Содержание
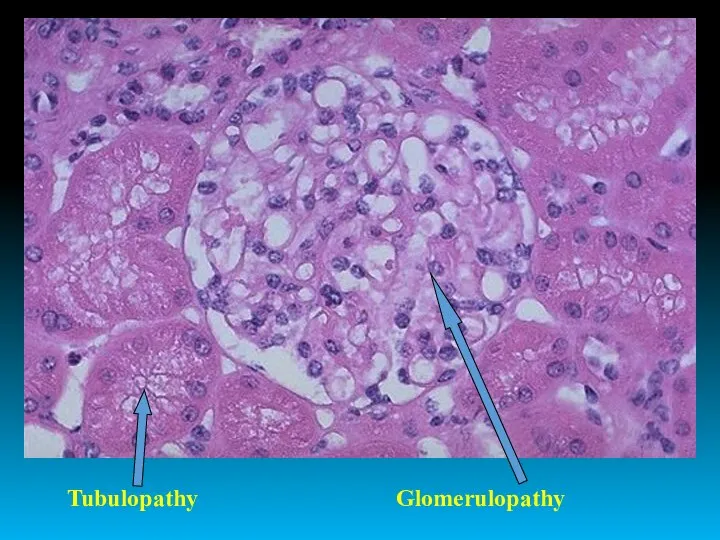
- 3. - Glomerulopathy - Tubulopathy - Interstitial diseases - Tumors - Congenital anomalies Diseases of Kidney
- 5. Renal and extrarenal symptoms
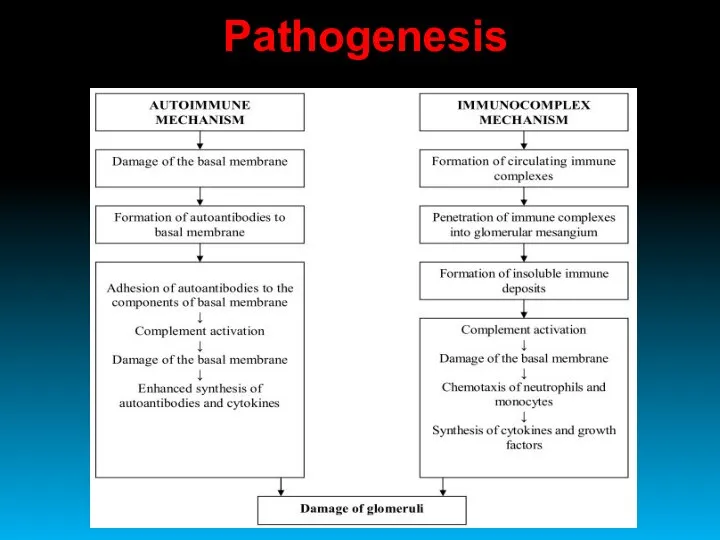
- 6. Glomerulonephritis is an infectious and allergic disease or disease of unknown nature, which is based on
- 7. Pathogenesis
- 8. 1) NEPHROTIC 2) NEPHRITIC 3) SLOWLY PROGRESSIVE UREMIA MAIN CLINICAL SYNDROMES
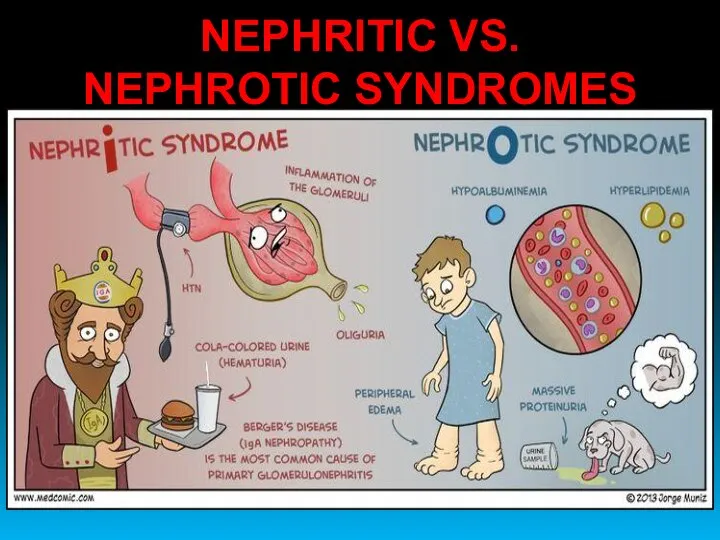
- 9. NEPHRITIC VS. NEPHROTIC SYNDROMES
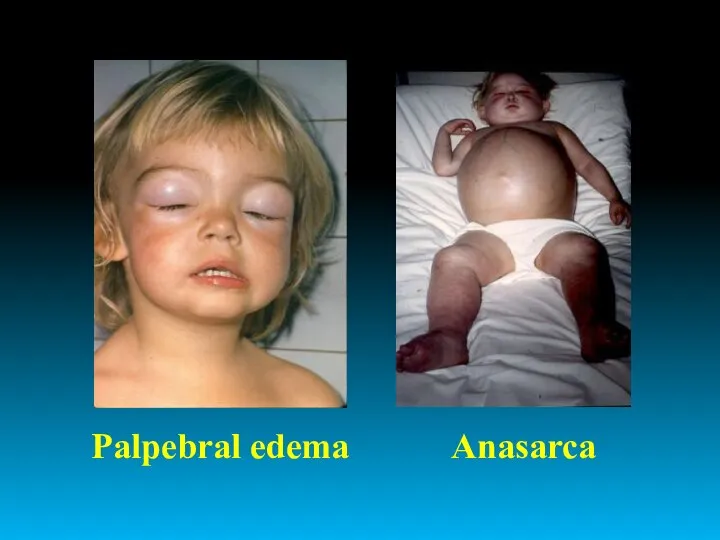
- 10. Palpebral edema Anasarca
- 11. 1. Primary, secondary, hereditary. 2. Acute, subacute, chronic. 3. Intracapillary, extracapillary. 4. Exudative, proliferative, mixed. 7.
- 12. According to the etiological factors: Primary glomerulonephritis: Acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis; Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis; Membranous glomerulonephritis;
- 13. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Diffuse intracapillary glomerulonephritis (acute glomerulonephritis). Extracapillary glomerulonephritis with crescents (rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis).
