Содержание
- 2. Pathology of the breast normal anatomy physiologic changes developmental abnormalities inflammations fibrocystic changes tumors benign malignant
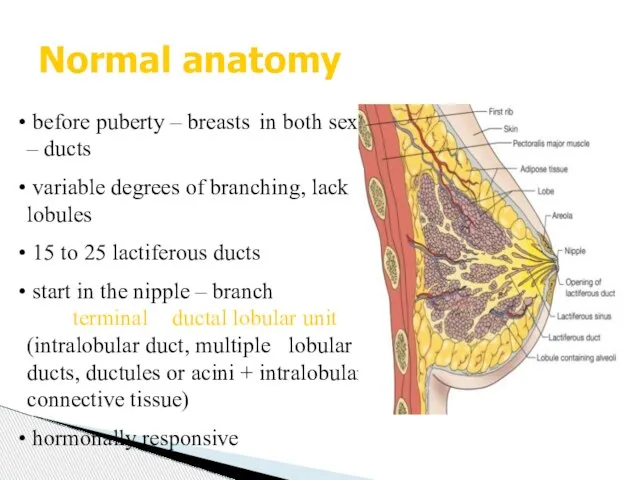
- 3. Normal anatomy before puberty – breasts in both sexes – ducts variable degrees of branching, lack
- 4. Physiologic changes at birth male and female breasts active secretion (transplacental passage of maternal hormones) bilateral
- 5. Macromastia diffuse enlargement of both breasts adolescence or pregnancy exaggerated response to hormonal stimulation Pubertal (Virginal)
- 6. Developmental abnormalities Aplasia and hypoplasia uncommon – associated with overdevelopment of the contralateral breast acquired (irradiation
- 8. Ectopic breast supernumerary breast (from ectopic breast tissue – along the milk lines (midaxillae – normal
- 10. Inflammatory and reactive conditions Fat necrosis can simulate carcinoma clinically and mammographically history of antecedent trauma,
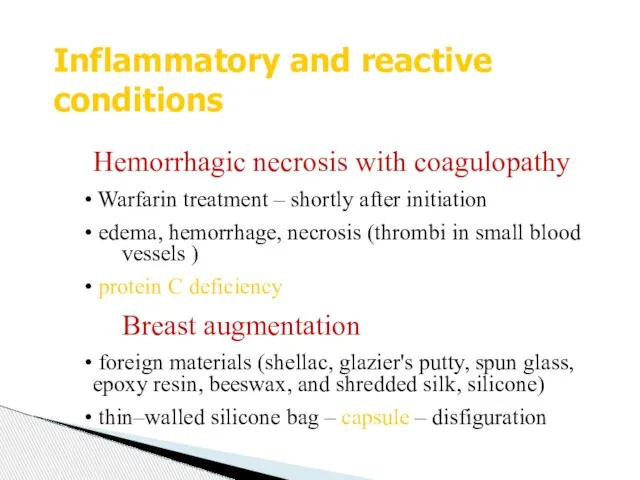
- 11. Inflammatory and reactive conditions Hemorrhagic necrosis with coagulopathy Warfarin treatment – shortly after initiation edema, hemorrhage,
- 12. Puerperal mastitis early stages (2nd and 3rd W) of lactation – 5% stasis of milk in
- 14. Benign proliferative lesions pathologic spectrum of seemingly related clinically benign breast abnormalities palpably irregular and painful
- 15. Benign proliferative lesions Adenosis elongation of the terminal ductules caricature of the lobule sclerosing adenosis apocrine
- 16. Benign tumors Fibroadenoma proliferation of epithelial and stromal elements most common breast tumor in adolescent and
- 17. Tubular adenoma far less common than fibroadenomas young women, discrete, freely movable masses uniform sized ducts
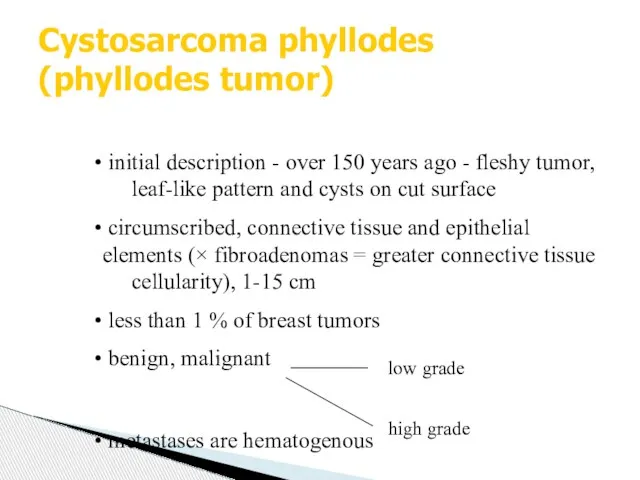
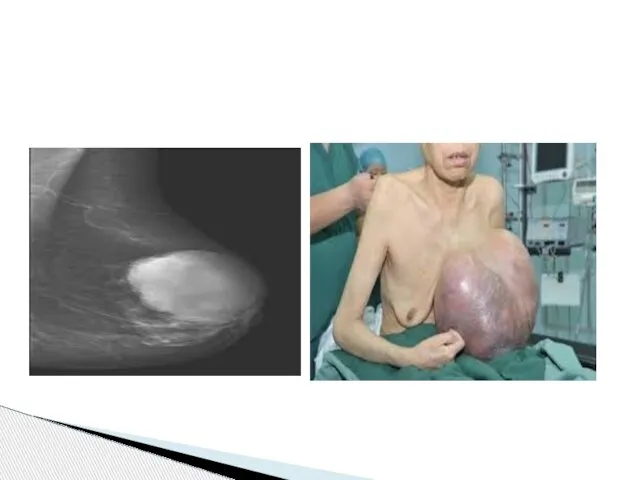
