Содержание
- 2. Электрокардиогра́фия definition - a technique for recording and studying the electric fields generated during the work
- 3. Hystory В 1901 году Виллем Эйнтховен, работавший в Лейдене (Нидерланды), использовал струнный гальванометр: первый практический ЭКГ-аппарат.
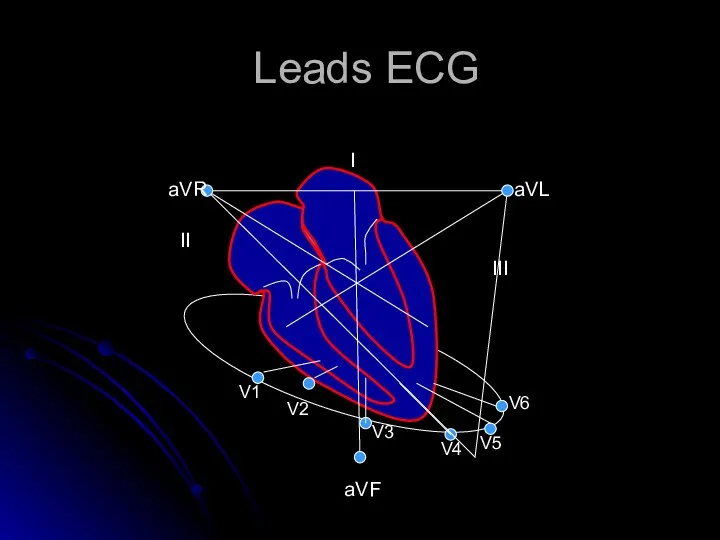
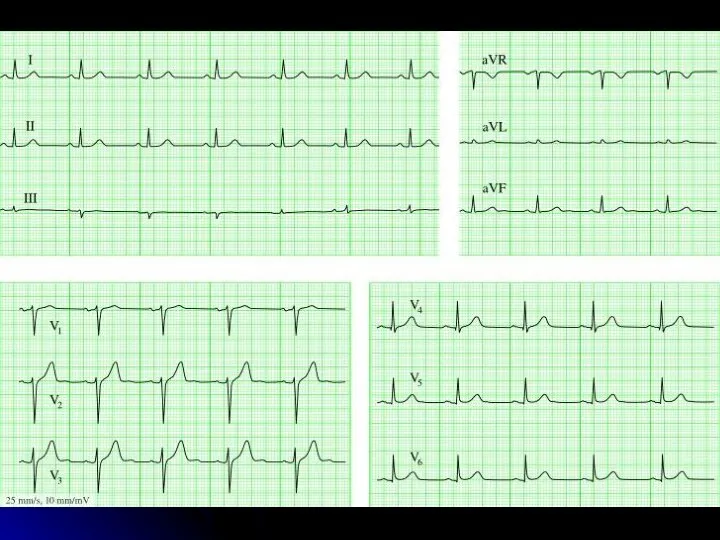
- 4. Leads ECG II III I aVR aVL aVF V1 V2 V4 V5 V6 V3
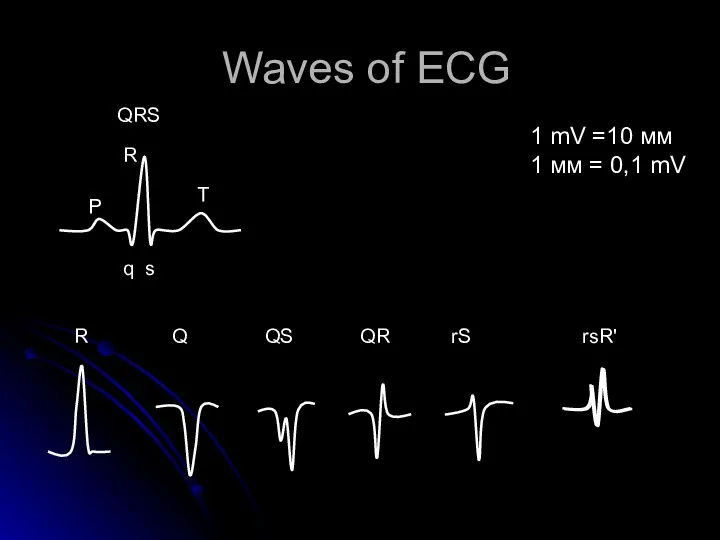
- 5. Waves of ECG Р q s T R QRS R Q QS QR rS rsR' 1
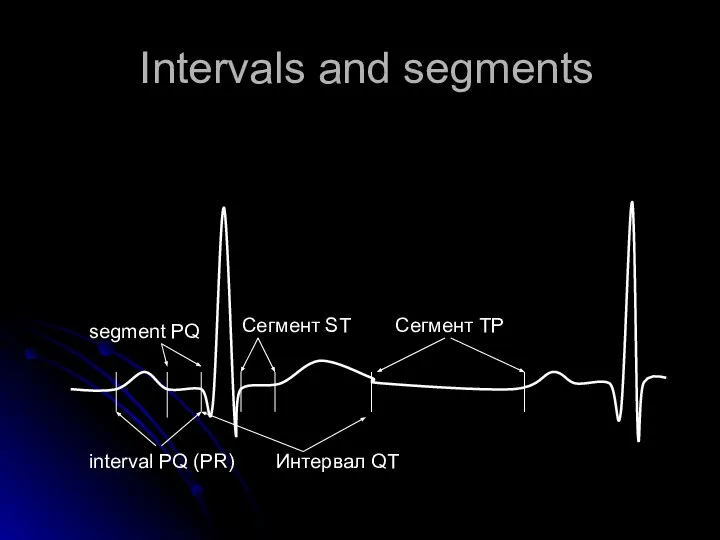
- 6. Intervals and segments interval PQ (PR) Сегмент ST segment PQ Интервал QT Сегмент ТР
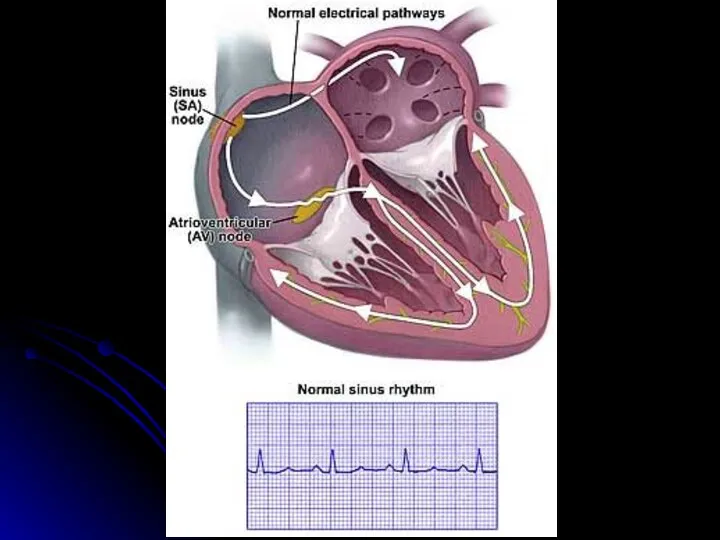
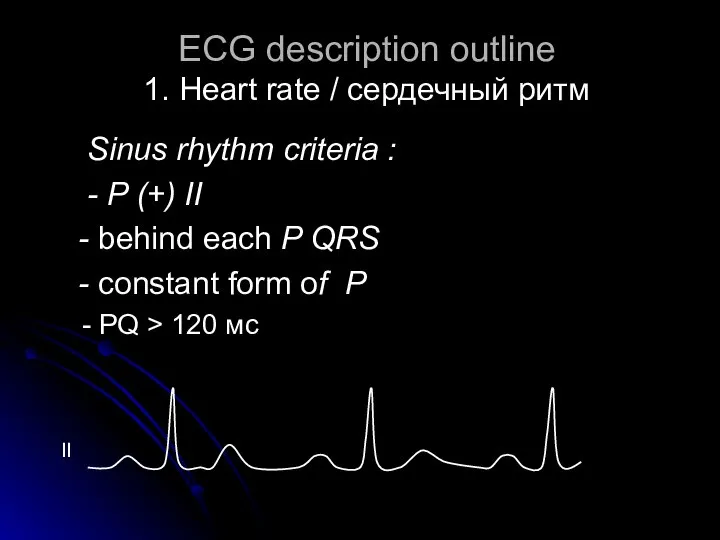