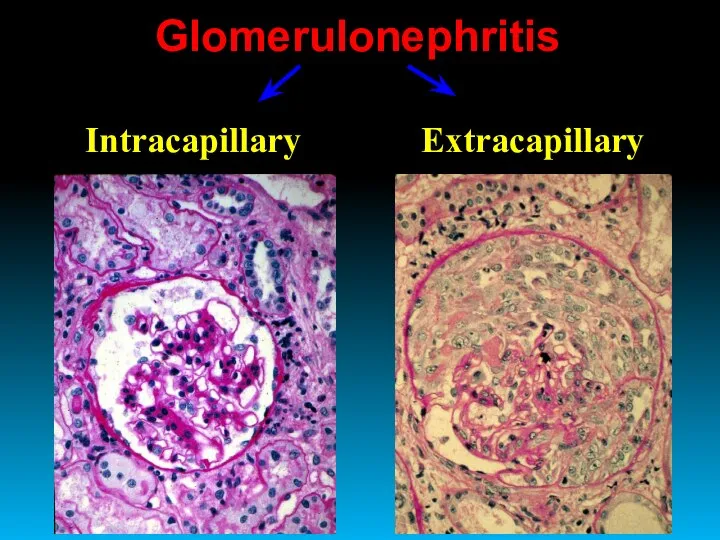
- 14. Glomerulonephritis Intracapillary Extracapillary
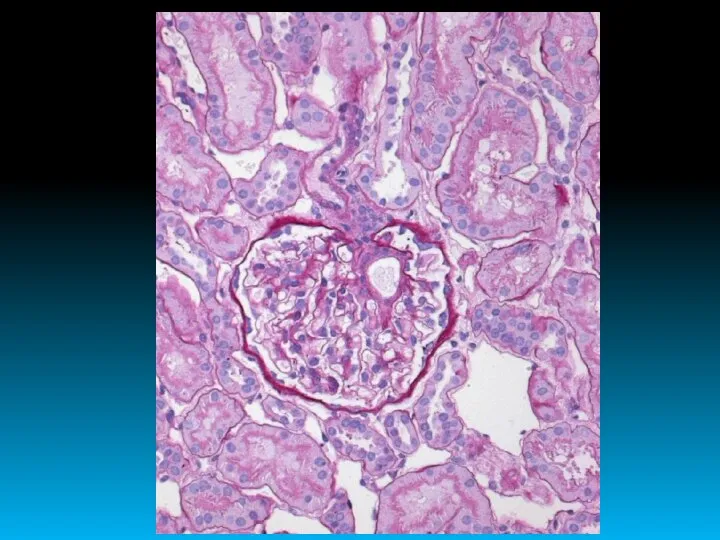
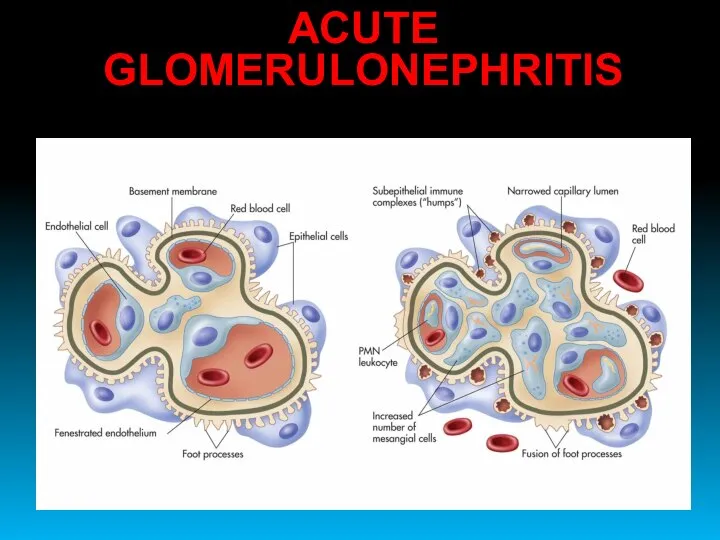
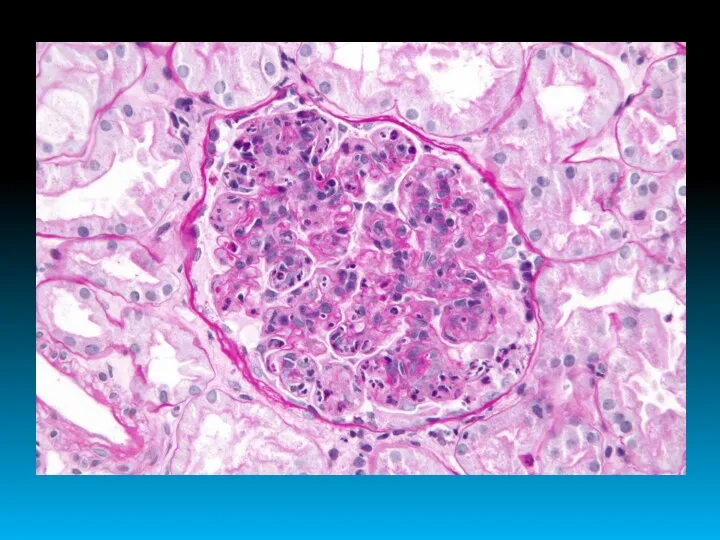
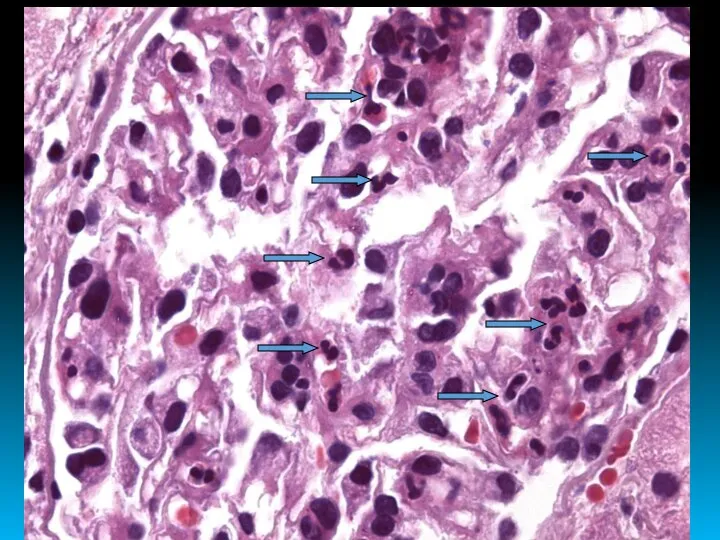
- 15. ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
- 16. WITH NEPHRITIC SYNDROME Edema, shortness of breath, headache, nausea, vomiting, weakness; Arterial hypertension; Hematuria; Diuresis ↓;
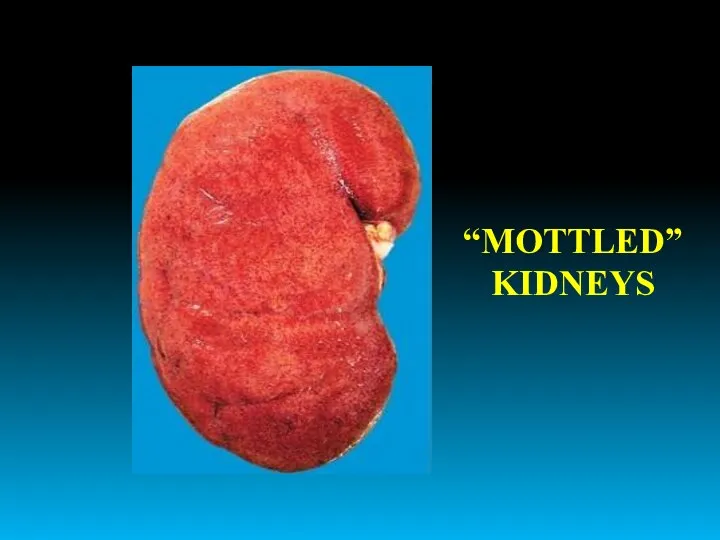
- 17. “MOTTLED” KIDNEYS
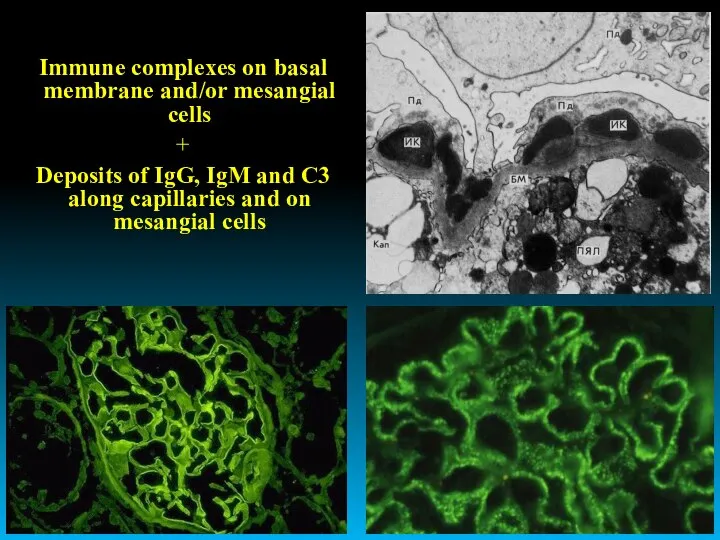
- 20. Immune complexes on basal membrane and/or mesangial cells + Deposits of IgG, IgM and C3 along
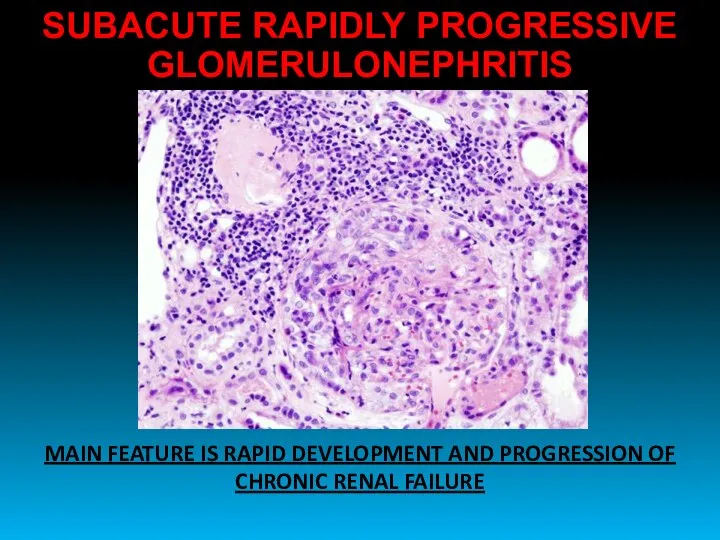
- 21. SUBACUTE RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS MAIN FEATURE IS RAPID DEVELOPMENT AND PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
