Содержание
- 2. 2.15 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition Counter-controlled repetition requires Name of control variable/loop counter Initial value of
- 3. 1 // Fig. 2.16: fig02_16.cpp 2 // Counter-controlled repetition. 3 #include 4 5 using std::cout; 6
- 4. 2.15 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition The declaration int counter = 1; Names counter Declares counter to
- 6. 2.16 for Repetition Structure General format when using for loops for ( initialization; LoopContinuationTest; increment )
- 7. 1 // Fig. 2.17: fig02_17.cpp 2 // Counter-controlled repetition with the for structure. 3 #include 4
- 8. 2.16 for Repetition Structure for loops can usually be rewritten as while loops initialization; while (
- 9. 1 // Fig. 2.20: fig02_20.cpp 2 // Summation with for. 3 #include 4 5 using std::cout;
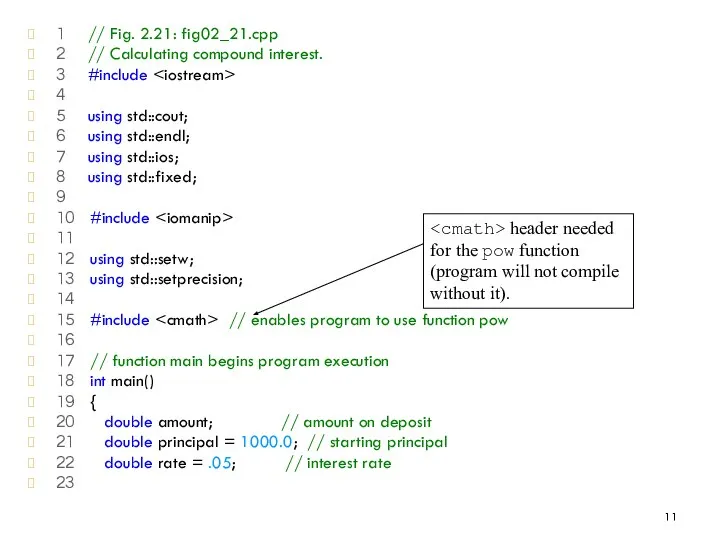
- 10. 2.17 Examples Using the for Structure Program to calculate compound interest A person invests $1000.00 in
- 11. 1 // Fig. 2.21: fig02_21.cpp 2 // Calculating compound interest. 3 #include 4 5 using std::cout;
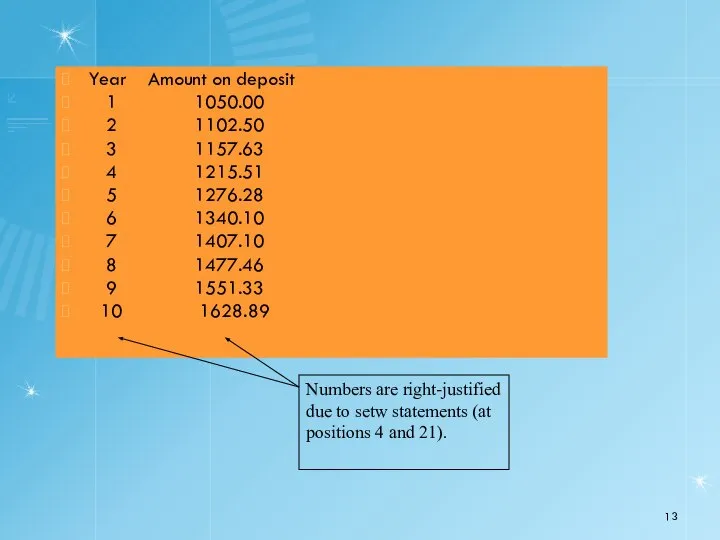
- 12. 24 // output table column heads 25 cout 26 27 // set floating-point number format 28
- 13. Year Amount on deposit 1 1050.00 2 1102.50 3 1157.63 4 1215.51 5 1276.28 6 1340.10
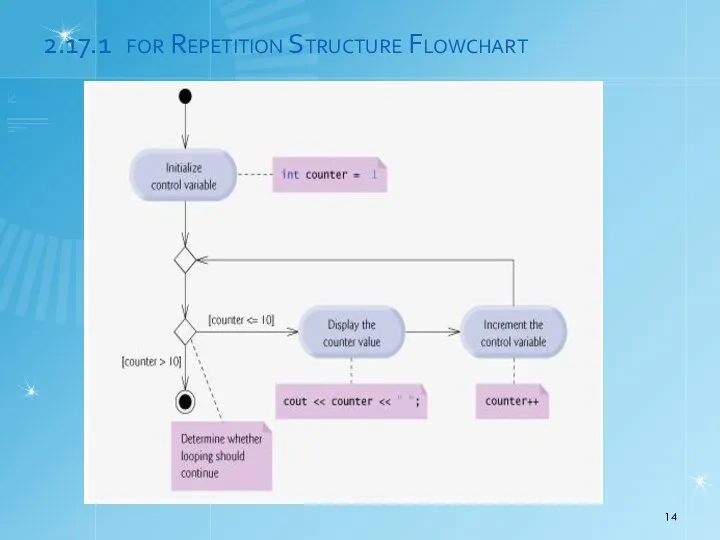
- 14. 2.17.1 for Repetition Structure Flowchart
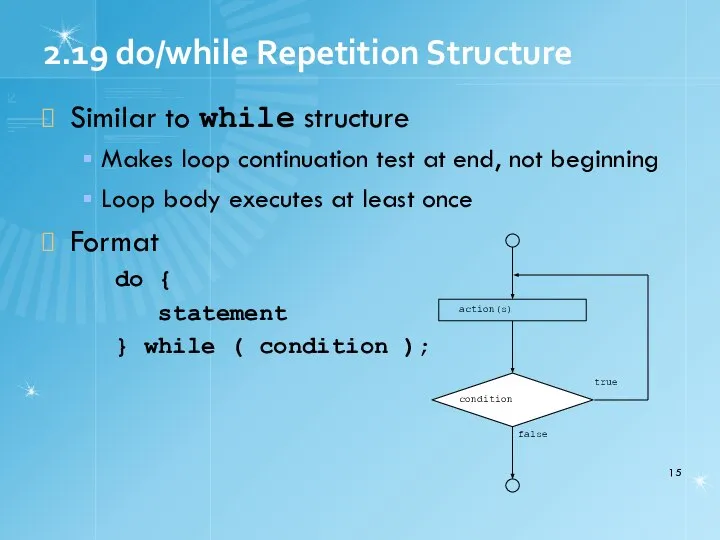
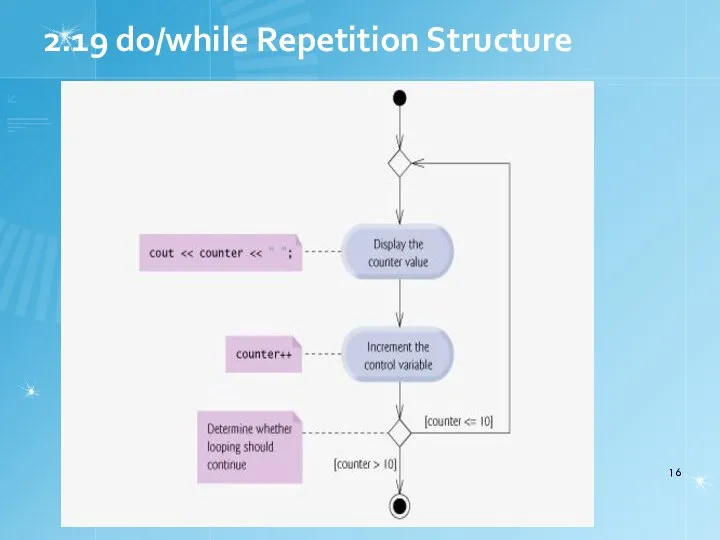
- 15. 2.19 do/while Repetition Structure Similar to while structure Makes loop continuation test at end, not beginning
- 16. 2.19 do/while Repetition Structure
- 17. 1 // Fig. 2.24: fig02_24.cpp 2 // Using the do/while repetition structure. 3 #include 4 5
- 18. 2.20 break and continue Statements break statement Immediate exit from while, for, do/while, switch Program continues
