Содержание
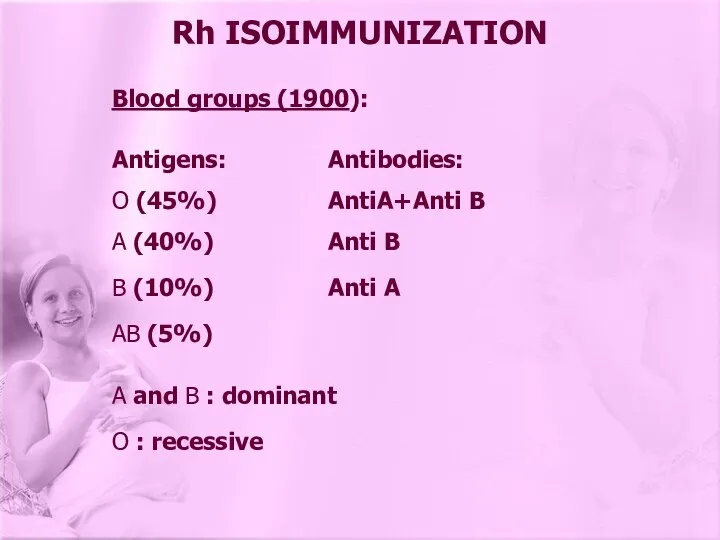
- 2. Blood groups (1900): Antigens: Antibodies: O (45%) AntiA+Anti B A (40%) Anti B B (10%) Anti
- 3. Rhesus factor (1940): Agglutinogen (C,D,E) - mainly D C,D,E - dominant antigen d,e - recessive antigen
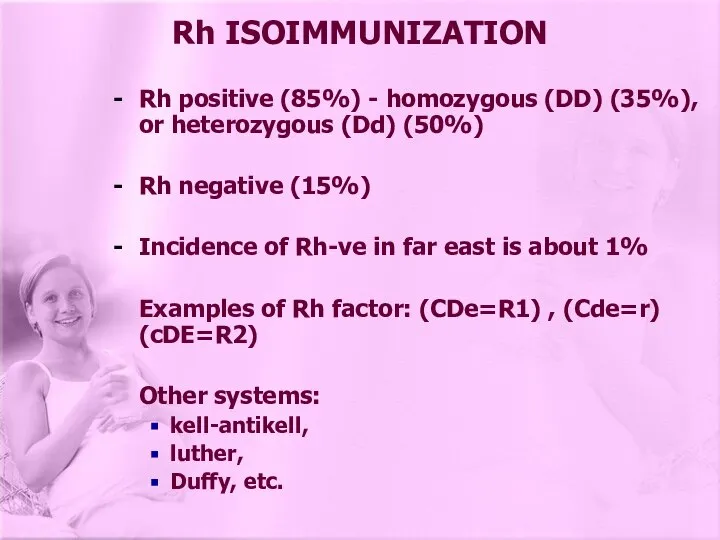
- 4. Rh positive (85%) - homozygous (DD) (35%), or heterozygous (Dd) (50%) Rh negative (15%) Incidence of
- 5. Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION So in response to introduction of foreign protein (antigen) ? production of antibody to
- 6. Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION Feto-maternal haemorrhage: during pregnancy leakage of fetal cells in the maternal circulation (Rh+ fetal
- 7. Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION Development of Rhesus antibodies: depends on factors: 1- Inborn ability to respond 2- protection
- 8. 1- If ABO is incompatible: Red blood cells is easily destroyed, so not reaching enough immunological
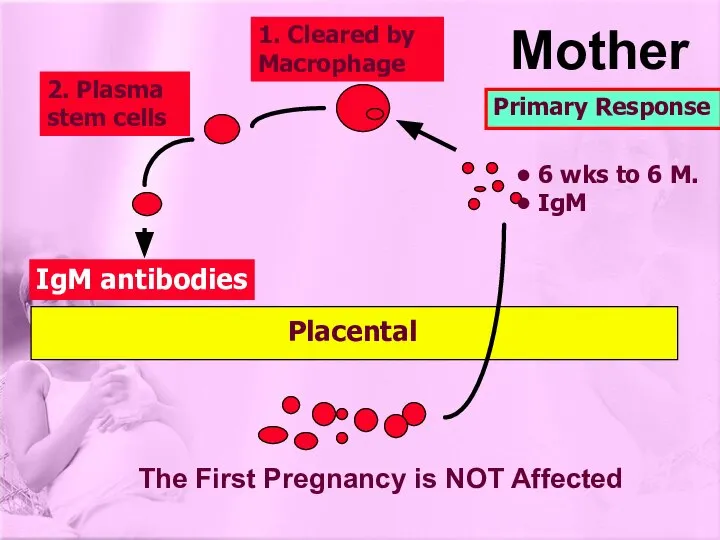
- 9. IgM antibodies 1. Cleared by Macrophage 2. Plasma stem cells The First Pregnancy is NOT Affected
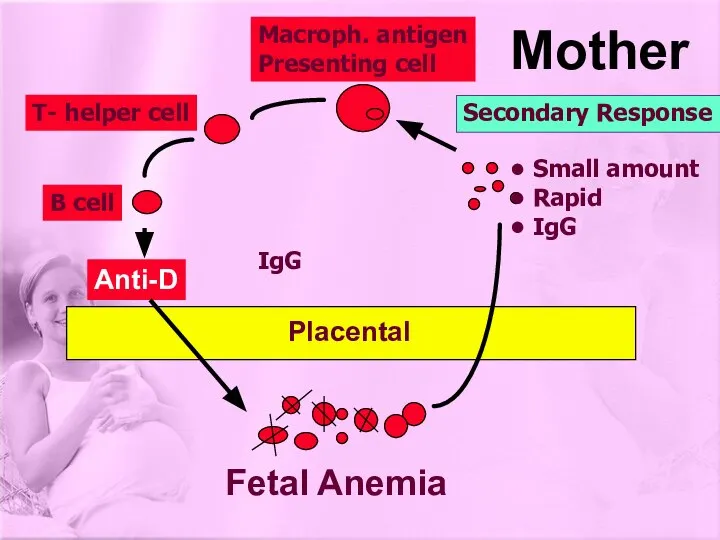
