Содержание
- 2. Peritoneum structure. M.A.Baron (1939) presented the most full knowledge of abdomen structure. He distinguished 6 layers
- 3. Кафедра факультетской хирургии и онкологии
- 4. Blood support and innervation Blood support Parietal Perineum – segmental artery from aorta, epigastric artery Visceral
- 5. The classification of peritonitis 1) Etiology: The primary peritonitis and secondary 2) Clinical passed: acute and
- 6. Pathomorphology of the acute peritonitis. It is determined that the functional status of the peritoneum and
- 7. The third phase (terminal stage). Третья фаза (конечная стадия). There is a significant quantity of the
- 8. pathogenesys The peritonitis pathogenesis is complicated; the changes in organ and functional systems are different during
- 9. Clinical signse In the reactive stage (the first 24 hours) the leading symptoms of peritonitis are
- 10. Diagnostic Shetkin – Blumderg symptom Paralytic bowel obstruction signs Vaginal, rectal examination Laboratory investigation: Leukocitosis Relative
- 11. The differential diagnostic of acute peritonitis Urolithiasis Poisoning of heavy metals hemorrhagic diathesis cardiac infarction, fractures
- 13. Скачать презентацию
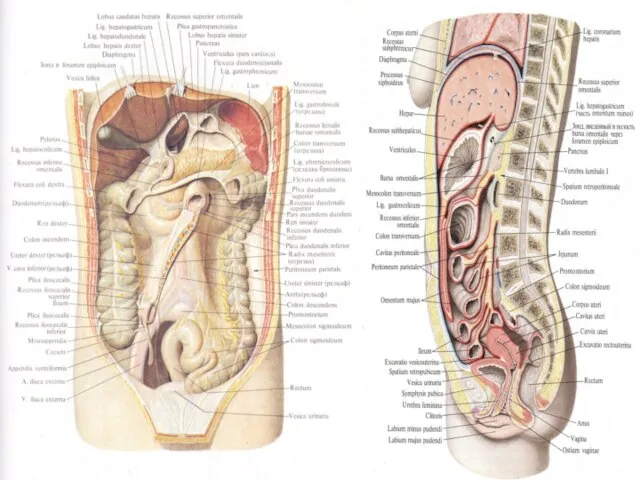
Peritoneum structure.
M.A.Baron (1939) presented the most full knowledge of abdomen
Peritoneum structure.
M.A.Baron (1939) presented the most full knowledge of abdomen
- mesothelium, covering the surface of serous membrane;
- basal membrane;
- the superficial wave collagen layer;
- the superficial diffuse elastic net;
- deep longitudinal elastic net;
- deep lattice collagenoelastic layer.
Кафедра факультетской хирургии и онкологии
Кафедра факультетской хирургии и онкологии
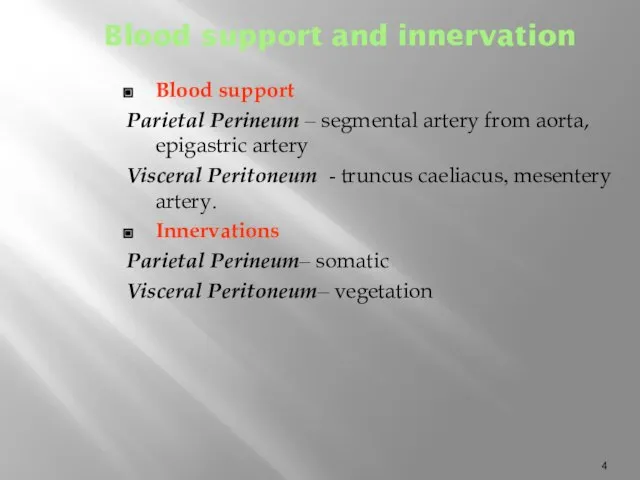
Blood support and innervation
Blood support
Parietal Perineum – segmental artery from aorta,
Blood support and innervation
Blood support
Parietal Perineum – segmental artery from aorta,
Visceral Peritoneum - truncus caeliacus, mesentery artery.
