Содержание
- 2. Elements covered HEALTH & SAFETY Training explained Why we need training HASAWA 1974 PUWER 1998 LOLER
- 3. Health & Safety
- 4. Training explained Valid MHE Medical Basic Training Refreshed every 3 years Site Training Refreshed every year
- 5. Why we need training 1. Safe Practice Encourage good practice, develop safe procedures and to provide
- 6. The act is far ranging and covers: Employers Employees The self employed The general public Health
- 7. Health & Safety at Work Act 1974 EMPLOYERS responsibilities (section 2) 2(a) Provide and maintain plant
- 8. Health & Safety at Work Act 1974 EMPLOYEES Responsibilities Section 7(a) Duty to take reasonable care
- 9. Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 These regulations apply to the provision and use
- 10. Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations 1998 All lifting equipment should be: Well designed and constructed
- 11. Management of Health & Safety at Work Regulations 1999 Risk assessment L’Oreal carries out a risk
- 12. Accidents and associated risks Accidents don’t just happen They are caused by, among other things: Operator
- 13. The cost of accidents The COST of accidents: Personal injury Social and emotional costs Legal costs
- 14. Personal risk assessment What is the task? Make sure you know exactly what the task involves
- 15. Personal risk assessment Do I know who or what could be harmed? Am I aware of
- 16. Personal protective equipment PPE Types Gloves, goggles, aprons, safety footwear PPE Requirements Check what PPE is
- 17. Alcohol and drugs The law considers a fork lift truck to be a motor vehicle This
- 18. Equipment Introduction
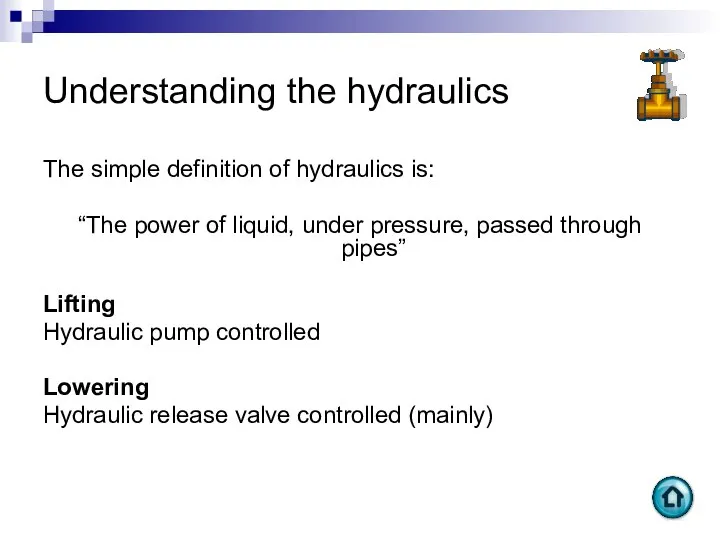
- 19. Understanding the hydraulics The simple definition of hydraulics is: “The power of liquid, under pressure, passed
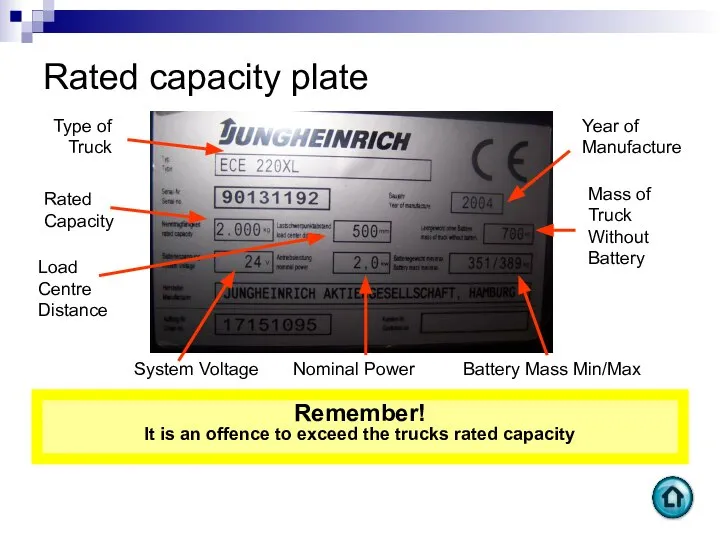
- 20. Rated capacity plate Rated Capacity Load Centre Distance Year of Manufacture Mass of Truck Without Battery
- 21. Load centre plate The load centre is the distance from the vertical face of the forks
- 22. Stability Triangle
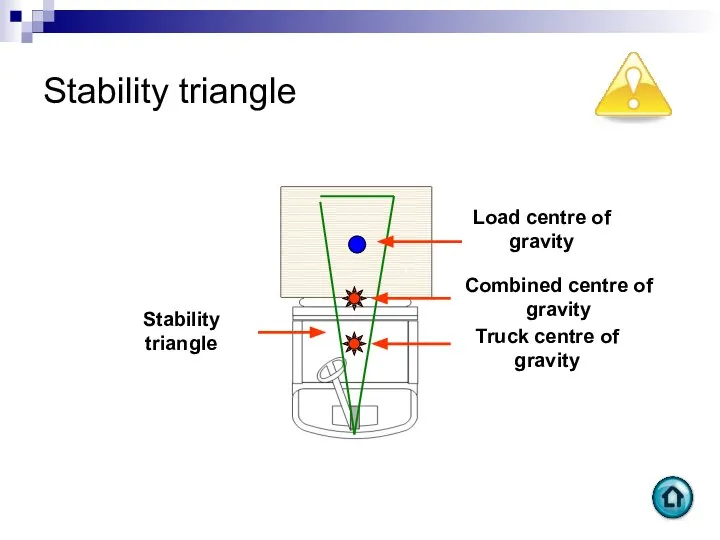
- 23. Stability triangle Stability triangle Truck centre of gravity Combined centre of gravity Load centre of gravity
- 24. Lengthwise instability Overloading Causing the truck to tip forward Harsh braking Centre of gravity moving quickly
- 25. Sideways instability Ground conditions If one wheel drops into a pothole Turning at speed Even if
- 26. General Safe Driving Rules
