Содержание
- 2. Classification: on I. Pathogenesis II. Character of pathological process III. Condition gravity IV. Complications
- 3. I. Pathogenesis 1. Bronchogenic (in-cluding aspirational and obturatio- nal) 2.Hematogenic (including embolic) 3. Posttraumatic
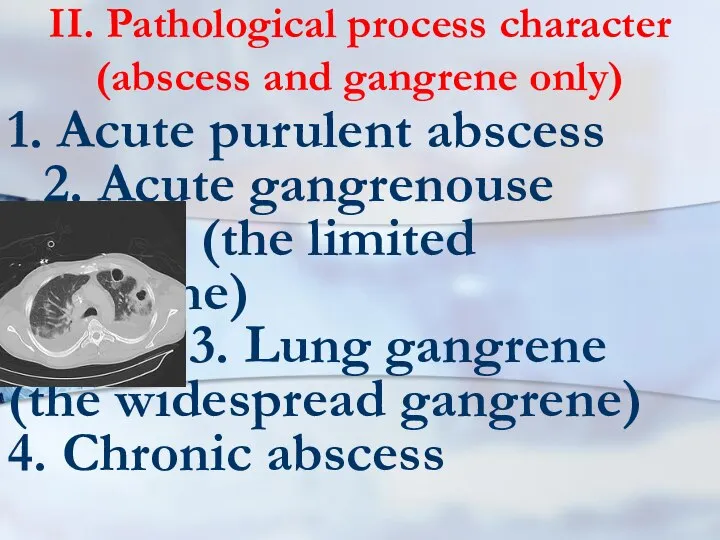
- 4. II. Pathological process character (abscess and gangrene only) 1. Acute purulent abscess 2. Acute gangrenouse abscess
- 5. III. Condition gravity easy middle heavy
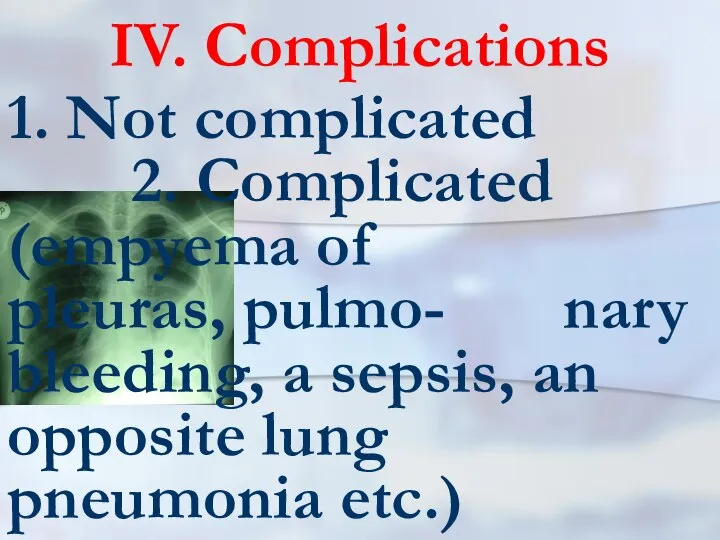
- 6. IV. Complications 1. Not complicated 2. Complicated (empyema of pleuras, pulmo- nary bleeding, a sepsis, an
- 7. lung abscess classification Pathogenesis Localization Patient con- dition gravity Clinical current Complications
- 8. pathogenesis postpneumonic aspirational hematogenic- embolic traumatic
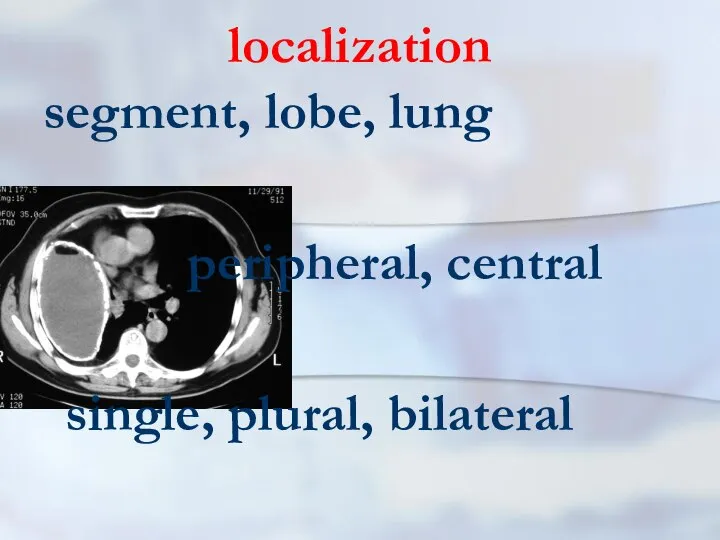
- 9. localization segment, lobe, lung peripheral, central single, plural, bilateral
- 10. Condition gravity easy middle heavy
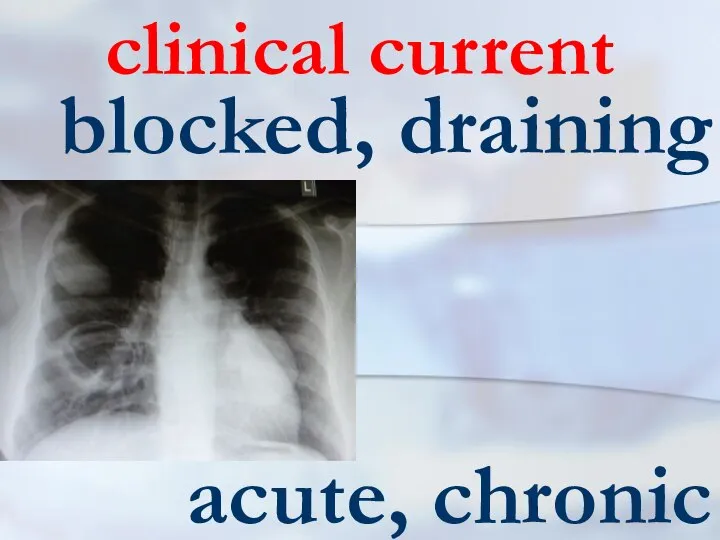
- 11. clinical current blocked, draining acute, chronic
- 12. complications Bleeding Pyopneu- mothorax sepsis
- 13. definition The abscess of lung (a suppuration, apostema, an abscess) is a nonspecific puru- lent disintegration