- 22. CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS LATENT WITH HYPERTENSIVE SYNDROME WITH HEMATURIA WITH NEPHROTIC SYNDROME MIXED
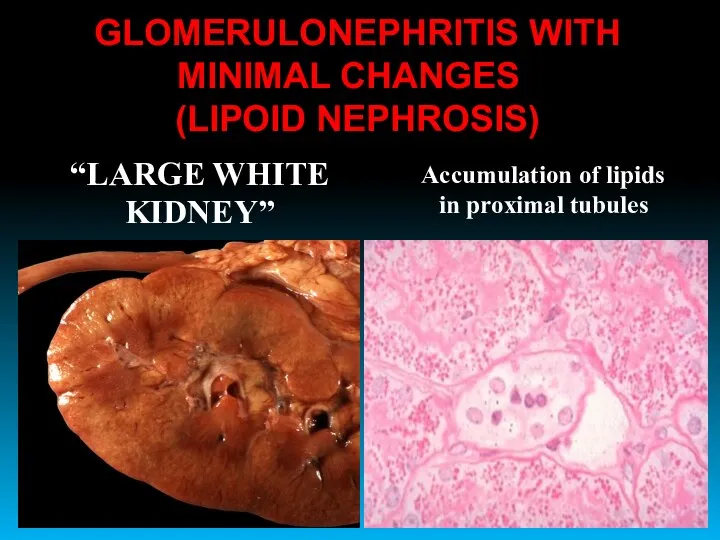
- 23. “LARGE WHITE KIDNEY” Accumulation of lipids in proximal tubules GLOMERULONEPHRITIS WITH MINIMAL CHANGES (LIPOID NEPHROSIS)
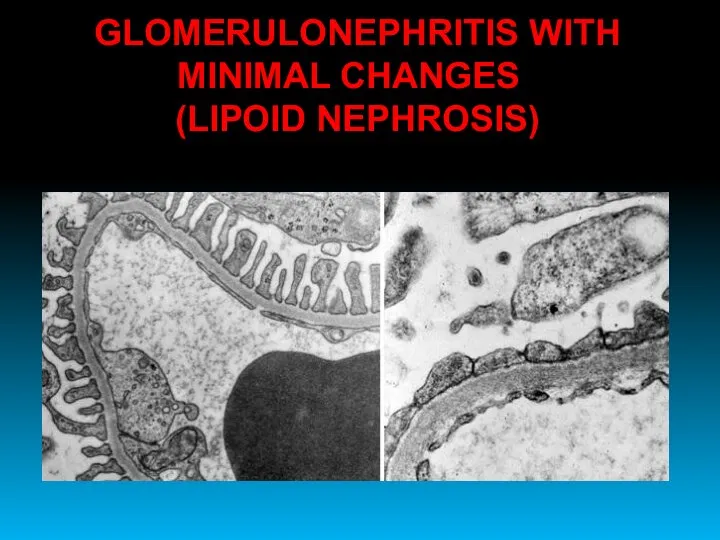
- 24. GLOMERULONEPHRITIS WITH MINIMAL CHANGES (LIPOID NEPHROSIS)
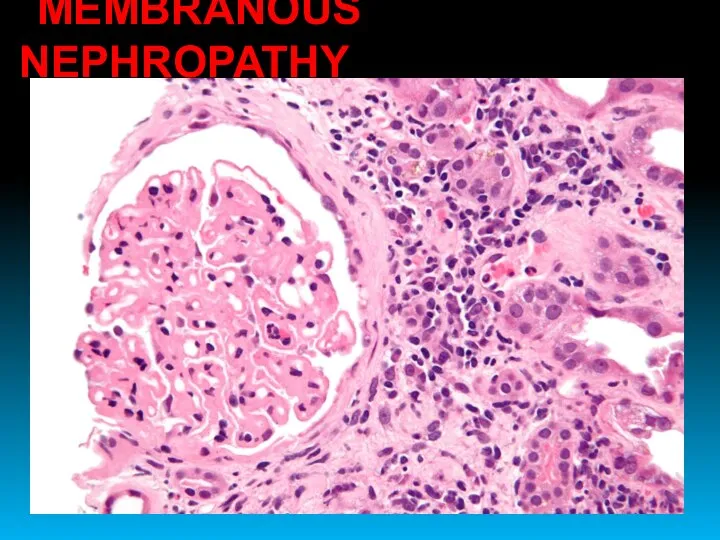
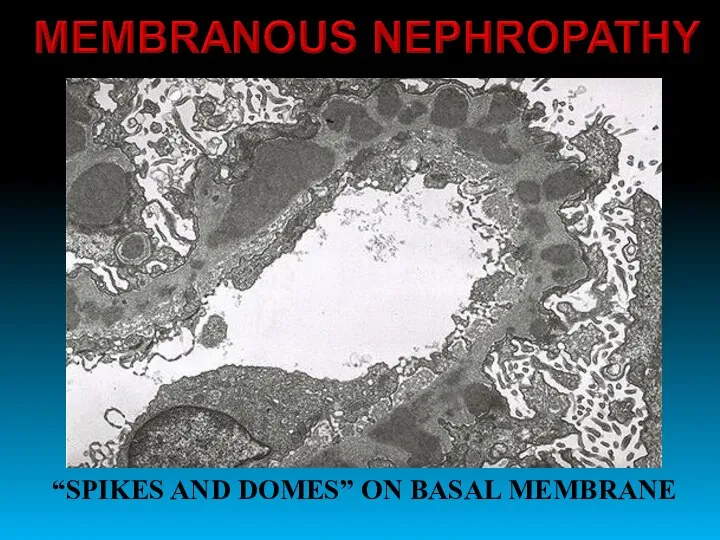
- 25. MEMBRANOUS NEPHROPATHY
- 26. “SPIKES AND DOMES” ON BASAL MEMBRANE
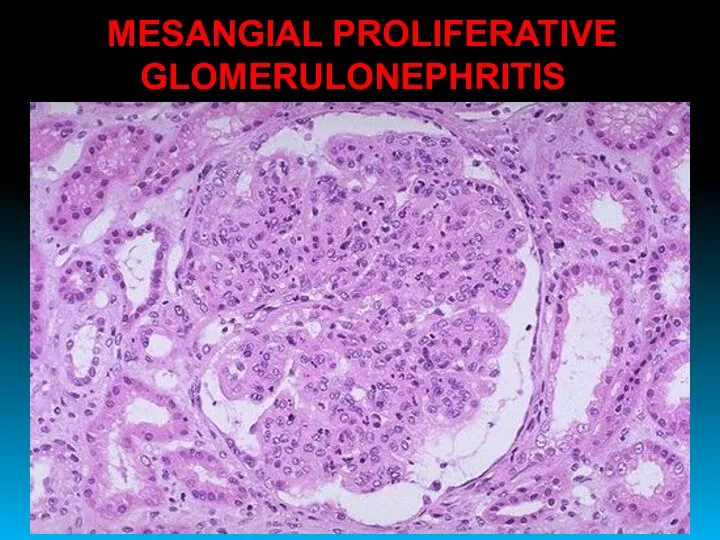
- 27. MESANGIAL PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
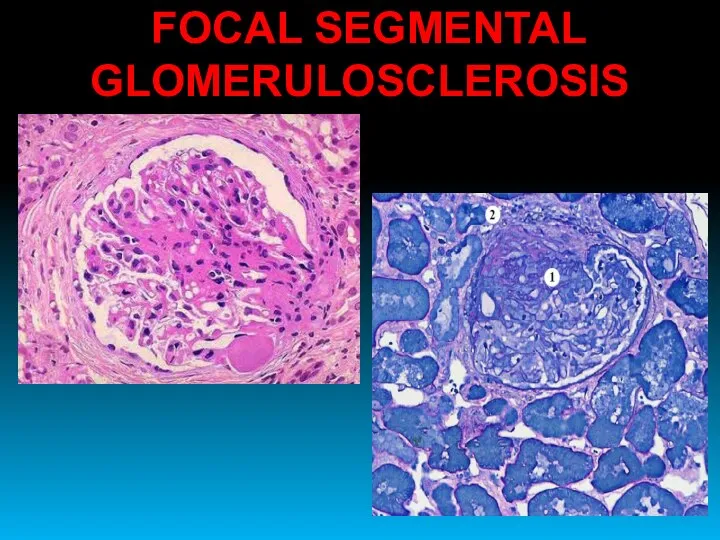
- 28. FOCAL SEGMENTAL GLOMERULOSCLEROSIS
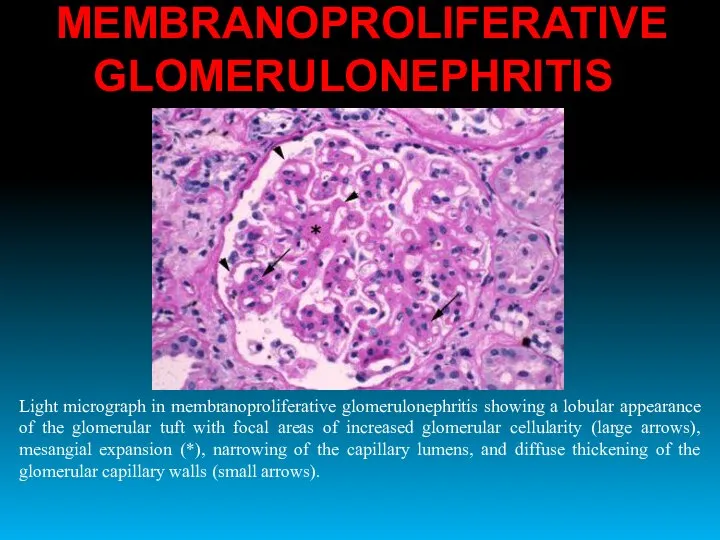
- 29. MEMBRANOPROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Light micrograph in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis showing a lobular appearance of the glomerular tuft with