- 27. General safe driving rules Park properly: With key removed or logged out Forks lowered to the
- 28. General safe driving rules Obey all signs and travel direction restrictions Make smooth use of controls
- 29. General safe driving rules Be aware of pedestrians at all times Always park safely Only handle
- 30. General safe driving rules Always look in the direction of travel When turning in reverse, your
- 31. General safe driving rules A moving truck is at its most stable when driven: In a
- 32. General safe driving rules Concentrate – no eating, drinking, smoking, using a mobile phone etc No
- 33. General safe driving rules When approaching a blind corner: Slow down and manoeuvre slowly Be prepared
- 34. Driving on inclines Drive slowly Do not turn, even with an unladen truck Always drive directly
- 35. Ergonomics All MHE are Ergonomically designed for safety & comfort You must ensure all your limbs
- 36. Pallet Types & Load Assessment
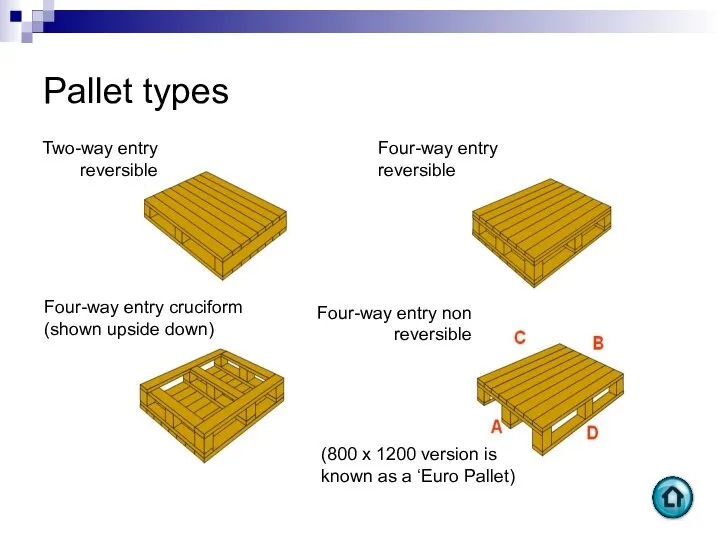
- 37. Four-way entry non reversible Pallet types Four-way entry reversible Two-way entry reversible Four-way entry cruciform (shown
- 38. Pallet types Normally metal so take extra care when handling as metal forks against metal pallet
- 39. Pallet and load assessment Make sure the weight falls within the rated capacity of the truck
- 40. Pallet and load assessment Load Centre: Ensure the load centre and weight of the load fall
- 41. Pallet and load assessment Size of the Load: Ensure the load is not too large to
- 42. Battery Care & Charging
- 43. Battery care and charging Batteries are the most expensive single item on truck and often the
- 44. Battery care and charging Electricity Always use the correct charger for the type of truck you
- 45. Battery care and charging Sulphuric acid (burns) Wear appropriate safety equipment, e.g. rubber gloves, goggles, rubber
- 46. Battery care and charging Hydrogen and Oxygen Do not smoke whilst handling or charging the battery
- 47. Pre Use Checks
- 48. Pre use checks Pre-use checks must be carried out each day, or at the start of
- 49. Pre use checks Forks Check for cracks, fractures, excessive wear, deformity and ensure they are equally
- 50. Pre use checks Drive and braking Move the truck backwards and forwards and test both the
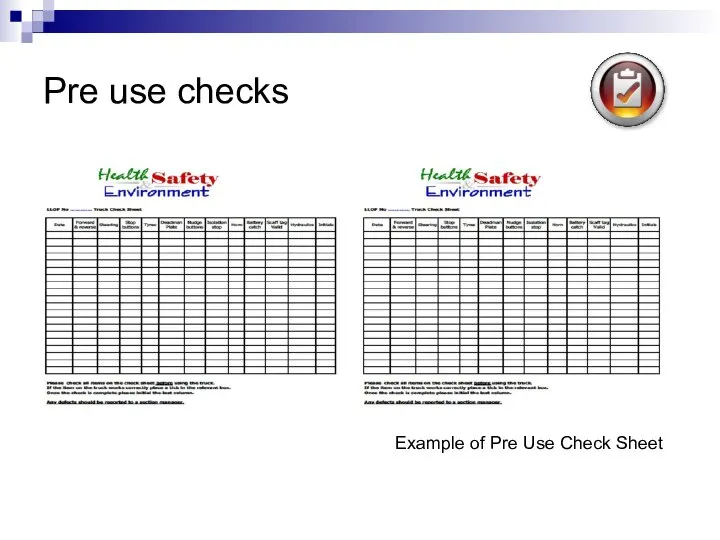
- 51. Pre use checks Example of Pre Use Check Sheet
- 52. Use of the manufacturers operating manual The manufacturers operating manual provides important information on the safe
- 53. Any Questions?