- 8. ECG description outline 1. Heart rate / cердечный ритм Sinus rhythm criteria : - P (+)
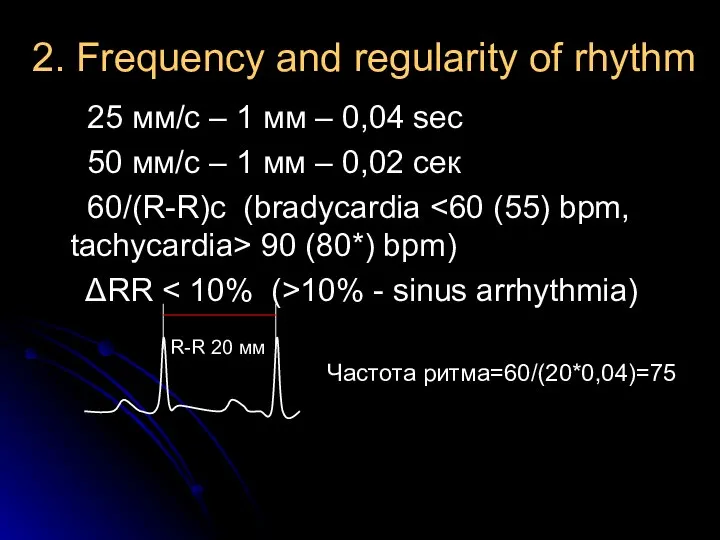
- 9. 2. Frequency and regularity of rhythm 25 мм/с – 1 мм – 0,04 sec 50 мм/с
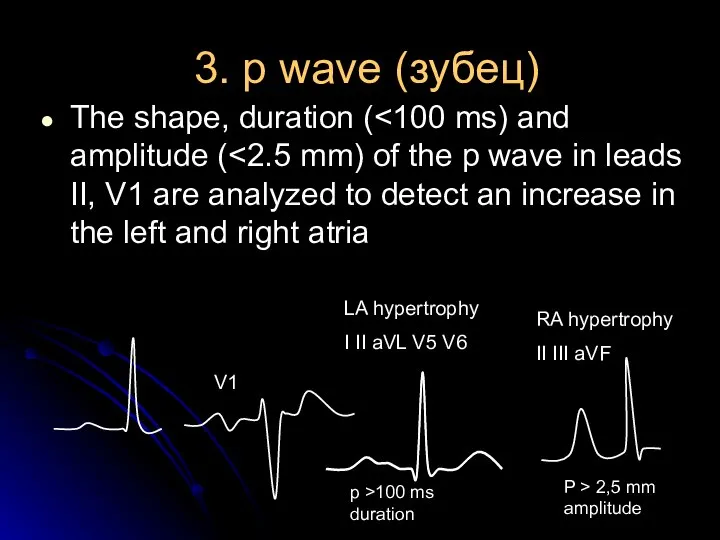
- 10. 3. p wave (зубец) The shape, duration ( LA hypertrophy I II aVL V5 V6 RA
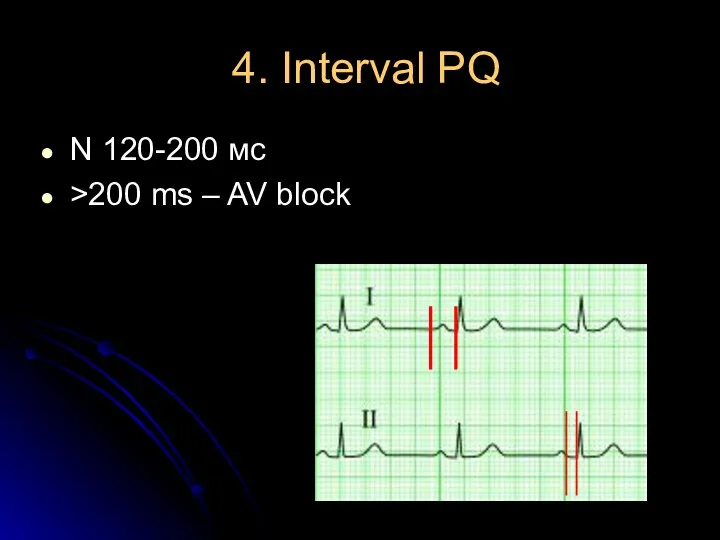
- 11. 4. Interval PQ N 120-200 мс >200 ms – AV block
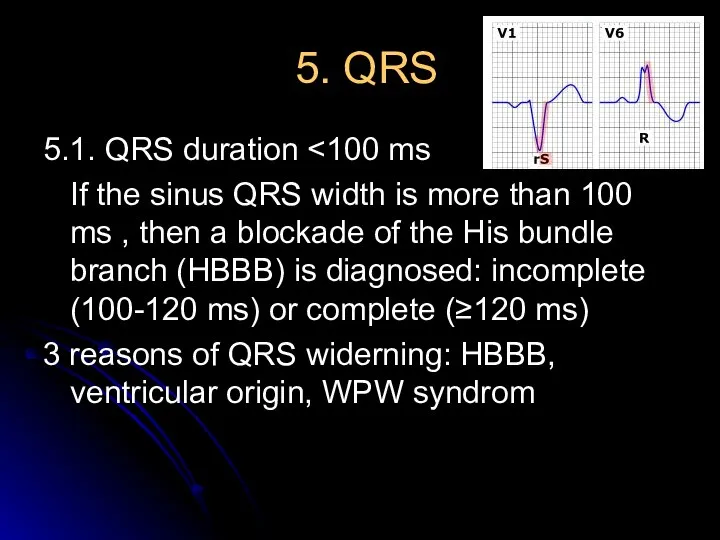
- 12. 5. QRS 5.1. QRS duration If the sinus QRS width is more than 100 ms ,
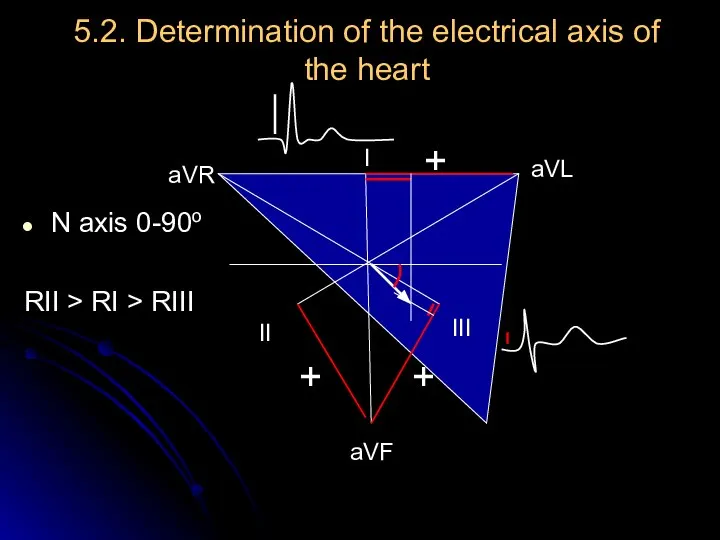
- 13. 5.2. Determination of the electrical axis of the heart N axis 0-90o RII > RI >
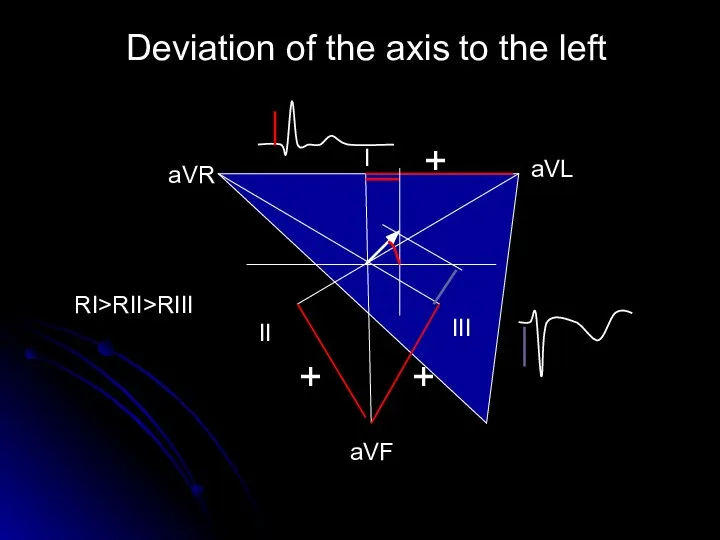
- 14. Deviation of the axis to the left aVL аVR aVF I II III + + +