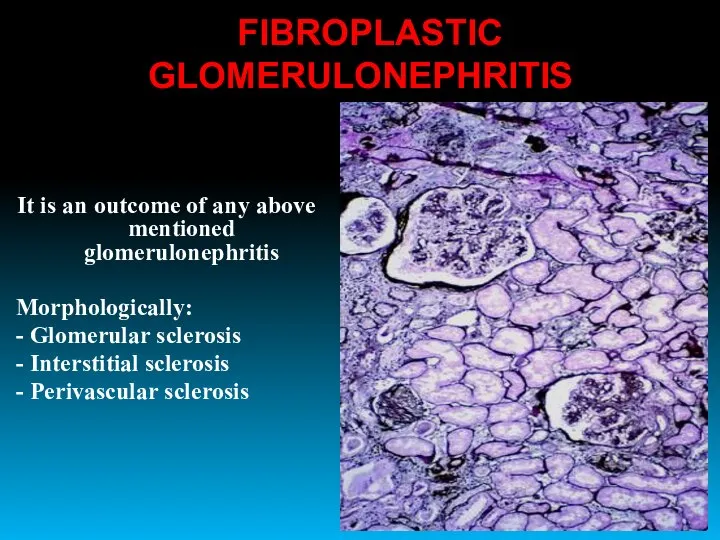
- 30. FIBROPLASTIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS It is an outcome of any above mentioned glomerulonephritis Morphologically: - Glomerular sclerosis -
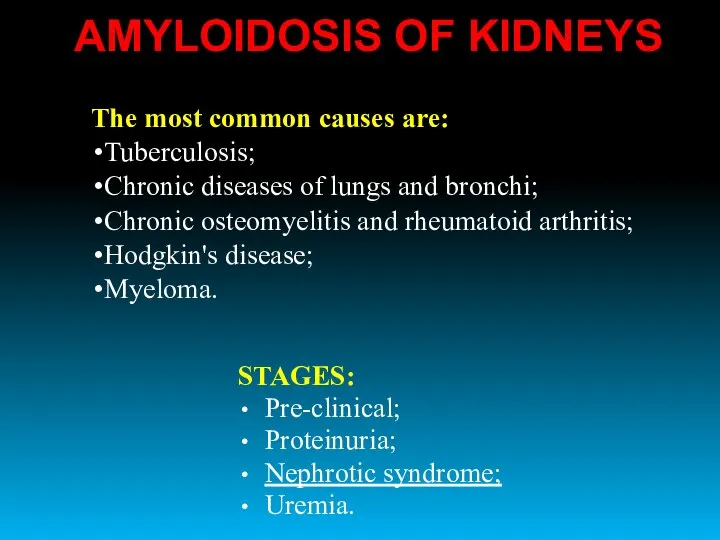
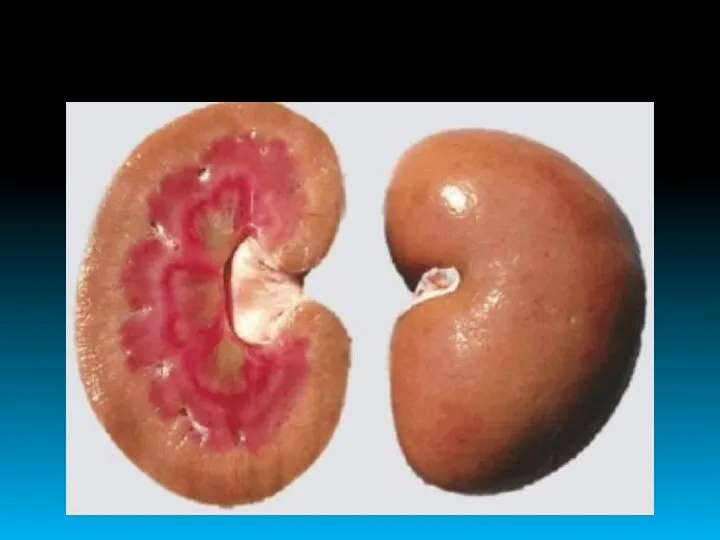
- 31. The most common causes are: Tuberculosis; Chronic diseases of lungs and bronchi; Chronic osteomyelitis and rheumatoid
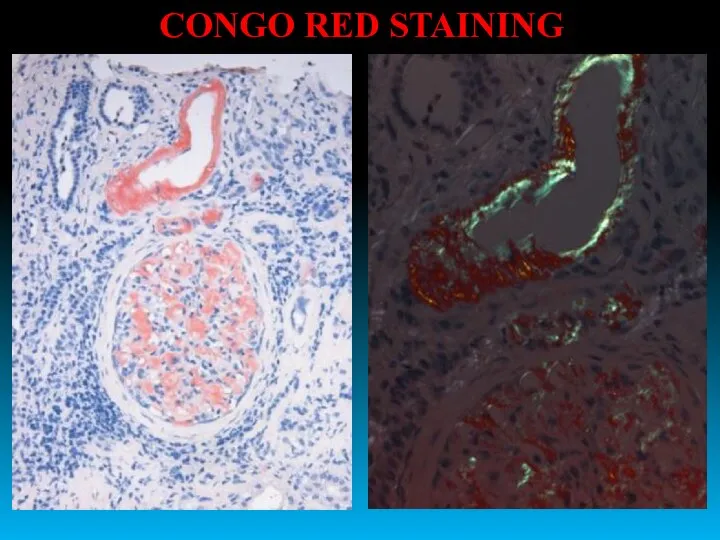
- 33. CONGO RED STAINING
- 34. Amyloid (А) can be seen as fibrillar masses under the basal membrane (BM). ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
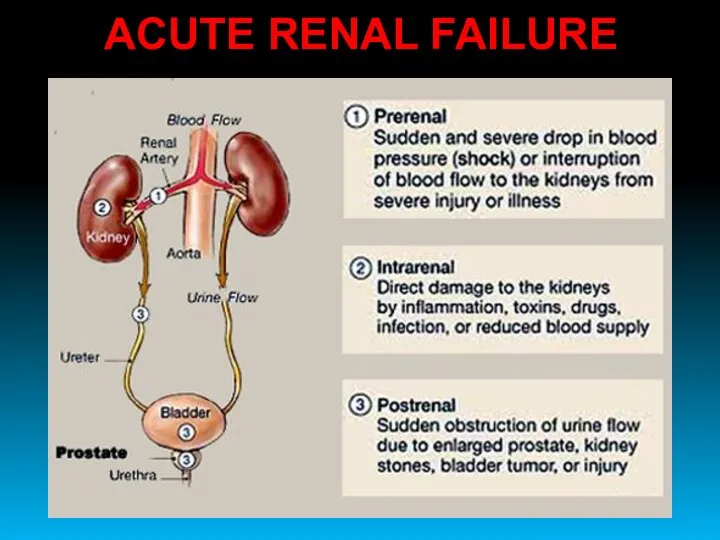
- 35. ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
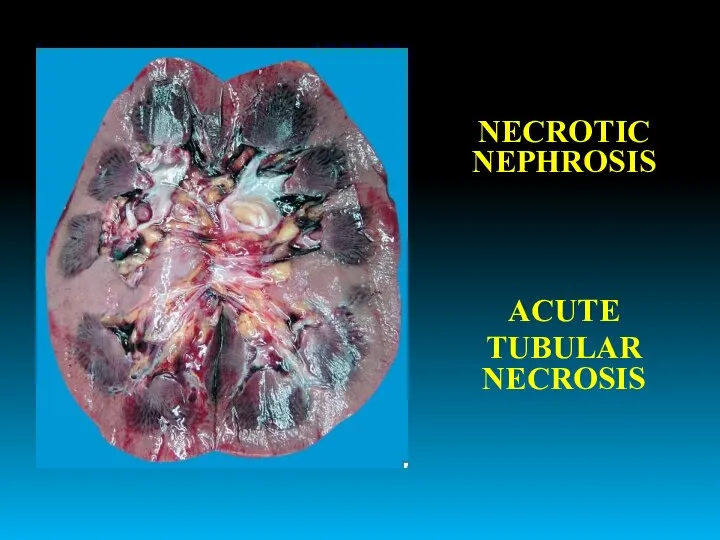
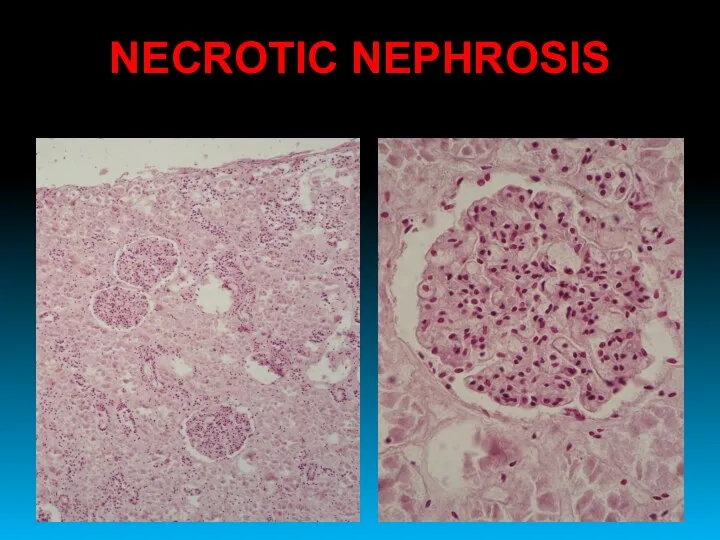
- 36. NECROTIC NEPHROSIS ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS
- 37. NECROTIC NEPHROSIS