- 10. Anti-D Macroph. antigen Presenting cell T- helper cell B cell Fetal Anemia Mother Placental Secondary Response
- 11. 2 - If ABO is compatible: Rh+ fetal cells ? remain in circulation (life span) until
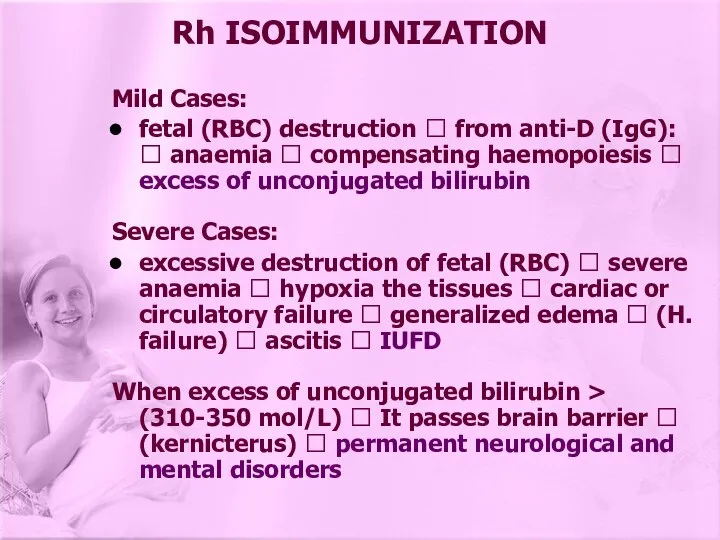
- 13. Mild Cases: fetal (RBC) destruction ? from anti-D (IgG): ? anaemia ? compensating haemopoiesis ? excess
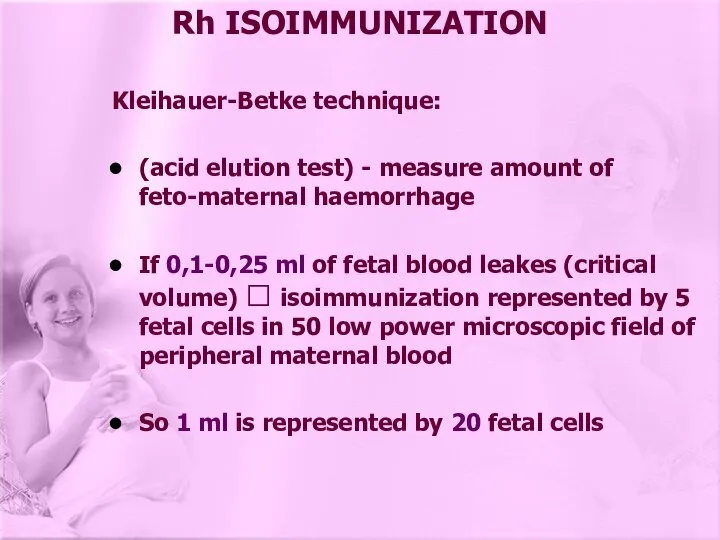
- 14. Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION Kleihauer-Betke technique: (acid elution test) - measure amount of feto-maternal haemorrhage If 0,1-0,25 ml
- 15. Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION Fetal and Neonatal Effects: Haemolytic anaemia of newborn Hb=14-18g/dl Icterus gravis neonatorum Hb=10-14g/dl Hydrops
- 16. MANAGEMENT OF Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION I) PROPHYLAXIS 1 - Prevention of Rhesus isoimmunization: Anti D (RhoD IgG)
- 17. MANAGEMENT OF Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION K-B test if large amount of leaking ? another SD if mother
- 18. MANAGEMENT OF Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION II) 1- Antibody Screening: for all pregnant women in ANC for irregular
