Содержание
- 2. Subject and tasks of municipal hygiene Municipal hygiene – section of hygiene, studying influence factors of
- 3. The basic sections of municipal hygiene: . Hygiene of air (action of it physical and chemical
- 4. Concept about climate and microclimate Climate – it is average long-term complex of physical parameters of
- 5. HEAT REGULATION SYSTEM OF ORGANISM AND INFLUENCE FACTORS OF MICROCLIMATE HEAT REGULATION SYSTEM CHEMICAL HEAT REGULATION
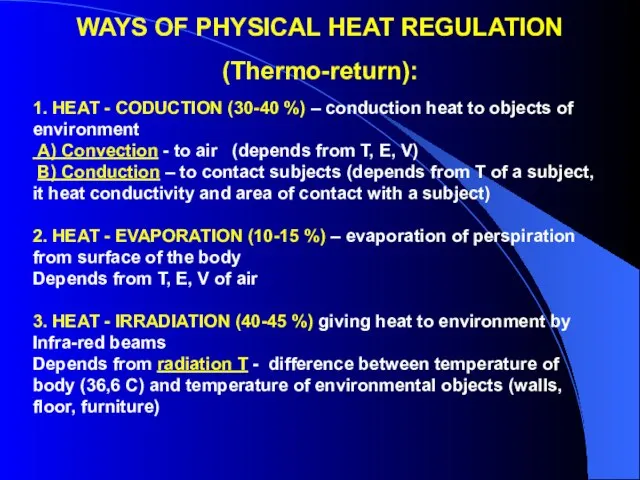
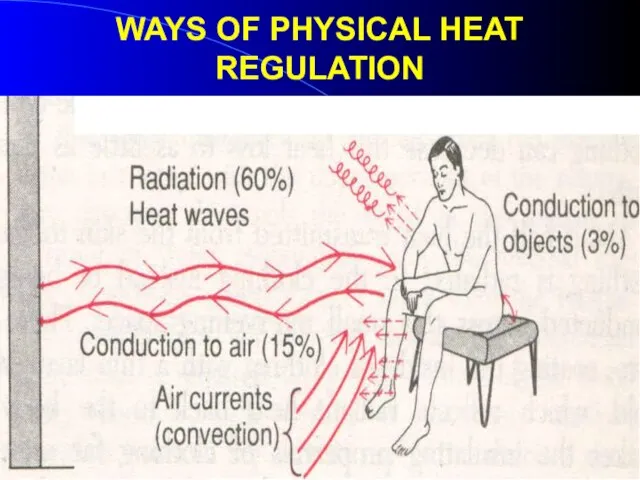
- 6. WAYS OF PHYSICAL HEAT REGULATION (Thermo-return): 1. HEAT - CODUCTION (30-40 %) – conduction heat to
- 7. WAYS OF PHYSICAL HEAT REGULATION
- 8. THE NORMS OF MICROCLIMATE FOR DIFFERENT PREMISES AND DEVICES FOR IT INVESTIGATION
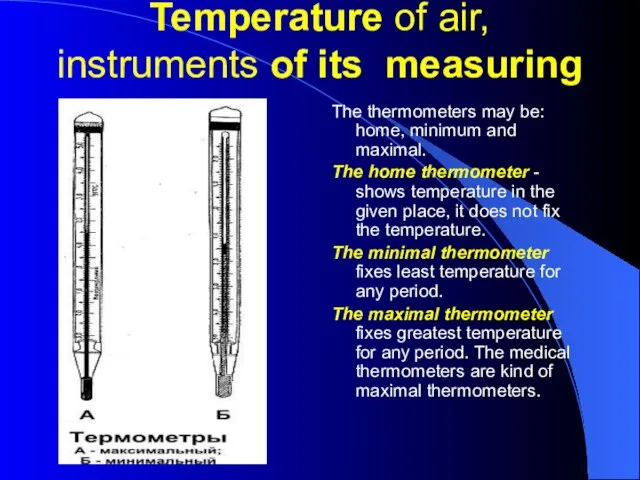
- 9. Temperature of air, instruments of its measuring The thermometers may be: home, minimum and maximal. The
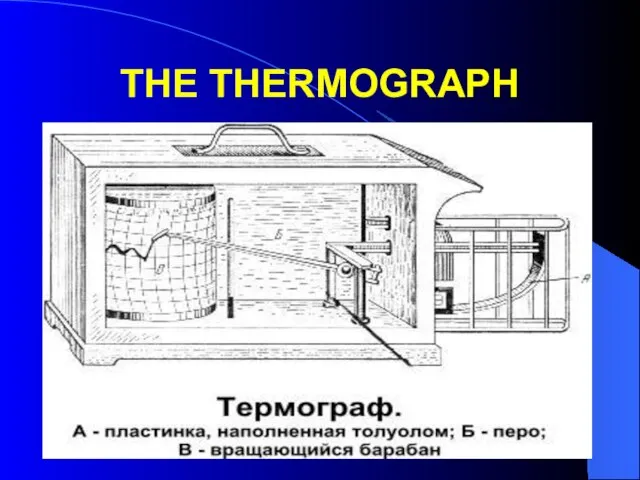
- 10. THE THERMOGRAPH
- 11. Humidity of air Kinds of humidity: а) Absolute – amount of water pairs in air in
- 12. Devices for measurement of humidity of air: AUGUST’S PSYCHROMETER
- 13. ASSMAN’S PSYCHROMETER (Aspiration)
- 14. Devises for estimation speed movement of air 1. ANEMOMETER
- 15. 2. KATATERMOMETER By the katatermometer we investigate Cooling ability of air (CAA). Then we calculate speed
- 16. " Rose of winds " The direction of a wind can be: north - east, north,
- 17. DEVICES FOR ESTIMATION ATHMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
- 19. METHODS OF COMPLEX ESTIMATION OF MICROCLIMATE It is estimation of all factors of microclimate in room
- 20. METHOD KATATHERMOMETRY We investigate the cooling-off period of dry katatermometer from 38 С up to 35
