Содержание
- 2. Objectives Student should be able to … describe location, size, consistency, and other attributes of lymphadenopathy
- 3. Overview This is a short lecture! A major goal is to synthesize the lymphatic system as
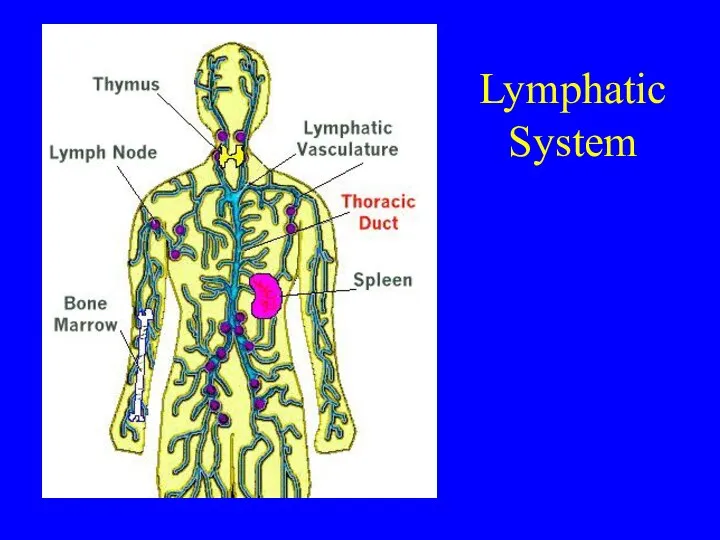
- 4. Lymphatic System
- 5. Lymph Node Examination Head/neck Axillary Inguinal/femoral
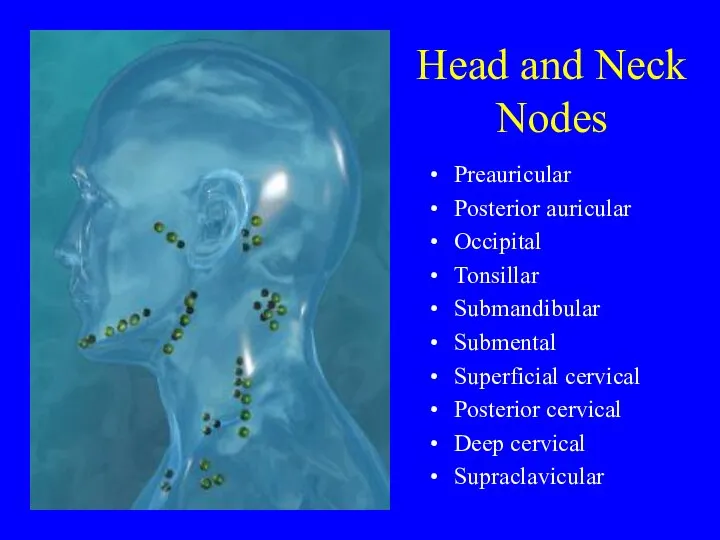
- 6. Head and Neck Nodes Preauricular Posterior auricular Occipital Tonsillar Submandibular Submental Superficial cervical Posterior cervical Deep
- 7. Axillary A pectoral (anterior) L lateral P posterior C central Ap apical
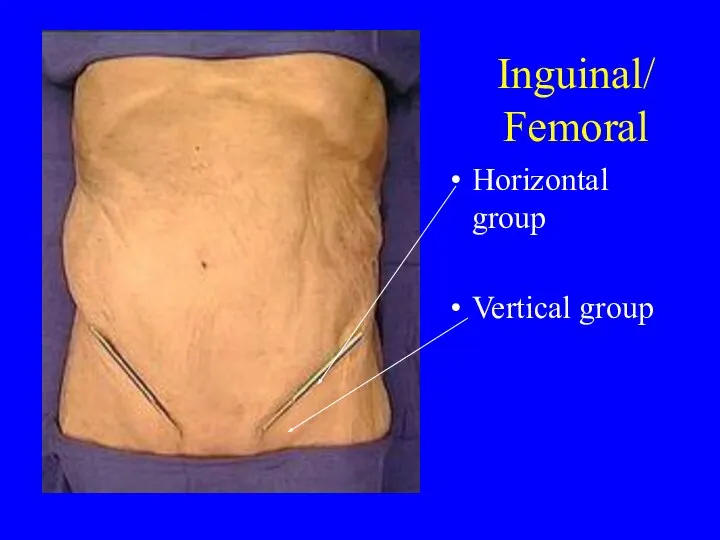
- 8. Inguinal/ Femoral Horizontal group Vertical group
- 9. Descriptors of Lymphadenopathy Location…obvious Mobility Size Texture Shape Tender/non-tender Associated erythema or warmth…signs of inflammation
- 10. Spleen Left upper quadrant Palpation most specific for detecting enlarged spleen (89-99% specificity) Spleen palpable to
- 11. Case 28 yo man presents with c/o fevers, night sweats and 30 pound weight loss. He
- 12. Case painless lymphadenopathy in anterior axilla and anterior cervical as well as supraclavicular areas bilaterally. Lymph
- 13. Differential Diagnosis Lymphoma Infection Cancer—metastatic Granulomatous disease
- 14. Anemia- Signs/Symptoms Dyspnea on exertion Palpitations Angina pectoris Intermittent claudication Headache Syncope anorexia Dizziness/vertigo Nausea Cold
