Содержание
- 2. Objectives As you read this chapter, consider the following questions: What are social networks, how do
- 3. What Is a Social Networking Web Site? Creates an online community of Internet users that eliminates
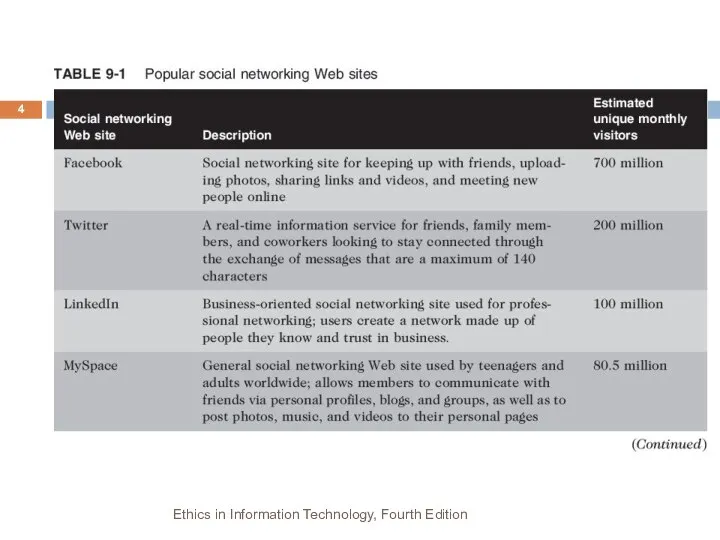
- 4. Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition
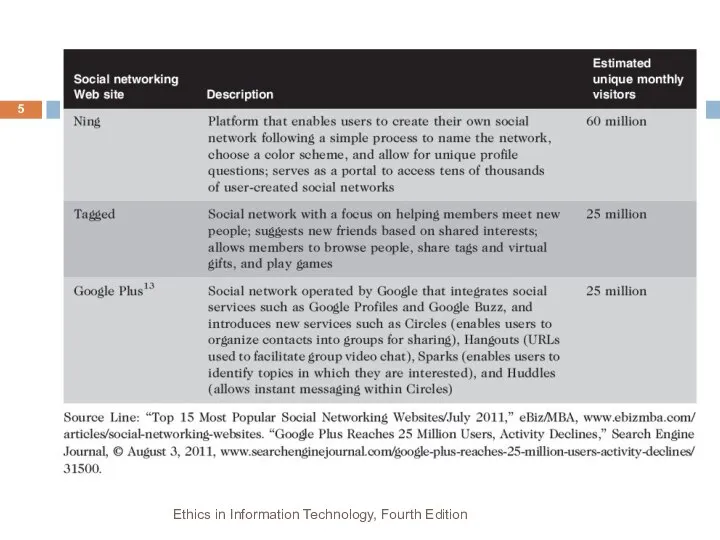
- 5. Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition
- 6. What Is a Social Networking Web Site? (cont’d.) Endless range of interests and a wide range
- 7. Business Applications of Online Social Networking Social network advertising Uses social networks to communicate and promote
- 8. Business Applications of Online Social Networking (cont’d.) Social network advertising strategies (cont’d.) Indirect advertising through groups
- 9. The Use of Social Networks in the Hiring Process 89% of recruiters المجندين use some form
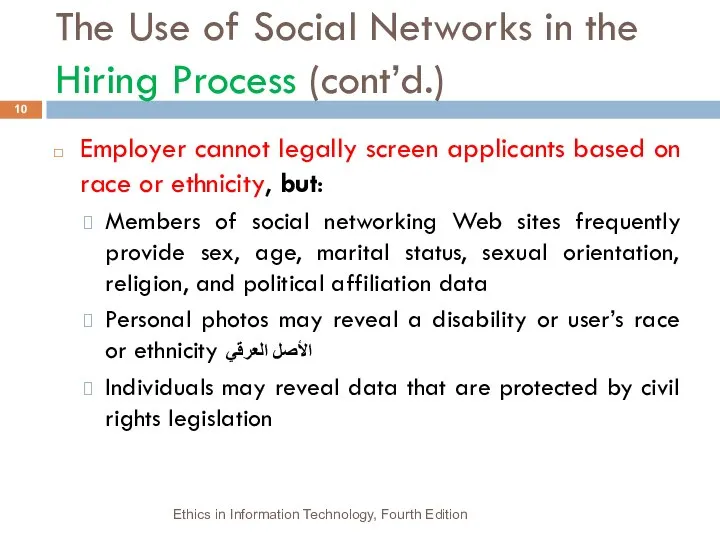
- 10. The Use of Social Networks in the Hiring Process (cont’d.) Employer cannot legally screen applicants based
- 11. Use of Social Media to Improve Customer Service Consumers use social networks to share their experiences,
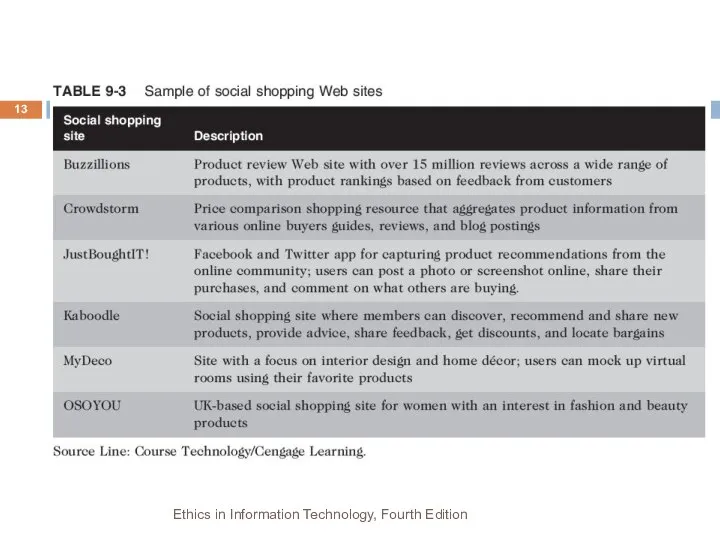
- 12. Social Shopping Web Sites Combine two highly popular online activities: shopping and social networking Shoppers and
- 13. Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition
- 14. Social Networking Ethical Issues Ethical issues for social networking Web sites are: Cyberbullying Cyberstalking Sexual predators
- 15. Ethics in Information Technology, Fourth Edition
- 16. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Numerous forms of cyberbullying Sending mean-spirited or threatening messages Sending thousands
- 17. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Numerous forms of cyberbullying (cont’d.) Posting mean, personal, or false information
- 18. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Cyberstalking المطاردة عبر الإنترنت Threatening behavior or unwanted advances using the
- 19. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Cyberstalking (cont’d.) Over three dozen states have laws prohibiting cyberstalking Current
- 20. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Encounters لقاءات with sexual predators المفترس Some social networking Web sites
- 21. Social Networking Ethical Issues (cont’d.) Uploading of inappropriate material Social networking Web sites have policies against
- 22. Online Virtual Worlds Virtual world is a shared multimedia, computer-generated environment in which users represented by
- 23. Online Virtual Worlds (cont’d.) Avatars can do everything one can do in real life Shop, hold
- 24. Crime in Virtual Worlds Should law enforcement—real or virtual—get involved in acts that occur in virtual
