Содержание
- 5. Illustrative Pathological problems Consolidation Atelectasis Pleural effusion Pneumothorax Mass Diffuse lung disease
- 12. Steps General Examination Mediastinal position Chest expansion Lung resonance Breath sounds Adventitious sounds Voice transmission
- 13. General Examination Respiratory rate Pattern of breathing Cyanosis Clubbing Weight Cough Hospital setting Effort of ventilation
- 14. Respiratory Rate Bradypnea: rate less than 8 per minute Tachypnea: rate greater than 25 per minute
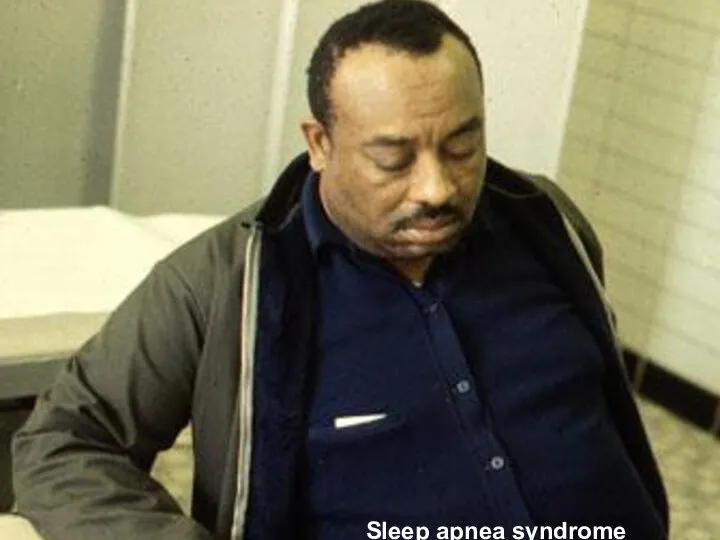
- 15. Pattern of Breathing Kussmals Sleep apnea Cheyne strokes Pursed lip breathing Orthopnoea: Short of breath in
- 16. Sleep apnea syndrome
- 17. Central Cyanosis Results from pulmonary dysfunction, the mucous membrane of conjunctiva and tongue are bluish. If
- 18. Central Cyanosis
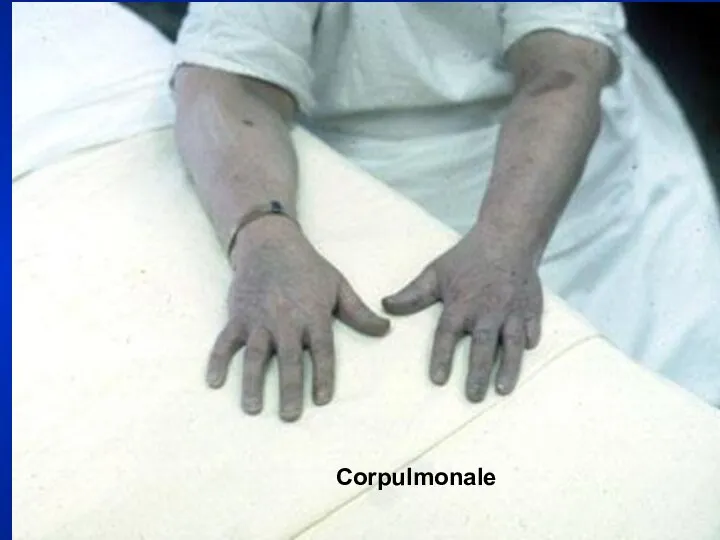
- 19. Corpulmonale
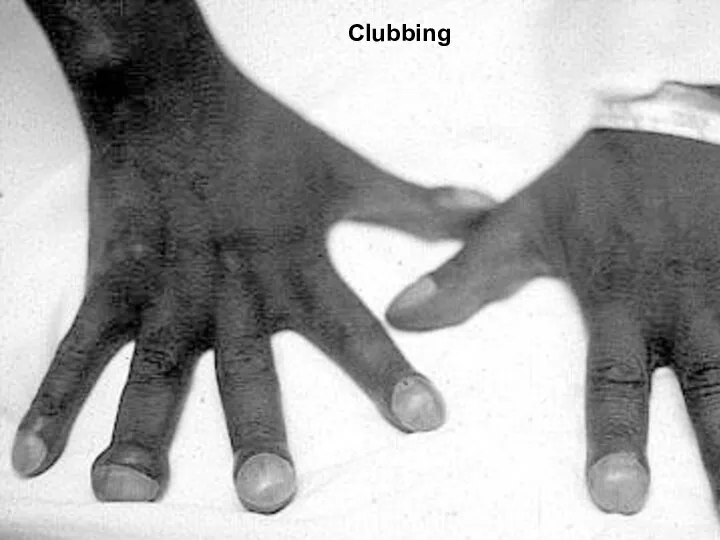
- 20. Clubbing
- 21. Clubbing In clubbing, there is widening of the AP and lateral diameter of terminal portion of
- 22. Significance: Clubbing Observed In: Intrathoracic malignancy: Primary or secondary (lung, pleural, mediastinal) Suppurative lung disease: (lung
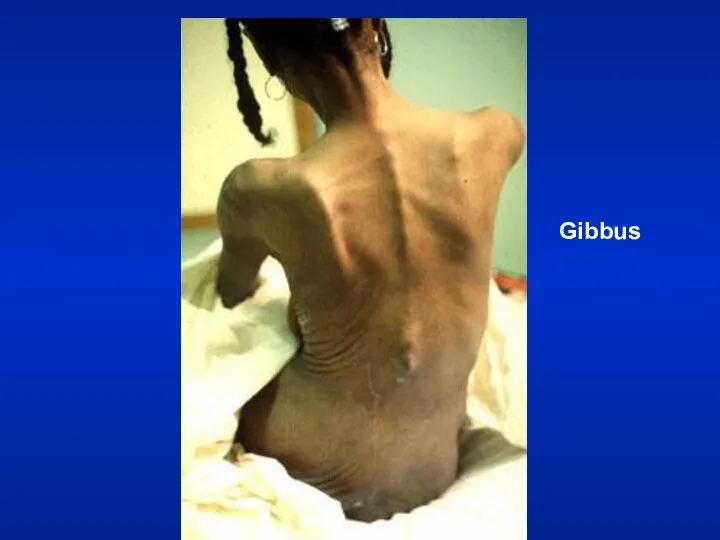
- 23. Gibbus
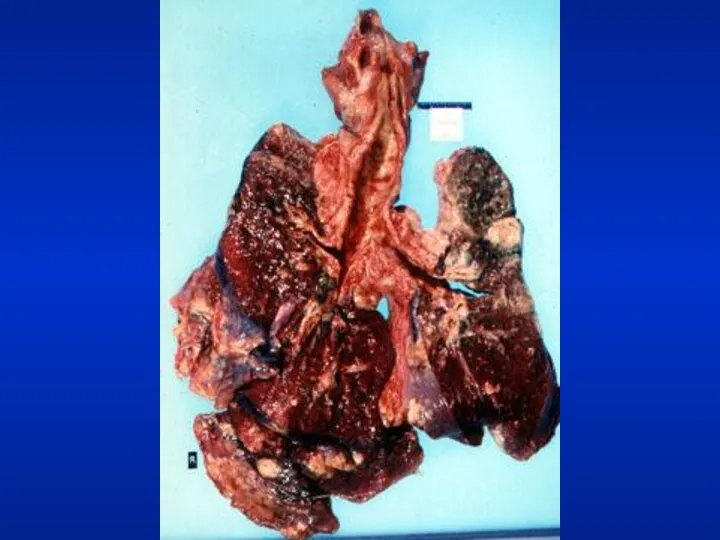
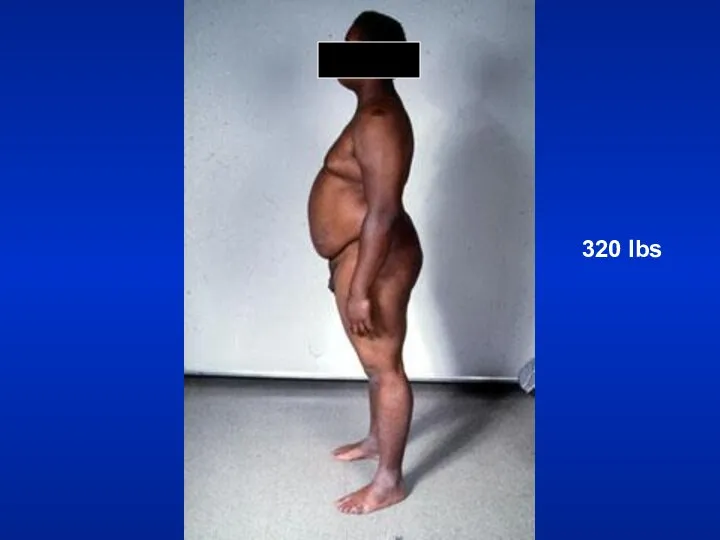