- 15. Anemia Blood loss Hemolysis/sequestration Deficiencies Decreased production
- 16. Symptoms Symptoms based on acuity of HgB drop Acute blood loss usually creates rapid onset of
- 17. Anemia of Acute Blood Loss Trauma or GI tract loss most common Menstrual/vaginal loss Urinary tract
- 18. Hemolysis and Sequestration Causes for hemolytic anemias include: Autoimmune Drug induced Cell membrane disorders Hereditary Splenomegaly
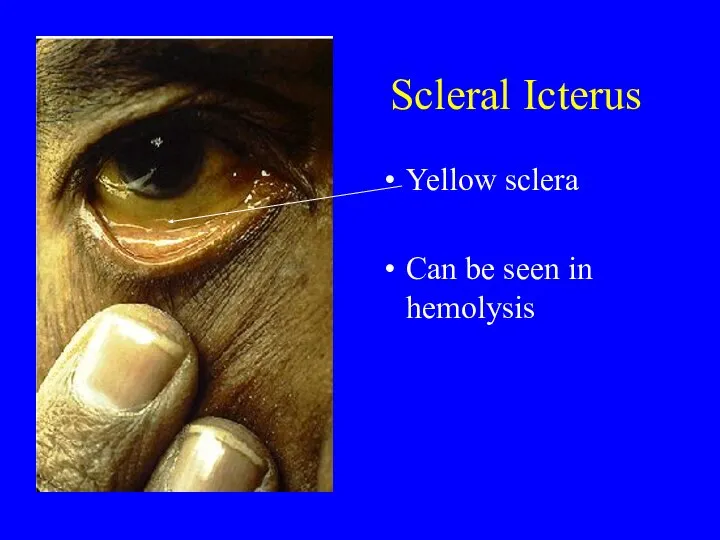
- 19. Scleral Icterus Yellow sclera Can be seen in hemolysis
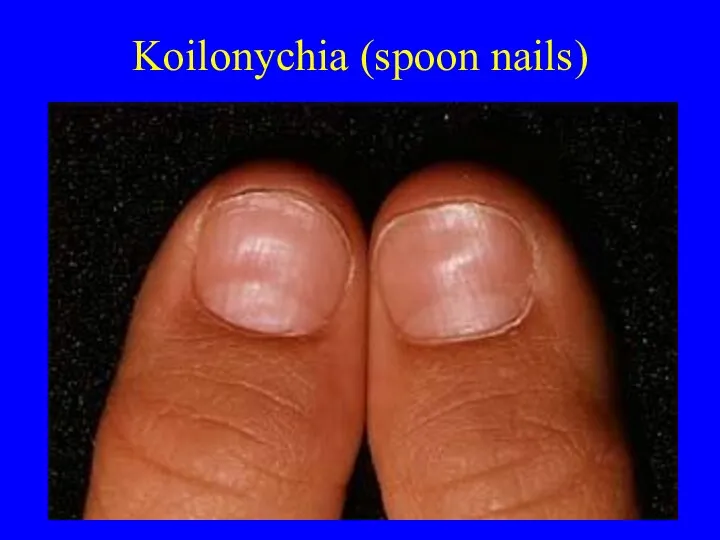
- 20. Deficiencies Iron deficiency anemia is most common worldwide and in US-spoon nails and pica Megaloblastic anemias
- 21. Koilonychia (spoon nails)
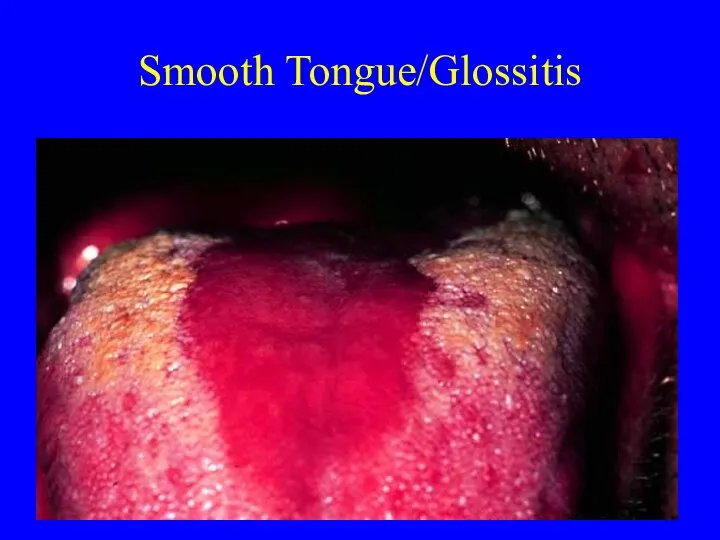
- 22. Smooth Tongue/Glossitis
- 23. Signs and Symptoms of Coagulation Disorders Bleeding Ecchymoses Petechiae Hemarthroses Hematomas
- 24. Platelets versus Coags Petechiae—platelets low or dysfunctional Ecchymoses, hematomas, hemarthroses—seen more frequently with low clotting factors
- 25. Petechiae
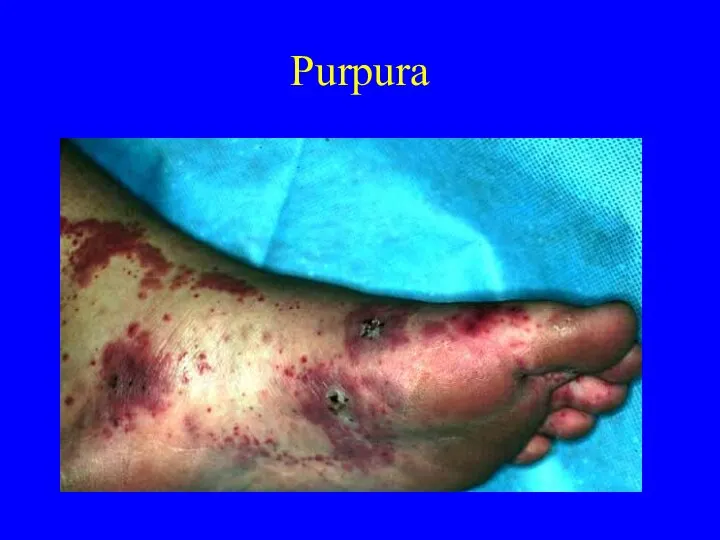
- 26. Purpura
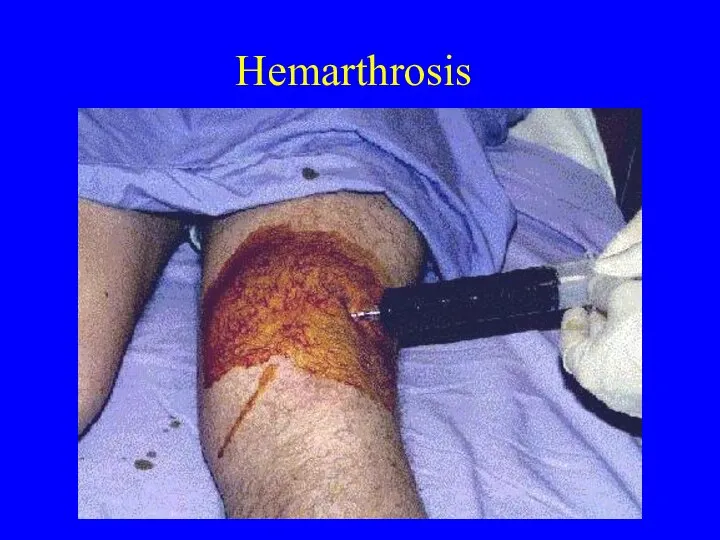
- 27. Hemarthrosis
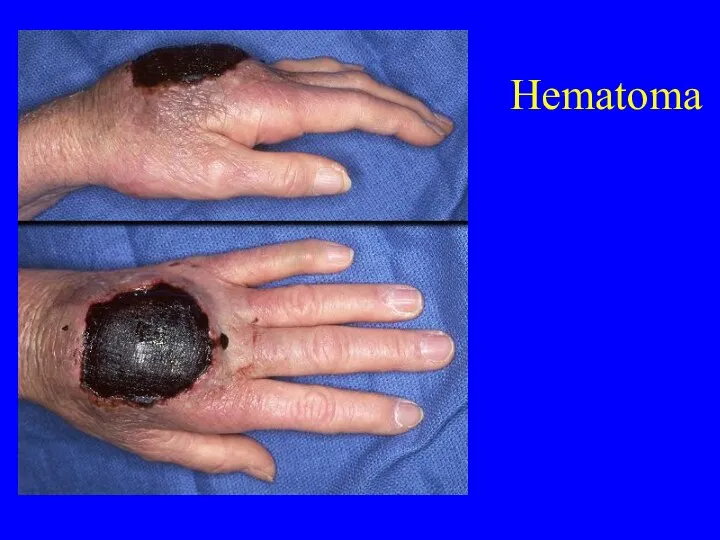
- 28. Hematoma
- 30. Скачать презентацию
















 Современный этап развития медицины
