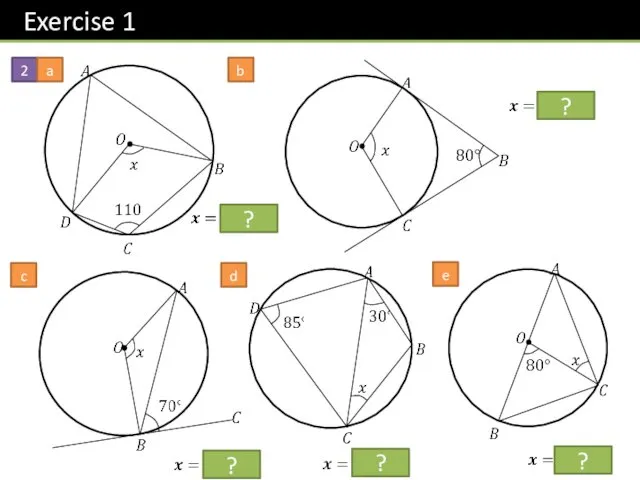
- 17. 2 a b c d e ? ? ? ? ?
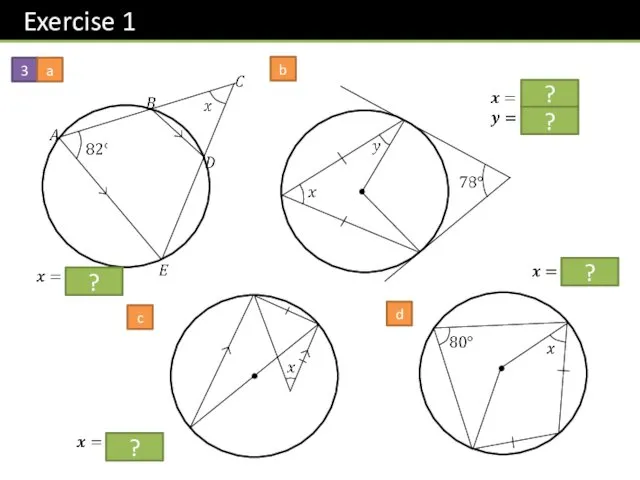
- 18. 3 a b c d ? ? ? ? ?
- 19. 4 ? ? ?
- 20. ☠ a b c ? ? ?
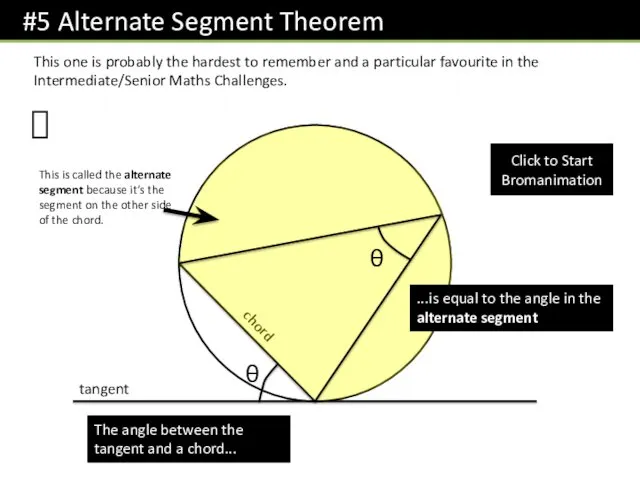
- 21. This one is probably the hardest to remember and a particular favourite in the Intermediate/Senior Maths
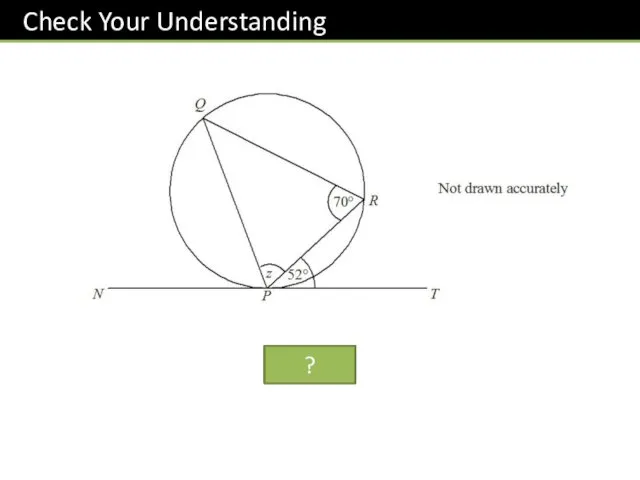
- 22. z = 58° ?