- 14. exciting cause More often activators of an abscess is pyogenic cocci, anaerobic microorga-nisms nonclosrtidium type and
- 15. Infections ways More often the pyogenic infection gets in pulmo- nary parenchi- me through aerogenous ways
- 16. Infections ways Direct infection of pulmonary tissue is possible at penetra- ting damages. As casuality, distribu-
- 17. Infections ways It is necessary to note, that hit of pathogenic microflora in pulmonary tissue not
- 18. Infections ways More often it arises at aspiration or mycroas- piration of sli- me, a saliva,
- 19. Infections ways Aspiration, as a rule, is marked at infringements of consciousness owing to intoxi- cation,
- 20. Infections ways Aspiration at times happens at dysphagias of various origin
- 21. Infections ways After aspiration deve- lops atelectasis of the part of lung, and then in it
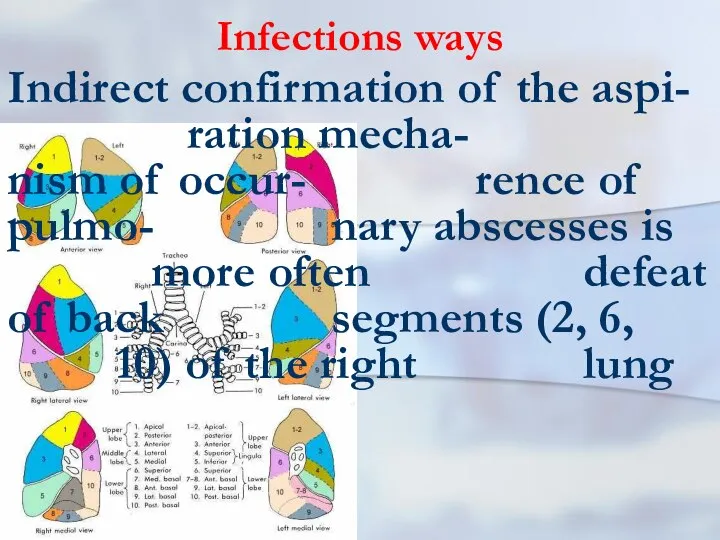
- 22. Infections ways Indirect confirmation of the aspi- ration mecha- nism of occur- rence of pulmo- nary
- 23. drainage function Infringements of drainage function lung are available at chronic nonspecific lung disea- ses: chro-nic
- 24. background disease Therefore, at the certain situations, some diseases promote occur- rence of pulmo- nary abscesses.