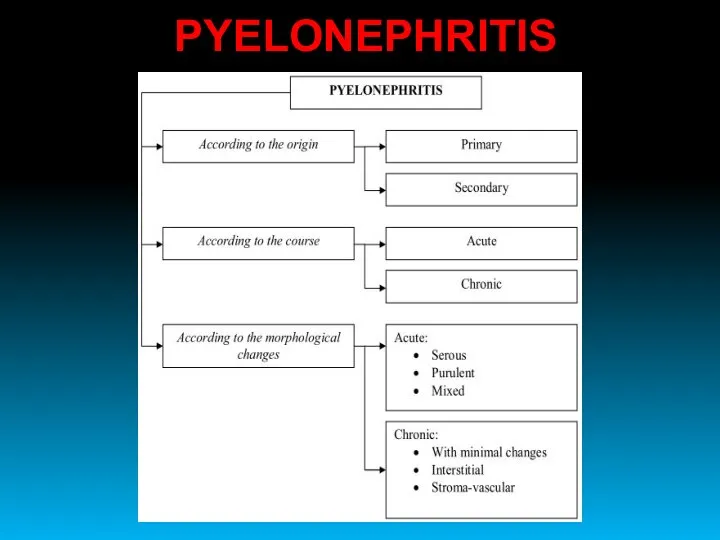
- 38. PYELONEPHRITIS
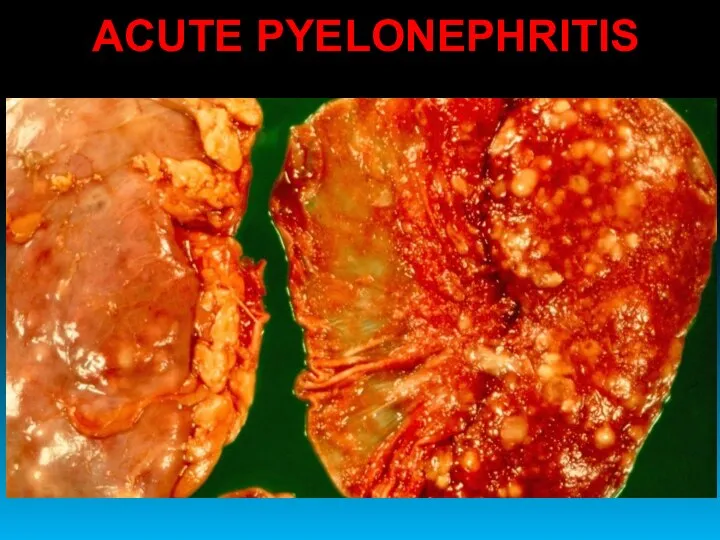
- 39. ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS
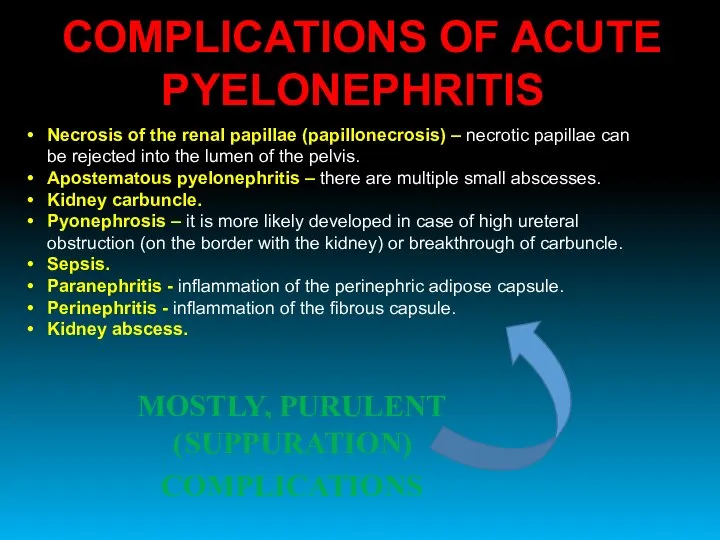
- 40. COMPLICATIONS OF ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS Necrosis of the renal papillae (papillonecrosis) – necrotic papillae can be rejected
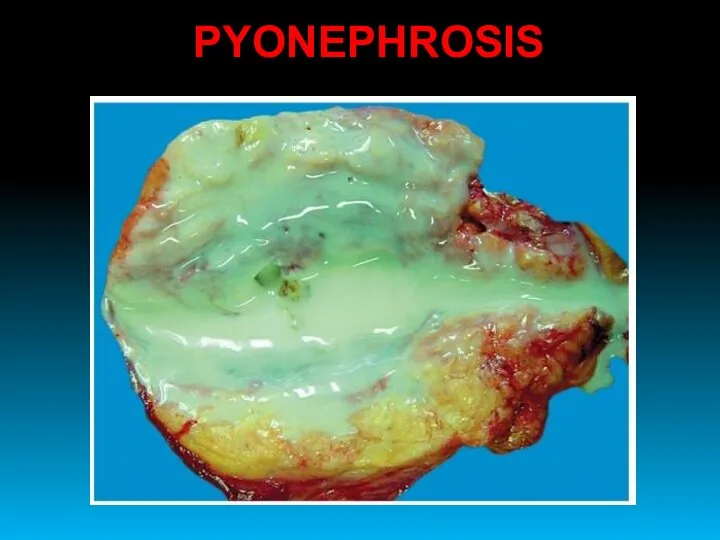
- 41. PYONEPHROSIS
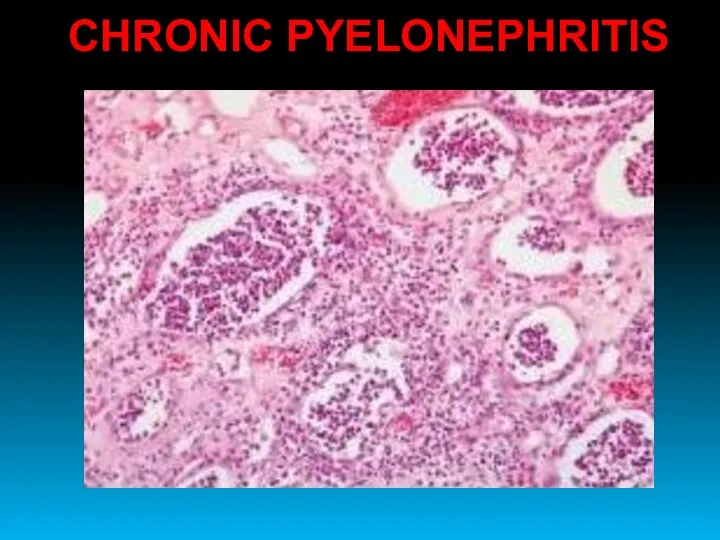
- 42. CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS
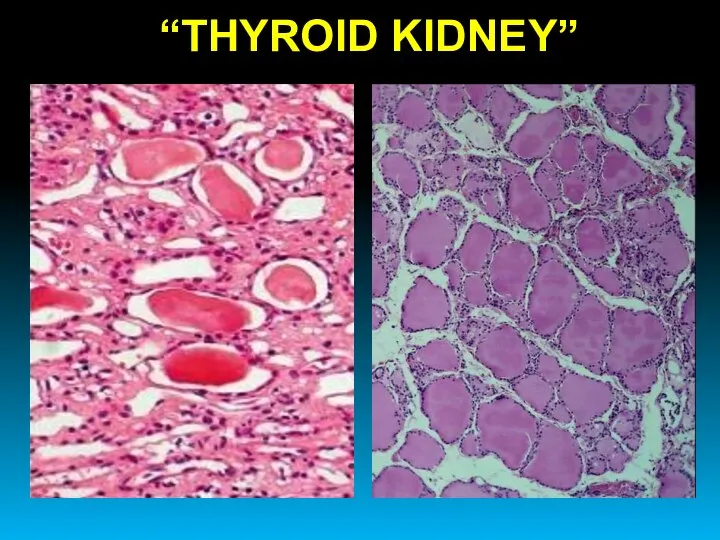
- 43. “THYROID KIDNEY”
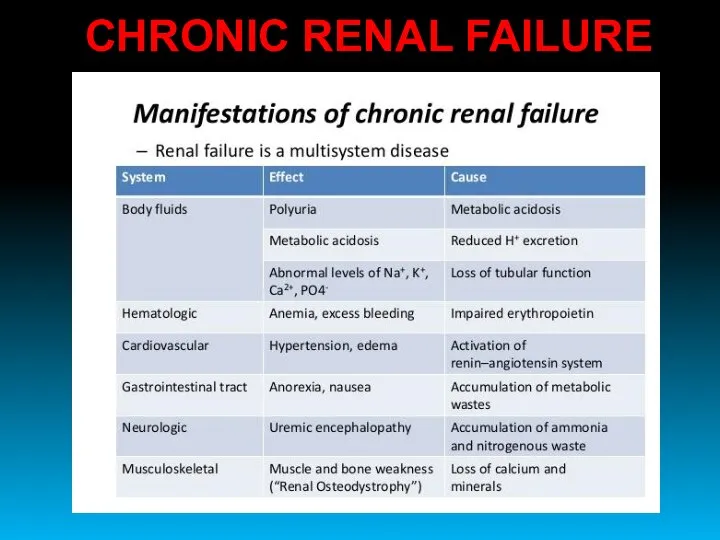
- 44. CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
- 45. CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
- 47. Скачать презентацию











 Қан жасау және лимфоидты тіндер ісіктерінің патоморфологиясы, классификациясы. Тромбопения және тромбоцитопатиялардың