- 54. Equipment Specific LLOP EPT STACKER
- 55. Low Level Order Picker (LLOP)
- 56. Main Components: LLOP
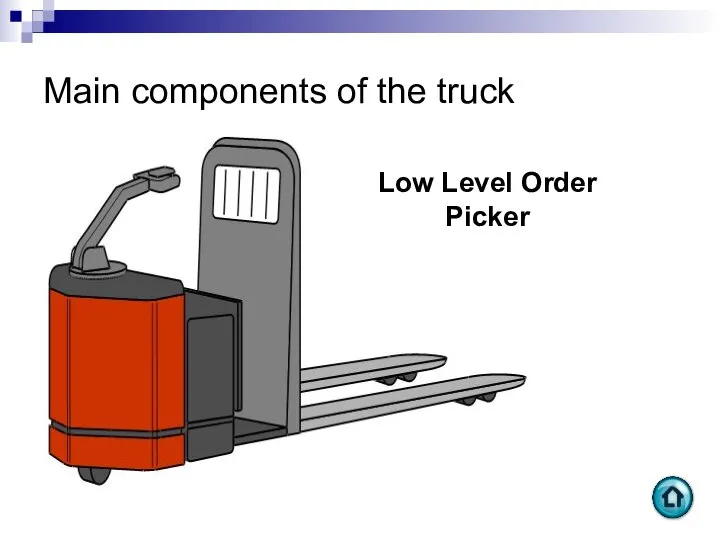
- 57. Main components of the truck Low Level Order Picker
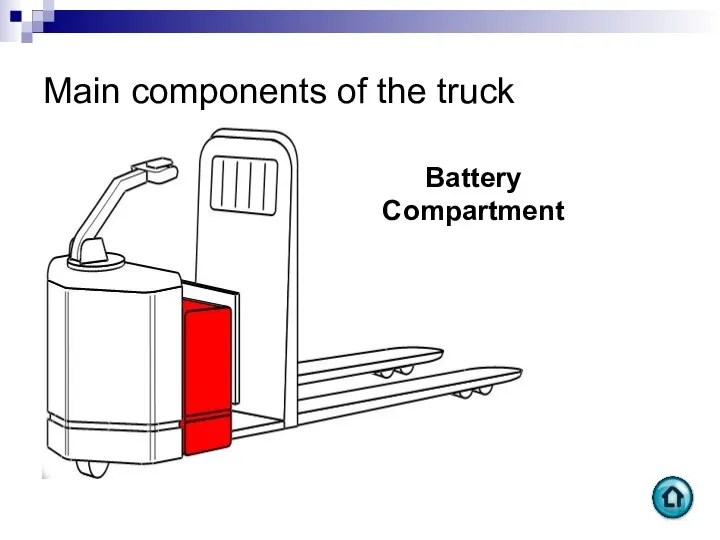
- 58. Main components of the truck Battery Compartment
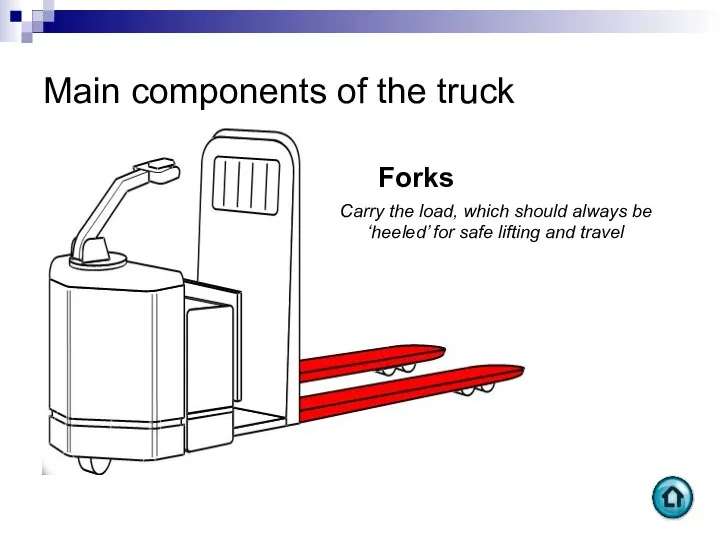
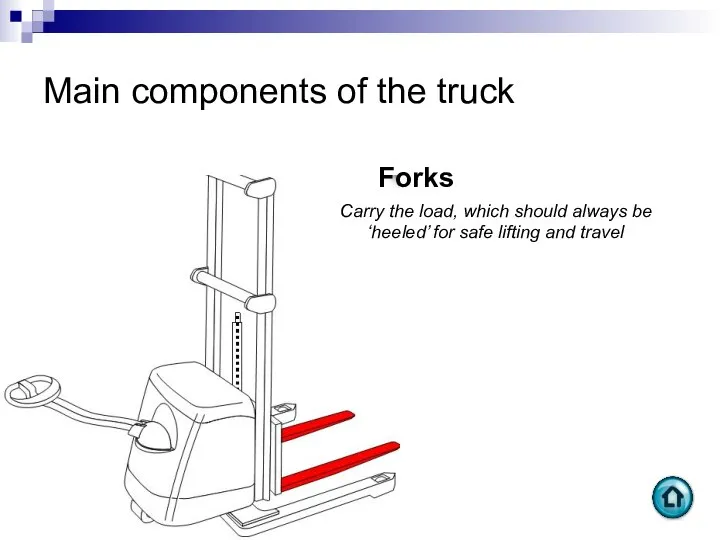
- 59. Main components of the truck Forks Carry the load, which should always be ‘heeled’ for safe
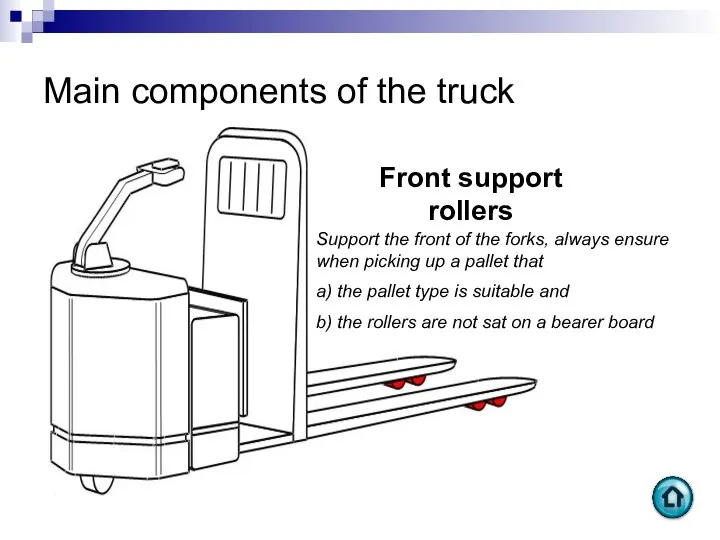
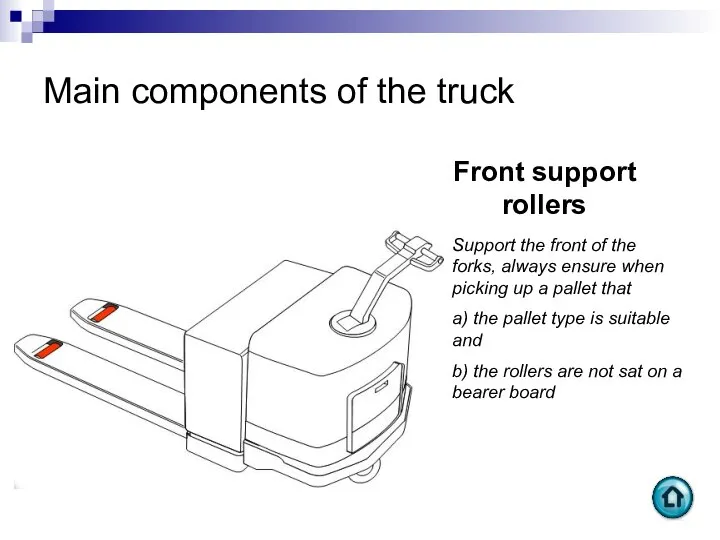
- 60. Main components of the truck Front support rollers Support the front of the forks, always ensure
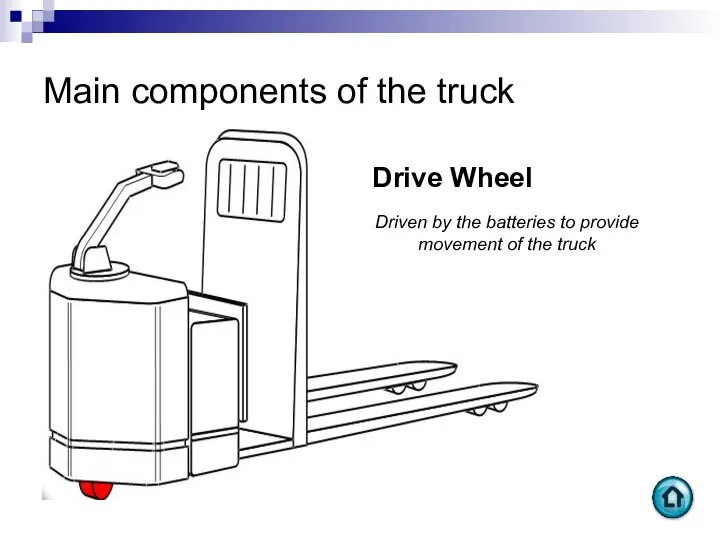
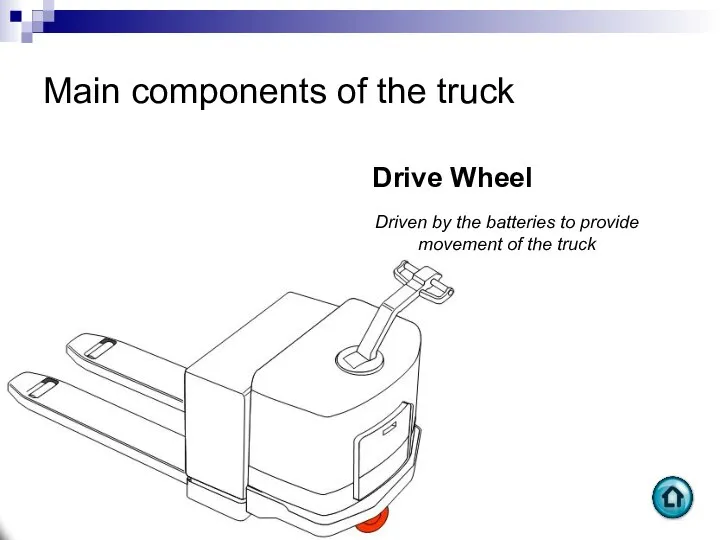
- 61. Main components of the truck Drive Wheel Driven by the batteries to provide movement of the
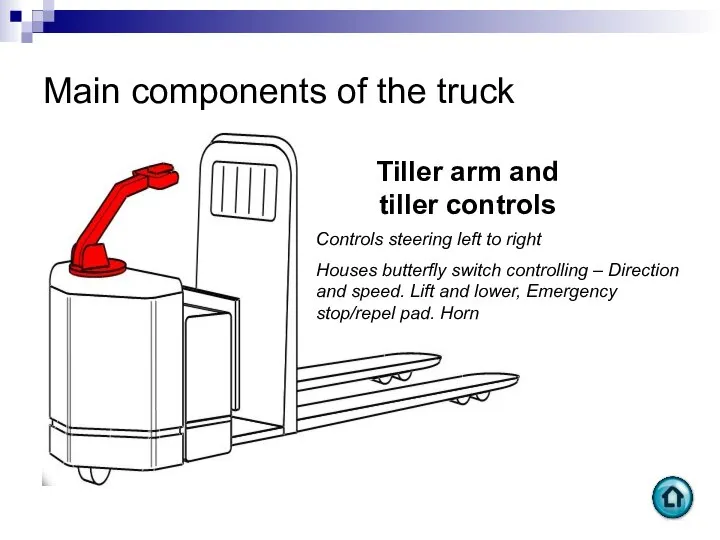
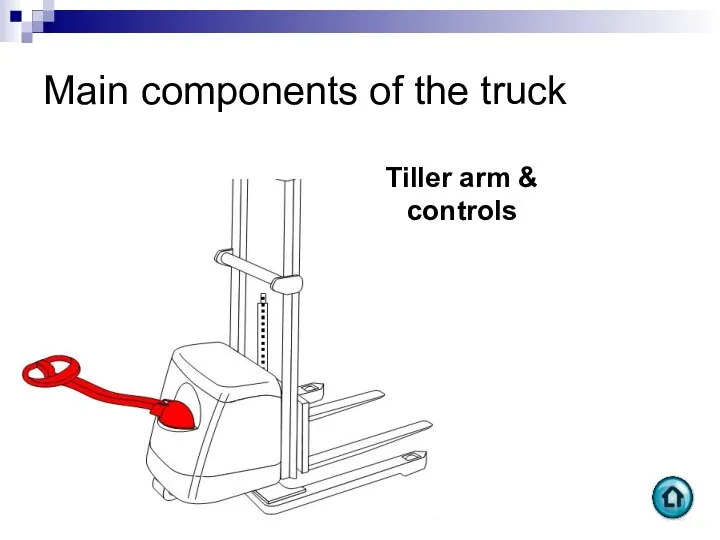
- 62. Main components of the truck Tiller arm and tiller controls Controls steering left to right Houses
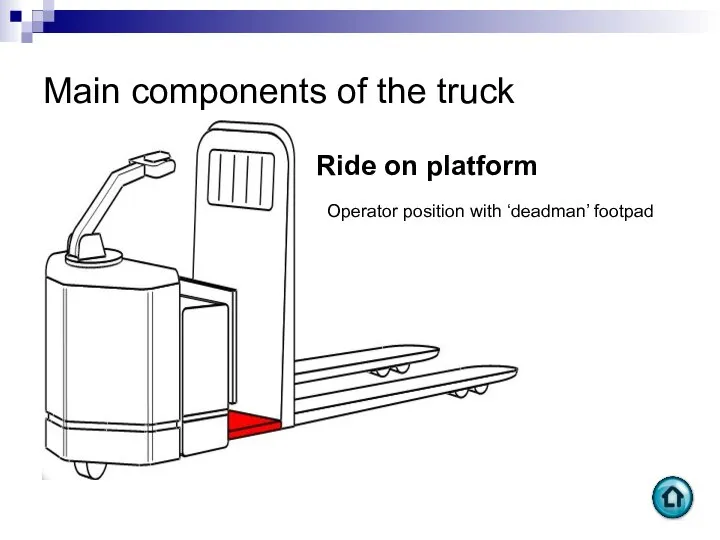