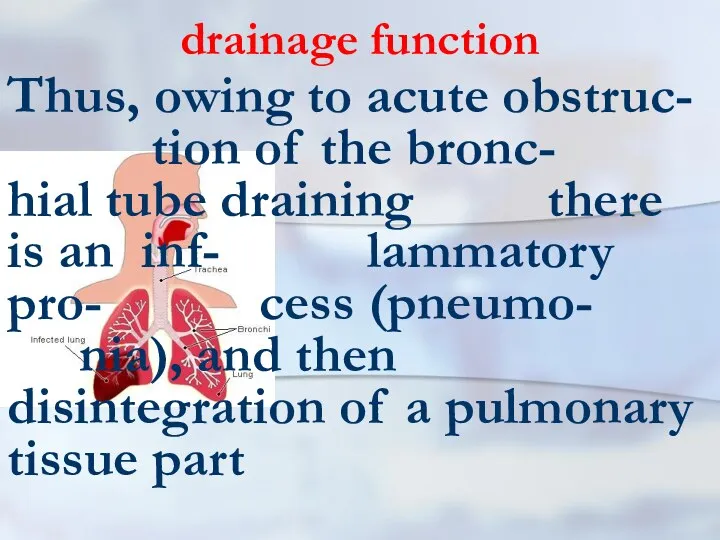
- 25. drainage function Thus, owing to acute obstruc- tion of the bronc- hial tube draining there is
- 26. sepsis At a sepsis are marked metas-tatic abscesses in lung. Heavy bruises, hematomas and damages of
- 27. causes Hence, the reasons of pulmonary abscesses are diverse. Nevertheless, at their occurren- ce interaction of
- 28. 60 and more 30-59 29 and younger Clinical picture Most frequently pulmonary abscesses meet at middle-aged
- 29. Clinical picture First of all it is caused by that among them more of- ten there
- 30. Adverse factors Besides adverse production factors matter also: the dust content and a gas- sed condition
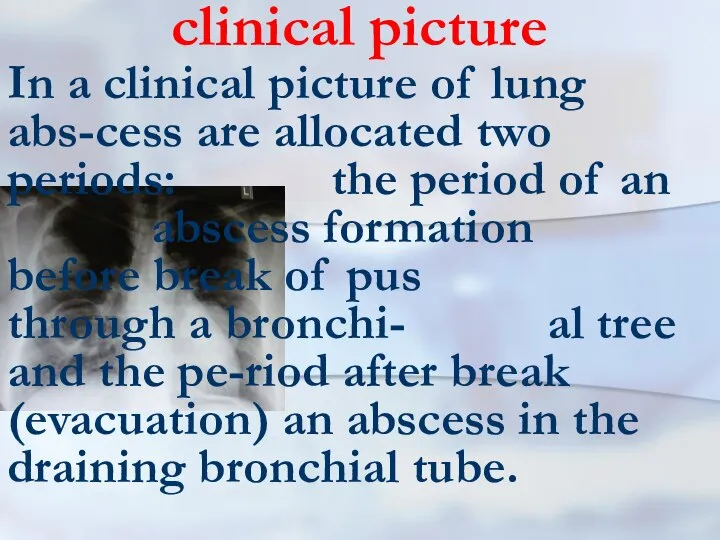
- 31. clinical picture In a clinical picture of lung abs-cess are allocated two periods: the period of
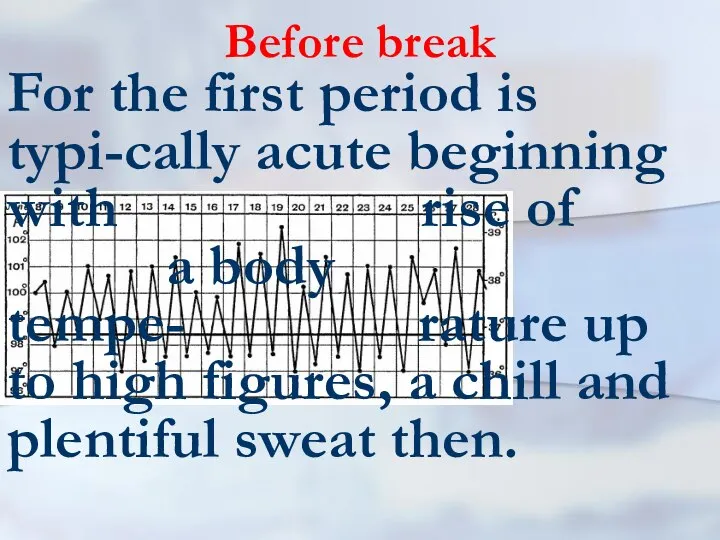
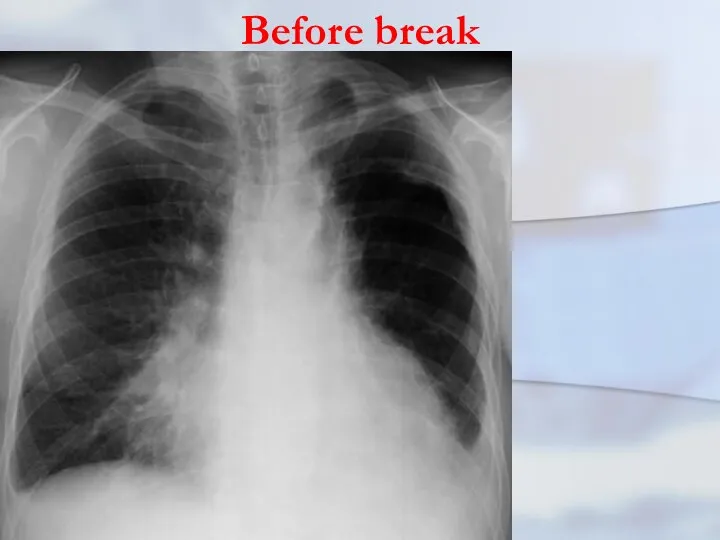
- 32. Before break For the first period is typi-cally acute beginning with rise of a body tempe-
- 33. Before break There may be pains in a thorax on the side of defeat, dyspnoea and
- 34. Before break Infringements of the common condi- tion as a head- ache, indisposi- tions and weak-ness
- 35. Before break The clinic purulent-resorptive fevers is totally marked. At x- ray in this period in
- 36. Before break On the average, this clinic pro- ceeds within 7-10 days. As a rule, the
- 37. Before break