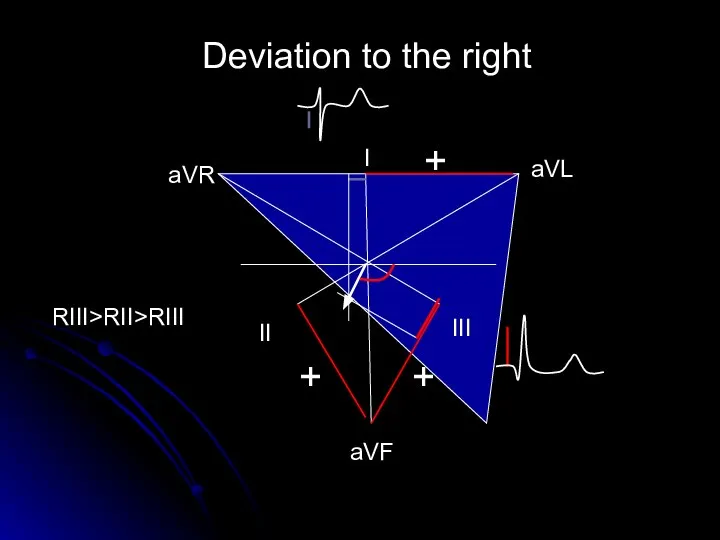
- 15. Deviation to the right aVL аVR aVF I II III + + + RIII>RII>RIII
- 16. 0º (I) +90º (aVF) -90º - + -50º +45º +120º Отклонение ЭОС влево Нормальное расположение ЭОС
- 17. 5.3. Q wave– along or preceding negative wave in QRS A normal q wave is recorded
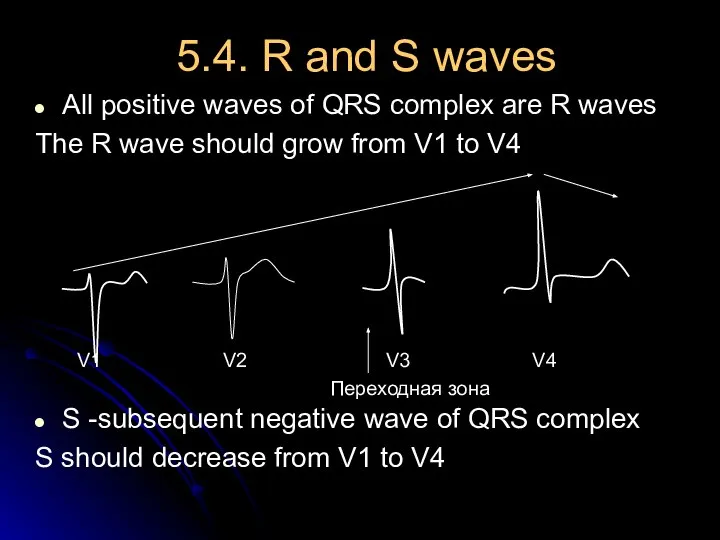
- 18. 5.4. R and S waves All positive waves of QRS complex are R waves The R
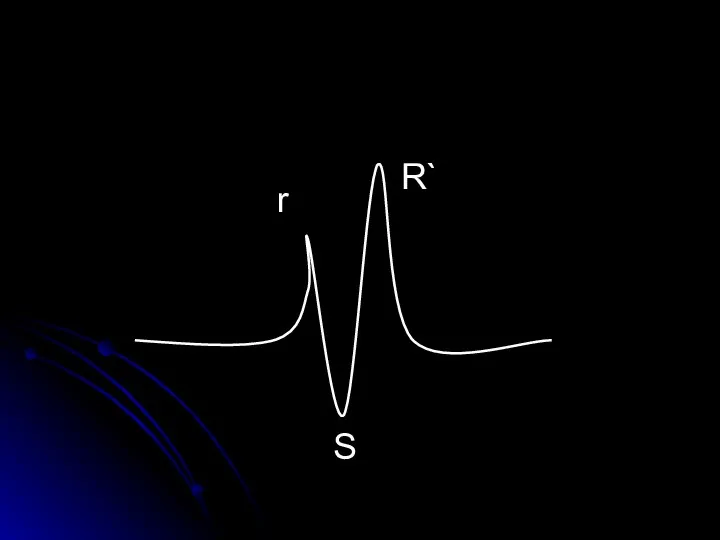
- 19. r S R`
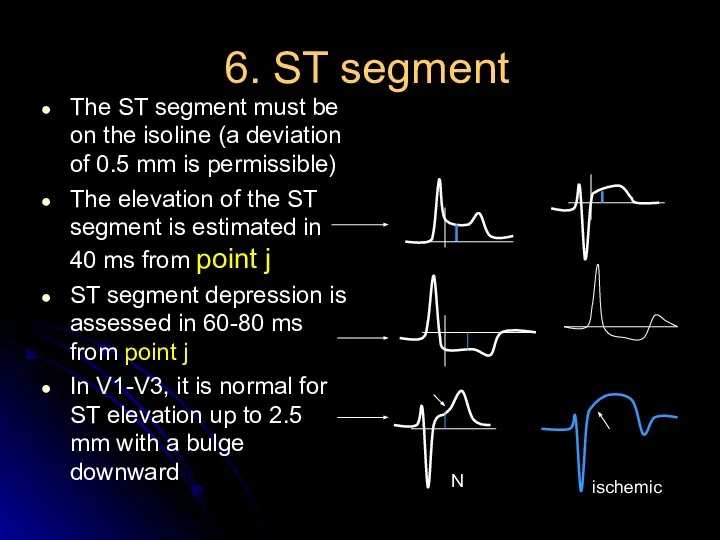
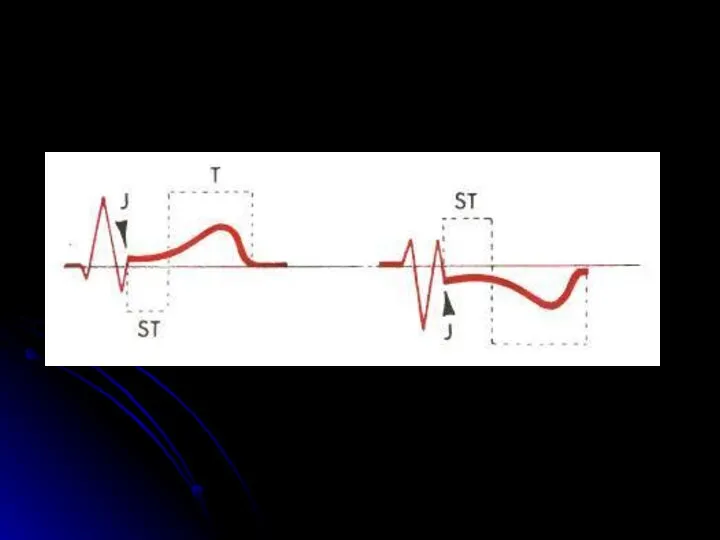
- 20. 6. ST segment The ST segment must be on the isoline (a deviation of 0.5 mm
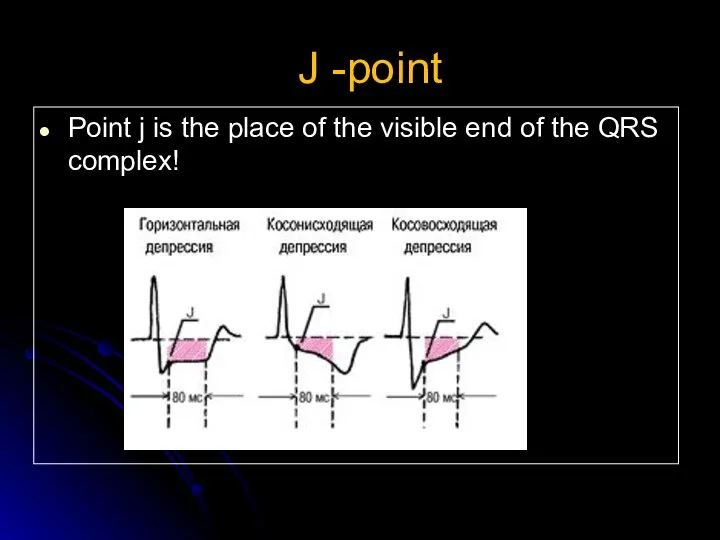
- 21. J -point Point j is the place of the visible end of the QRS complex! J-точка