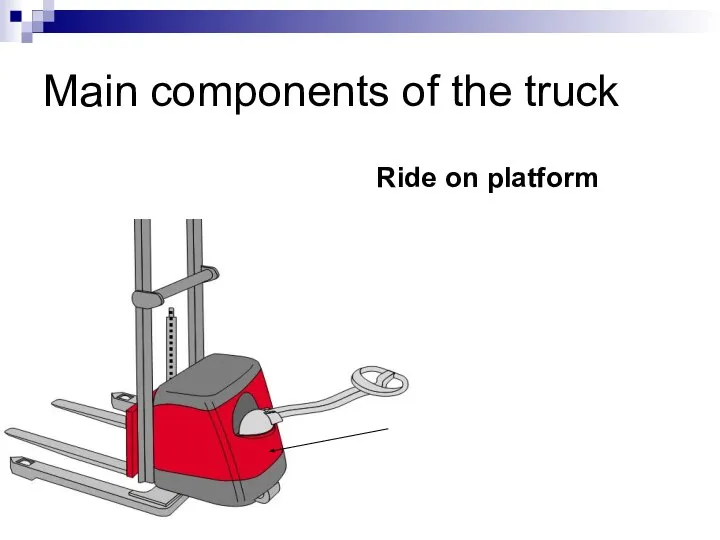
- 63. Main components of the truck Ride on platform Operator position with ‘deadman’ footpad
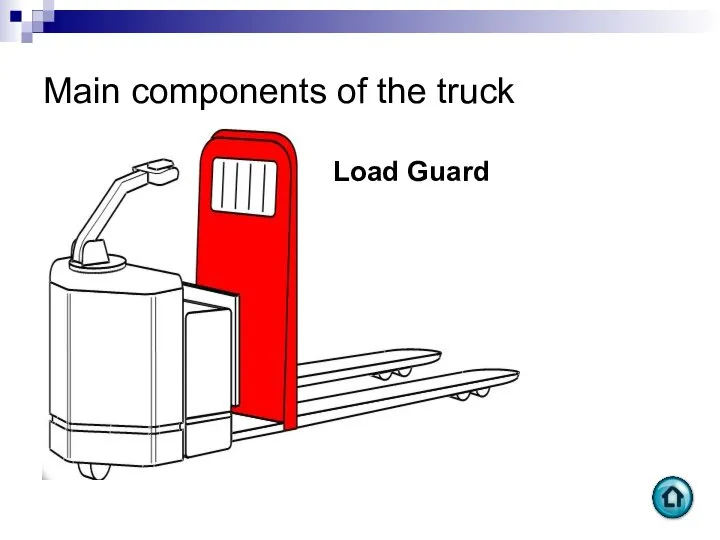
- 64. Main components of the truck Load Guard
- 65. LLOP Safe Driving Rules
- 66. General safe driving rules Stay in control: You must have two hands on the controls whenever
- 67. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Always face the direction you are travelling. Drive forwards
- 68. General safe driving rules Mount / Dismount & Parking: Ensure equipment has come to a complete
- 69. Electric Pedestrian Truck (EPT)
- 70. Main Components: EPT
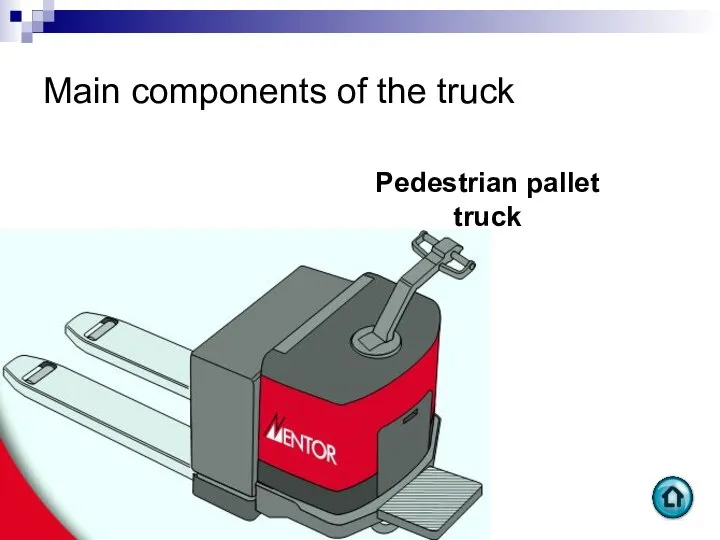
- 71. Main components of the truck Pedestrian pallet truck
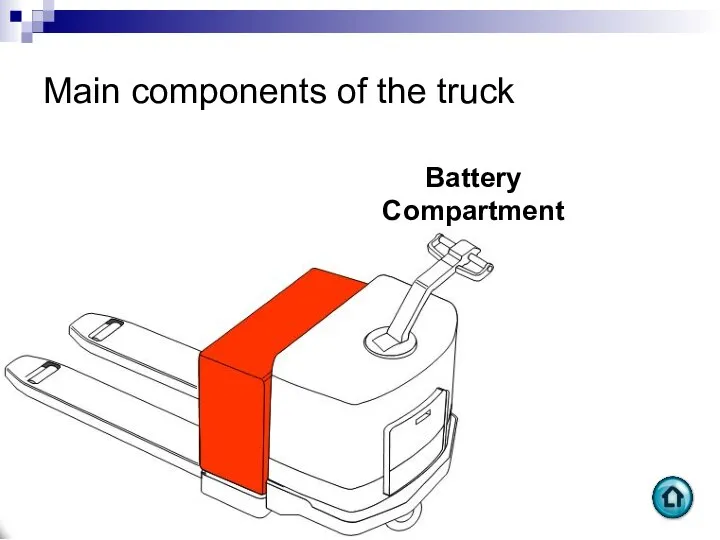
- 72. Main components of the truck Battery Compartment
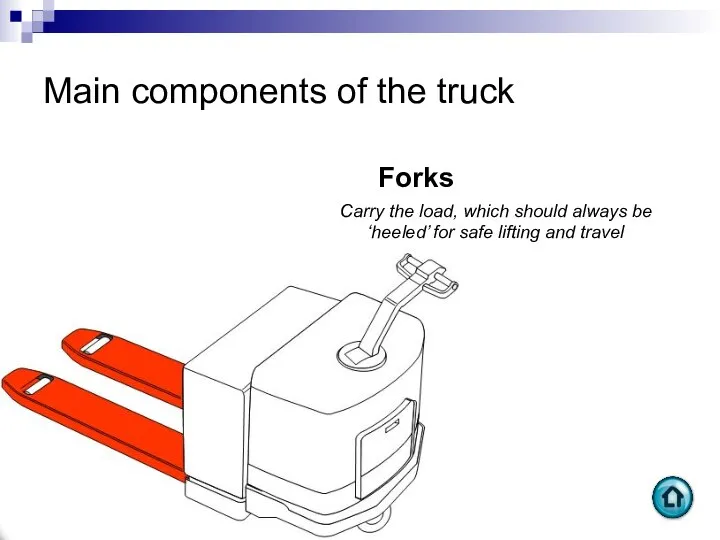
- 73. Main components of the truck Forks Carry the load, which should always be ‘heeled’ for safe
- 74. Main components of the truck Front support rollers Support the front of the forks, always ensure