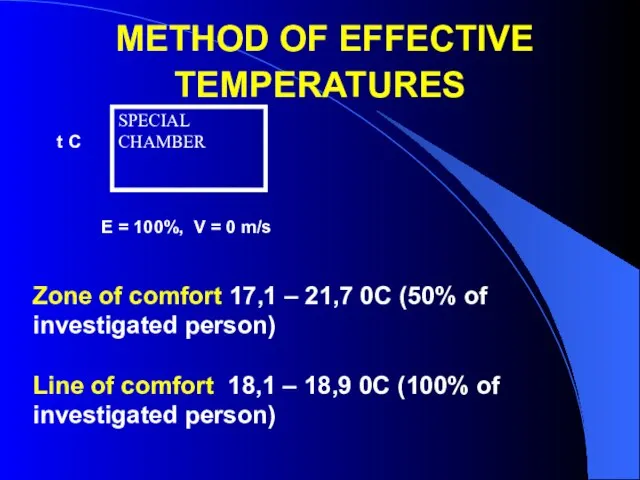
- 21. METHOD OF EFFECTIVE TEMPERATURES SPECIAL CHAMBER t C E = 100%, V = 0 m/s Zone
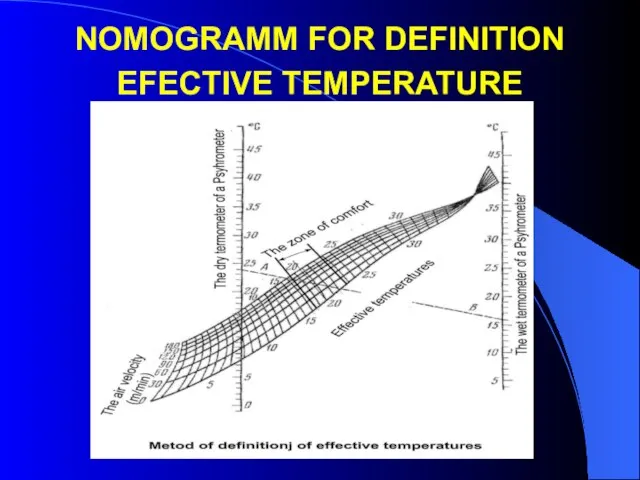
- 22. NOMOGRAMM FOR DEFINITION EFECTIVE TEMPERATURE
- 23. METHOD OF EQUIVALENT - EFFECTIVE TEMPERATURES In other special chambers were changed parameters of T, E,
- 24. METHOD OF EQUIVALENT - EFFECTIVE RADIATION TEMPERATURES Besides other factors of microclimate was taken into account
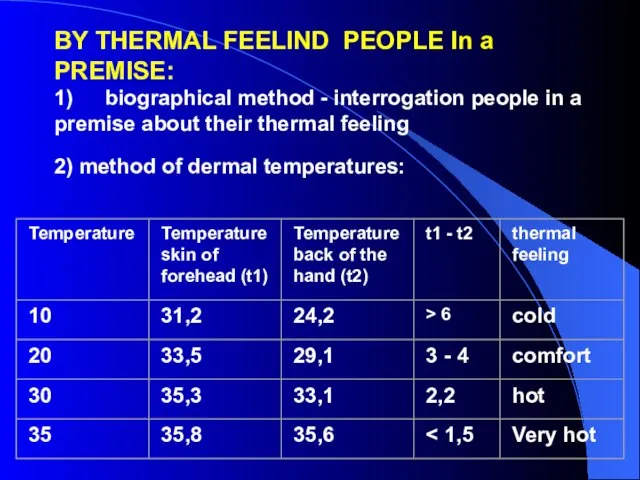
- 25. BY THERMAL FEELIND PEOPLE In a PREMISE: 1) biographical method - interrogation people in a premise
- 26. DEVICE FOR ESTIMATION SKIN TEMPERATURE
- 27. Concept “weather” and “climate” Weather - dynamic complex of physical properties of air for a short
- 28. BASIC GROUPS WEATHER FORMING FACTORS GELIOPHYSICAL - intensity solar radiation, solar activity. PARAMETERS OF SOLAR ACTIVITY:
- 29. 4. METEOROLOGICAL - temperature, humidity, speed and direction of air, atmospheric pressure, etc. 5. SYNOPTIC -
- 30. Types of atmospheric circulation: Cyclone - atmospheric whirlwind with low pressure in the center and movement
- 31. ANTICYСLONE CYСLONE CYСLONE ANTICYСLONE CYСLONE
- 32. The reasons of Metheotropic Reactions. At a periodical sharp changes of weather factors at people can
- 33. Displays of MR 1) Easy degree - asteno-vegetative syndrome. (Mass character and synchronism with changes of
- 34. Diseases, at which are marked MR 1) Diseases, at which presence МR is authentically proved: -
- 35. 2) Diseases, at which there are data on presence МR: - Diseases gastro-enteritis way (stomach ulcer,
- 36. Medical estimation of weather In a basis of all medical classifications - the concept of N.Vvedenski