Қан жасау және лимфоидты тіндер ісіктерінің патоморфологиясы, классификациясы. Тромбопения және тромбоцитопатиялардың ЖИТС-пен ауыратын науқастардағы комплаенс
ЖИТС-пен ауыратын науқастардағы комплаенс Советы для ведения личного дневника
Советы для ведения личного дневника Мониторинг распространенности различных форм хронического тонзиллита у детей
Мониторинг распространенности различных форм хронического тонзиллита у детей Влияние погодных факторов на здоровье. Профилактика гелиометеотропных реакций (кейс-задание)
Влияние погодных факторов на здоровье. Профилактика гелиометеотропных реакций (кейс-задание) Вирусные заболевания кожи
Вирусные заболевания кожи Түсті металлургия саласындағы жұмысшылардың кәсіби аурушаңдығы және алдын - алу жолдары
Түсті металлургия саласындағы жұмысшылардың кәсіби аурушаңдығы және алдын - алу жолдары Lektsia_Besplodny_brak
Lektsia_Besplodny_brak Психология
Психология Паллиативная помощь в онкологии
Паллиативная помощь в онкологии Патофизиология почек
Патофизиология почек Заболевания бронхолегочной системы
Заболевания бронхолегочной системы График работы врачей ОАПП №1 18.09.2021
График работы врачей ОАПП №1 18.09.2021 Лучевая диагностика туберкулёза органов дыхания
Лучевая диагностика туберкулёза органов дыхания Психология, как наука и ее структура
Психология, как наука и ее структура Последствия ранней половой жизни
Последствия ранней половой жизни Қантсыз диабет
Қантсыз диабет Пневмония. Эпидемиология пневмоний
Пневмония. Эпидемиология пневмоний Инфекционные болезни. Воздушно-капельные инфекции, бактериальной этиологии
Инфекционные болезни. Воздушно-капельные инфекции, бактериальной этиологии Фармацевтические аэрозоли. Определение, технологическая схема производства
Фармацевтические аэрозоли. Определение, технологическая схема производства Ортобиотическая система комплексной реабилитации и социальной адаптации детей с тяжёлыми нарушениями речи
Ортобиотическая система комплексной реабилитации и социальной адаптации детей с тяжёлыми нарушениями речи Рак гайморовой пазухи, клиника, диагностика, лечение
Рак гайморовой пазухи, клиника, диагностика, лечение Первая помощь при кровотечении
Первая помощь при кровотечении Бактериальные инфекции: Кандидоз слизистой оболочки полости рта
Бактериальные инфекции: Кандидоз слизистой оболочки полости рта Congenital heart diseases
Congenital heart diseases Некроз. Смерть, признаки смерти. Посмертные изменения
Некроз. Смерть, признаки смерти. Посмертные изменения Лимфатическая система. Влияние окружающей среды на здоровье и иммунитет человека
Лимфатическая система. Влияние окружающей среды на здоровье и иммунитет человека Оптимальные методы визуализации и дифференциальная диагностика заболеваний печени и желчевыводящих путей
Оптимальные методы визуализации и дифференциальная диагностика заболеваний печени и желчевыводящих путей