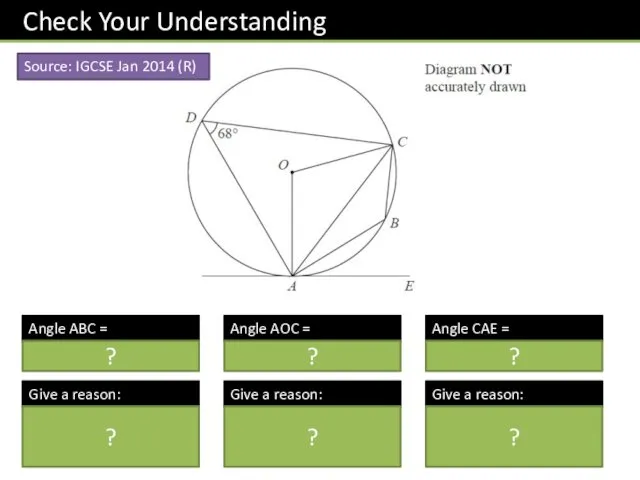
- 23. Angle ABC = Give a reason: Angle AOC = Give a reason: Angle CAE = Give
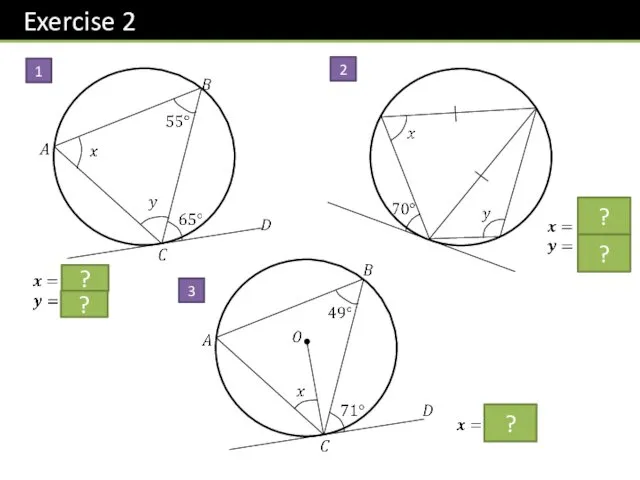
- 24. 1 2 3 ? ? ? ? ?
- 25. 4 5 6 ? ? ?
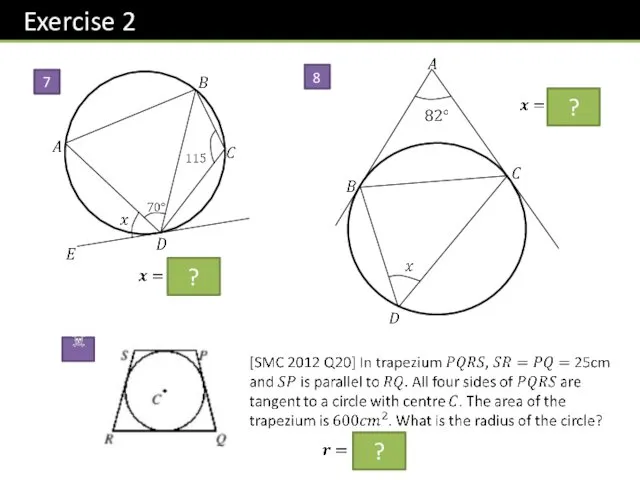
- 26. 7 8 ☠1 ? ? ?
- 27. ☠2 ?