- 19. Cystosarcoma phyllodes (phyllodes tumor) initial description - over 150 years ago - fleshy tumor, leaf-like pattern
- 22. Proliferative changes ductal and lobular hyperplasia atypical ductal and lobular hyperplasia higher risk for the cancer
- 23. Breast carcinoma most frequent malignant tumor in females (followed by cervix and colon) highest incidence –
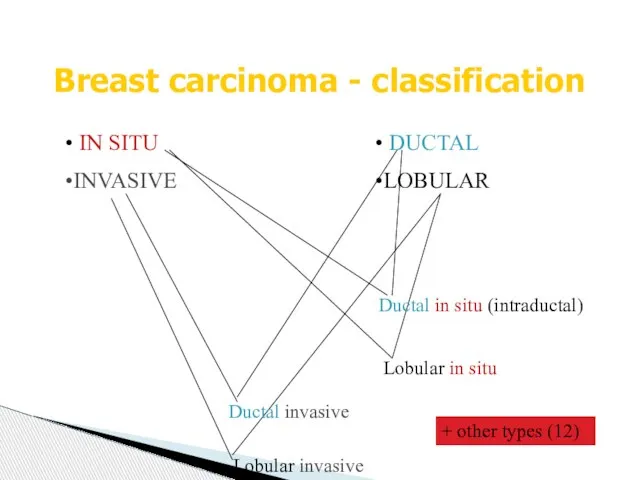
- 24. Breast carcinoma - classification IN SITU INVASIVE DUCTAL LOBULAR Ductal in situ (intraductal) Lobular in situ
- 25. Carcinoma in situ preinvasive - does not form a palpable tumor not detected clinically (only X-ray
- 26. Invasive carcinoma Invasive ductal carcinoma largest group (65 to 80 % of mammary carcinomas) mid to
- 27. other types: tubular, mucinous, medullary, inflammatory – together about 10 % of breast ca metastases: regional
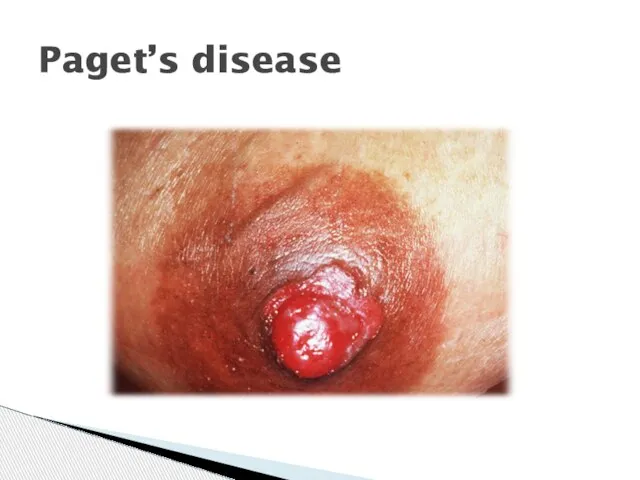
- 28. Paget‘s disease of the nipple result of intraepithelial spread of intraductal carcinoma large pale-staining cells within
- 29. Paget’s disease
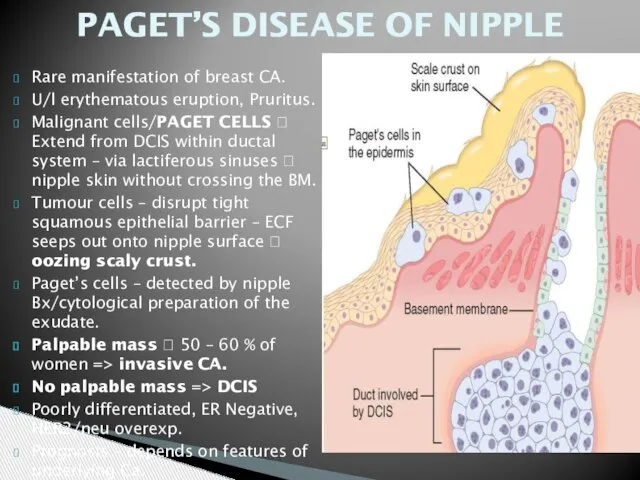
- 30. PAGET’S DISEASE OF NIPPLE Rare manifestation of breast CA. U/l erythematous eruption, Pruritus. Malignant cells/PAGET CELLS
- 31. Pathology of the male breast Gynecomastia most common clinical and pathologic abnormality of the male breast
- 35. Скачать презентацию























 Противомикробные средства
Противомикробные средства Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения
Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения Доғалы протездің құрылымы, қолдану көрсеткіштері, қарсы көрсеткіштері. Артықшылықтары мен кемшіліктері
Доғалы протездің құрылымы, қолдану көрсеткіштері, қарсы көрсеткіштері. Артықшылықтары мен кемшіліктері Псевдоперитонеальды синдром
Псевдоперитонеальды синдром Воспалительный процесс
Воспалительный процесс Патология восприятия и мышления
