Содержание
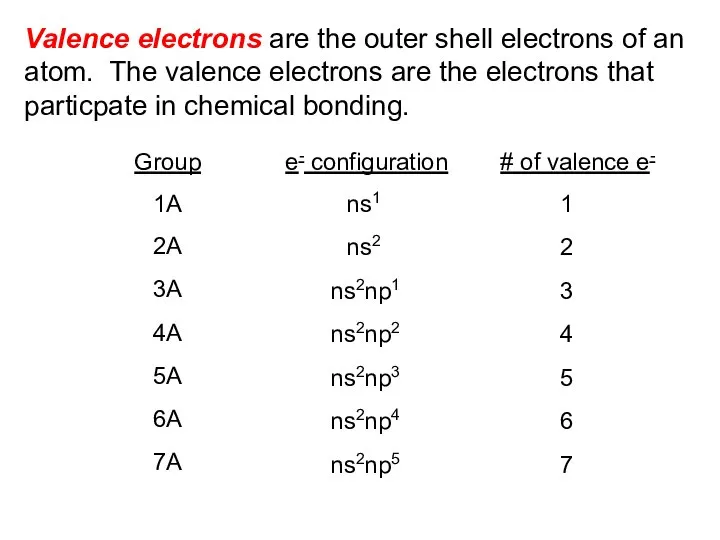
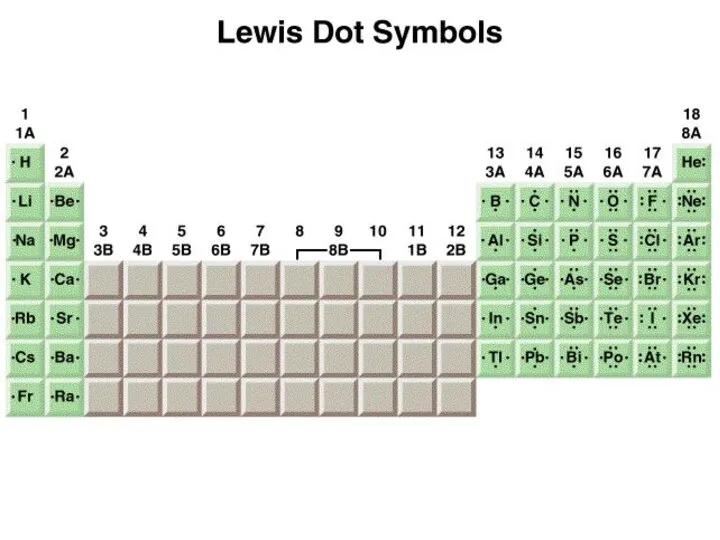
- 2. Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons
- 4. The Ionic Bond 1s22s1 1s22s22p5 1s2 1s22s22p6 [He] [Ne]
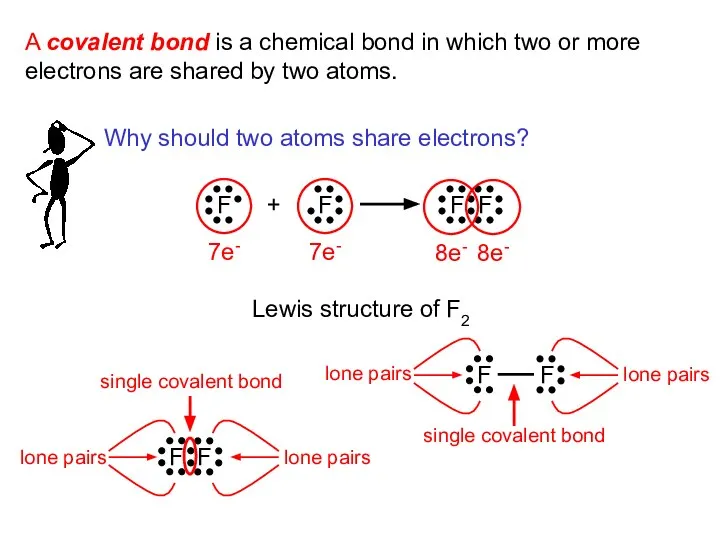
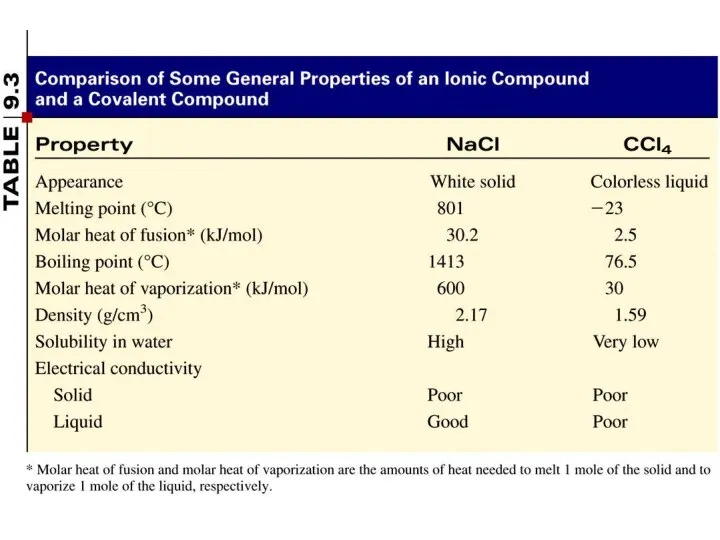
- 5. A covalent bond is a chemical bond in which two or more electrons are shared by
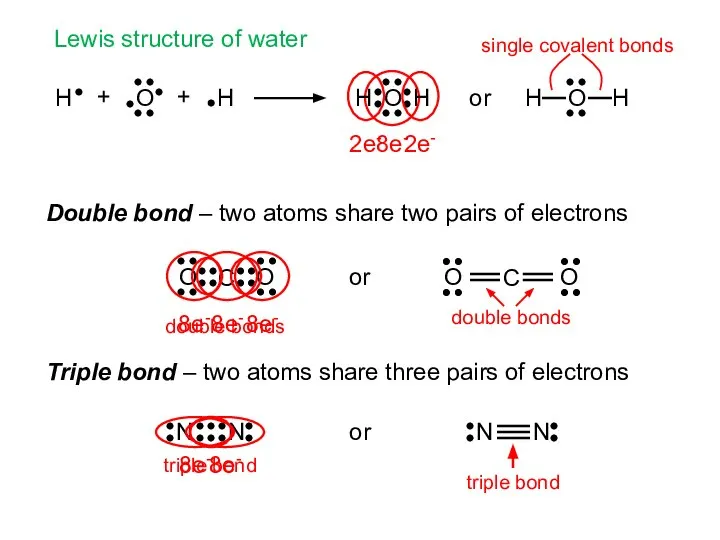
- 6. + + Lewis structure of water Double bond – two atoms share two pairs of electrons
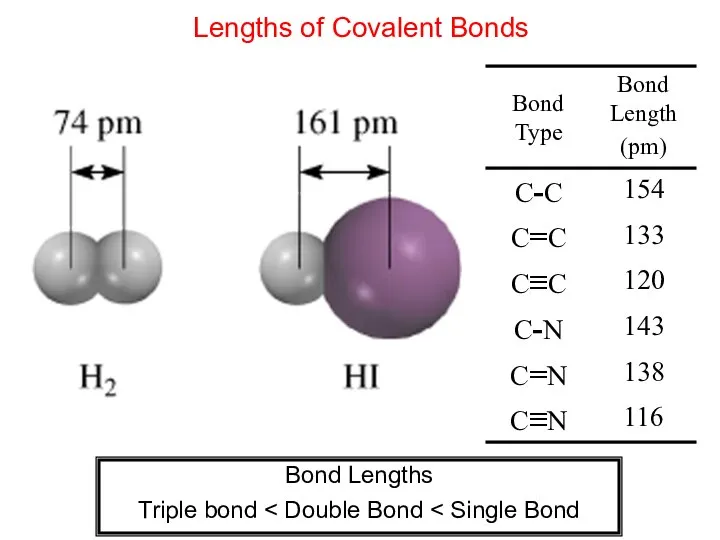
- 7. Lengths of Covalent Bonds Bond Lengths Triple bond
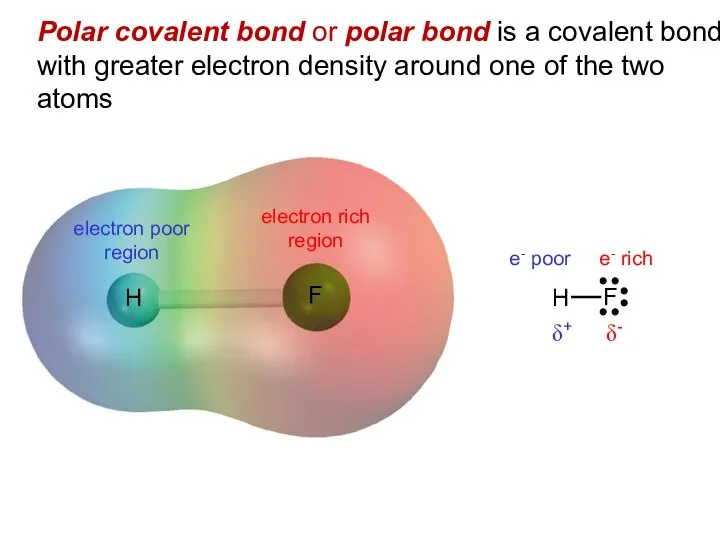
- 9. Polar covalent bond or polar bond is a covalent bond with greater electron density around one