- 38. after break In the second period when an abs-cess evacuates through a bronchial tree, the clinical
- 39. after break In other cases discharge of sputum occurs gradually. At once after discharge of purulent
- 40. after break The x-ray picture becomes typical for an abscess lung: there is a site of
- 41. after break The cavity of an abs- cess eventually de- creases, and in 6-8 weeks it
- 42. after break In some situations it is formed thin-walled roun- dish formation without contents – pseudocyst,
- 43. bad draining In some cases, when it is marked bad draining of the abscess, pro- cess
- 44. bad draining Clinically the constant disharge of purulent sputum is marked and the phenomena of an
- 45. gangrenous abscess Still allocate the gangreno-us abscess. As a rule, it is a huge abscess in
- 46. pyopneumothorax Sometimes the acute abscess of lung may break in a pleural cavity that results in
- 47. Radial methods In diagnosis of pulmonary abscesses it is used roentgenography and tomography of lung. Also
- 48. Conservative treatment Conservative treatment of an acute abscess of lung includes three obligatory components: optimum draining
- 49. draining Sometimes bronchoscopy is car-ried out with cateterization of ca- vities of an abs- cess. Suppressi-
- 50. draining In case of insufficient sanitation with the help of a puncture, it will be carried
- 51. antibacterial therapy Sometimes these preparations are entered in pulmonary and bronchial arteries, and also endolym- phatic.
