Содержание
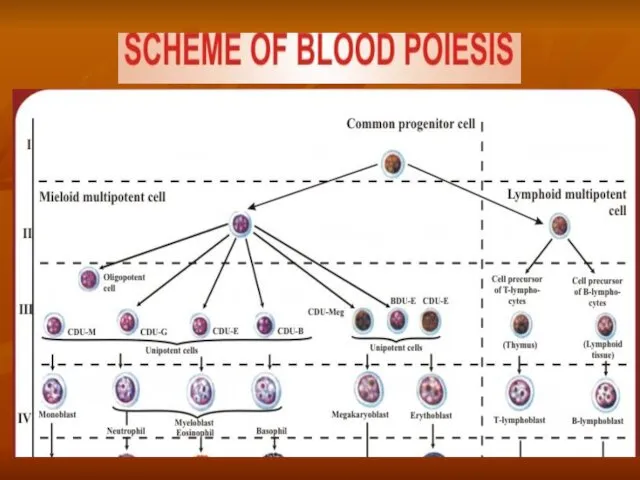
- 2. Blood system Blood system firstly was proposed by Lung in 1936. It consist of - blood
- 3. Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Blood consist of - plasma - blood cells –
- 4. plasma erythrocytes Leucocytes and platelets
- 6. Amount of blood The amount of blood in the body has been measured in various ways.
- 7. Plasma Water – 90 % Solids – 10 % Inorganic chemicals: sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium, chloride,
- 8. Proteins One liter of plasma has 65-85 gram of proteins. Concentration of albumins is 35-50 g/L;
- 9. Albumins Albumins: on 80 % it provides oncotic pressure, contacts with bilirubin, fat acids, antibiotics, sulfanilamids.
- 10. Globulins Globulins produces in lymphatic nodes, in liver, in bone marrow in average quantity of 5
- 11. Fibrinogen Fibrinogen is a protein which are produced by liver and take place in hemostasis system.
- 12. Quantity of cells, their changing Erythrocytes (In men – 4,0-5,1 Tera/L; in women – 3,7-4,7 Tera/L.
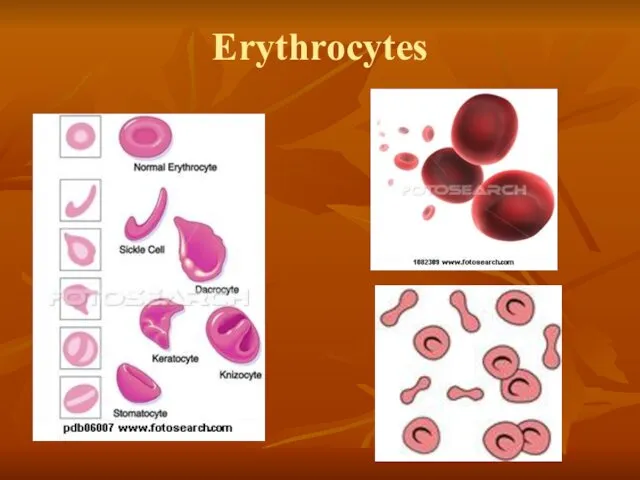
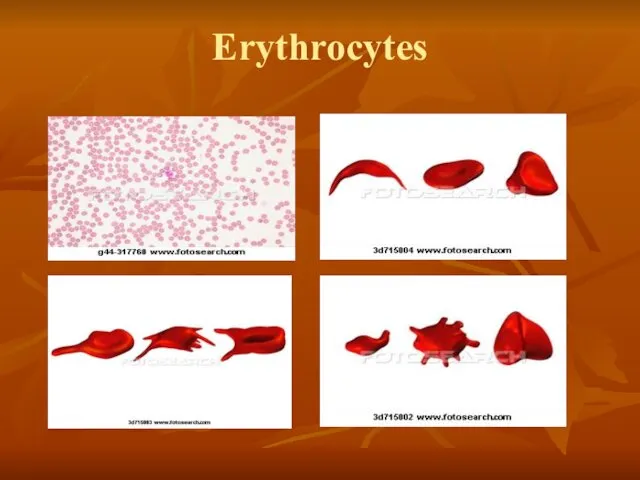
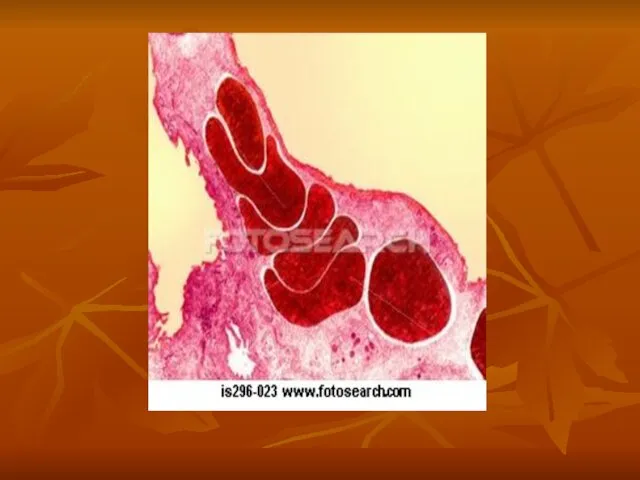
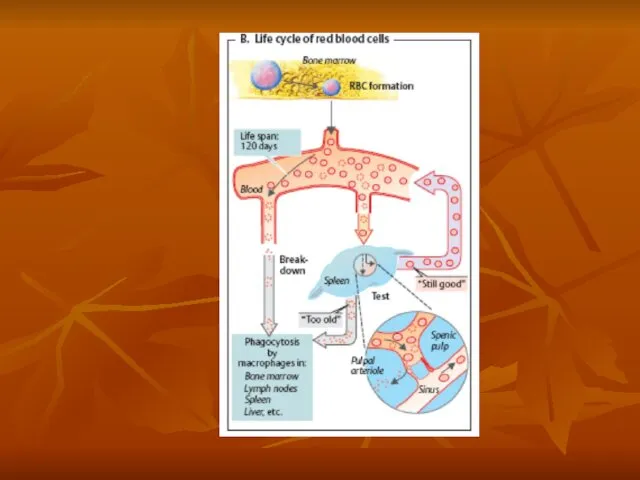
- 15. Erythrocytes
- 16. Erythrocytes
- 19. Functions of blood 1. Breathing function of blood. 2. Trophic function of blood. 3. Excretory function