Патология восприятия и мышления Презентация по медицине Фенилкетонурия ФКУ финилпировиноградная олигофрения болезнь Фёллинга
Презентация по медицине Фенилкетонурия ФКУ финилпировиноградная олигофрения болезнь Фёллинга  Мейірбикелік үрдіс
Мейірбикелік үрдіс Пузырные дерматозы
Пузырные дерматозы Гонартроз. Артроз колінного суглобу (гонартроз, деформуючий артроз)
Гонартроз. Артроз колінного суглобу (гонартроз, деформуючий артроз) Кардиотонические, антиангинальные и антиаритмические средства
Кардиотонические, антиангинальные и антиаритмические средства Триггеры. Чтобы решить задачу, нужно сделать так, чтобы сработал триггер
Триггеры. Чтобы решить задачу, нужно сделать так, чтобы сработал триггер Введение в патологическую анатомию
Введение в патологическую анатомию Производные аминоалкилбензолов. (Тема 3)
Производные аминоалкилбензолов. (Тема 3) Острые инфекции у детей
Острые инфекции у детей СПИД - синдром приобретенного иммунодефицита
СПИД - синдром приобретенного иммунодефицита Клинические формы ихтиоза
Клинические формы ихтиоза Тератология
Тератология Аудиометрия. Звуковые методы исследования в медицине: перкуссия, аускультация. Фонокардиография
Аудиометрия. Звуковые методы исследования в медицине: перкуссия, аускультация. Фонокардиография ZhVP
ZhVP Диагностическое выскабливание слизистой матки
Диагностическое выскабливание слизистой матки Ауру сезімі және терапиялық стоматология клиникасында жансыздандыру
Ауру сезімі және терапиялық стоматология клиникасында жансыздандыру Pneumonia
Pneumonia Перитонит. Классификация, диагностика, лечение
Перитонит. Классификация, диагностика, лечение Основы_сбалансированного_питания
Основы_сбалансированного_питания Туберкулезді спецификалық алдын алу
Туберкулезді спецификалық алдын алу Микробиологическая диагностика заболеваний, передающихся половым путем
Микробиологическая диагностика заболеваний, передающихся половым путем Философия совершенного гостеприимства
Философия совершенного гостеприимства