- 24. Weight Emaciation cachectic Malignancy Tuberculosis
- 25. 320 lbs
- 26. Weight Obese: Sleep apnea syndrome
- 27. 3 Layered sputum
- 28. Cough Productive Dry Whooping Bovine
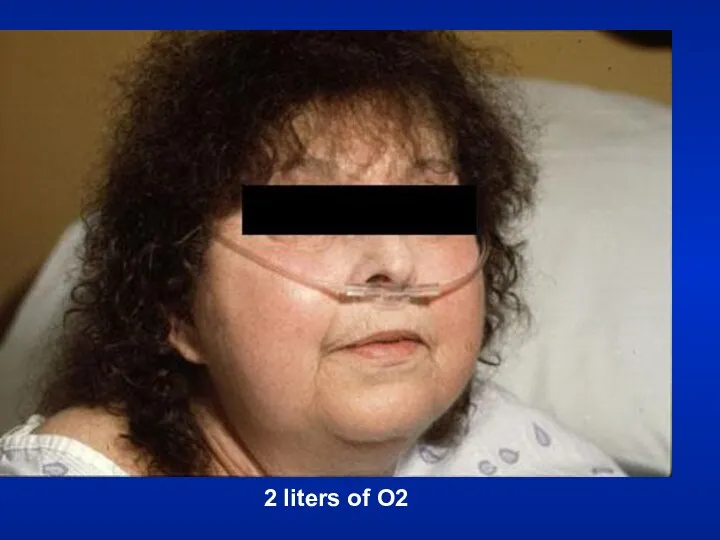
- 29. 2 liters of O2
- 30. Hospital Setting Isolation room Oxygen set up
- 31. Effort of Ventilation Person appears uncomfortable. Breathing seems voluntary. Accessory muscles are in use, expiratory muscles
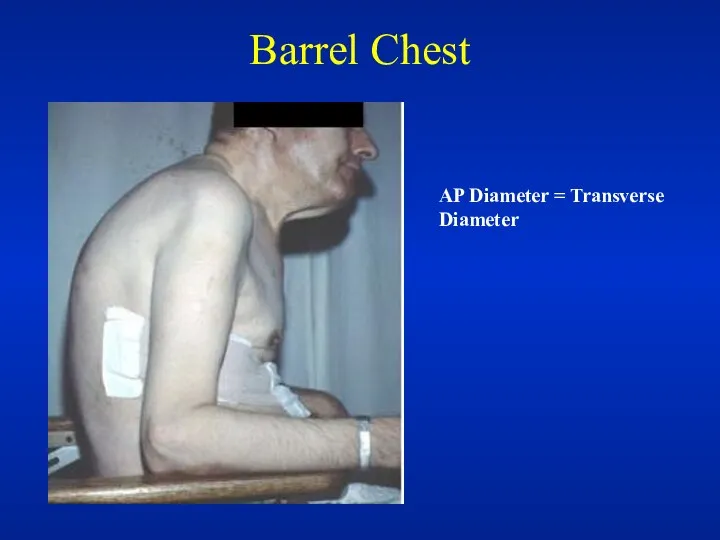
- 32. Resting Size and Shape of Thorax Barrel chest Kyphosis Scoliosis Pectus excavatum Gibbus
- 33. Barrel Chest AP Diameter = Transverse Diameter
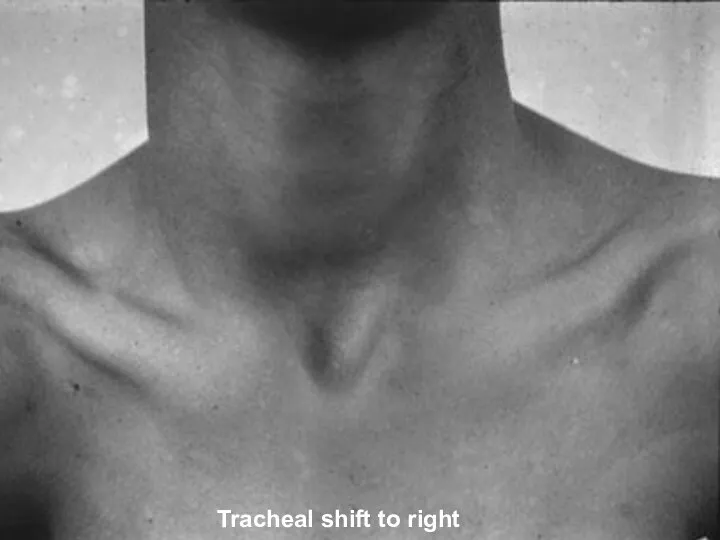
- 34. Tracheal Position: Mediastinum Any deviation of the mediastinum is abnormal Lateral shift: The mediastinum can be
- 35. Tracheal shift to right
- 36. Chest Expansion Asymmetrical chest expansion is abnormal The abnormal side expands less and lags behind the
- 37. Percussion: Decreased or Increased Resonance is Abnormal Dullness Decreased resonance is noted with pleural effusion and
- 38. Breath Sounds: Diminished or Absent Intensity of breath sounds, in general, is a good index of
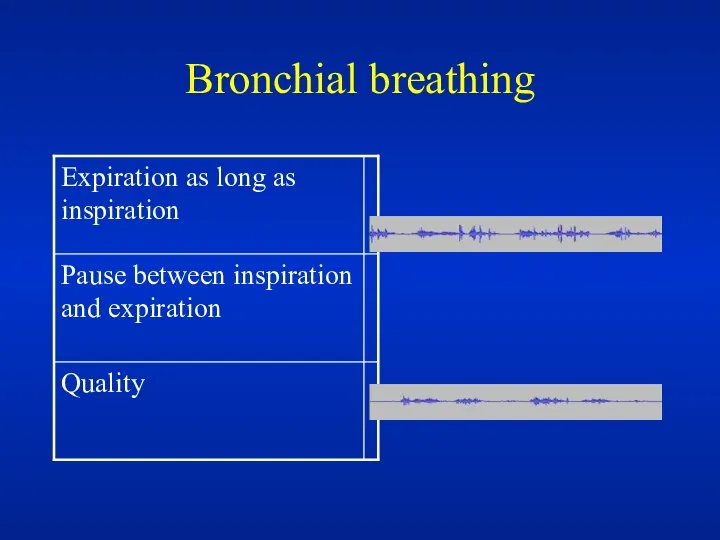
- 39. Bronchial Bronchial breathing anywhere other than over the trachea, right clavicle or right inter-scapular space is
- 40. Bronchial breathing
