Содержание
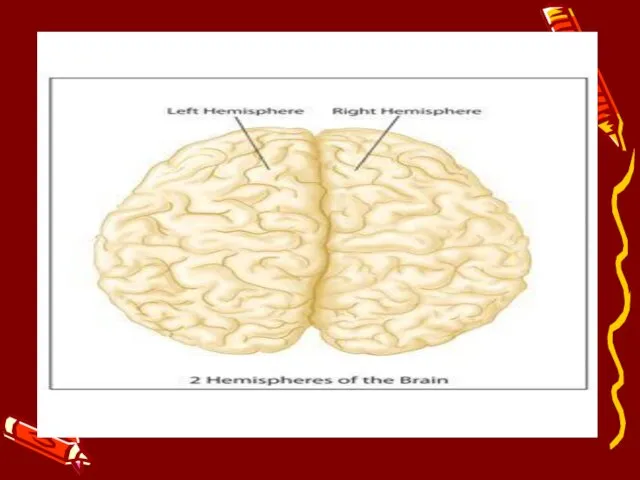
- 3. TWO HEMISPHERES
- 5. AMYGDALA FUNCTIONS Processing emotions Memory of Emotional reactions
- 6. Adolescent Psychology Psychological Issues ↓ Recklessness and Risk-taking behaviour
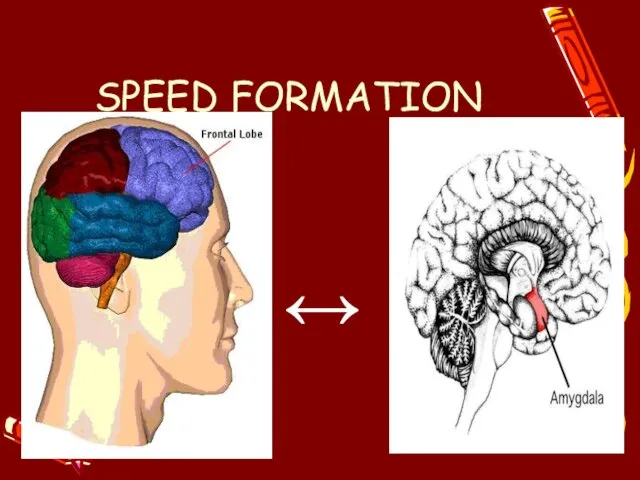
- 7. SPEED FORMATION ↔
- 8. SUBSTANCE ABUSE Overindulgence in and dependence of a drug or chemicals
- 9. Alcohol Abuse ↓ Focus It is Drug Abuse!!
- 10. Alcohol tragedy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZLbndJKMtCk
- 11. Why teens start to take drugs? Curiosity and Experimentation Peer Pressure To Relax or to Have
- 12. Curiosity and Experimentation The desire to try something new, different Wanting to take risk
- 13. Peer Pressure “Most of my friends were doing it” Teens seek out friends who engage in
- 14. Depression or Personal Problems To feel better To get confidence and self-esteem To escape from psychological
- 15. Family and other factors Unhappy childhood Conflict with parents or teachers To rebel: Because parents said
- 16. Commonly used drugs Just 20% had tried cannabis Just 2% had tried amphetamines for non-medical reasons
- 17. Risk Taking in Adolescence
- 18. Why Take the Risk? Adolescents take more risks than children or adults The crash rate per
- 19. Why Take the Risk? Adolescents and adults reason about risk in similar ways Educational interventions designed
- 20. Why Take the Risk? Evidence from Developmental Neuroscience Risk taking in adolescence is the product of
- 21. Socioemotional Network Sensitive to social and emotional stimuli Important for reward processing Localized in limbic and
- 22. Cognitive Network Functions such as planning, thinking ahead, and self-regulation Mainly consists of outer regions of
- 23. Why During Adolescence? Teenagers spend so much time with their peers Presence of peers makes the
- 24. Why During Adolescence? Preference for smaller immediate rewards over larger delayed rewards Immediate rewards are emotionally
- 25. Raising the price of cigarettes More attentively enforcing laws governing the sale of alcohol Expanding adolescents’
- 26. Limit the hours teenagers are allowed to drive Limit passengers in the car with a teenage
- 27. Teen Behavioural Problems Your Teen Seems To Hate You “…Part of adolescence is about separating and
- 28. Staying Out Too Late “Part of what teens do is test limits, but the fact is
- 29. Everything's a Drama "What happens is that kids feel misunderstood, and eventually they will stop telling
- 30. Teen pregnancies
- 31. Problems to Teen Mothers: Left out of crowds Likely to drop out of school Poverty Face
- 32. Affects the Babies Born: A former U.S. Surgeon General, Dr. M. Jocelyn Elders stated that, "ninety
- 33. Letting out a secret What girls like but they wont tell boys
- 34. Girls like the chase: They like to be chased Don’t be too obsessed with them Give
- 35. Talking opposites: Is they answer a question in a short phrase then there is a problem.
- 36. Give them some time off They prefer it when you hang out with your “GUY” friends.
