Содержание
- 2. This presentation is to be completed in conjunction with exercise worksheet 4. Objectives: By the end
- 3. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems As we have previously covered the techniques necessary to complete
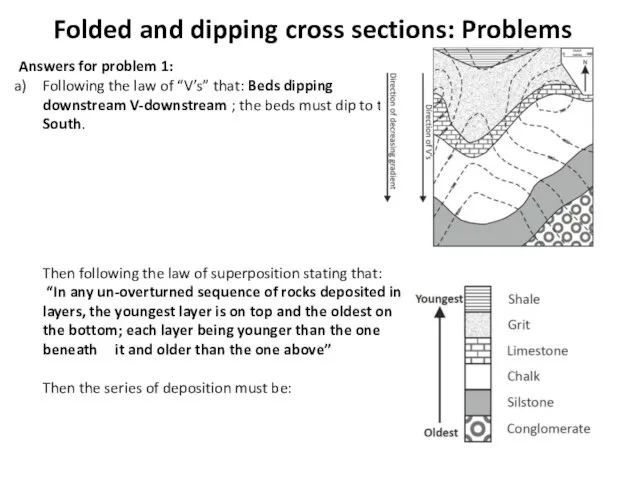
- 4. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 1: Following the law of “V’s” that:
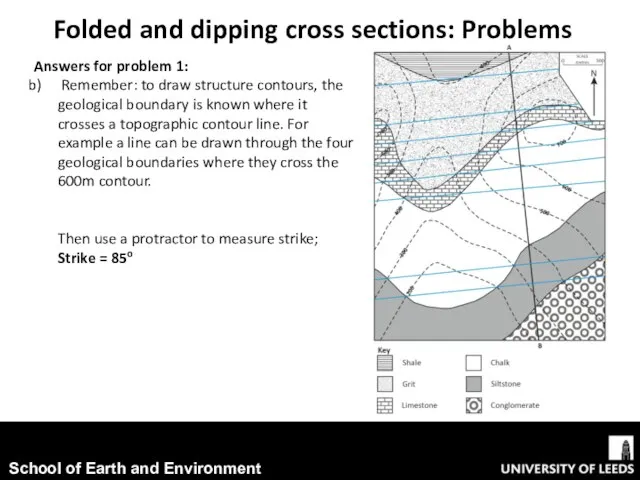
- 5. Answers for problem 1: Remember: to draw structure contours, the geological boundary is known where it
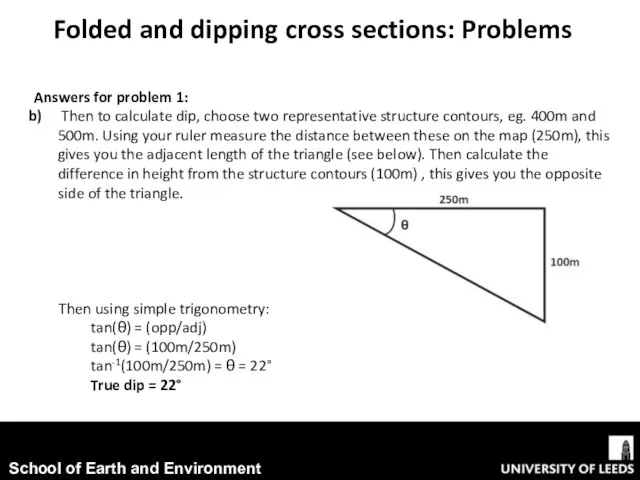
- 6. Then using simple trigonometry: tan(θ) = (opp/adj) tan(θ) = (100m/250m) tan-1(100m/250m) = θ = 22° True
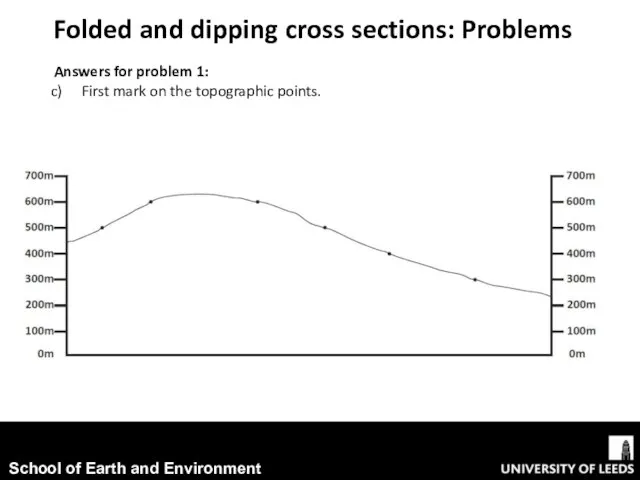
- 7. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 1: First mark on the topographic points.