- 19. 1 // Fig. 2.26: fig02_26.cpp 2 // Using the break statement in a for structure. 3
- 20. 26 27 return 0; // indicate successful termination 28 29 } // end function main 1
- 21. 2.20 break and continue Statements continue statement Used in while, for, do/while Skips remainder of loop
- 22. 1 // Fig. 2.27: fig02_27.cpp 2 // Using the continue statement in a for structure. 3
- 23. 26 27 } // end function main 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
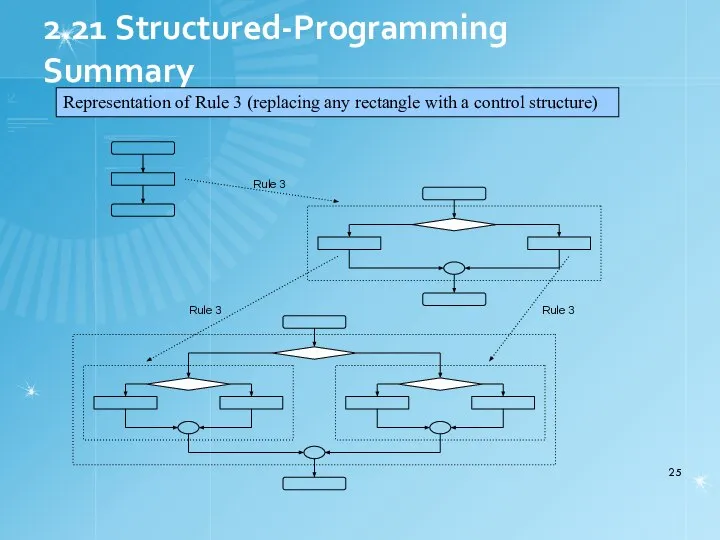
- 24. 2.21 Structured-Programming Summary Structured programming Programs easier to understand, test, debug and modify Rules for structured
- 25. 2.21 Structured-Programming Summary Representation of Rule 3 (replacing any rectangle with a control structure)
- 26. 2.21 Structured-Programming Summary All programs broken down into Sequence Selection if, if/else, or switch Any selection
- 27. Readings: C++ How to Program, By H. M. Deitel Chapter 5. Control Statements: Part 2
- 29. Скачать презентацию




















 Ландшафтное проектирование. Причины и методы реконструкции зеленых насаждений
Ландшафтное проектирование. Причины и методы реконструкции зеленых насаждений РОМАНТИЗМ Романтизм в зарубежной литературе первой половины XIX века
РОМАНТИЗМ Романтизм в зарубежной литературе первой половины XIX века Строки, символы и регулярные выражения. (Лекция 6)
Строки, символы и регулярные выражения. (Лекция 6) Разрез по зданию. Ограждающие конструкции
Разрез по зданию. Ограждающие конструкции Мировая культура в системе гуманитарного знания
Мировая культура в системе гуманитарного знания Актуальные особенности организации документооборота образовательной организации в условиях глобальной информатизации
Актуальные особенности организации документооборота образовательной организации в условиях глобальной информатизации Психические свойства личности: темперамент и характер