- 52. general improving health therapy treatment The pharmacotherapy is directed also on stimulation secretolysis and ex-pectorations, struggle
- 53. acute abscesses Hence, acute abscesses, as a rule, are trea- ted conservati- vely. At occurrence pyopneumo-thorax
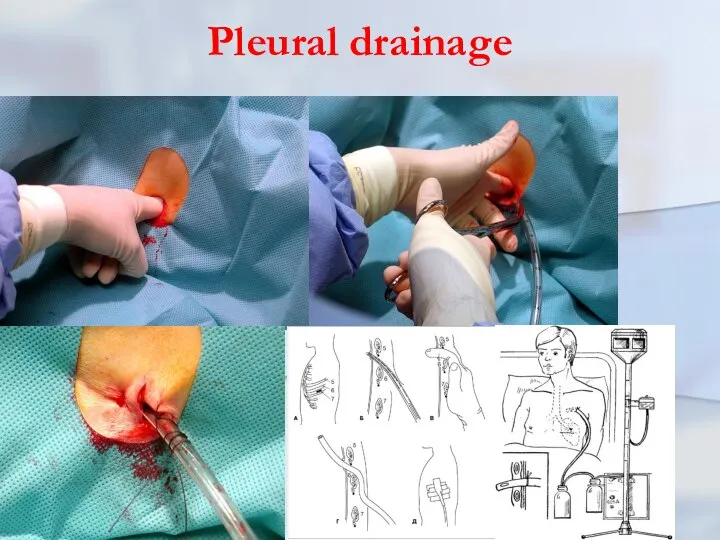
- 54. Pleural drainage
- 55. Pleural drainage rules (K.Mattox) 1. NEVER just aspirate blood in a trau-matic hemothorax. It just does
- 56. Pleural drainage rules (K.Mattox) 6. In teenage patients and adults for trau-matic hemothorax use a 36
- 57. Pleural drainage rules (K.Mattox) 8. ALWAYS connect to suction at about 20 CM negative pressure. ALWAYS
- 58. Pleural drainage rules (K.Mattox) 11. ALWAYS have the best person available to insert the tube who
- 59. sequestration in an abscess At the sequestration in an abscess is possible performance of pneu- motomy
- 60. emergency operation In the extremely rare cases when current of an acute abscess may become compli-cated
- 61. chronic abscess The basic indication to operation is the chronic abscess. The choice of a method
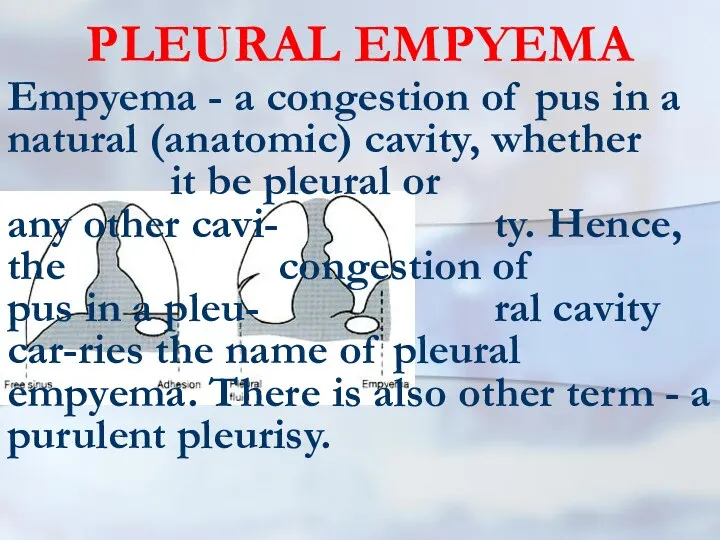
- 62. PLEURAL EMPYEMA Empyema - a congestion of pus in a natural (anatomic) cavity, whether it be
- 63. Pleural empyema The purulent pleurisy is the inflam-mation of pleural lists accompanying exudating in a pleural
- 64. Pleural empyema Pleural empyema in 90% of cases is complication of purulent lung disea- ses. First
- 65. Pleural empyema To outpulmonary diseases resulting in development of pleural empyema, concern: a pancreatitis, paranephrities and
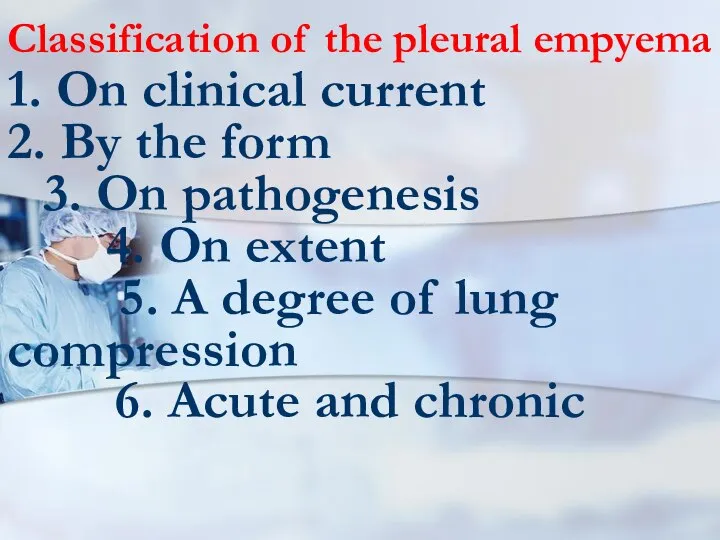
- 66. Classification of the pleural empyema 1. On clinical current 2. By the form 3. On pathogenesis
- 67. Classification of the pleural empyema 1. On clinical current: the purulent-resorptive fever and exhaustion. 2. By
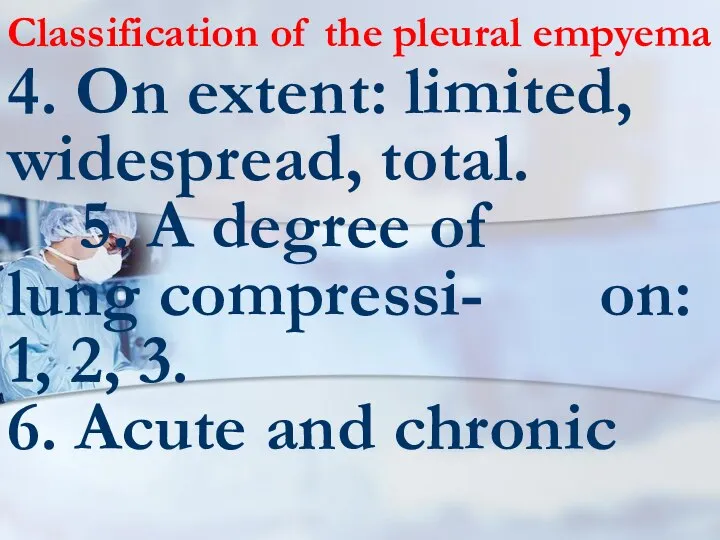
- 68. Classification of the pleural empyema 4. On extent: limited, widespread, total. 5. A degree of lung
- 69. Classification of the pleural empyema For the characteristic of intensity of purulent process both in lung,
- 70. Classification of the pleural empyema Limited empyema are in cases of involving in purulent process only
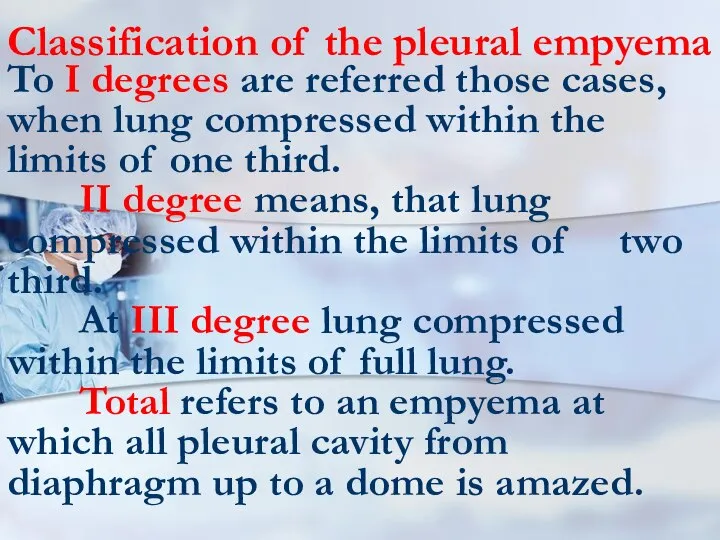
- 71. Classification of the pleural empyema To I degrees are referred those cases, when lung compressed within