- 19. MANAGEMENT OF Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION 2 - Management following detection of Rh antibodies Should be treated in
- 20. 3 - Amniocentesis: Should be performed under ultrasound guidance if titre > 1\16 = 0.5-1 ugm
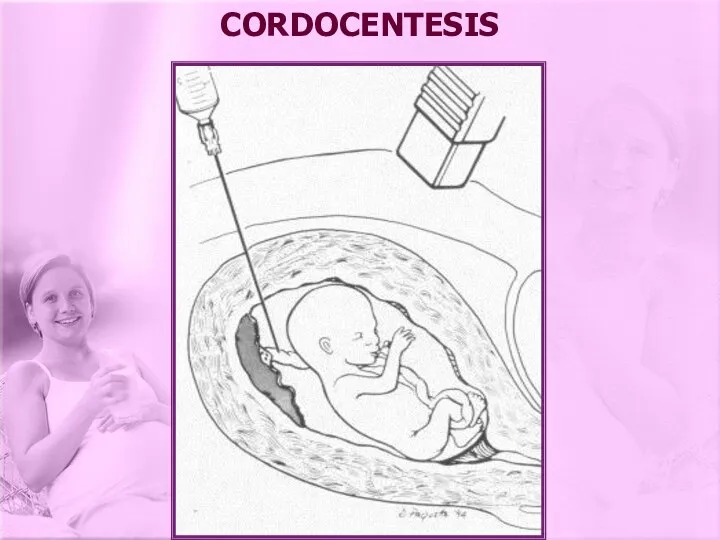
- 21. CORDOCENTESIS
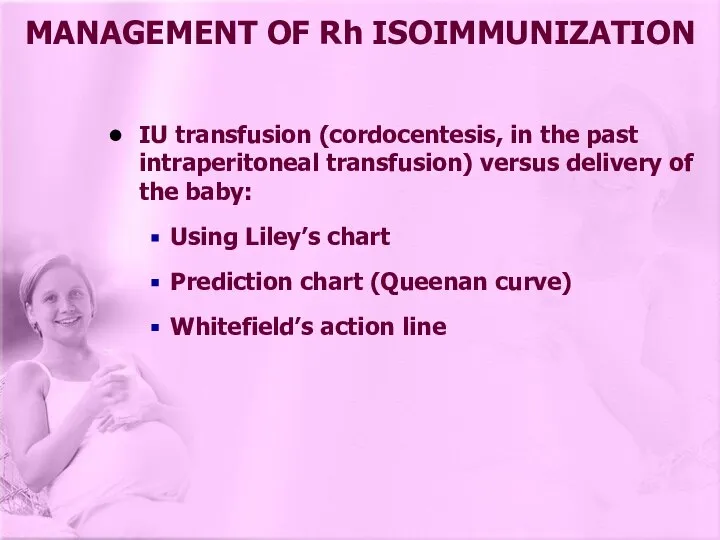
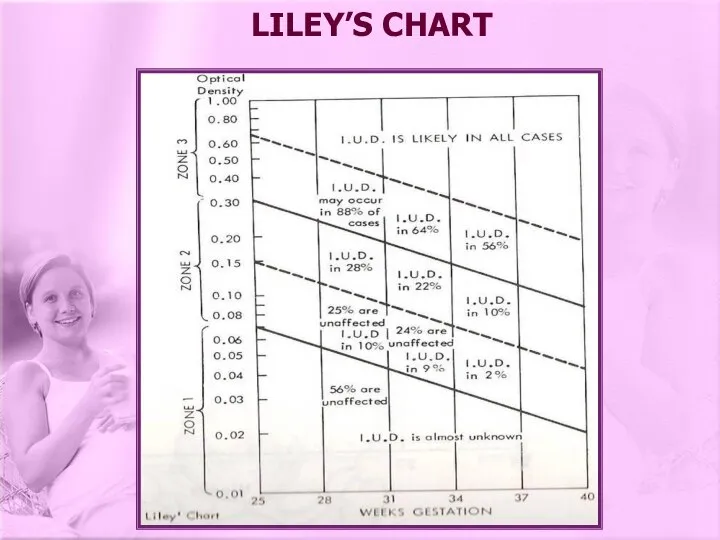
- 22. IU transfusion (cordocentesis, in the past intraperitoneal transfusion) versus delivery of the baby: Using Liley’s chart
- 23. LILEY’S CHART
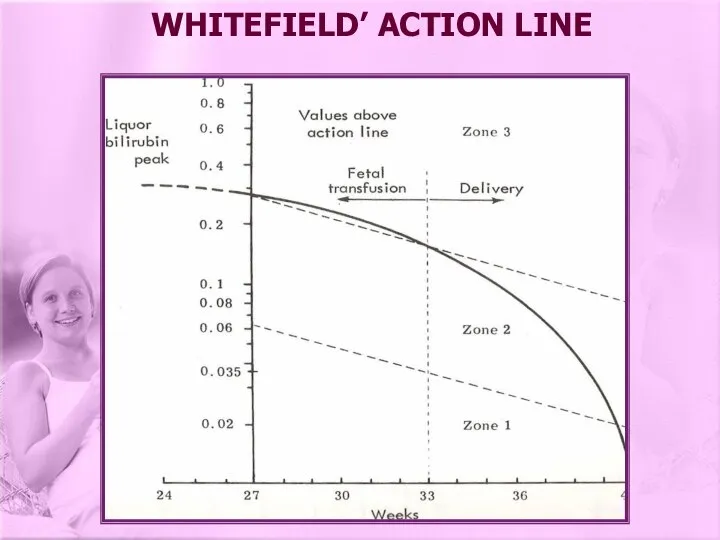
- 24. WHITEFIELD’ ACTION LINE
- 25. MANAGEMENT OF Rh ISOIMMUNIZATION Alternatively follow up with Doppler study for the fetal middle cerebral artery
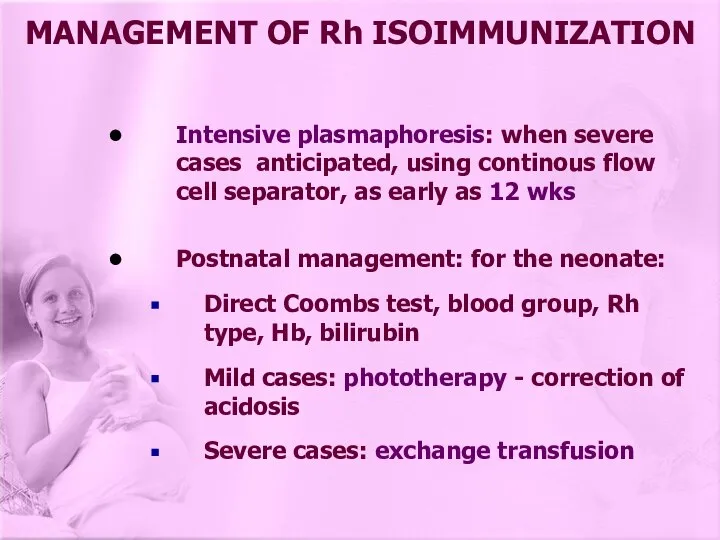
- 26. Intensive plasmaphoresis: when severe cases anticipated, using continous flow cell separator, as early as 12 wks
- 28. Скачать презентацию














 Атопический дерматит в развитии бронхиальной астмы
Атопический дерматит в развитии бронхиальной астмы Артериялық гипертензия
Артериялық гипертензия МикроРНК. Роль в развитии злокачественных новообразований
МикроРНК. Роль в развитии злокачественных новообразований Ультрасонография селезенки