- 41. Rhonchi Rhonchi are long continuous adventitious sounds, generated by obstruction to airways. When detected, note whether
- 42. Rhonchi Asthmatic Continuous
- 43. Rhonchi Localized rhonchi suggests obstruction of any etiology e.g., tumor, foreign body or mucous. Mucous secretions
- 44. Pleural Rub Normal parietal and visceral pleura glide smoothly during respiration. If the pleura is roughened
- 45. Pleural rub Scratching, Grating Related to respiration
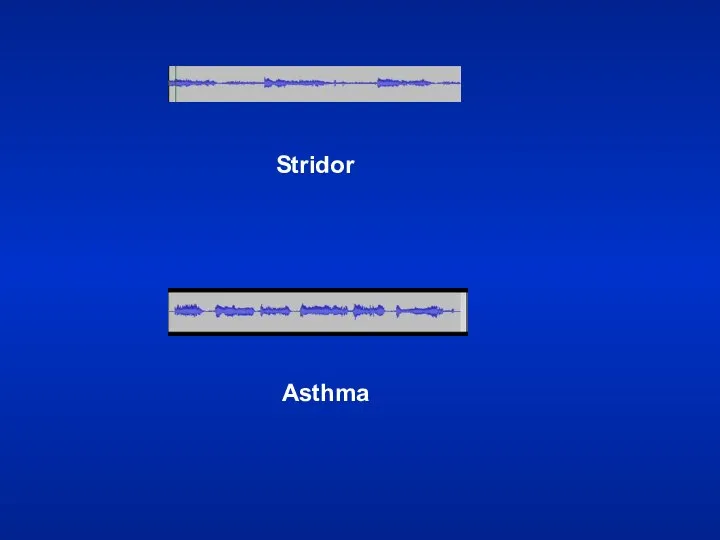
- 46. Stridor Loud audible inspiratory rhonchi is called a stridor. Inspiratory rhonchi in general, implies large airway
- 47. Stridor Asthma
- 48. Crackles Interrupted adventitious sounds are called crackles. Make a notation about timing, intensity, effect with respiration,
- 49. Crackles When the crackles are heard at the end of inspiration and the beginning of expiration
- 50. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance) Asymmetrical voice transmission points to disease on one side. Increased:
- 51. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance) Decreased: A quantitative decrease in voice transmission could be due
- 53. Скачать презентацию



































 Массаж. Вид приема
Массаж. Вид приема Сонная болезнь
Сонная болезнь Экстракорпоральные методы детоксикации