- 72. Classification of the pleural empyema Introduction in classification of empyema with destruction and without destruction pulmonary
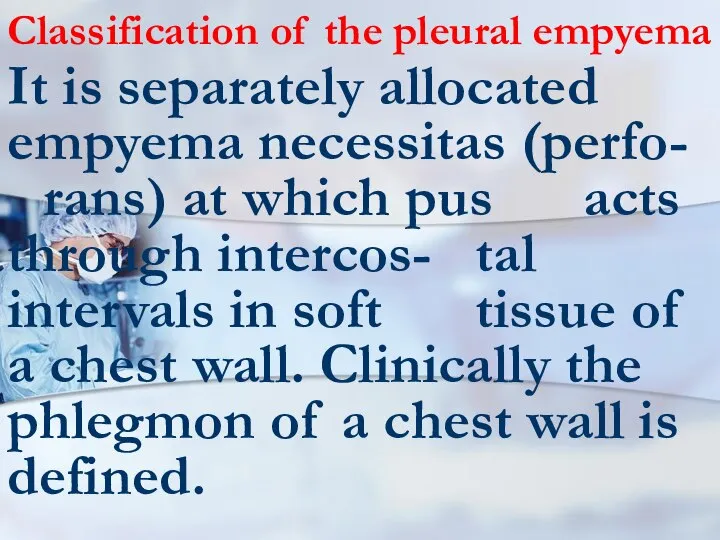
- 73. Classification of the pleural empyema It is separately allocated empyema necessitas (perfo- rans) at which pus
- 74. pathogeny As a rule, the purulent inflammation of pleura begins from fibrinous pleurisy and arises in
- 75. Pneumonia and pleurisy Pneumonias may divide on two groups: exudative type with insignificant defeat of bronchial
- 76. clinic Clinical picture. At pleural empyema occur pains in a thorax on the side of defeat,
- 77. clinic The typical answer of an organism to any form of a suppuration including pleural cavity
- 78. clinic As it is marked above, frequently by the beginning empyema happens the absceding pneumonia, therefore
- 79. clinic In other cases the clinical picture of deve-lopment pleural empyema proceeds latent-ly. It would seem,
- 80. clinic At the acute form it is observed con-dition as a shock. Suddenly at per-cussion there
- 81. clinic At the soft form, as a rule, an abscess evacuate in closed incapsulated spa-ce. This
- 82. clinic The raised body temperature is one of the major attributes of empyema of pleura. Temperature
- 83. clinic Frequently pains amplify at breath, there-fore patients avoid deep breath. Trying to spare the struck
- 84. clinic Restriction of respiratory excursions of a chest is marked on the side of defeat. At
- 85. diagnosis One of the important methods of diag-nosis of the pleural empyema is the x-ray inspection.
- 86. diagnosis Sometimes x-ray research will be carried out in lateroposition (on one side). Also are applied
- 87. treatment Treatment begins with a puncture of a cavity empyema. During a puncture con-tents with the
- 88. treatment After pleural cavity sanitation the drainage tube joins system active aspiration. At absence of aspira-tion
- 89. treatment All patient will carry out intensive antibacte-rial treatment in view of sensitivity of micro-flora. Correction
- 90. treatment At destructions of the lung tissues, in necessary cases, bronchoscopic sanitation will be carried out.
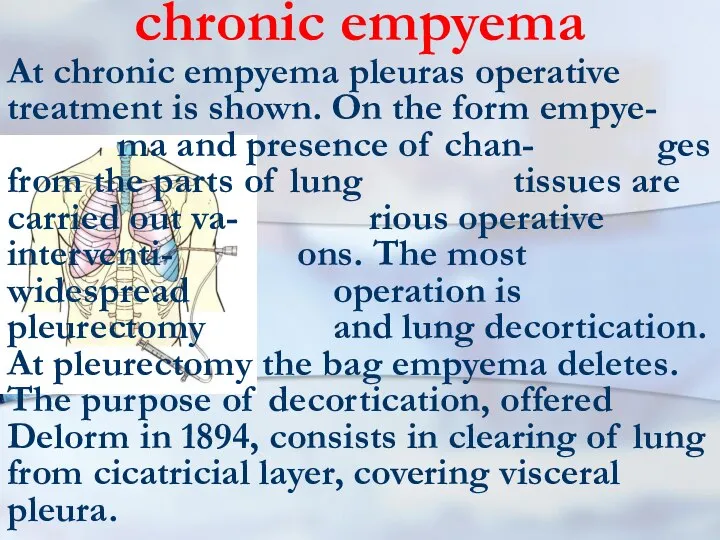
- 91. chronic empyema At chronic empyema pleuras operative treatment is shown. On the form empye- ma and