- 37. They don’t like it when you hang around their friends Fear that one of their dirty
- 38. Heightened jealousy They fear that you might cheat on them. The want to have other girls
- 39. References: http://www.humanillnesses.com/images/hdc_0000_0001_0_img0044.jpg http://www.paulnussbaum.com/brain/hemispheres.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adolescent_psychology http://farm2.static.flickr.com/1400/1418754315_564de0de3e_m.jpg http://files.easyfocus.net/pictures/frontal-lobe.bmp http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adolescent_psychology http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Substance_abuse http://www.helpguide.org/mental/alcohol_abuse_alcoholism_signs_effects_treatment.htm http://www.themodernreligion.com/Alcohol.gif
- 41. Скачать презентацию




































 Фармацевтична опіка при спастичних станах
Фармацевтична опіка при спастичних станах Пренатальная диагностика
Пренатальная диагностика Личность. Теория личности
Личность. Теория личности Диагностика и основные синдромы при патологии почек
Диагностика и основные синдромы при патологии почек Сестринское дело в лабораторной диагностике
Сестринское дело в лабораторной диагностике Первичные и вторичные формы туберкулеза органов дыхания
Первичные и вторичные формы туберкулеза органов дыхания Платные медицинские услуги
Платные медицинские услуги Острое кровотечение в просвет органов пищеварительного канала
Острое кровотечение в просвет органов пищеварительного канала Гарднеллалар. Gardnerella vaginalis
Гарднеллалар. Gardnerella vaginalis Вертикальная стабильная деформация таза III степени: неправильно срастающийся перелом
Вертикальная стабильная деформация таза III степени: неправильно срастающийся перелом Медлительные дети
Медлительные дети Инфаркт миокардын емдеуде қолданылатын фракционды емес фармакоинвазивті гепарин мен эноксапариннің
Инфаркт миокардын емдеуде қолданылатын фракционды емес фармакоинвазивті гепарин мен эноксапариннің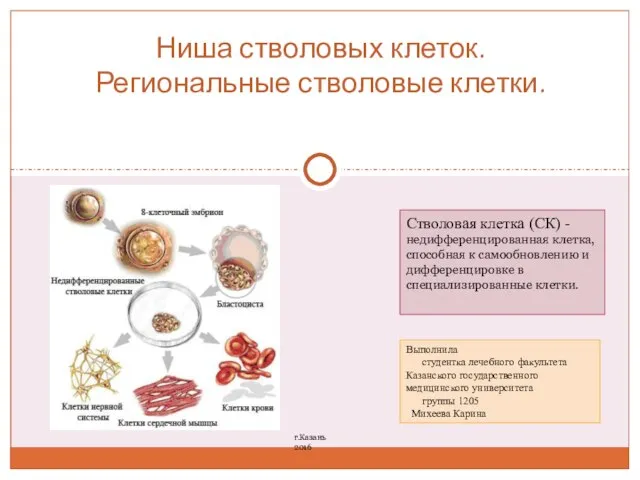 Ниша стволовых клеток. Региональные стволовые клетки
Ниша стволовых клеток. Региональные стволовые клетки Как правильно написать статью в медицинский журнал
Как правильно написать статью в медицинский журнал Григорий Антонович Захарьин
Григорий Антонович Захарьин Выбор направления работы тренера. Поиск своей «ниши»
Выбор направления работы тренера. Поиск своей «ниши» Менің мамандығым - жан амандығына арналады
Менің мамандығым - жан амандығына арналады Сестринский процесс при язвенной болезни желудка и 12-перстной кишки
Сестринский процесс при язвенной болезни желудка и 12-перстной кишки Патология иммунной системы
Патология иммунной системы Экзамены. Умей владеть собой
Экзамены. Умей владеть собой Эмоционально-волевая 4-6 лет
Эмоционально-волевая 4-6 лет Анализ психологической уязвимости студентов СГАФКСТ к употреблению психоактивных веществ
Анализ психологической уязвимости студентов СГАФКСТ к употреблению психоактивных веществ Консультативная беседа и основные требования к её проведению
Консультативная беседа и основные требования к её проведению Сестринская помощь при заболеваниях органов пищеварения и прободении полых органов
Сестринская помощь при заболеваниях органов пищеварения и прободении полых органов Көмек көрсету деңгейіне сәйкес емдеуге жатқызу өлшемдері
Көмек көрсету деңгейіне сәйкес емдеуге жатқызу өлшемдері Балалардың тістерін, жұмсақ тіндерін жарақаттағанда және бет қаңқасының сүйегіндегі сынықтарды реабилитациялау
Балалардың тістерін, жұмсақ тіндерін жарақаттағанда және бет қаңқасының сүйегіндегі сынықтарды реабилитациялау Особенности строения черепа у детей
Особенности строения черепа у детей Эпидемии. Профилактика заболеваний
Эпидемии. Профилактика заболеваний