- 25. Crime in Virtual Worlds (cont’d) Virtual worlds have rules against offensive behavior in public, such as
- 26. Educational and Business Uses of Virtual Worlds New Media Consortium (NMC) International consortium of hundreds of
- 27. Educational and Business Uses of Virtual Worlds Second Life Work Microsites Enable businesses and government agencies
- 28. Summary Social networking Web sites Create an online community of Internet users Break down barriers created
- 29. Summary (cont’d.) Social network advertising strategies Direct advertising Advertising using network of friends Indirect advertising through
- 30. Summary (cont’d) Consumers use social networks to share their experiences and seek help and advice Unless
- 32. Скачать презентацию

























 Родителей не выбирают
Родителей не выбирают Ділові папери. Протокол. (Лекция 2)
Ділові папери. Протокол. (Лекция 2) Линейный компрессор
Линейный компрессор Взаимодействие фигур
Взаимодействие фигур Лекция 1
Лекция 1 Как написать отчет?
Как написать отчет? Яркая зима
Яркая зима выпуск2020
выпуск2020 Международная ассоциация дилеров АО Автоваз РК по направлению качество продукта
Международная ассоциация дилеров АО Автоваз РК по направлению качество продукта 20141203_urok_matematikm2kl
20141203_urok_matematikm2kl Оформление плана участка
Оформление плана участка МПФ_06-2022-ТОШ_17.08.2022
МПФ_06-2022-ТОШ_17.08.2022 Презентация Петленко С.А. М506-1
Презентация Петленко С.А. М506-1 Интерактивная викторина 1
Интерактивная викторина 1 11 А/Б класс
11 А/Б класс Расчет параметров трансформатора для моделирования в MULTISIM
Расчет параметров трансформатора для моделирования в MULTISIM 20120512_aleksandr_sergeevich_pushkin
20120512_aleksandr_sergeevich_pushkin Испытания материалов ООО Барнаульский химический завод в Испытательном Центре АО ПО Алтайский шинный комбинат
Испытания материалов ООО Барнаульский химический завод в Испытательном Центре АО ПО Алтайский шинный комбинат Об организации профилактики суицидального поведения несовершеннолетних
Об организации профилактики суицидального поведения несовершеннолетних Применение ТЭН для интенсификации добычи нефти
Применение ТЭН для интенсификации добычи нефти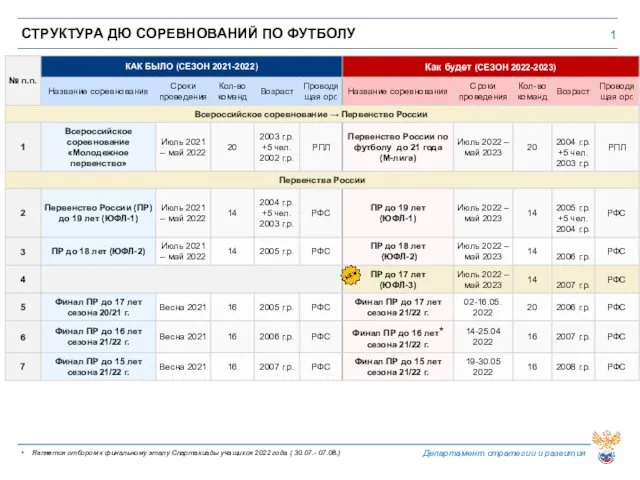 Структура соревнований по футболу
Структура соревнований по футболу Розрахунок економічної ефективності автоматизації процесу випічки хліба
Розрахунок економічної ефективності автоматизації процесу випічки хліба Кола – большая глава в книге истории нашего края
Кола – большая глава в книге истории нашего края Игра Один-много
Игра Один-много Врожденные пороки развития у новорожденных
Врожденные пороки развития у новорожденных Дуга. Сварка
Дуга. Сварка Метод смещения негативной оценки
Метод смещения негативной оценки Компания Unitronic. Технический тюнинг для автомобилей
Компания Unitronic. Технический тюнинг для автомобилей