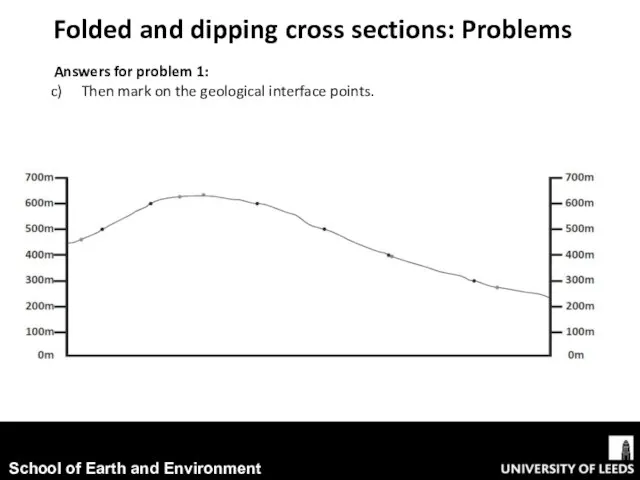
- 8. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 1: Then mark on the geological interface
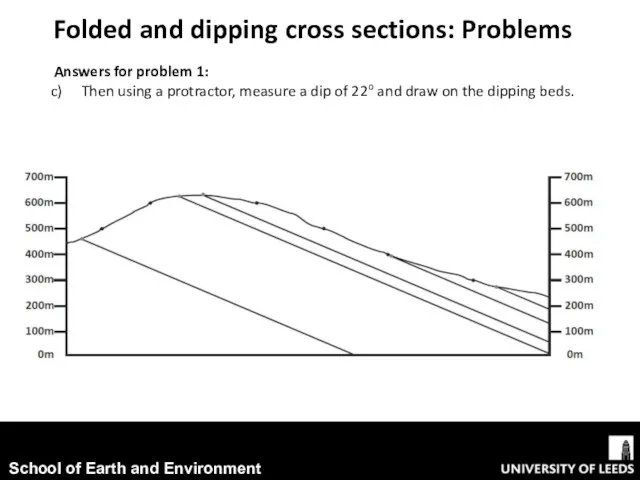
- 9. Answers for problem 1: Then using a protractor, measure a dip of 22o and draw on
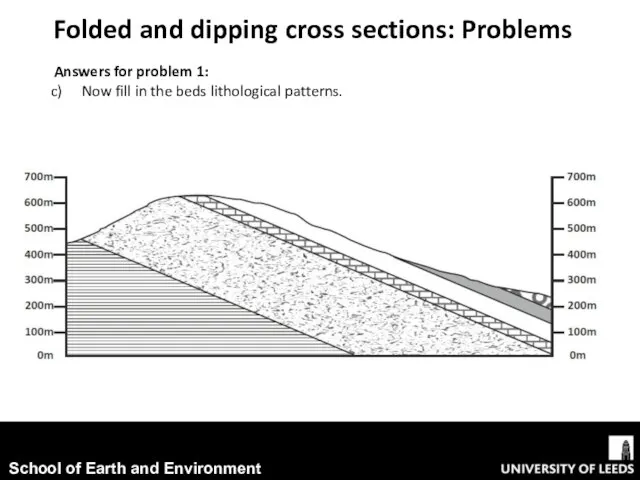
- 10. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 1: Now fill in the beds lithological
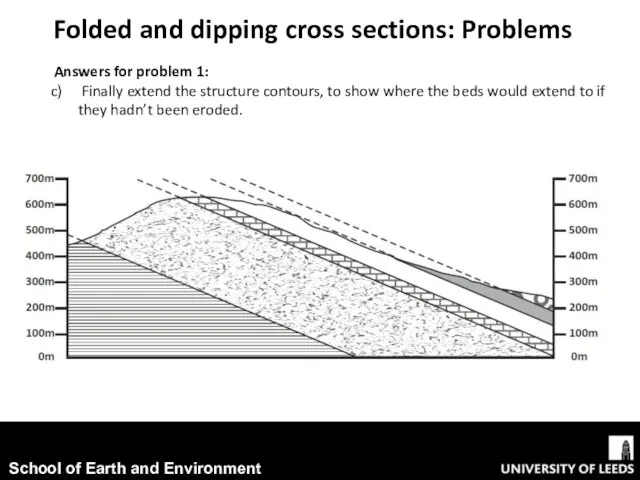
- 11. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 1: Finally extend the structure contours, to
