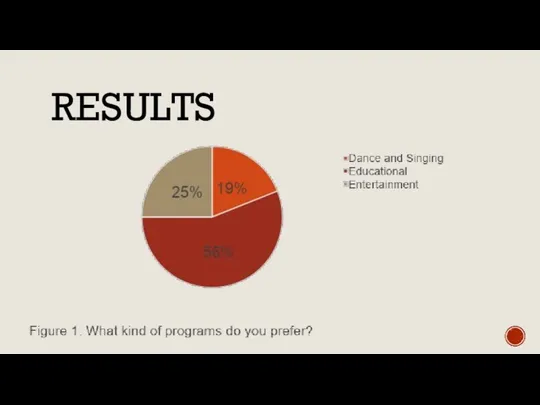
PROS & CONS
Glenn Thomas Ellis and Francis Sekyra (1972)- first-grade students
that are constantly watching aggressive cartoons tend to show more violent behavior at home or in school than those who do not.
Ali Hassan and Muhammad Daniyal (2013)- violence is unrealistically shown in cartoons; children that observe them do not perceive this aspect as the real violence, and as a result, amount of violence cases from the children increased.
Habibur Rahman (2012)- watching cartoons positively affects children’s ability to communicate with peers, especially while studying in primary school; children possess more social skills.
Michaela Minárechová (2016)-cartoons presents deeper understanding of the real world to the children.








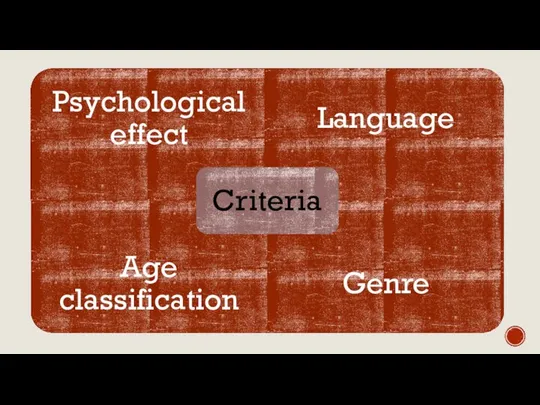


 Анафилактикалық шокты емдеу принціптері
Анафилактикалық шокты емдеу принціптері Гепатиты
Гепатиты Сахарный диабет
Сахарный диабет Желчнокаменная болезнь. Острый холецистит
Желчнокаменная болезнь. Острый холецистит Переломы. Виды переломов. Первая помощь при открытых переломах
Переломы. Виды переломов. Первая помощь при открытых переломах Череп человека. Мозговой и лицевой отделы
Череп человека. Мозговой и лицевой отделы Электрокардиография. Стандартные отведения
Электрокардиография. Стандартные отведения Невропатия лицевого нерва
Невропатия лицевого нерва Информация для медицинских и фармацевтических работников CP-266252
Информация для медицинских и фармацевтических работников CP-266252 Медицина средневековой Европы V-XVII вв
Медицина средневековой Европы V-XVII вв Деформации зубных рядов. Этиология. Патогенез. Клиника. Диагностика. Ортопедическое лечение
Деформации зубных рядов. Этиология. Патогенез. Клиника. Диагностика. Ортопедическое лечение ДНК-вирусы
ДНК-вирусы Инактивированные вакцины
Инактивированные вакцины Инсулиновая помпа. Болюсное введение
Инсулиновая помпа. Болюсное введение Предмет психологии, ее задачи и методы
Предмет психологии, ее задачи и методы Репродуктивная система женщины. Лекция 14
Репродуктивная система женщины. Лекция 14 Организация работы специализированных (БИТ) и линейных бригад скорой помощи
Организация работы специализированных (БИТ) и линейных бригад скорой помощи Стронгилятозы дыхательных путей животных
Стронгилятозы дыхательных путей животных Чувствительность и её нарушения
Чувствительность и её нарушения Цветопсихосоматика
Цветопсихосоматика Жүрек ырғағының бұзылысы. Пароксизмальды тахикардия
Жүрек ырғағының бұзылысы. Пароксизмальды тахикардия Адам тағамының құрамы. Органикалық және минералды компоненттер
Адам тағамының құрамы. Органикалық және минералды компоненттер Anadangəlmə qüsurların və qazanılma ürək xəstəliklərinin şüa diaqnostikası
Anadangəlmə qüsurların və qazanılma ürək xəstəliklərinin şüa diaqnostikası Применение цветотерапии Биоптрон для оздоровления часто болеющих детей
Применение цветотерапии Биоптрон для оздоровления часто болеющих детей Руководство для ведения пациентов с острым коронарным синдромом с подъемом сегмента ST
Руководство для ведения пациентов с острым коронарным синдромом с подъемом сегмента ST Генетикалық карталар
Генетикалық карталар Доврачебная помощь при травмах
Доврачебная помощь при травмах Артериялдық қысымды тәуліктік мониторлау
Артериялдық қысымды тәуліктік мониторлау