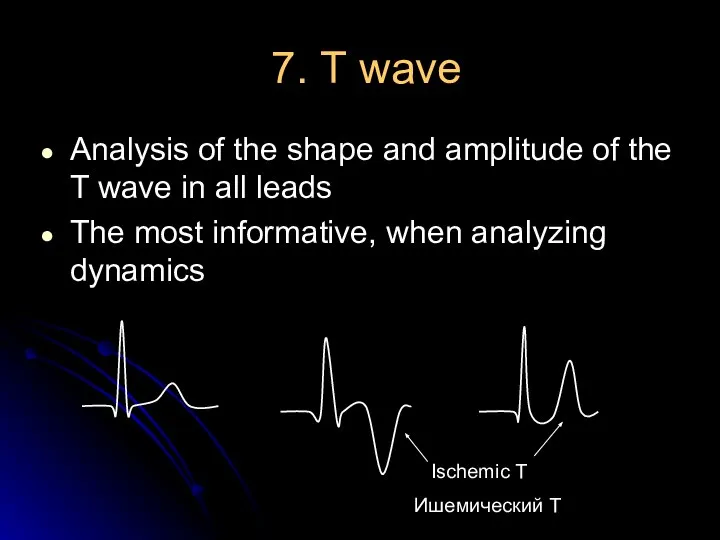
- 23. 7. Т wave Analysis of the shape and amplitude of the T wave in all leads
- 24. 8. QT interval N 450 ms QT has a significant direct dependence on the duration of
- 27. Скачать презентацию





 Б±ќаралыќ аќпарат ќ±ралдары
Б±ќаралыќ аќпарат ќ±ралдары Защити себя от ВИЧ
Защити себя от ВИЧ Состояние здоровья и физическое развитие детей и подростков
Состояние здоровья и физическое развитие детей и подростков ЗОЖ
ЗОЖ Гепатит A, C, G, T вирусы
Гепатит A, C, G, T вирусы Остеохондроз позвоночника. Рентгенографические признаки остеохондроза
Остеохондроз позвоночника. Рентгенографические признаки остеохондроза Вплив алкоголю та паління на репродуктивну систему і потомство