- 75. Main components of the truck Drive Wheel Driven by the batteries to provide movement of the
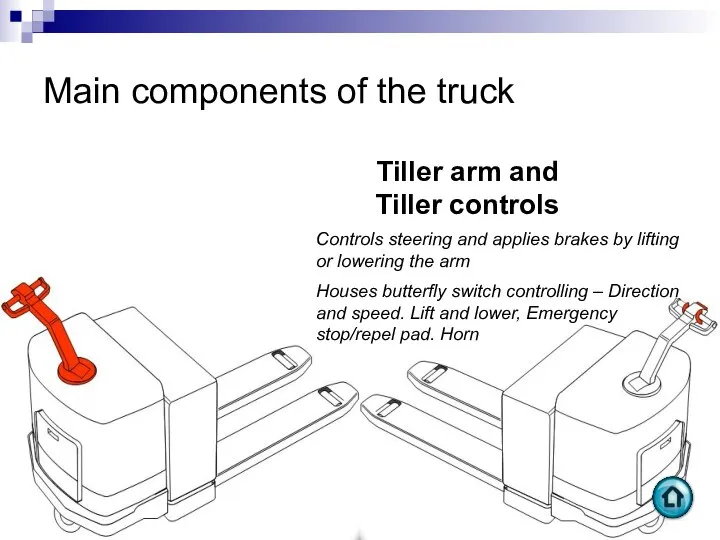
- 76. Main components of the truck Tiller arm and Tiller controls Controls steering and applies brakes by
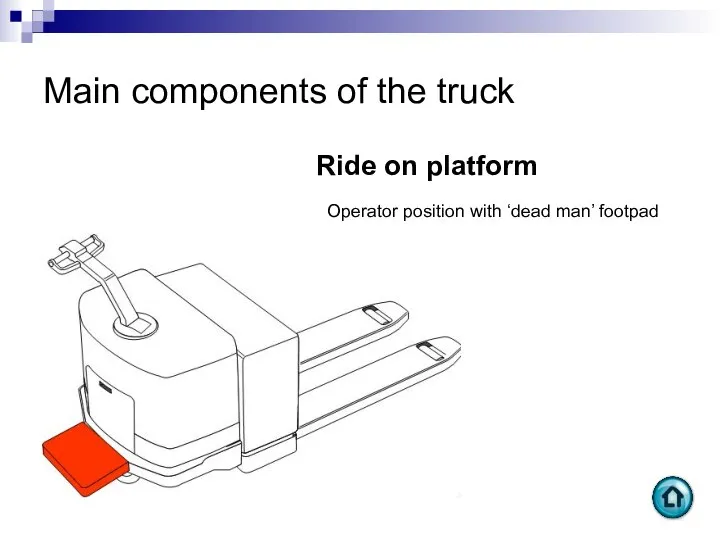
- 77. Main components of the truck Ride on platform Operator position with ‘dead man’ footpad
- 78. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Keep both hands on the steering controls at all
- 79. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Always face the direction you are travelling. You may
- 80. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Trafford Park Only specially adapted Red Pyroban EPT’s are
- 81. General safe driving rules Mount & Dismount: Ensure equipment has come to a complete stop before
- 82. Vehicle loading and unloading Precautions to be taken whilst loading/unloading over dock leveller… Bend knees to
- 83. Vehicle loading and unloading (general rules) As a lift truck driver you should liaise with the
- 84. Pedestrian Stacker Truck
- 85. Main Components: Stacker Truck