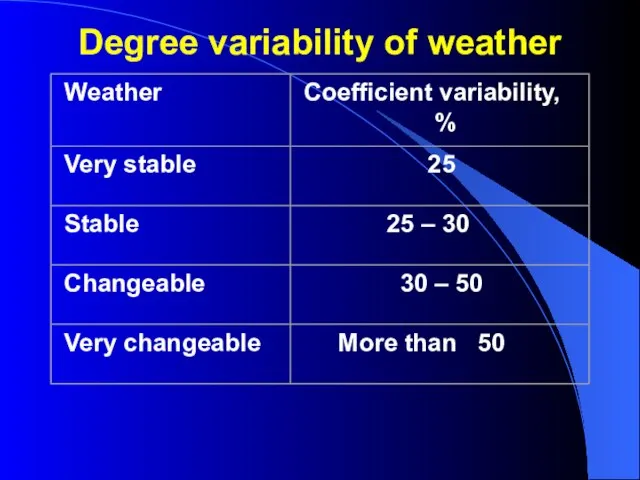
- 37. Definition degree variability of weather. N К = -------- х 100 %, n Where: K -
- 38. Degree variability of weather
- 39. Scientists Yalta scientific research institute named by Sechenov have offered General Clinical Index of Pathogenicity of
- 40. System of prevention of MR 1) General hygienical methods - improvement conditions of life and work,
- 41. 3) Treatment-and-prophylactic measures: а) Increase nonspecific resistancy of organism - stay on fresh air, vitamins, balanced
- 42. Seasons for seasonal prophylaxis cardiovascular diseases for the south of Ukraine and in Crimea (V.Bardov, 1990)
- 43. Hygienic value climate Climate - a long-term mode of weather in the given district. CLIMATE FORMING
- 44. COEFFICIENT INSTABILITY of CLIMATE К = А/В, Where: A - amount days with labile weather В
- 45. ACCLIMATIZATION Acclimatization - complex functional - morphological changes in organism, directed to the adaptation to new
- 47. Скачать презентацию




































 jd presentation - Update February 2014_ru
jd presentation - Update February 2014_ru Презентация
Презентация Доступный город
Доступный город Определение в слове
Определение в слове Дипломная работа для семинара итоговый вариант
Дипломная работа для семинара итоговый вариант Стекло и его разновидности
Стекло и его разновидности Система работы с молодежью на приходе
Система работы с молодежью на приходе Статистическое определение вероятности. Вероятность как предельное значение частоты
Статистическое определение вероятности. Вероятность как предельное значение частоты Авторская игрушка
Авторская игрушка Гидроэнергетика
Гидроэнергетика 20150324_igra_umniki_i_umnitsy