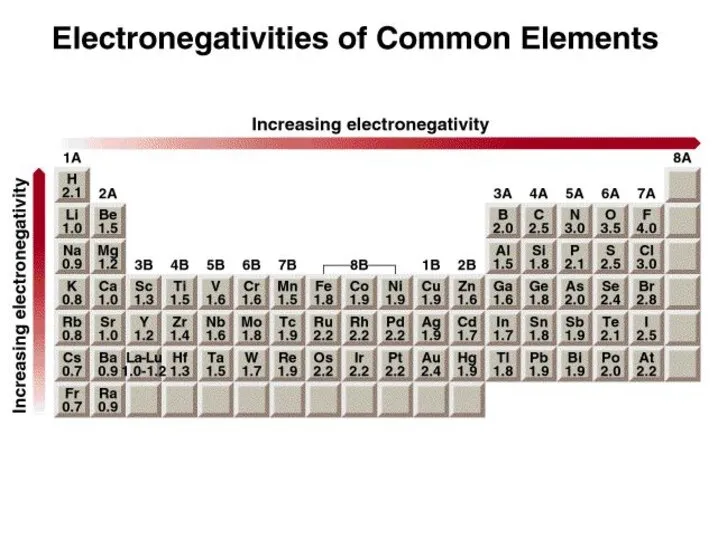
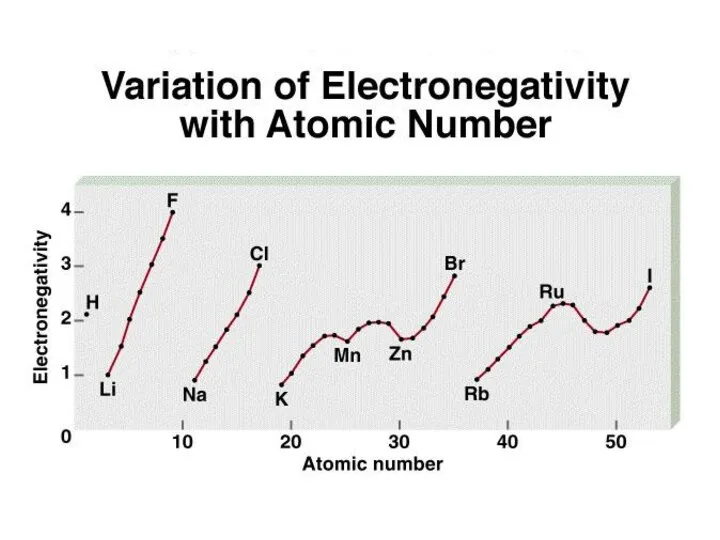
- 10. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electrons in a chemical
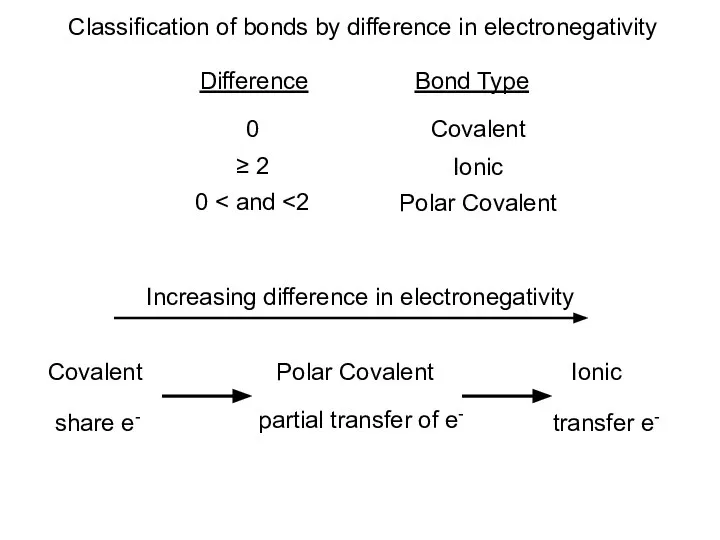
- 13. Classification of bonds by difference in electronegativity Difference Bond Type 0 Covalent ≥ 2 Ionic 0
- 14. Cs – 0.7 Cl – 3.0 3.0 – 0.7 = 2.3 Ionic H – 2.1 S
- 15. Draw skeletal structure of compound showing what atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative
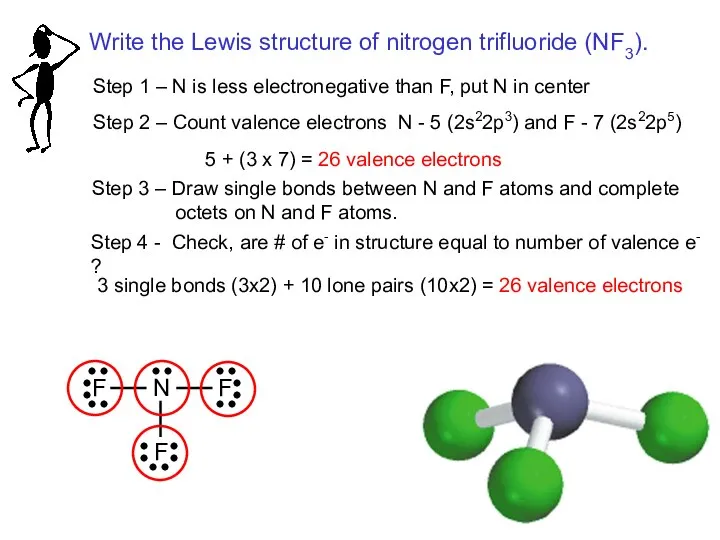
- 16. Step 1 – N is less electronegative than F, put N in center Step 2 –
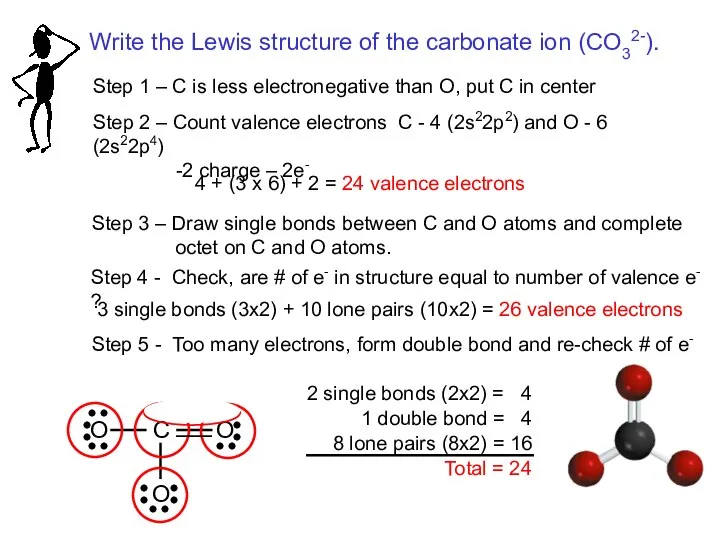
- 17. Step 1 – C is less electronegative than O, put C in center Step 2 –
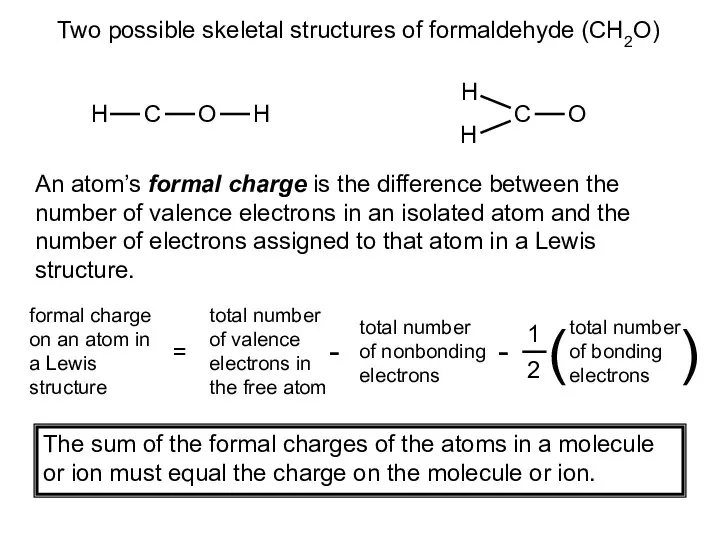