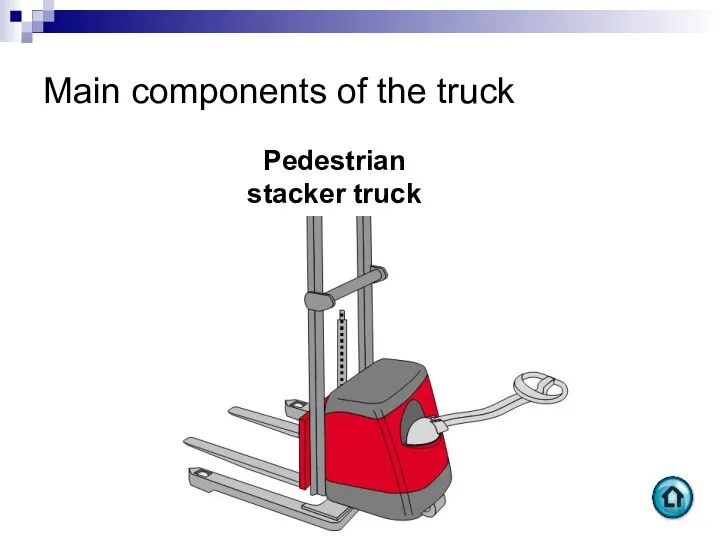
- 86. Main components of the truck Pedestrian stacker truck
- 87. Main components of the truck Battery Compartment
- 88. Main components of the truck Forks Carry the load, which should always be ‘heeled’ for safe
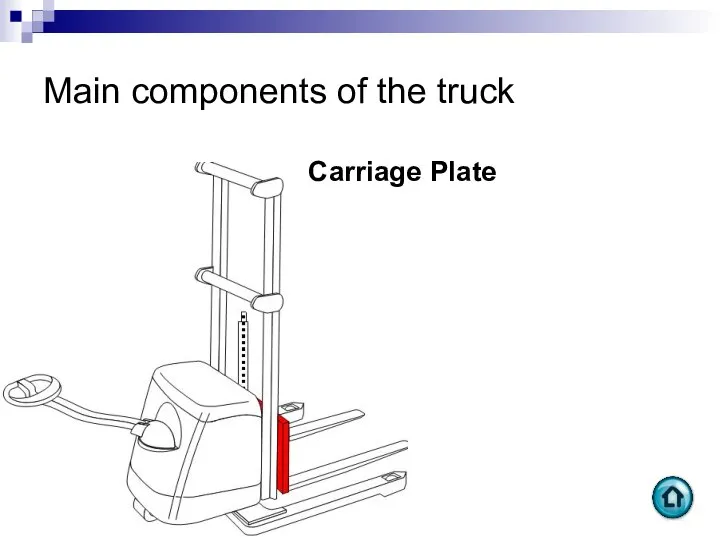
- 89. Main components of the truck Carriage Plate
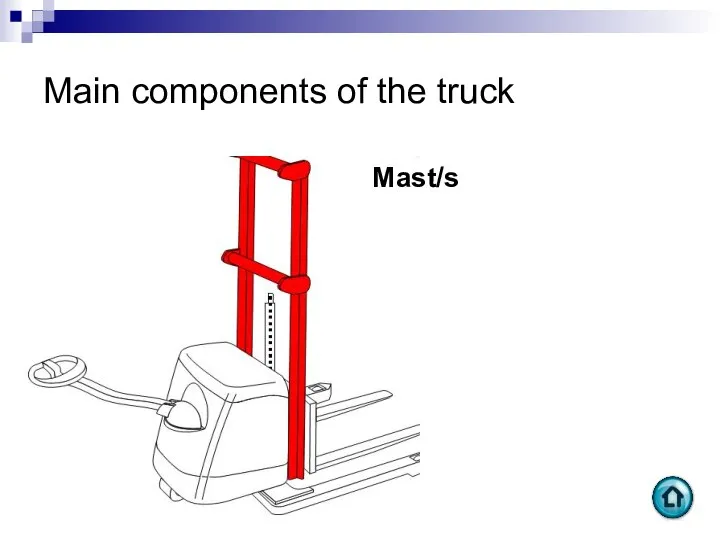
- 90. Main components of the truck Mast/s
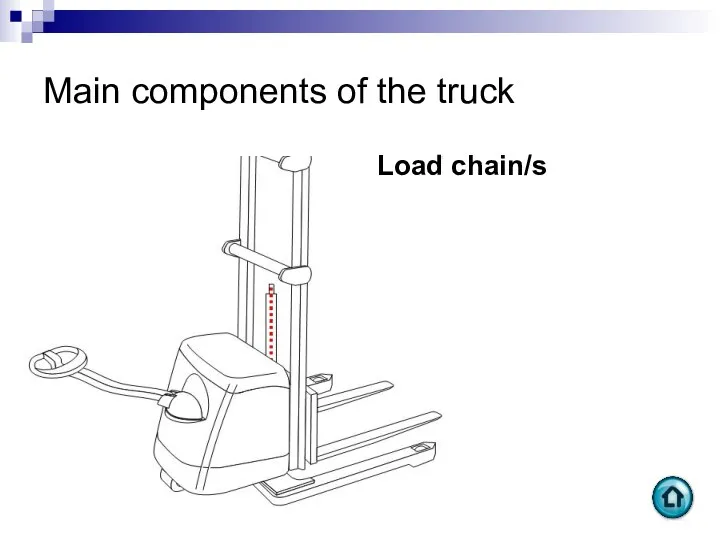
- 91. Main components of the truck Load chain/s
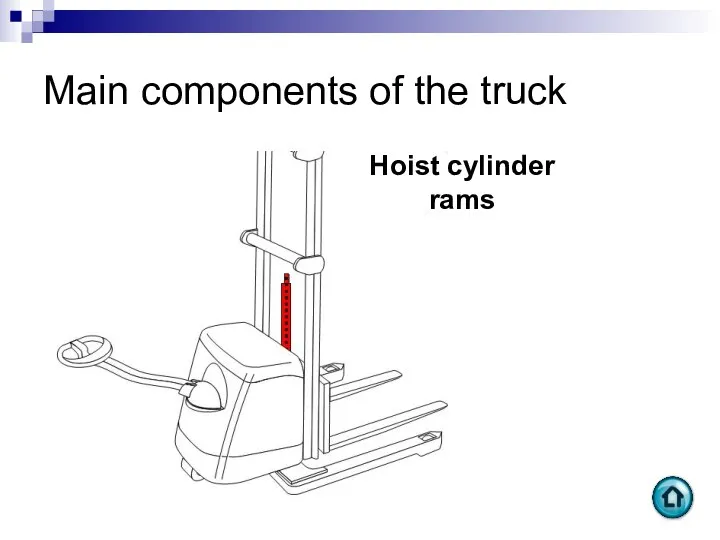
- 92. Main components of the truck Hoist cylinder rams
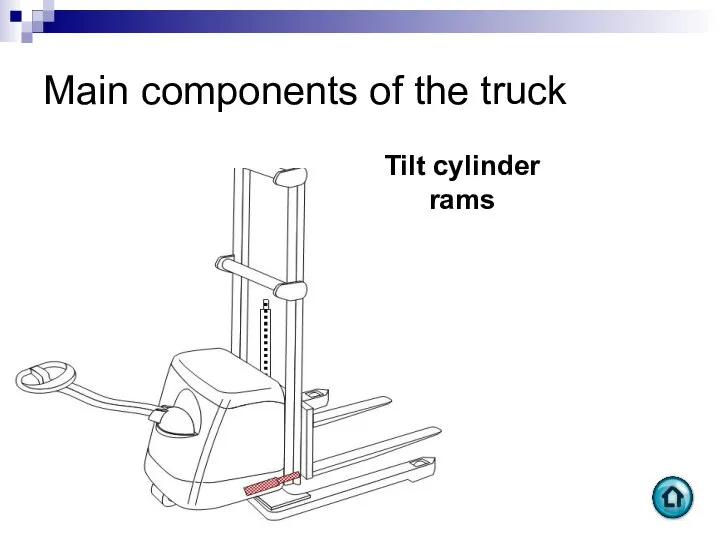
- 93. Main components of the truck Tilt cylinder rams
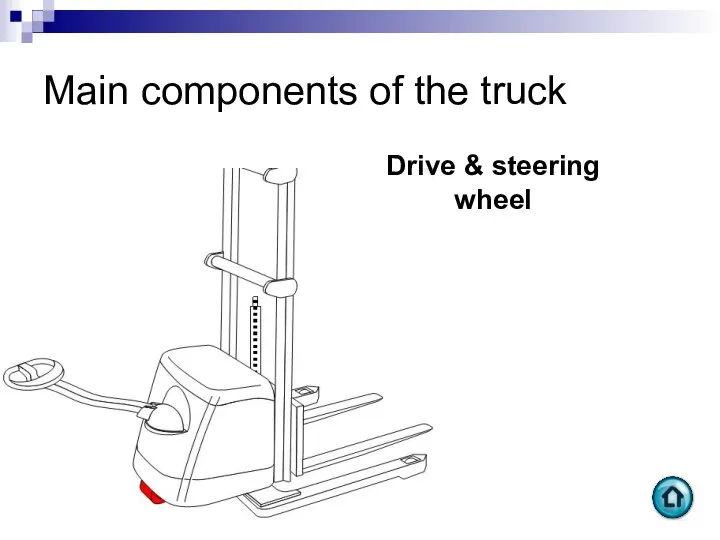
- 94. Main components of the truck Drive & steering wheel
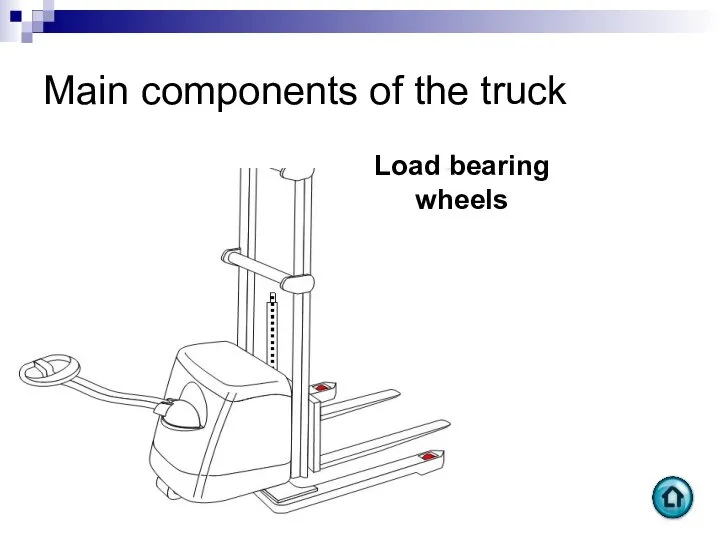
- 95. Main components of the truck Load bearing wheels
- 96. Main components of the truck Tiller arm & controls
- 97. Main components of the truck Ride on platform
- 98. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Keep both hands on the steering controls at all
