Слайд 25

Jandt, Fred E. (2003). An Introduction to Intercultural Communication: identities in
a global community (4thed.). USA
Kulich, Steve (2002). Using a Measure of Cross-Cultural Adaptability to develop Intercultural Communications in China, in Foreign Language and Culture Studies, Vol 2, Wu Youfu, ed., Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press.
Kulich, Steve (2003). Beyond Language to Culture’s Interdisciplinary Dimensions – Toward A Broader Focus in Intercultural Communications (Introducing the “Advancing Intercultural Studies” Project) Foreign Language and Culture Studies, Volume 3, Shanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language and Education Press.
Kulich, Steve and Zhang, Rui (2009). The multiple frames of “Chinese” values: from tradition to modernity and beyond, Oxford Hand book (Michael Bond, Ed., 2010)
Lippmann, Walter (1922). Public opinion (New York: Harcourt, Brace) 25.
Lustig, M.W., & Koester, J. (2006). Intercultural competence: Interpersonal communication across cultures (5thed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education/Allyn and Bacon.
Martin, J.N., & Nakayama, T.K., (1999). International Communication in Contexts (4thed.). California: Mayfield Publishing Company.
Mcdougall, W. (1908). An introduction to social psychology. Londres: Methuen.
Nisbett, R. E. (2003). The geography of thought: How Asians and Westerns think differently and why. New York, NY: The Free Press.
Schwartz, S. H., & Struch, N. (1989). Values, stereotypes, and intergroup antagonism. In D. Bar-Tal, C. F. Graumann, A.W. Kruglanski, & W. Stroebe (Eds.), Stereotyping and prejudice: Changing conceptions. New York, NY:
Tajfel, H., Billig, M. G., Bundy, R. P., & Flament, C. (1971). Social categorization and intergroup behavior. European journal of social psychology, 1(2), 149-178.
Tajfel, H. (1978). Differentiation between social groups. London, UK: Academic Press.
Tajfel, H. (1982). Human groups and social categories. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.

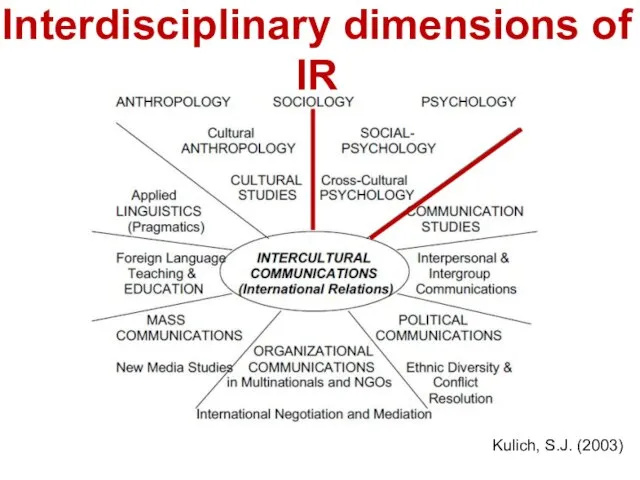












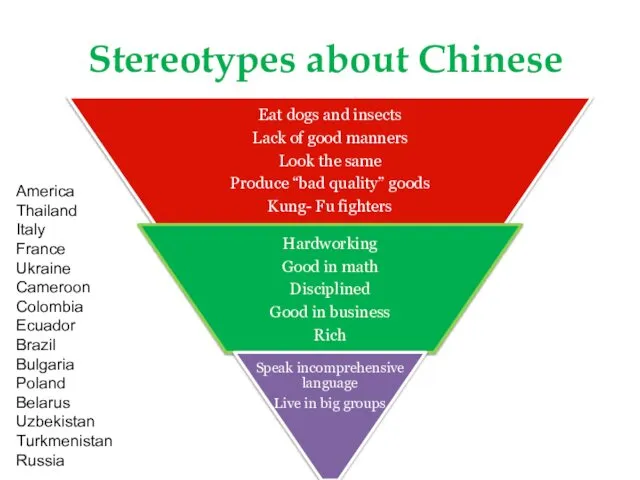








 Экспресс-метод оценки психологического климата коллектива
Экспресс-метод оценки психологического климата коллектива Самооценка и уровень притязаний
Самооценка и уровень притязаний Развитие ребенка от рождения до трех лет
Развитие ребенка от рождения до трех лет Кинесика. Жесты. Невербальные коммуникации
Кинесика. Жесты. Невербальные коммуникации Rīgas Stradiņa Universitāte Komunikācijas fakultāte Socioloģijas un psiholoģijas katedra Bakalaura programma Psiholoģija
Rīgas Stradiņa Universitāte Komunikācijas fakultāte Socioloģijas un psiholoģijas katedra Bakalaura programma Psiholoģija Своеобразие психологии народов ближнего зарубежья Украинцы и Белорусы
Своеобразие психологии народов ближнего зарубежья Украинцы и Белорусы Единая методика социально-психологического тестирования (ЕМ СПТ): методика и организация тестирования
Единая методика социально-психологического тестирования (ЕМ СПТ): методика и организация тестирования Психическое развитие как развитие личности: психоаналитический подход
Психическое развитие как развитие личности: психоаналитический подход Настольная игра Активити
Настольная игра Активити Расизм
Расизм Психолого-социальные аспекты манипулирования. Биологическая, социальная, психологическая, управленческая сторона манипулирования
Психолого-социальные аспекты манипулирования. Биологическая, социальная, психологическая, управленческая сторона манипулирования Понятие и виды мышления
Понятие и виды мышления Родительская несдержанность: учимся управлять собой
Родительская несдержанность: учимся управлять собой Психофизиология творчества
Психофизиология творчества Туризм как рекреационно-оздоровительных услуг
Туризм как рекреационно-оздоровительных услуг Психология управления временем
Психология управления временем Загальна психологічна характеристика студентського віку
Загальна психологічна характеристика студентського віку Переосмысление аналитической психологии: между наукой и паранаукой
Переосмысление аналитической психологии: между наукой и паранаукой Мотивация и мотивы
Мотивация и мотивы Психические состояния и особенности их проявления в экстремальной ситуации
Психические состояния и особенности их проявления в экстремальной ситуации Мышление и интеллект. Лекция 4
Мышление и интеллект. Лекция 4 Память и внимание. Психические познавательные процессы
Память и внимание. Психические познавательные процессы How to Solve Family Problems
How to Solve Family Problems 15 минут о механизме привыкания
15 минут о механизме привыкания Самопізнання та самооцінка
Самопізнання та самооцінка Тұлғаның танымдық іс-әрекетнің сипаттамасы (Зейін, Түйсік, Қабылдау, Ес, Ойлау, Сөйлеу,Қиял)
Тұлғаның танымдық іс-әрекетнің сипаттамасы (Зейін, Түйсік, Қабылдау, Ес, Ойлау, Сөйлеу,Қиял) Личностные и межличностные коммуникации
Личностные и межличностные коммуникации Муниципальное бюджетное учреждение Центр патриотического воспитания Отечество
Муниципальное бюджетное учреждение Центр патриотического воспитания Отечество