- 12. Using exercise worksheet 4, complete problem 2 before continuing onto the next slide. Questions for problem
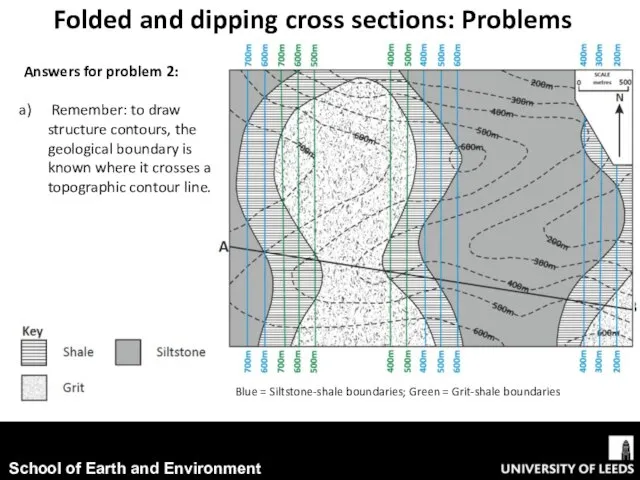
- 13. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: Remember: to draw structure contours, the
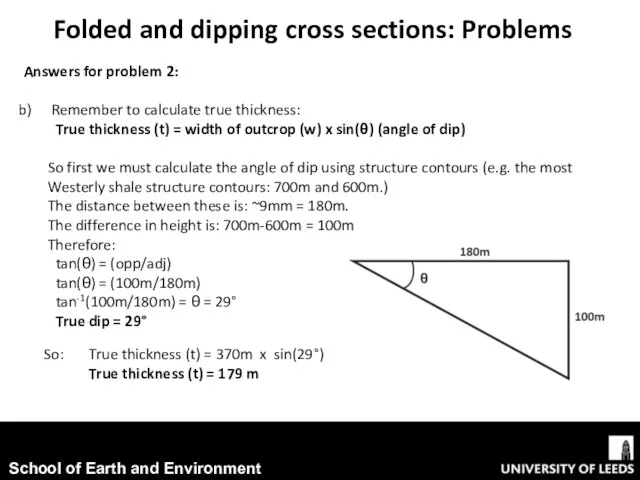
- 14. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: Remember to calculate true thickness: True
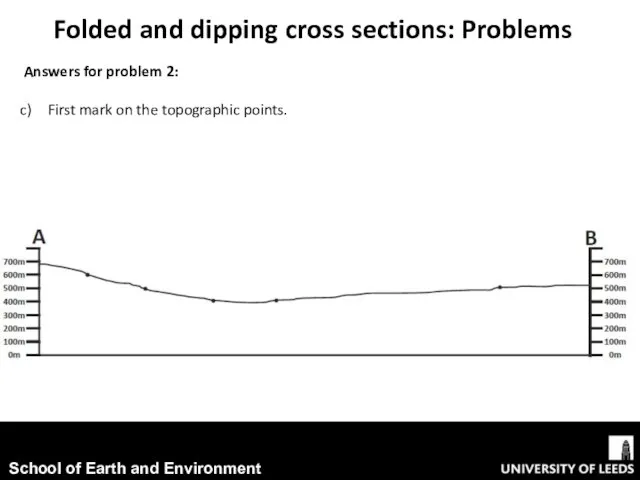
- 15. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: First mark on the topographic points.