Экстракорпоральные методы детоксикации Методика «Несуществующее животное»
Методика «Несуществующее животное» Первичная профилактика инсульта
Первичная профилактика инсульта Что нужно знать о ВИЧ-инфекции каждому
Что нужно знать о ВИЧ-инфекции каждому Ингарон. Лекарственная форма
Ингарон. Лекарственная форма Сестринская помощь при хронической сердечной недостаточности. Тема 4.3
Сестринская помощь при хронической сердечной недостаточности. Тема 4.3 Апластическая анемия
Апластическая анемия Антиаритмические ЛС
Антиаритмические ЛС Анатомо-физиологические особенности мочевыделительной системы
Анатомо-физиологические особенности мочевыделительной системы Психологиядағы және наркологиядағы сараптама түрлері
Психологиядағы және наркологиядағы сараптама түрлері Формирование единого регионального профилактического пространства на территории Архангельской области
Формирование единого регионального профилактического пространства на территории Архангельской области Мозг и разум. Личностные компетенции молодого ученого: современные механизмы реализации и коммуникации
Мозг и разум. Личностные компетенции молодого ученого: современные механизмы реализации и коммуникации Теории и типы любви
Теории и типы любви Вирусный гепатит В, желтушная форма, тяжелое течение. Клинический случай
