Содержание
- 2. DISCUSSION Do you think personality traits can influence language learning? Make a list of traits that
- 3. Write your ideas in the chat box WHAT IS PERSONALITY?
- 4. DEFINITION The Collins Cobuild Dictionary defines personality as one’s “whole character and nature” Pervin and John
- 5. WHEN DID IT ALL START? Clark and Watson (2008): the concept of temperament originated in ancient
- 6. TEMPERAMENT ≠ PERSONALITY Temperament and personality can be seen as broadly overlapping domains, with temperament providing
- 7. PERSONALITY TAXONOMY the Classic Greek taxonomy of personality was proposed over 2,000 years ago by Hippocrates
- 8. Originally coined by Lewis Goldberg (1981), but in recent years most closely associated with the work
- 10. Dornyei, Z., & Ryan, S. (2015). The psychology of the language learner revisited.
- 11. Extensive empirical studies that have tested the model (for a recent review, see John et al.,
- 12. HTTP://WWW.PERSONALITYTEST.ORG.UK/
- 13. Few significant relationships between personality measures and linguistic variables have been identified “like Arthur’s knights, stumbling
- 14. EXTRAVERSION / INTROVERSION • Trait most investigated in terms of SLL. Two main hypotheses: More introverted
- 16. • Are ‘good’ language learners more extrovert? Canadian high school learners of L2 French Looked for
- 17. Measures two of the big five: Extraversion- Introversion and Neuroticism-Stability 57 Y/N items; The ‘SD score’
- 18. RESULTS No positive correlation found between written test scores and extent of extraversion Perhaps finding not
- 19. VERHOEVEN AND VERMEER (2002) This study was the first to use the Big Five personality construct
- 20. RESULTS It was found that only Openness to Experience correlated substantially with the linguistic abilities of
- 21. DEWAELE, J.-M. & FURNHAM, A. (1999). EXTRAVERSION: THE UNLOVED VARIABLE IN APPLIED LINGUISTIC RESEARCH. LANGUAGE LEARNING,
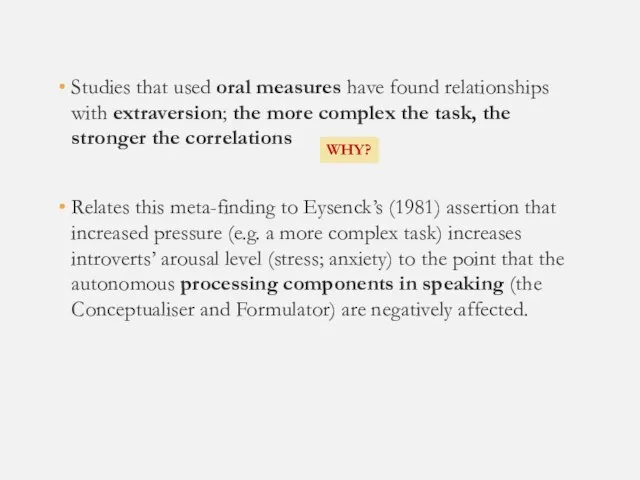
- 22. Studies that used oral measures have found relationships with extraversion; the more complex the task, the
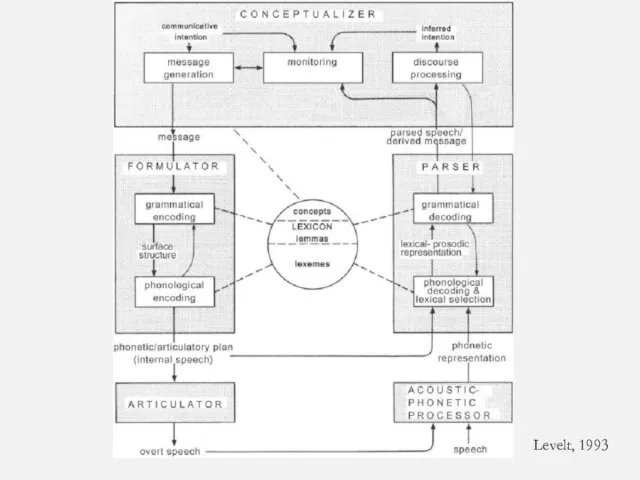
- 23. Levelt, 1993
- 25. Скачать презентацию



















 Методическое пособие. Трафарет Ручные швы (демонстрационное пособие)
Методическое пособие. Трафарет Ручные швы (демонстрационное пособие) Арабо-мусульманская цивилизация
Арабо-мусульманская цивилизация ID Abonent_саморегистрация абонента
ID Abonent_саморегистрация абонента Служебный этикет
Служебный этикет Электроизмерительные приборы
Электроизмерительные приборы Художник. Последовательность
Художник. Последовательность занятие2 Марина
занятие2 Марина Кофеин
Кофеин Устройство поиска на землю
Устройство поиска на землю Развитие железнодорожного транспорта России
Развитие железнодорожного транспорта России Измерение частоты и интервалов времени
Измерение частоты и интервалов времени Особенности тушения пожара, спасательных и других неотложных работ
Особенности тушения пожара, спасательных и других неотложных работ Ракообразные. Раки
Ракообразные. Раки Инструкция по организации дистанционного обучения
Инструкция по организации дистанционного обучения Соц.проетк Баженова
Соц.проетк Баженова Анализ материалов и обоснованные предложения по номенклатуре составляющих величины ущерба от дорожно-транспортных происшествий
Анализ материалов и обоснованные предложения по номенклатуре составляющих величины ущерба от дорожно-транспортных происшествий Стропальщики, обслуживающие грузоподъемные краны и имеющие удостоверения об аттестации
Стропальщики, обслуживающие грузоподъемные краны и имеющие удостоверения об аттестации Устройство и история шлюзов
Устройство и история шлюзов Системы охлаждения компьютера
Системы охлаждения компьютера Тоқыма өнеркәсібінің технологиясы
Тоқыма өнеркәсібінің технологиясы Принтеры
Принтеры КП1
КП1 Storyboard sandmalerei. 35 jahre HUBTEX
Storyboard sandmalerei. 35 jahre HUBTEX ОМПТ-2. Часть 2
ОМПТ-2. Часть 2 Религия и роль в современном мире
Религия и роль в современном мире Бесплатный_шаблон_презентаций_9
Бесплатный_шаблон_презентаций_9 Математика, 2 класс, 13.04.20
Математика, 2 класс, 13.04.20 Системы комбинированного цикла на базе газовых турбин GE модели 9F
Системы комбинированного цикла на базе газовых турбин GE модели 9F