Innervations
Parietal Perineum– somatic
Visceral Peritoneum– vegetation
The classification of peritonitis
1) Etiology: The primary peritonitis and secondary
2)
The classification of peritonitis
1) Etiology: The primary peritonitis and secondary
2)
3) In dependence of the character of effusion in abdominal cavity peritonitis differ to - serous, fibrinous, purulent (suppurative), hemorrhagic, ichorous etc., and their combinations (serofibrinous, fibrinopurulent etc.).
4) In dependence from the infection agent types there are peritonitis caused by:
1) Intestinal microorganisms: Escherichia Coli, Streptococcus: aerobe (Enterococcus) and anaerobes (Peptococcus), gas-making (Clostridia) and not gas-making (bacteroids) anaerobes, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa etc.
2) Not gastrointestinal bacteria: Gonococcus (Neisseria), Pneumococcus, Hemolytic Streptococcus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc.
And : aseptic peritonitis
fibroplastic peritonitis
Pathomorphology of the acute peritonitis.
It is determined that the functional
Pathomorphology of the acute peritonitis. It is determined that the functional
The first phase (early stage).
abundant volume of the turbid exudates in the abdominal cavity
serous cover’s hyperemia
The inflammatory process yet is usual localized in one or another area of the abdominal cavity in this phase.
The second phase (late stage).
Besides the turbid effusion in the abdominal cavity, there are the fibrinous applications in the form of threads among the intestine loops.
The pus is denser and has a typical odor. The expressed hyperemia of the serous cover, edema and swelling of the intestine is detected. In some places, especially in diaphragm area, all peritoneum layers are infiltrated with leucocytes and lymphocytes.
The inflammation has a diffuse character in this phase of the peritonitis.
Вторая фаза (поздняя стадия).
- в брюшной полости отложения фибрина; - гной более густой и имеет характерный запах; - отмечается резкая гиперемия серозных покровов;
- отечность и вздутие кишечника; - воспаление имеет диффузный характер.
The third phase (terminal stage).
Третья фаза (конечная стадия).
There is a significant
The third phase (terminal stage).
Третья фаза (конечная стадия).
There is a significant
- значительное количество гнойного выпота; - брюшина покрыта отложениями фибрина; - кишечник резко вздут, отечен, темно-красного цвета; - воспалительный процесс охватывает всю брюшную полость; - в близлежащих к брюшине мышцах наблюдается отек и геморрагии.
pathogenesys
The peritonitis pathogenesis is complicated; the changes in organ and functional
pathogenesys
The peritonitis pathogenesis is complicated; the changes in organ and functional
1. The reaction to the local inflammatory process. These changes are peculiar to the inflammation of any localization. They are characteristic for the early reactive peritonitis stage and for the diseases of the abdominal cavity organs, preceding to it.
2. The reaction of the toxins that outcome to the system bloodstream, which is sometimes characterized with the symptoms, peculiar to end toxic shock, that corresponds mainly to the toxic stage of the peritonitis.
3. The organism reaction on the complicated combinations of factors that is peculiar to the terminal stage of peritonitis, which passes with the predominance of the septic shock signs.
Clinical signse
In the reactive stage (the first 24 hours) the leading
Clinical signse
In the reactive stage (the first 24 hours) the leading
The vomiting with stomach content don’t bring the relief usually, it can be sole or rare. The pulse become more frequent up to 90 – 100 per minute, arterial pressure is normal or decreased. In the case of some diseases that cause the peritonitis, the development of shock is possible (perforation of the hollow organs, wound, thrombosis and emboli of mesenterial vessels, strangulate ileus, acute pancreonecrosis and others).
During the superficial palpation of the abdomen the defensive tension of muscles (defense muscular) is detected accordingly to the zone of parietal peritoneum of the front abdominal wall, which is affected with the inflammatory process.
