Содержание
- 2. Impact on Constitution Crucial to British Constitution Provide links between Parliament and executive Citizens and government
- 3. The British Party System A two or ‘few’ party system Up to a dozen parties contesting
- 4. The Labour Party: Established by the Trade Union Congress (TUC) in 1900 Becomes a Socialist Party
- 5. The Conservatives 18th c roots a mass party, from 1869 Historic principle: Willingness to adapt, accept
- 6. Liberal Democrats: Liberals 18 & 19th c roots 19th c & early 20th c force for
- 7. Other parties: Scottish National Party (SNP) British National Party (BNP) Unionists Social Democratic and Labour Party
- 8. What parties divide over 19th c Liberals vs. Conservatives Religion Pace of reform 20th c Social
- 9. 20th C Party Battle Until 1911 Liberals v. Conservatives, with Liberals as majority party Interwar period:
- 10. From 1945 1945 Labour wins majority Builds welfare state 1951-64 Conservatives in power Accept & expand
- 11. From 1970 End of postwar consensus Decline of older industries Increased tensions, strikes Conservatives move to
- 12. From 1979 From 1997 ‘New Labour Tony Blair (until 2007) Gordon Brown (from 2007)
- 14. Скачать презентацию











 Реологические и технологические свойства бетонной смеси
Реологические и технологические свойства бетонной смеси Вишивка гладдю
Вишивка гладдю Проект электрической части ТЭЦ-400 МВт в г. Петрозаводск
Проект электрической части ТЭЦ-400 МВт в г. Петрозаводск Без названия
Без названия Проекции и виды
Проекции и виды неотложные состояния в акушерстве
неотложные состояния в акушерстве Dzieci uczą się tego, w czym i z czym żyją
Dzieci uczą się tego, w czym i z czym żyją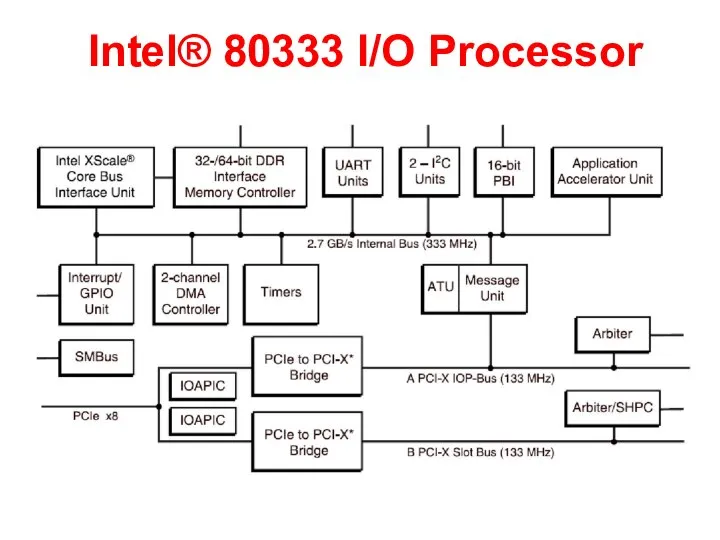 Intel® 80333
Intel® 80333  Подготовили: Польчак Е.К. Левшанова Е.В.
Подготовили: Польчак Е.К. Левшанова Е.В.  Конституция Российской Федерации
Конституция Российской Федерации Морфологическая типология языков и морфологическая классификация языков
Морфологическая типология языков и морфологическая классификация языков Посвящается 374 летию со дня рождения Исаака Ньютона (1643-1727), английского математика, физика, астронома
Посвящается 374 летию со дня рождения Исаака Ньютона (1643-1727), английского математика, физика, астронома Презентация на тему "Помощь депрессивным детям" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Помощь депрессивным детям" - скачать презентации по Педагогике 骑车旅行记
骑车旅行记 Современная философия качества
Современная философия качества  Молитва и любовь спасают
Молитва и любовь спасают Разработка рекомендаций по использованию солнечных батарей в условиях Республики Марий Эл
Разработка рекомендаций по использованию солнечных батарей в условиях Республики Марий Эл Степень с натуральным показателем - презентация по Алгебре__
Степень с натуральным показателем - презентация по Алгебре__ Оценка стабильности работы компьютера с использованием контрольных карт
Оценка стабильности работы компьютера с использованием контрольных карт Кому нужны «столетние»
Кому нужны «столетние» Территориальное разделение труда
Территориальное разделение труда КАЧЕСТВО ПЛАНОВО-КАРТОГРАФИЧЕСКОГО МАТЕРИАЛА
КАЧЕСТВО ПЛАНОВО-КАРТОГРАФИЧЕСКОГО МАТЕРИАЛА Регулируемый блок питания на транзисторах
Регулируемый блок питания на транзисторах Зачетная работа по риторике. Как интернет влияет на учебу и жизнь человека.
Зачетная работа по риторике. Как интернет влияет на учебу и жизнь человека. Логика. Софисты и Сократ
Логика. Софисты и Сократ  我的一天
我的一天 Электр ортадан тепкіш сораптық қондырғы
Электр ортадан тепкіш сораптық қондырғы Монополия в рыночной экономике
Монополия в рыночной экономике