- 99. General safe driving rules Stay in control: Always face the direction you are travelling. You may
- 101. Скачать презентацию
































































 Сільське господарство України. Рослинництво
Сільське господарство України. Рослинництво Свойства топлив Механические примеси и вода в бензине
Свойства топлив Механические примеси и вода в бензине Звук и буква Х
Звук и буква Х 10 интересных фактов о порте Южный
10 интересных фактов о порте Южный покупка гуггла
покупка гуггла ф.г.лорка
ф.г.лорка Lexicography. Types of dictionaries
Lexicography. Types of dictionaries Лекция №3. Этика делового общения. Основные функции общения
Лекция №3. Этика делового общения. Основные функции общения Cui trebuie să ne închinăm?
Cui trebuie să ne închinăm? 20151201_hram_neporochnogo_zachatiya_presvyatoy_devy_marii
20151201_hram_neporochnogo_zachatiya_presvyatoy_devy_marii Хранение подвижного состава автомобильного транспорта
Хранение подвижного состава автомобильного транспорта Соціальний пакет
Соціальний пакет Специфические свойства аглопорита
Специфические свойства аглопорита День святых жён - мироносиц
День святых жён - мироносиц Робот бабочка
Робот бабочка Звери и птицы весной
Звери и птицы весной Система технічного регулювання при виробництві та обігу фіточаїв
Система технічного регулювання при виробництві та обігу фіточаїв Твердотельная электроника. Семинар №7. Расчет характеристик МОПТ в рамках идеальной модели
Твердотельная электроника. Семинар №7. Расчет характеристик МОПТ в рамках идеальной модели Год Российской науки
Год Российской науки Петр Просто Великий
Петр Просто Великий Монтажные и обмоточные провода
Монтажные и обмоточные провода Миниатюрные ландшафтные композиции из тропических растений
Миниатюрные ландшафтные композиции из тропических растений ФФЯ собрание с 1 курсом
ФФЯ собрание с 1 курсом Автопаркинг на 500 автомобилей
Автопаркинг на 500 автомобилей 5 - Г класс- Звезды. Фотоальбом
5 - Г класс- Звезды. Фотоальбом аграм дисгр
аграм дисгр 20140625_pril_0
20140625_pril_0 Interview Questions-Basics of Electronics and Communication Engg
Interview Questions-Basics of Electronics and Communication Engg