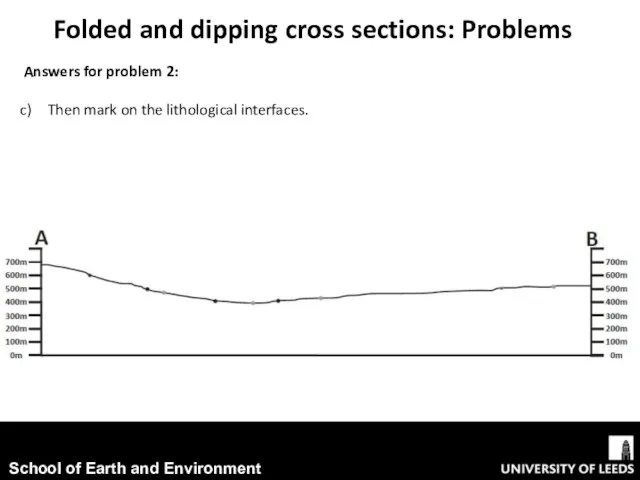
- 16. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: Then mark on the lithological interfaces.
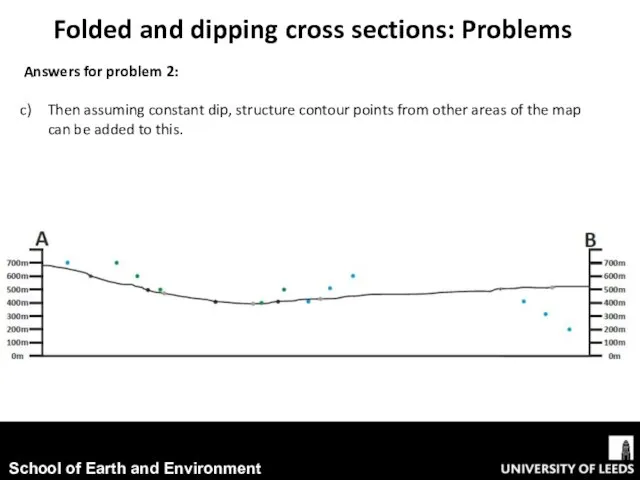
- 17. Answers for problem 2: Then assuming constant dip, structure contour points from other areas of the
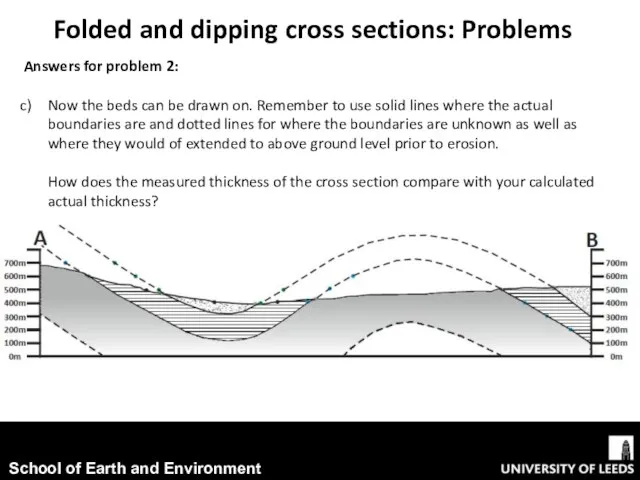
- 18. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: Now the beds can be drawn
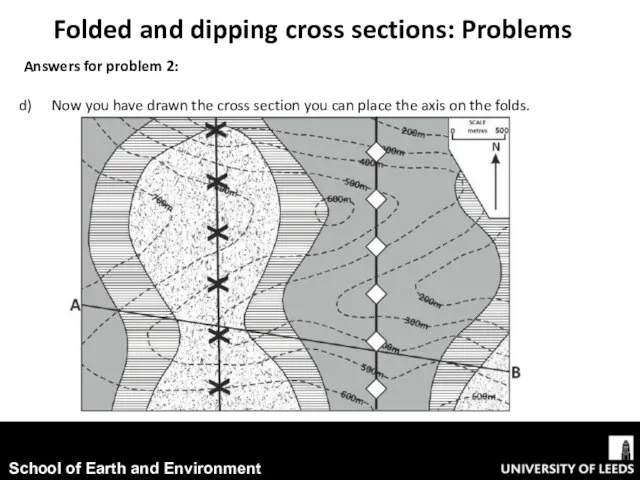
- 19. Folded and dipping cross sections: Problems Answers for problem 2: Now you have drawn the cross
- 21. Скачать презентацию


 doglyad
doglyad 30.08.2022 (3)
30.08.2022 (3) Кастрюля
Кастрюля 20151214_vechnye_problemy_v_tragediyah_u_0
20151214_vechnye_problemy_v_tragediyah_u_0 Фотоальбом 1
Фотоальбом 1 20141014_servirovka_stola
20141014_servirovka_stola Манипуляция сигналов. Лекция 8
Манипуляция сигналов. Лекция 8 Виды зависимости у человека
Виды зависимости у человека Птицы вестники весны
Птицы вестники весны Повторить уже известные правила речевого этикета
Повторить уже известные правила речевого этикета Выбор режима ручной дуговой сварки
Выбор режима ручной дуговой сварки Уважаемые учащиеся!
Уважаемые учащиеся! Оценка эффективности транспортно – логистической деятельности
Оценка эффективности транспортно – логистической деятельности Верстка с иллюстрациями
Верстка с иллюстрациями Футбольный турнир Новые Имена
Футбольный турнир Новые Имена Альтернативные источники энергии