Ультрасонография селезенки Электрокардиография – ЭКГ Electrocardiography - ECG
Электрокардиография – ЭКГ Electrocardiography - ECG Острый и хронический гломерулонефрит
Острый и хронический гломерулонефрит Ұйқы физилогиясы. Ұйқы фазасы
Ұйқы физилогиясы. Ұйқы фазасы Паранеопластический синдром
Паранеопластический синдром Оттискные массы
Оттискные массы Пути и способы применения лекарственных средств
Пути и способы применения лекарственных средств Основные принципы выявления, диагностики, изоляции и лечения, больных особо опасными инфекциями на этапах медицинской эвакуации
Основные принципы выявления, диагностики, изоляции и лечения, больных особо опасными инфекциями на этапах медицинской эвакуации Правила производства и контроля качества лекарственных средств
Правила производства и контроля качества лекарственных средств Почечное кровообращение и его регуляция
Почечное кровообращение и его регуляция Адаптация және компенсация процесстерінің морфологиялық суреттемесі: атрофия, гипертрофия (гиперплазия)
Адаптация және компенсация процесстерінің морфологиялық суреттемесі: атрофия, гипертрофия (гиперплазия) Трансплантация сердца
Трансплантация сердца Основы СЛР для врачей общей практики
Основы СЛР для врачей общей практики Массаж лица и шеи
Массаж лица и шеи Жоғарғы жүйке жүйесі
Жоғарғы жүйке жүйесі Intussusception definition
Intussusception definition Клещевой энцефалит. Описторхоз
Клещевой энцефалит. Описторхоз Бесплодный брак. Итоги работы кабинета бесплодия
Бесплодный брак. Итоги работы кабинета бесплодия Анафилактикалық шок
Анафилактикалық шок Дезинфекция растворами, газами, аэрозолями
Дезинфекция растворами, газами, аэрозолями Эффективность и переносимость блокатора рецепторов к альдостерону- эплеренона у больных с острым инфарктом миокарда
Эффективность и переносимость блокатора рецепторов к альдостерону- эплеренона у больных с острым инфарктом миокарда Синдром Бругада
Синдром Бругада Финансирование здравоохранения
Финансирование здравоохранения Микробиологические основы химиотерапии и химиопрофилактики инфекционных болезней
Микробиологические основы химиотерапии и химиопрофилактики инфекционных болезней АИВ инфекциясының аурухана ішілік инфекциясына қарсы эпидемиологиялық бақылауды ұйымдастыру
АИВ инфекциясының аурухана ішілік инфекциясына қарсы эпидемиологиялық бақылауды ұйымдастыру