- 18. Two possible skeletal structures of formaldehyde (CH2O) An atom’s formal charge is the difference between the
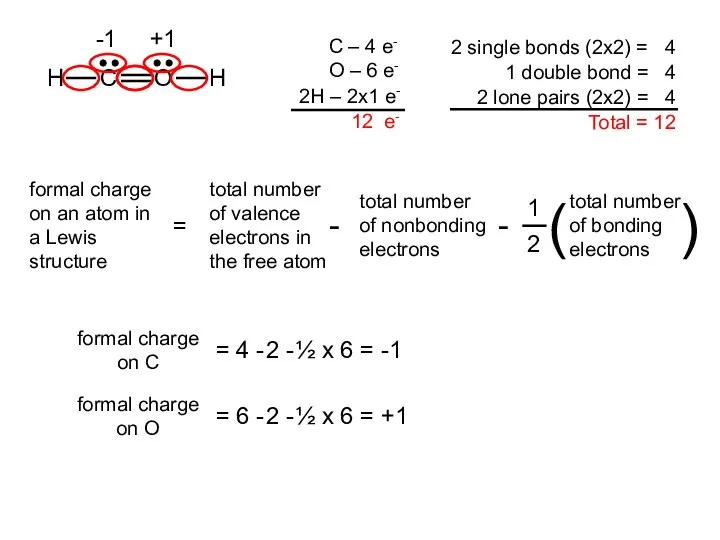
- 19. formal charge on C = 4 - 2 - ½ x 6 = -1 formal charge
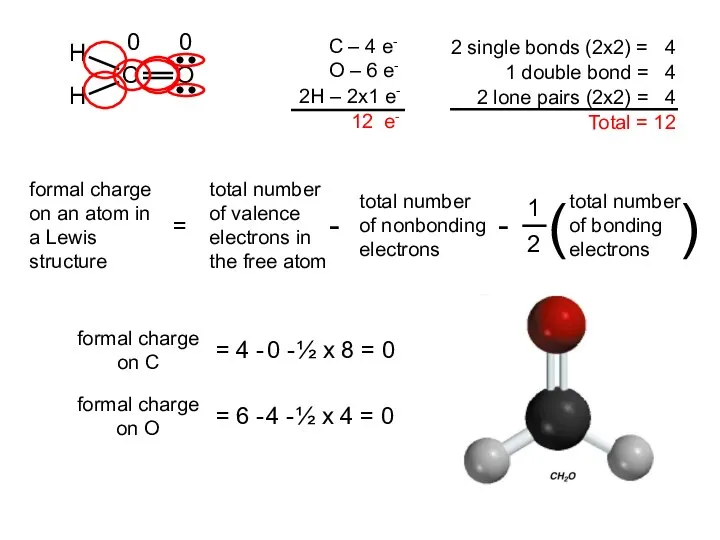
- 20. formal charge on C = 4 - 0 - ½ x 8 = 0 formal charge
- 22. Скачать презентацию
![The Ionic Bond 1s22s1 1s22s22p5 1s2 1s22s22p6 [He] [Ne]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1482804/slide-3.jpg)



 Налоговые правонарушения и налоговая ответственность
Налоговые правонарушения и налоговая ответственность Региональное кровообращение
Региональное кровообращение Презентация как один из способов предъявления достижений классного коллектива