- 92. chronic empyema treatment As a rule, both operations (pleurectomy and decortica- tion) are united. Sometimes pleurectomy
- 93. chronic empyema treatment One of the most hardest operative interventions is pleuropulmonectomy. It is caused by
- 94. bronchial stump unsufficiency By the most often reason of a similar sort empyema happens an inconsistency
- 95. chronic empyema treatment Concluding this section, it is necessary to note, that ade- quate treatment of
- 96. lung gangrene Purulent-putrefactive necrosis of lobe or all of lung, with ab- sence of a zone
- 97. lung gangrene As a rule, the gangrene is formed owing to putrid disintegration of the massive,
- 98. lung gangrene Etiopathogen moments of a gangrene in many re- spects are similar to those at
- 99. lung gangrene It is frequently marked aspira-tion on a background of alco- holic intoxication. The big
- 100. lung gangrene The significant role is played with previous chronic non- specific diseases of lung. More
- 101. Clinic As a rule, the gangrene of lung begins shar-ply, with significant rise of a body
- 102. Clinic Sometimes cough out small slices lifeless lung tissues. Even being on significant distance from the
- 103. Clinic Frequently current of a gangrene of lung is complicated by development of empyema pleuras. In
- 104. Clinic At percussion zones of dullness above lung are quickly increased. On a back- ground of
- 105. x-ray At x-ray comes to light diffuse blackout of the struck parts of lung (a lobe,
- 106. prognosis The prognosis at a lung gangrene frequently adverse. Especially it concerns cases when all lung
- 107. gangrene lung treatment It should be started with intensive therapy in reanimation department. This treatment should
- 108. gangrene lung treatment The main thing in treatment is stabilization of process in probab- ly short
- 110. Скачать презентацию





















































































 Принципы проведения реанимационных мероприятий при терминальных нарушениях ритма
Принципы проведения реанимационных мероприятий при терминальных нарушениях ритма Двигательный компонент эмоций. Язык мимики, поз, жестов
Двигательный компонент эмоций. Язык мимики, поз, жестов odgAssist. Pharmacy
