Left–Right Political Spectrum: Overview [2/4]
In democratic systems political offers have often
been distinguished by using as a criterion of their position with regard to a hypothetical right-left ideological continuum in correspondence with the seats held by political parties and their representatives in parliamentary assemblies.
At the beginning, right and left have reflected the positions held by those defending stability versus those pursuing change, namely the interest of those who benefited from their wealth and status versus the interests of common people who instead desired to affirm their rights against the undeserved privileges of the former and to free themselves from need and serfdom.

![Left–Right Political Spectrum: Overview [1/4] Ideologies - systems of ideas that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/552327/slide-2.jpg)
![Left–Right Political Spectrum: Overview [2/4] In democratic systems political offers have](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/552327/slide-3.jpg)
![Left–Right Political Spectrum: Overview [3/4]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/552327/slide-4.jpg)
 Как вы будете изучать географию в 7 кл
Как вы будете изучать географию в 7 кл Электронное обучение. Массовый открытый онлайн-курс
Электронное обучение. Массовый открытый онлайн-курс Организация ТО и ремонта на универсальных и специализированных постах
Организация ТО и ремонта на универсальных и специализированных постах 20141019_zakony_khammurapi_5
20141019_zakony_khammurapi_5 СОУ — Система обнаружения утечек
СОУ — Система обнаружения утечек 2 Session 1 Part 1
2 Session 1 Part 1 Праздник Всемирный день качества
Праздник Всемирный день качества Выпускной 4-б, 2018 года
Выпускной 4-б, 2018 года Грибочки для белочки
Грибочки для белочки Слово о полку Игореве
Слово о полку Игореве Создание уникального товарного предложения для жилого района Арбеково Парк
Создание уникального товарного предложения для жилого района Арбеково Парк Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа ЮДИП
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа ЮДИП Мобильные сотовые сети
Мобильные сотовые сети Цветик семицветик
Цветик семицветик prezentatsiya1_0
prezentatsiya1_0 Поздравление для именинника Анатолия, smotra.ru
Поздравление для именинника Анатолия, smotra.ru Деление с остатком
Деление с остатком Путешествие по стране творчества ДЕКУПАЖ
Путешествие по стране творчества ДЕКУПАЖ Свойства шерстяных и шелковых тканей
Свойства шерстяных и шелковых тканей Системы отопления и вентиляции
Системы отопления и вентиляции Дворовые стоянки личного транспорта
Дворовые стоянки личного транспорта Viktorina
Viktorina Прогнозирование и анализ музыкальных композиций при помощи машинного обучения
Прогнозирование и анализ музыкальных композиций при помощи машинного обучения Основные сведения о теплоснабжении, вентиляции и газоснабжении
Основные сведения о теплоснабжении, вентиляции и газоснабжении Обезжелезивание воды
Обезжелезивание воды Мировые религии
Мировые религии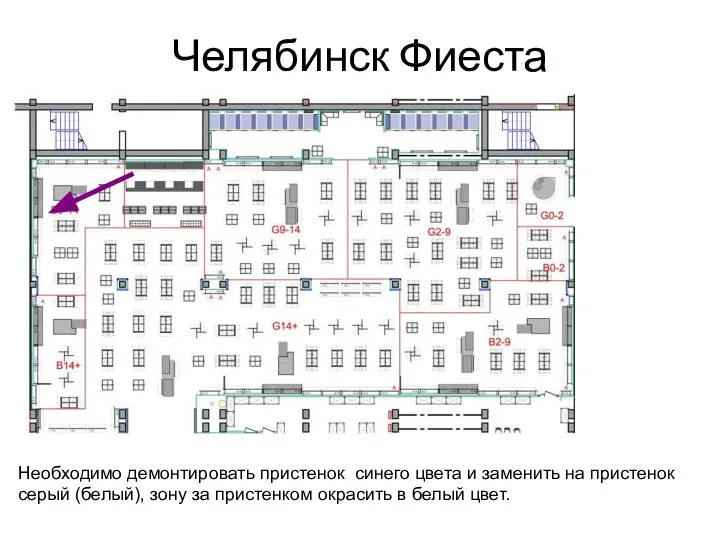 Новое зонирование Челябинск
Новое зонирование Челябинск Новые формы культурно-досуговой деятельности в условиях самоизоляции и карантина
Новые формы культурно-досуговой деятельности в условиях самоизоляции и карантина