Альтернативные источники энергии А прочно ли куриное яйцо?
А прочно ли куриное яйцо? Процесс проведения входного контроля двухрядного роликового подшипников качения
Процесс проведения входного контроля двухрядного роликового подшипников качения Мероприятия по энергосбережению в системах отопления, вентиляции и кондиционирования воздуха. (Лекция 5)
Мероприятия по энергосбережению в системах отопления, вентиляции и кондиционирования воздуха. (Лекция 5) Поздравление с 8 Марта
Поздравление с 8 Марта История маленькой девочки, собиравшей стадионы для Иисуса
История маленькой девочки, собиравшей стадионы для Иисуса Я знаю, что мы делали прошлым летом
Я знаю, что мы делали прошлым летом Учет материалов, счет 10
Учет материалов, счет 10 20170407_povtorenie_razdroblennost_rusi
20170407_povtorenie_razdroblennost_rusi Разработка технологии утилизации отходов масложировой индустрии
Разработка технологии утилизации отходов масложировой индустрии Железобетонные конструкции. Расчет элементов бетонных конструкций. (Лекция 9. Раздел 2)
Железобетонные конструкции. Расчет элементов бетонных конструкций. (Лекция 9. Раздел 2) Организация технического обслуживания и ремонт электрооборудования радиально-сверлильных станков
Организация технического обслуживания и ремонт электрооборудования радиально-сверлильных станков Организация учета металла в цехах согласно технологическим операциям обработки
Организация учета металла в цехах согласно технологическим операциям обработки