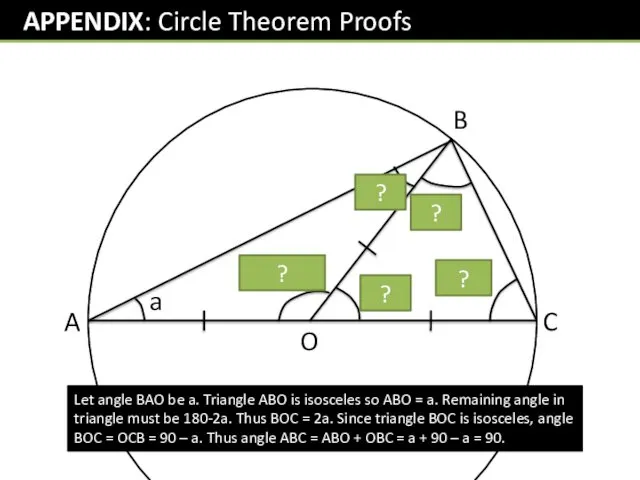
- 28. A B C O a a 180-2a 2a 90-a 90-a Let angle BAO be a. Triangle
- 29. ? x a b b a ? ? Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral add up to
- 31. Скачать презентацию





 Генетический подход в изучении геометрии
Генетический подход в изучении геометрии Дифференциальное исчисление функции одной переменной
Дифференциальное исчисление функции одной переменной Золотое сечение
Золотое сечение Формулы сокращенного умножения
Формулы сокращенного умножения Презентация "Математики"
Презентация "Математики" Метод координат
Метод координат Формула разности квадратов. 7 класс
Формула разности квадратов. 7 класс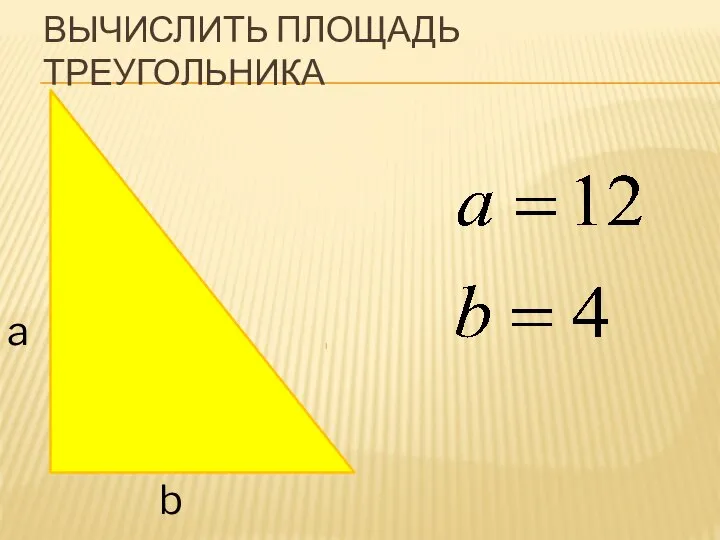 Вычисление площади треугольника
Вычисление площади треугольника Теория вероятностей
Теория вероятностей Математика Л. Г. Петерсон, 2 класс Устный счет по теме «Многозначные числа»
Математика Л. Г. Петерсон, 2 класс Устный счет по теме «Многозначные числа» Простейшие задачи в координатах
Простейшие задачи в координатах Геометрическая прогрессия. Урок 1
Геометрическая прогрессия. Урок 1 Математика – царица наук. Умножение на 1 и 0
Математика – царица наук. Умножение на 1 и 0 Неравенство треугольника
Неравенство треугольника Квадратичная функция. 9 класс
Квадратичная функция. 9 класс Повторение по математике
Повторение по математике Способы вычисления неопределенных интегралов (лекция 26)
Способы вычисления неопределенных интегралов (лекция 26) Задачи практического характера в разных областях науки и техники
Задачи практического характера в разных областях науки и техники Теория вероятностей, математическая статистика и случайные процессы
Теория вероятностей, математическая статистика и случайные процессы Решение задач на проценты
Решение задач на проценты 20161216_den_fibonachchi
20161216_den_fibonachchi Презентация по математике "Вычитание" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Вычитание" - скачать бесплатно Вычитание векторов. Умножение вектора на число
Вычитание векторов. Умножение вектора на число Проценты
Проценты Зерттеудің нәтижелерін. Талдау
Зерттеудің нәтижелерін. Талдау Интерактивная игра-тренажёр по теме: «Сложение и вычитание в пределах 20» Математика 2 класс
Интерактивная игра-тренажёр по теме: «Сложение и вычитание в пределах 20» Математика 2 класс  Средние величины в статистике
Средние величины в статистике Реализация деятельностного подхода на уроках математики.
Реализация деятельностного подхода на уроках математики.