Презентация как один из способов предъявления достижений классного коллектива Алгоритмізація та програмування. Базові структури алгоритму
Алгоритмізація та програмування. Базові структури алгоритму Гематогенный остеомиелит челюстей в детском возрасте
Гематогенный остеомиелит челюстей в детском возрасте Иоханнес Иттен. Искусство цвета
Иоханнес Иттен. Искусство цвета Солнце и растения
Солнце и растения  Требования. Анализ требований. Тестирование документации. Виды и направления тестирования
Требования. Анализ требований. Тестирование документации. Виды и направления тестирования Леонардо да Винчи
Леонардо да Винчи Präpositionen - mit Akk
Präpositionen - mit Akk Элементы линейной алгебры. Системы линейных уравнений
Элементы линейной алгебры. Системы линейных уравнений  Электронная коммерция
Электронная коммерция Автор: ученик 8ого «А» класса МБОУ «СОШ №3 г. Шебекино» Тарасов Сергей
Автор: ученик 8ого «А» класса МБОУ «СОШ №3 г. Шебекино» Тарасов Сергей Определение психологической защиты
Определение психологической защиты Continuous integration
Continuous integration Влияние системы учета преступлений на степень соответствия статистических данных действительного положения дела
Влияние системы учета преступлений на степень соответствия статистических данных действительного положения дела Монолитные здания каркасной конструктивной системы
Монолитные здания каркасной конструктивной системы Сатирические образы человека. 6 класс
Сатирические образы человека. 6 класс Игровые тестовые задания «Знатоки птиц» - презентация для начальной школы_
Игровые тестовые задания «Знатоки птиц» - презентация для начальной школы_ Теория алгоритмов. (Лекция 3)
Теория алгоритмов. (Лекция 3) Контроль качества при производстве тыквенных цукат
Контроль качества при производстве тыквенных цукат Сімейні обряди козацької доби
Сімейні обряди козацької доби Негізгі және қосымша шағымдарын анықтау
Негізгі және қосымша шағымдарын анықтау Терминология корпоративных информационных систем
Терминология корпоративных информационных систем Путь Пифагора Психоматрица или уроки нумерологии
Путь Пифагора Психоматрица или уроки нумерологии Переменные и базовые типы данных языка С
Переменные и базовые типы данных языка С Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel
Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel Ввод и вывод
Ввод и вывод