odgAssist. Pharmacy Генетические аспекты ортодонтической патологии
Генетические аспекты ортодонтической патологии Психологическая программа реабилитации лиц пожилого возраста при ИБС
Психологическая программа реабилитации лиц пожилого возраста при ИБС Сестринская помощь при слабости
Сестринская помощь при слабости Кожные болезни у детей, аллергии. ЛК №6
Кожные болезни у детей, аллергии. ЛК №6 Профилактика кризисных ситуаций в подростковом возрасте
Профилактика кризисных ситуаций в подростковом возрасте Что должен знать о ВИЧ/СПИДе каждый
Что должен знать о ВИЧ/СПИДе каждый Строение половой системы
Строение половой системы Изучение стоматологического статуса здоровых детей, и детей, больных атопическим дерматитом
Изучение стоматологического статуса здоровых детей, и детей, больных атопическим дерматитом Аритмии сердца
Аритмии сердца Бет жақсүйек аймағының жедел одонтогенді қабыну аурулары
Бет жақсүйек аймағының жедел одонтогенді қабыну аурулары Болезнь Ауески (morbus Aujezky)
Болезнь Ауески (morbus Aujezky) Отчет о работе детского хирургического отделения
Отчет о работе детского хирургического отделения Психология негіздері және коммуникативтік дағдылар кафедрасы
Психология негіздері және коммуникативтік дағдылар кафедрасы The weaknesses of the international business in Ukraine during pandemic COVID-19
The weaknesses of the international business in Ukraine during pandemic COVID-19 Повреждения органов мочеполовой системы. Неотложные состояния в урологии
Повреждения органов мочеполовой системы. Неотложные состояния в урологии Выделение. Строение и работа почек
Выделение. Строение и работа почек Опиоиды как адъюванты для регионарной анестезии
Опиоиды как адъюванты для регионарной анестезии Гравидограмманы жүргізу
Гравидограмманы жүргізу Ent. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Ent. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma Основы общей патологии
Основы общей патологии Жұқпалы емес аурулар эпидемиологиясының өзекті мәселелер
Жұқпалы емес аурулар эпидемиологиясының өзекті мәселелер Шизофрения
Шизофрения Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция)
Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция) Гипертоническая болезнь II стадии. Ситуационная задача
Гипертоническая болезнь II стадии. Ситуационная задача Hospital (in-patient department)
Hospital (in-patient department)