Современный этап развития медицины Физиология заживления острой и хронической раны. Факторы, влияющие на заживление, и способы ускорения её регенерации
Физиология заживления острой и хронической раны. Факторы, влияющие на заживление, и способы ускорения её регенерации Эвтаназия, за и против. (Лекция 11)
Эвтаназия, за и против. (Лекция 11) Меланома кожи
Меланома кожи Менингококковая инфекция
Менингококковая инфекция Вакцинопрофилактика
Вакцинопрофилактика Всероссийская Акция Здоровое питание - активное долголетие в рамках движения Сделаем вместе
Всероссийская Акция Здоровое питание - активное долголетие в рамках движения Сделаем вместе Асептика. Комплекс мероприятий, направленных на предупреждение попадания инфекции в рану
Асептика. Комплекс мероприятий, направленных на предупреждение попадания инфекции в рану Skin cancer. Melanoma
Skin cancer. Melanoma Лекция №1
Лекция №1 Лучевая диагностика заболеваний и повреждений костно-суставной системы
Лучевая диагностика заболеваний и повреждений костно-суставной системы Девиации в семье и особенности взаимоотношений между ее членами
Девиации в семье и особенности взаимоотношений между ее членами Ошибки телефонного диалога и искусство его завершения
Ошибки телефонного диалога и искусство его завершения Виды авторитета
Виды авторитета Туберкулез, туберкулездің санитарлық және химиялық алдын алу
Туберкулез, туберкулездің санитарлық және химиялық алдын алу Influenza