Вирусный гепатит В, желтушная форма, тяжелое течение. Клинический случай Разработка медицинской цифровой платформы для связи врачей и пациентов
Разработка медицинской цифровой платформы для связи врачей и пациентов Шесть шляп мышления. Эдвард Де Боно
Шесть шляп мышления. Эдвард Де Боно Пропедевтика внутренних болезней
Пропедевтика внутренних болезней Диагностика тромбоэмболии легочной артерии (ТЭЛА)
Диагностика тромбоэмболии легочной артерии (ТЭЛА) Өкпе туберкулемасы
Өкпе туберкулемасы Бронхиальная астма у детей
Бронхиальная астма у детей Хронические миелопролиферативные заболевания
Хронические миелопролиферативные заболевания Клинический случай HHV-6 ассоциированного менингоэнцефалита на фоне генерализованной кишечной инфекции
Клинический случай HHV-6 ассоциированного менингоэнцефалита на фоне генерализованной кишечной инфекции Фонокардиограф. Технические характеристики
Фонокардиограф. Технические характеристики Современные методы комплексного лечения больных туберкулезом. Современные схемы лечения различных групп больных
Современные методы комплексного лечения больных туберкулезом. Современные схемы лечения различных групп больных Охрана здоровья граждан в Российской Федерации
Охрана здоровья граждан в Российской Федерации Способы, с помощью которых возможно избежать последствия хронического недосыпания
Способы, с помощью которых возможно избежать последствия хронического недосыпания