20150324_igra_umniki_i_umnitsy Қазақ ойшылдары дін туралы
Қазақ ойшылдары дін туралы Prezentatsia
Prezentatsia Основы религиозной культуры и светской этики
Основы религиозной культуры и светской этики Направление подготовки ГМУ
Направление подготовки ГМУ 20170613_d_szhata_prezentatsiya_novogodnego_prazdnika_zimnyaya_skazka_-_kopiya_5
20170613_d_szhata_prezentatsiya_novogodnego_prazdnika_zimnyaya_skazka_-_kopiya_5 Первый год жизни Насти. Фотоальбом
Первый год жизни Насти. Фотоальбом Анализ ассортимента и разработка технологии изготовления полуфабриката
Анализ ассортимента и разработка технологии изготовления полуфабриката 20141229_voinskie_zvaniya
20141229_voinskie_zvaniya Системы жизнеобеспечения городов. Газоснабжение
Системы жизнеобеспечения городов. Газоснабжение 11г кл
11г кл Численное моделирование теплового состояния диска турбины высокого давления при модернизации турбореактивного двигателя
Численное моделирование теплового состояния диска турбины высокого давления при модернизации турбореактивного двигателя Waterfilm W-film / Wa-Fi
Waterfilm W-film / Wa-Fi 20130612_3_kurs_na_suverennuyu_demokratiyu_2004-2008
20130612_3_kurs_na_suverennuyu_demokratiyu_2004-2008 Ответы на итоговое тестирование
Ответы на итоговое тестирование Техническое обслуживание и ремонт системы питания двигателя ВАЗ 2107
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт системы питания двигателя ВАЗ 2107 Методические материалы по курсу “ИКТ в начальной школе в контексте реализации ФГОС”
Методические материалы по курсу “ИКТ в начальной школе в контексте реализации ФГОС” Аккумулирование и предварительное осветление поверхностного стока
Аккумулирование и предварительное осветление поверхностного стока