Diabetic coma Death
Hypoglycemic coma was defined as a state in which
the patient was not arousable (or responded only to pain), with a blood glucose concentration of 2.72 mmol/L (49 mg/dL) or less, and responded symptomatically (a return of consciousness) to the administration of intravenous glucose.
Hypoglycemic Coma
Hypoglycemia occurs predominantly in patients taking insulin but also in patients taking sulfonylureas, particularly long-acting preparations such as chlorpropamide and glibenclamide. The factors which commonly predispose to hypoglycemia, either alone or in combination, are:
•
too much insulin or sulfonylurea
•
too little food or delayed meal
•
too much physical exercise.








 Технологии проведения КТ исследований с внутривенным контрастированием
Технологии проведения КТ исследований с внутривенным контрастированием Дәлелді медицина мамандарының қоғамы туралы түсінік. ТМД және біздің елдегі дәлелді медицина орталықтары
Дәлелді медицина мамандарының қоғамы туралы түсінік. ТМД және біздің елдегі дәлелді медицина орталықтары Medicine. Remedy. Therapeutic action of a drug
Medicine. Remedy. Therapeutic action of a drug Леонид Михайлович Рошаль
Леонид Михайлович Рошаль Жасқа байланысты инсулинді мөлшерлеу ерекшелігі
Жасқа байланысты инсулинді мөлшерлеу ерекшелігі Практика 6 Частная психопатология
Практика 6 Частная психопатология Әйелдер консультациясы және отбасын жоспарлау орталықтарында жас ата-аналар мектебінің жұмысына қатысып есеп жазу
Әйелдер консультациясы және отбасын жоспарлау орталықтарында жас ата-аналар мектебінің жұмысына қатысып есеп жазу Система крови. Симптоматика. Пальпация
Система крови. Симптоматика. Пальпация Небезпечне харчування, його вплив на стан здоров'я дитини
Небезпечне харчування, його вплив на стан здоров'я дитини Технология изготовления и контроля гипериммунных и диагностических сывороток, антигенов, антибиотиков, бактериофагов
Технология изготовления и контроля гипериммунных и диагностических сывороток, антигенов, антибиотиков, бактериофагов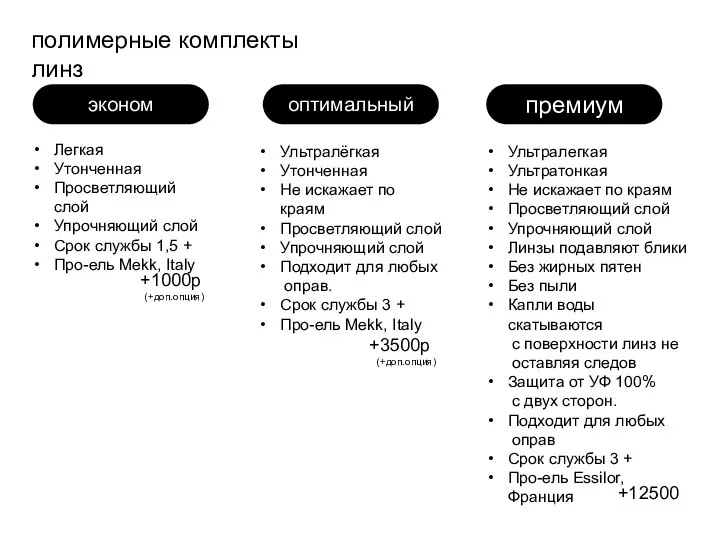 Комплекты линз
Комплекты линз Основные операции на сердце
Основные операции на сердце Методика самообследования молочных желёз
Методика самообследования молочных желёз Эндопротезирование аортального клапана (TAVI)
Эндопротезирование аортального клапана (TAVI) Неотложные хирургические заболевания у детей
Неотложные хирургические заболевания у детей Стресс-ЭхоКГ
Стресс-ЭхоКГ Дилатационная кардиомиопатия
Дилатационная кардиомиопатия Лучевая диагностика новообразований тимуса
Лучевая диагностика новообразований тимуса Емболізація маткових артерій. Показання до проведення
Емболізація маткових артерій. Показання до проведення Современные алгоритмы по управлению артериальной гипертонией
Современные алгоритмы по управлению артериальной гипертонией Туберкулез внутренних лимфатических узлов
Туберкулез внутренних лимфатических узлов Хронический колит
Хронический колит Проведение профилактического скрининга в Центрах Здоровья
Проведение профилактического скрининга в Центрах Здоровья Клиническая фармакология противотуберкулезных средств
Клиническая фармакология противотуберкулезных средств Пороки сердца (стеноз и недостаточность МК, стеноз и недостаточность АК)
Пороки сердца (стеноз и недостаточность МК, стеноз и недостаточность АК) Конфликтогены
Конфликтогены Ғылым және ғылыми зерттеулер. Ғылым және олардың жіктеулері. Ғылыми зерттеулер және олардың мәні
Ғылым және ғылыми зерттеулер. Ғылым және олардың жіктеулері. Ғылыми зерттеулер және олардың мәні Пиогенные (гноеродные) бактерии
Пиогенные (гноеродные) бактерии