Вплив алкоголю та паління на репродуктивну систему і потомство Причины нарушений зрения
Причины нарушений зрения Регуляторные системы организма. Органы иммунной системы. Нормальные и патологические реакции иммунной системы
Регуляторные системы организма. Органы иммунной системы. Нормальные и патологические реакции иммунной системы Гематологические исследования
Гематологические исследования Хронический бронхит
Хронический бронхит Заболевания щитовидной железы
Заболевания щитовидной железы Партограмма
Партограмма Сестринский уход при различных заболеваниях и состояниях. Сестринская помощь в хирургии. Кровотечение и гемостаз
Сестринский уход при различных заболеваниях и состояниях. Сестринская помощь в хирургии. Кровотечение и гемостаз Туберкулез кезіндегі шаралар стандарттары мен алгоритмдері
Туберкулез кезіндегі шаралар стандарттары мен алгоритмдері ICH процесі шеңберіндегі CTD жалпы техникалық құжаты
ICH процесі шеңберіндегі CTD жалпы техникалық құжаты Тестовый контроль по теме: Инфузии и основы трансфузиологии для специальности Сестринское дело
Тестовый контроль по теме: Инфузии и основы трансфузиологии для специальности Сестринское дело Рентгенографическая и компьютерно-томографическая диагностика острых и хронических синуситов
Рентгенографическая и компьютерно-томографическая диагностика острых и хронических синуситов Витамины
Витамины Вербальные и невербальные коммуникации
Вербальные и невербальные коммуникации Правильные ответы викторины по станции Медицинская
Правильные ответы викторины по станции Медицинская Вегетативная нервная система и синдромы ее нарушения
Вегетативная нервная система и синдромы ее нарушения Антибиотики: лечат или калечат
Антибиотики: лечат или калечат То что просто для детей, невозможно для взрослых. 2 класс
То что просто для детей, невозможно для взрослых. 2 класс Синдром марфана
Синдром марфана Эпидемиология РМЖ
Эпидемиология РМЖ Комбинированные поражения (лекция № 5)
Комбинированные поражения (лекция № 5) Обследование больного в ортопедическом отделении. Оформление документации. Деонтология и этика в ортопедической стоматологии
Обследование больного в ортопедическом отделении. Оформление документации. Деонтология и этика в ортопедической стоматологии