- 23. Respiratory pigments Hemoglobin Erythrocytes derive their colour from a complex protein called hemoglobin. This substance is
- 25. Respiratory pigments Myoglobin Hem is also part of the structure of myoglobin, an oxygen-binding pigment found
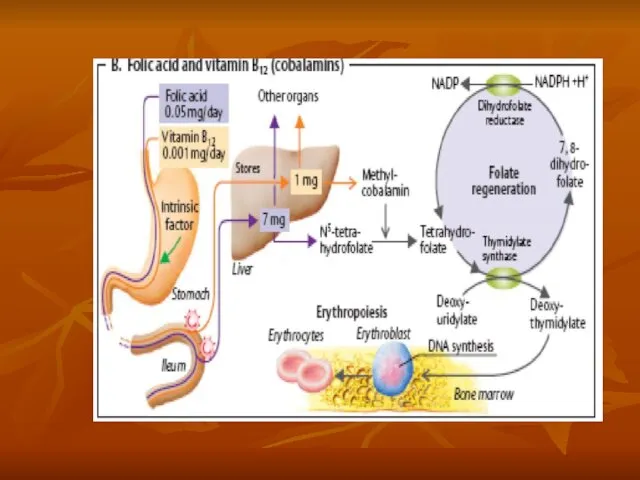
- 26. Exchange of iron in the organism In the blood-destroying organs, the hemoglobin breaks down into an
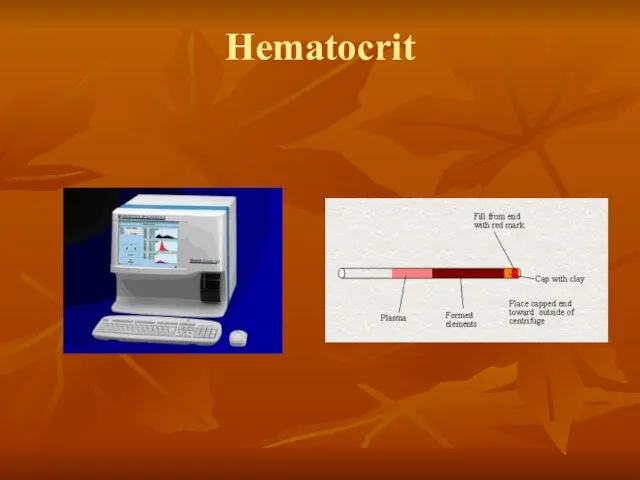
- 30. Hematocrit
- 31. ESS
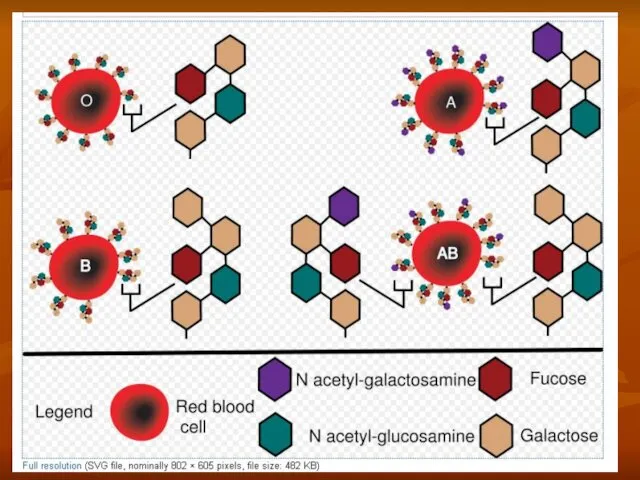
- 32. Blood types Blood types is the common of normal antigens signs, which are combined on immunologic
- 34. Erythrocytes blood types In the membrane of erythrocytes present agglutinogens (H, A, B) In plasma present
- 35. Antigens and antibodies of AB0 system Antigens Antibodies I group H alpha, beta II group A
- 36. Attention! Each of us has individual blood type! Now in practice is present 2 system АВ0
- 37. System АВ0 0(І)αβ ; А(ІІ)β ; В(ІІІ)α; АВ(ІV).
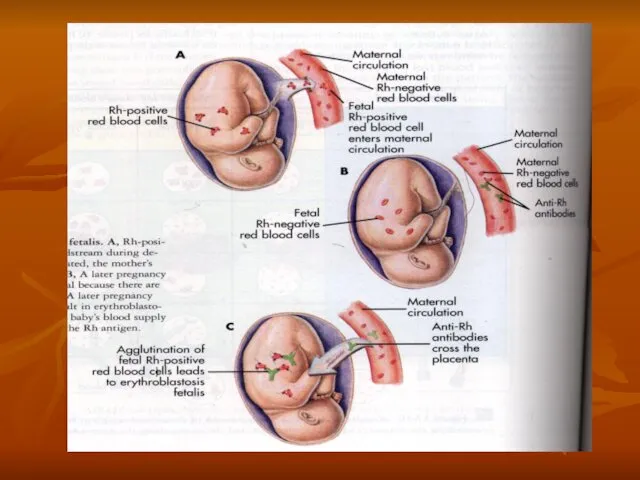
- 44. System СDЕ (rhesus). There are 6 main аntigens of rhesus system. System Fisher-Race. According to that
- 48. Leukocytes blood types 1. Common antigens of leukocytes (HLA system) 2. Antigens of granulocytes. 3. Antigens
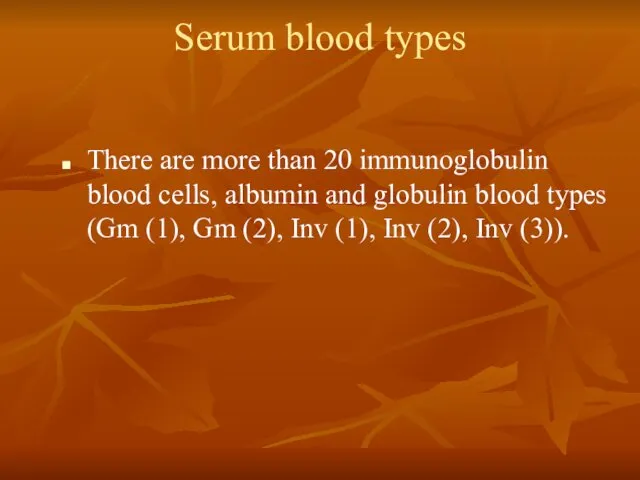
- 49. Serum blood types There are more than 20 immunoglobulin blood cells, albumin and globulin blood types
- 50. Transfusion of blood We must transfused only blood of one groop with recipient!!! Before the transfusion
- 52. Physiological effects of blood, which was transfused 1. stimulative 2. hemopoietic 3. immunologic 4. nutritive
- 53. Group of hem transfusion solution 1. Haemo dynamic. 2. Detoxycative. 3. Paranteral nutrition. 4. Regulation of
- 55. Скачать презентацию









































 Малая группа
Малая группа Інновації у лікуванні та профілактиці гострих респіраторних вірусних інфекцій у дітей
Інновації у лікуванні та профілактиці гострих респіраторних вірусних інфекцій у дітей Опий. Структура и направленность действия его алкалоидов. Классификация препаратов НА по происхождению
Опий. Структура и направленность действия его алкалоидов. Классификация препаратов НА по происхождению Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов
Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов Диагностические критерии и клиническая картина детского аутизма
Диагностические критерии и клиническая картина детского аутизма Босанған әйелдің гигиена және диетасы
Босанған әйелдің гигиена және диетасы Полимирезді тізбекті реакция (ПТР)
Полимирезді тізбекті реакция (ПТР) Противошоковые мероприятия на госпитальном этапе при сочетанной травме
Противошоковые мероприятия на госпитальном этапе при сочетанной травме Врожденные пороки сердца. Недостаточность кровообращения
Врожденные пороки сердца. Недостаточность кровообращения Виды имплантатов
Виды имплантатов Физиологическое и психологическое развитие подростков
Физиологическое и психологическое развитие подростков Первая доврачебная помощь при внезапных заболеваниях
Первая доврачебная помощь при внезапных заболеваниях Лучевая диагностика травматических повреждений
Лучевая диагностика травматических повреждений Иммунологические методы исследования в ветеринарии
Иммунологические методы исследования в ветеринарии Қан кетудің диагностикасы және дәрігерге дейінгі көмек
Қан кетудің диагностикасы және дәрігерге дейінгі көмек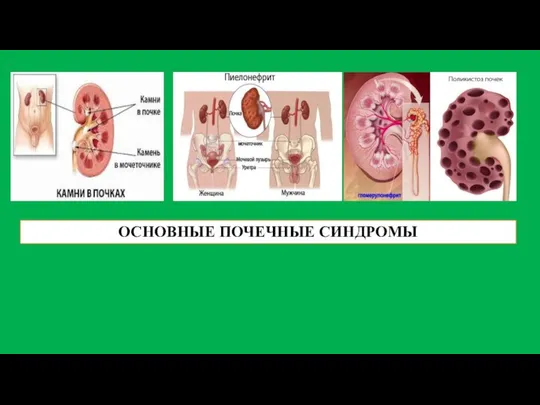 Основные почечные синдромы
Основные почечные синдромы Увага
Увага Молекулярная онкология
Молекулярная онкология janssaya
janssaya Эмбриогенез нервной системы. Основные этапы
Эмбриогенез нервной системы. Основные этапы Твоё здоровье в твоих руках
Твоё здоровье в твоих руках Опорно-двигательный аппарат. Первая помощь при травмах
Опорно-двигательный аппарат. Первая помощь при травмах Гигиена кожи
Гигиена кожи Изучение причин возникновения и профилактика пищевых отравлений и инфекционных заболеваний
Изучение причин возникновения и профилактика пищевых отравлений и инфекционных заболеваний Эндокринные заболевания у детей
Эндокринные заболевания у детей Глаукома
Глаукома Патоморфологическая характеристика пищевода Барретта
Патоморфологическая характеристика пищевода Барретта Гигиена рук в клинической практике
Гигиена рук в клинической практике