Diagnostic
Shetkin – Blumderg symptom
Paralytic bowel obstruction signs
Vaginal, rectal examination
Laboratory investigation:
Leukocitosis
Diagnostic
Shetkin – Blumderg symptom
Paralytic bowel obstruction signs
Vaginal, rectal examination
Laboratory investigation:
Leukocitosis
Relative high rate of Ht
Dysproteinemia
Hypercoagulation
High rate of bilirubin. Nitrous productes
acid-base balance, electrolyte rates
The differential diagnostic of acute peritonitis
Urolithiasis
Poisoning of heavy metals
hemorrhagic diathesis
cardiac infarction,
The differential diagnostic of acute peritonitis
Urolithiasis
Poisoning of heavy metals
hemorrhagic diathesis
cardiac infarction,
The most often a doctor has to differentiate the peritonitis that develops as a result of the pathologic process in the genitourinary apparatus (uratic diathesis, tuberculosis, inflammation etc.) from the different spastic diseases of the digestive system (spastic colitis, pylorospasm etc.),
chronic painful pancreatitis, the exacerbation of the ulcer disease of stomach and duodenum, and many other typical diseases that take a course with exacerbation.
All these diseases have their specific clinic, and in the case of the careful and attentive examination of the patient it is possible to avoid the mistakes.








 Медицинская помощь больным с менингитами на госпитальном этапе
Медицинская помощь больным с менингитами на госпитальном этапе Хронический холецистит. Желчнокаменная болезнь
Хронический холецистит. Желчнокаменная болезнь Лекарственные средства, влияющие на функции органов пищеварения
Лекарственные средства, влияющие на функции органов пищеварения Диагностическое выскабливание слизистой матки
Диагностическое выскабливание слизистой матки Гигиена и экология человека
Гигиена и экология человека Кальций регулирующие гормоны
Кальций регулирующие гормоны Аллергия. Аллергены
Аллергия. Аллергены Челюстно-лицевая ортопедия. Цель, задачи. Классификация переломов челюстей. Причины и механизм смещения отломков. (Тема 3)
Челюстно-лицевая ортопедия. Цель, задачи. Классификация переломов челюстей. Причины и механизм смещения отломков. (Тема 3) Шизофрения. Гипертоксическая форма (фебрильная, смертельная кататония)
Шизофрения. Гипертоксическая форма (фебрильная, смертельная кататония) Основы первой помощи. Принципы и навыки десмургии при ранах и кровотечениях. Освоение навыков наложения повязок, жгутов
Основы первой помощи. Принципы и навыки десмургии при ранах и кровотечениях. Освоение навыков наложения повязок, жгутов Методы исследования в микробиологии
Методы исследования в микробиологии Дәрігерлік деонтология, семиология
Дәрігерлік деонтология, семиология Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері
Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері Фронтотемпоральная деменция таупатия
Фронтотемпоральная деменция таупатия Созылмалы өкпелік жүрек
Созылмалы өкпелік жүрек Лучевая диагностика воспалительных процессов челюстно-лицевой области
Лучевая диагностика воспалительных процессов челюстно-лицевой области П. А. Сорокиннің әлеуметтік теңдік мәселесі. Қазақстандағы орта тап
П. А. Сорокиннің әлеуметтік теңдік мәселесі. Қазақстандағы орта тап Порядок и особенности ветеринарно-санитарной экспертизы туш и органов животных при лептоспирозе
Порядок и особенности ветеринарно-санитарной экспертизы туш и органов животных при лептоспирозе Оказание первой помощи пострадавшим на производстве
Оказание первой помощи пострадавшим на производстве Эмпиема плевры. Границы легких и плевры
Эмпиема плевры. Границы легких и плевры Ерітінділердің коллигативті қасиеттері. Осмос қысымы. Изотонды коэффициент
Ерітінділердің коллигативті қасиеттері. Осмос қысымы. Изотонды коэффициент Болезнь Паркинсона
Болезнь Паркинсона Оценка функциональной подготовленности
Оценка функциональной подготовленности Лечебное питание при заболеваниях органов пищеварения
Лечебное питание при заболеваниях органов пищеварения Postoperative therapy with infliximab for Crohn’s disease: a 2-year prospective randomized multicenter study in Japan
Postoperative therapy with infliximab for Crohn’s disease: a 2-year prospective randomized multicenter study in Japan Общие принципы лечения острых отравлений лекарственными средствами. СРСП
Общие принципы лечения острых отравлений лекарственными средствами. СРСП Методы диагностики в кардиологии
Методы диагностики в кардиологии Еда и боль
Еда и боль