Influenza Новое слово в иммунологии! вторая жизнь сенсационного научного открытия прошлого века
Новое слово в иммунологии! вторая жизнь сенсационного научного открытия прошлого века CAD/CAM система в ортопедической стоматологии
CAD/CAM система в ортопедической стоматологии Project Monarch
Project Monarch Хроническое гнойное воспаление среднего уха. Радикальная операция. Отогенные внутричерепные осложнения
Хроническое гнойное воспаление среднего уха. Радикальная операция. Отогенные внутричерепные осложнения Квалифицированная медицинская помощь
Квалифицированная медицинская помощь Қазіргі заманға сай балалар мен жасөспірімдер мекемелерін жоспарлау менн құрылыс жүргізу ерекшеліктері. (Дәріс 15)
Қазіргі заманға сай балалар мен жасөспірімдер мекемелерін жоспарлау менн құрылыс жүргізу ерекшеліктері. (Дәріс 15) Тяжелый комбинированный иммунодефицит
Тяжелый комбинированный иммунодефицит Тиреотоксикалық криз және тиреотоксикалық кома
Тиреотоксикалық криз және тиреотоксикалық кома ²êÆÜøðàÜ ØºøºÜ²Üºð
²êÆÜøðàÜ ØºøºÜ²Üºð Клиническое обследование (КО). Clinical investigation. Лекция 1
Клиническое обследование (КО). Clinical investigation. Лекция 1 俄 罗斯中医药
俄 罗斯中医药 DIC - disseminated intravascular coagulation.TTP - thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
DIC - disseminated intravascular coagulation.TTP - thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura