Содержание
- 2. PH - History History of smoking ETOH/recreational drug use Systemic hypertension Cyanosis/murmur as a child Joint/musculoskeletal
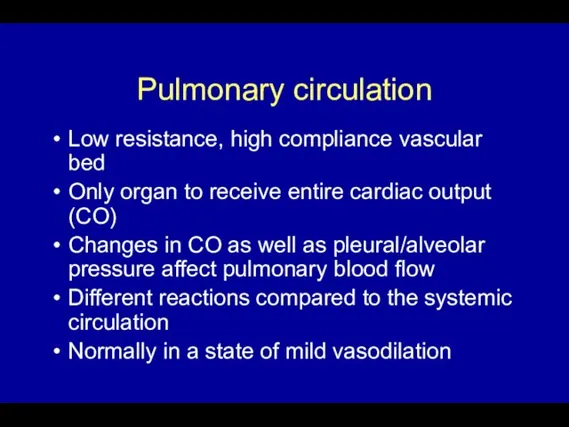
- 3. Pulmonary circulation Low resistance, high compliance vascular bed Only organ to receive entire cardiac output (CO)
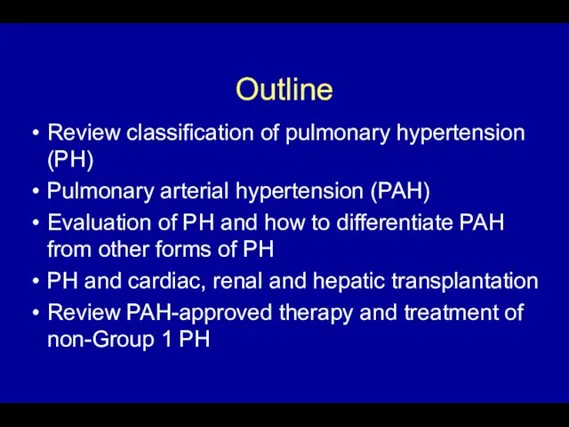
- 4. Outline Review classification of pulmonary hypertension (PH) Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) Evaluation of PH and how
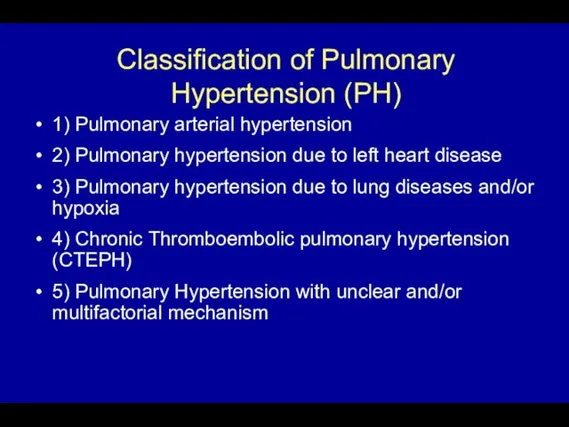
- 5. Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) 1) Pulmonary arterial hypertension 2) Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart
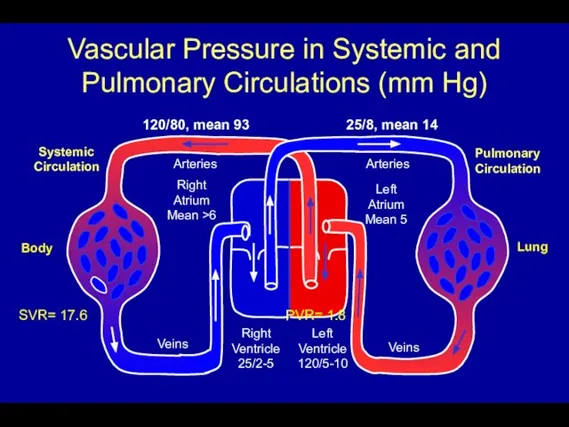
- 6. Vascular Pressure in Systemic and Pulmonary Circulations (mm Hg) Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Arteries Arteries Veins
- 7. PH- Symptoms DOE Fatigue, weakness Chest pain LE or abdominal swelling Syncope Not typical of PAH:
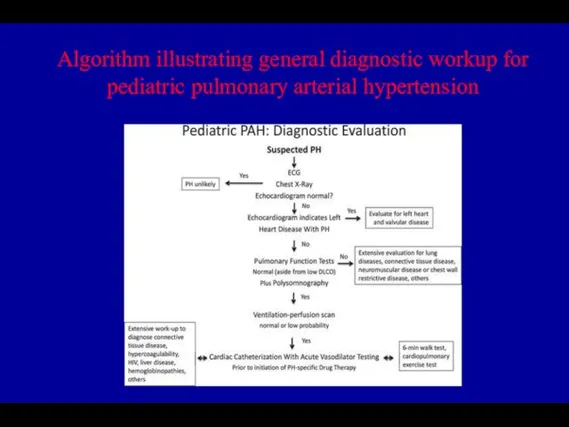
- 43. Algorithm illustrating general diagnostic workup for pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension
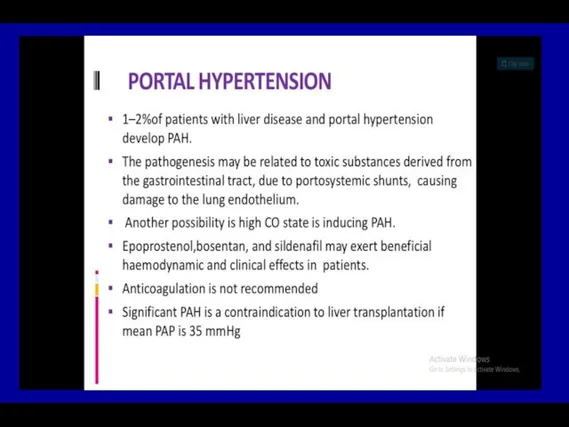
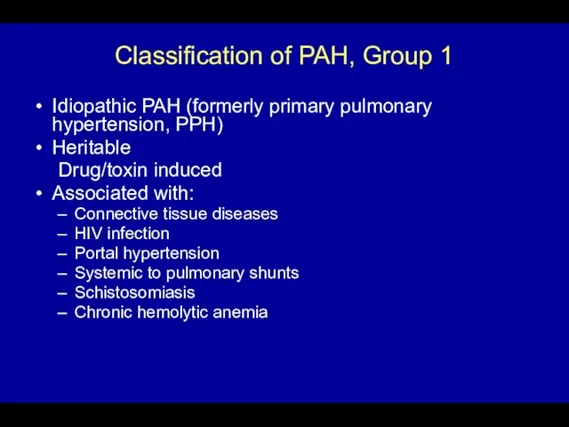
- 44. Classification of PAH, Group 1 Idiopathic PAH (formerly primary pulmonary hypertension, PPH) Heritable Drug/toxin induced Associated
- 45. Group 2 PH Pulmonary hypertension owing to left heart disease Systolic dysfunction Diastolic dysfunction Valvular disease
- 46. PH with unclear or multifactorial mechanisms: Group 5 1.Hematologic disorders 2.Systemic disorders: vasculitis 3.Metabolic disorders 4.Others:
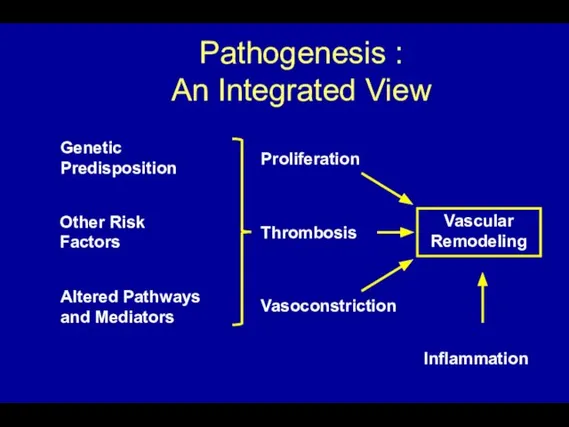
- 47. Vascular Remodeling Pathogenesis : An Integrated View Inflammation
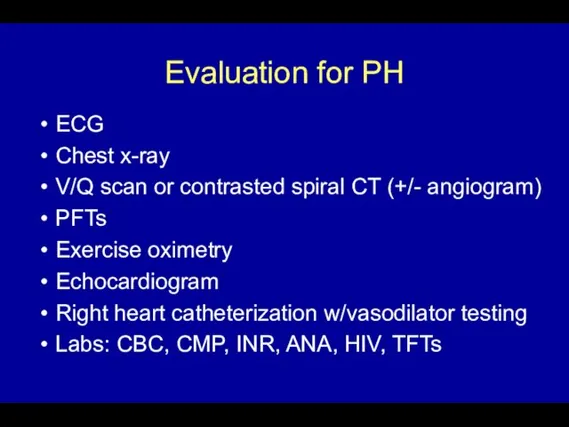
- 48. Evaluation for PH ECG Chest x-ray V/Q scan or contrasted spiral CT (+/- angiogram) PFTs Exercise
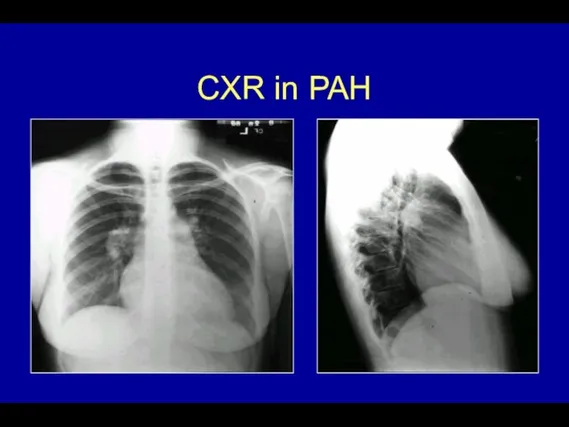
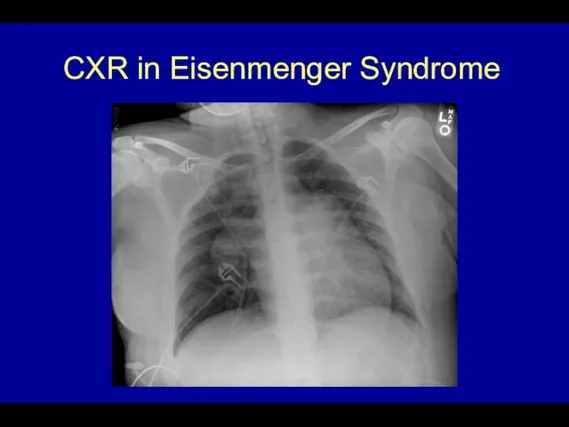
- 50. PH - Radiographic studies CXR: -large proximal PA with peripheral tapering (pruning) -cardiomegaly due to enlarged
- 51. CXR in PAH
- 52. CXR in Eisenmenger Syndrome
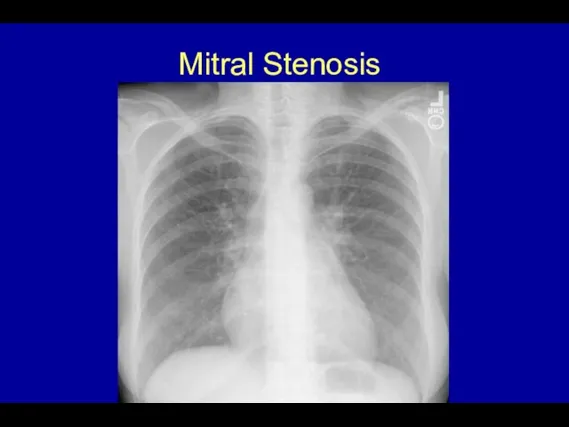
- 53. Mitral Stenosis
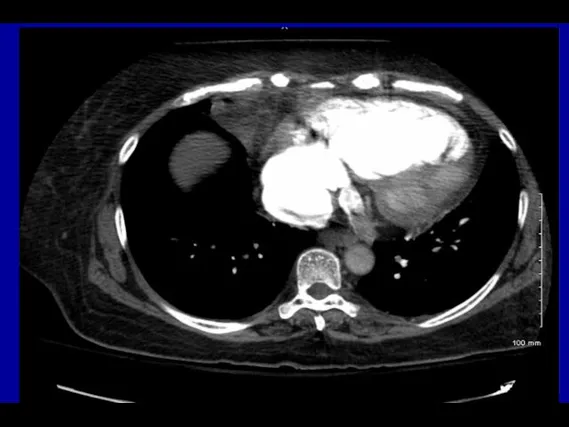
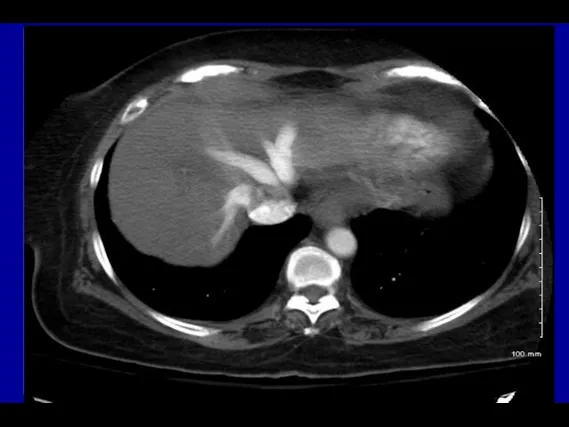
- 54. PA A Enlarged main PA on CT Standard view Coronal view
- 57. Ventilation Perfusion Lung Scan
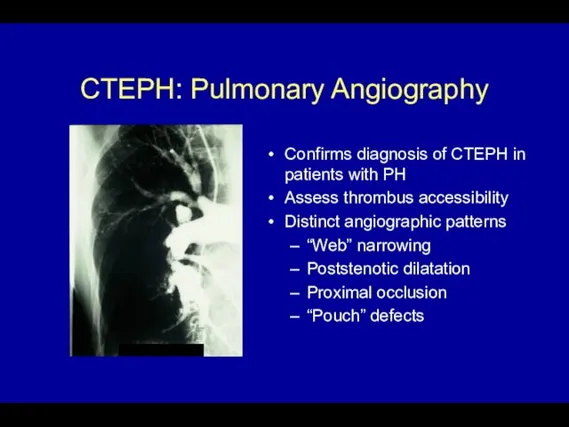
- 58. CTEPH: Pulmonary Angiography Confirms diagnosis of CTEPH in patients with PH Assess thrombus accessibility Distinct angiographic
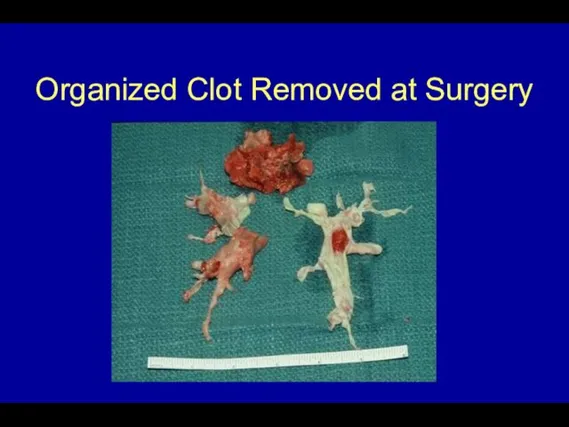
- 59. Organized Clot Removed at Surgery
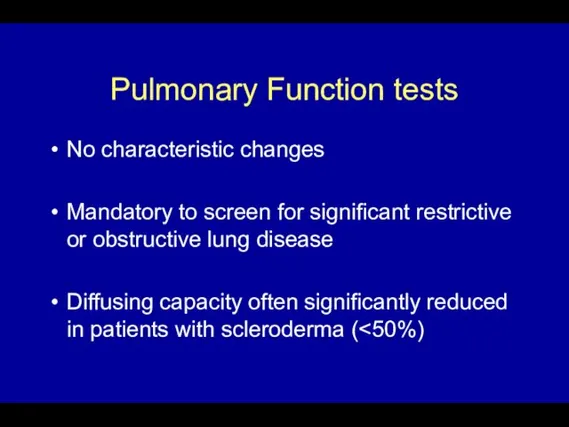
- 60. Pulmonary Function tests No characteristic changes Mandatory to screen for significant restrictive or obstructive lung disease
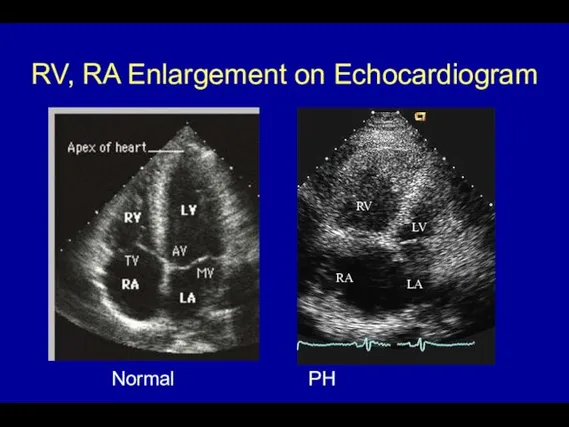
- 61. RV, RA Enlargement on Echocardiogram RV LV RA LA Normal PH
- 62. Other Helpful Diagnostic Tests (Determined by patient’s history) High resolution chest CT Cardiopulmonary exercise study Polysomnography
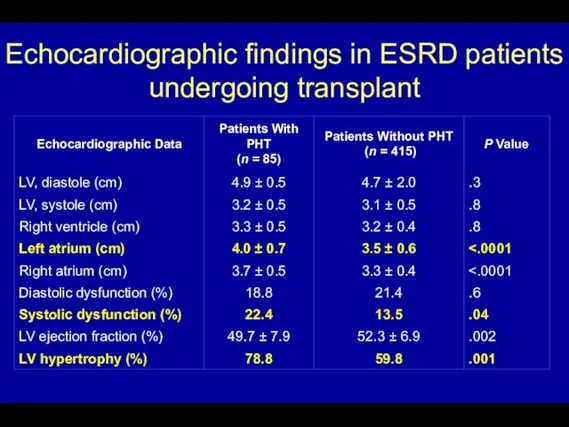
- 63. Echocardiographic findings in ESRD patients undergoing transplant
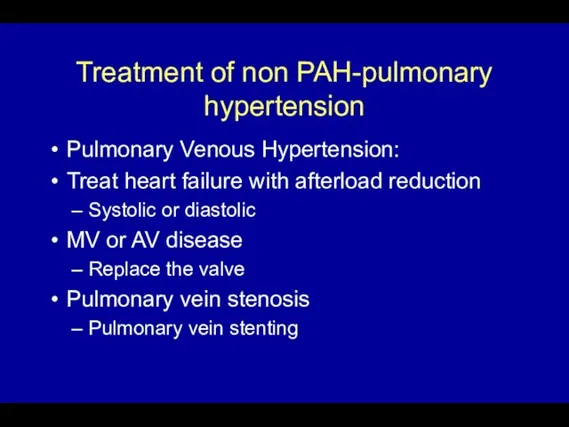
- 64. Treatment of non PAH-pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Venous Hypertension: Treat heart failure with afterload reduction Systolic or
- 65. Treatment of non PAH-pulmonary hypertension PH associated with disorders of the respiratory system and/or hypoxemia: Rx
- 66. Adjunctive treatments of PAH Anticoagulation Diuretics Digoxin Oxygen Calcium channel blockers Exercise Salt restriction
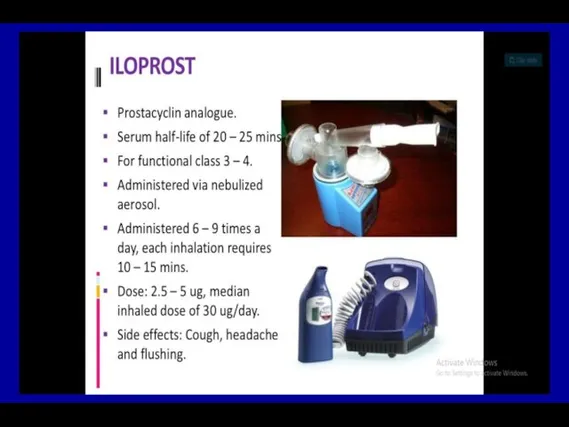
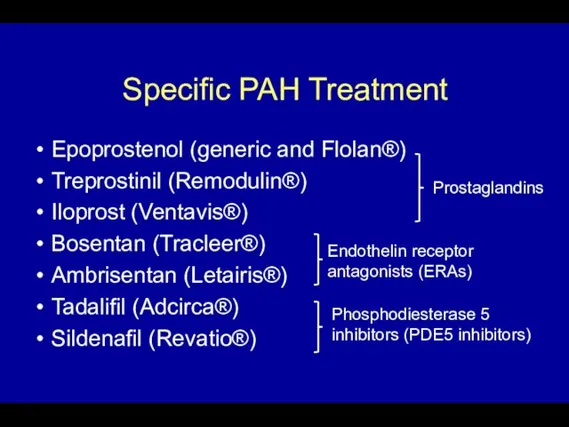
- 67. Specific PAH Treatment Epoprostenol (generic and Flolan®) Treprostinil (Remodulin®) Iloprost (Ventavis®) Bosentan (Tracleer®) Ambrisentan (Letairis®) Tadalifil
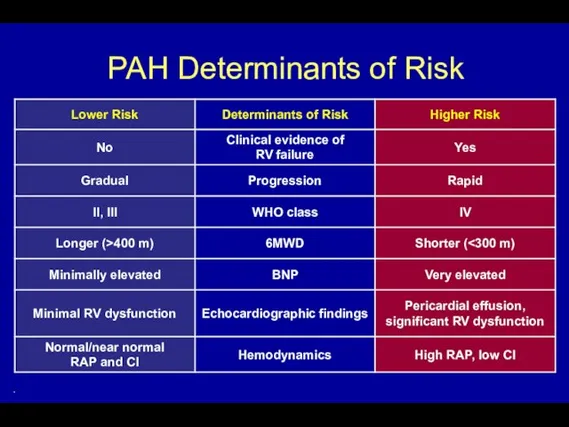
- 68. PAH Determinants of Risk .
- 69. Take Home Points PH can not be diagnosed by Echo alone, need a thorough evaluation for
- 71. Скачать презентацию










































 Анемический синдром
Анемический синдром Тетрациклины. Аминогликозиды
Тетрациклины. Аминогликозиды Основы медицинских знаний и здорового образа жизни
Основы медицинских знаний и здорового образа жизни Преждевременные роды
Преждевременные роды Living with a host family. Your expectations of a host family
Living with a host family. Your expectations of a host family Инфекционный эндокардит
Инфекционный эндокардит Средства гигиены
Средства гигиены Функциональная анатомия брюшины
Функциональная анатомия брюшины Геномные болезни: мышечная дистрофия Дюшенна
Геномные болезни: мышечная дистрофия Дюшенна Ембріотехнології. Виникнення ембріотехнологій
Ембріотехнології. Виникнення ембріотехнологій Понятие заикание
Понятие заикание ВИЧ-инфекция у детей
ВИЧ-инфекция у детей Дефекты длинных трубчатых костей и их лечение
Дефекты длинных трубчатых костей и их лечение Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь, интенсивная терапия
Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь, интенсивная терапия Клинические рекомендации по лечению хронической сердечной недостаточности
Клинические рекомендации по лечению хронической сердечной недостаточности Жүрек гипертрофиясы
Жүрек гипертрофиясы Предмет, история формирования и место социальной психологии в системе научного знания
Предмет, история формирования и место социальной психологии в системе научного знания Общесанитарные мероприятия и профилактика внутрибольничных инфекций
Общесанитарные мероприятия и профилактика внутрибольничных инфекций Морально-этические проблемы контрацепции и стерилизации
Морально-этические проблемы контрацепции и стерилизации Брюшной тиф, паратифы А и Б, сальмонеллёзы, дизентерия
Брюшной тиф, паратифы А и Б, сальмонеллёзы, дизентерия Лечение наркомании
Лечение наркомании Я-концепция
Я-концепция Психологические особенности нарушения речи
Психологические особенности нарушения речи Жасуша патофизиологиясы
Жасуша патофизиологиясы Патология складок коленного сустава
Патология складок коленного сустава Воспаление и его причины
Воспаление и его причины Бихевиоризм (от английского Behavior - поведение)
Бихевиоризм (от английского Behavior - поведение) Как говорить с детьми о коронавирусе
Как говорить с детьми о коронавирусе