Психические свойства личности: темперамент и характер  Нидерланды Выполнил ученик 3 а класса СШ № 7 Кучмасов Антон г. Шарыпово
Нидерланды Выполнил ученик 3 а класса СШ № 7 Кучмасов Антон г. Шарыпово Методы математического анализа при исследовании СЭП
Методы математического анализа при исследовании СЭП Общее учение о внутренностях
Общее учение о внутренностях  Unforgettable tour to Czech Republic
Unforgettable tour to Czech Republic Модернизм – общее обозначение всех авангардистских направлений в культуре конца XIX начала XX веков. Модернизм – современный,
Модернизм – общее обозначение всех авангардистских направлений в культуре конца XIX начала XX веков. Модернизм – современный,  Профилактика на репродуктивното здраве Д-р Мариела Даскалова лекар ембриолог. - презентация_
Профилактика на репродуктивното здраве Д-р Мариела Даскалова лекар ембриолог. - презентация_ Синергетика
Синергетика  Разработка проекта реализации услуги IPTV для типовой кабельной сети
Разработка проекта реализации услуги IPTV для типовой кабельной сети  ПРОЕКТ на тему «Золотая полка
ПРОЕКТ на тему «Золотая полка Российская экономика в 1-й четверти XVIII в.
Российская экономика в 1-й четверти XVIII в. Культура России в XVII – XVIII вв.
Культура России в XVII – XVIII вв.  ВАЛЕНТИН АЛЕКСАНДРОВИЧ СЕРОВ (1865-1911)
ВАЛЕНТИН АЛЕКСАНДРОВИЧ СЕРОВ (1865-1911)  Тема: «Времена глаголов» Учитель начальных классов МБОУ Новолакская СОШ №1 Сайдаева Товсият Саидовна
Тема: «Времена глаголов» Учитель начальных классов МБОУ Новолакская СОШ №1 Сайдаева Товсият Саидовна  Презентация РЫНОК МЕДА: ПРОБЛЕМЫ ОППОРТУНИСТИЧЕСКОГО ПОВЕДЕНИЯ И СПОСОБЫ ЕГО МИНИМИЗАЦИИ
Презентация РЫНОК МЕДА: ПРОБЛЕМЫ ОППОРТУНИСТИЧЕСКОГО ПОВЕДЕНИЯ И СПОСОБЫ ЕГО МИНИМИЗАЦИИ Графика в Pascal
Графика в Pascal Церковь и отношения
Церковь и отношения Урок русского языка 2 класс Учитель: Киданова М.Н.
Урок русского языка 2 класс Учитель: Киданова М.Н. Политическая элита
Политическая элита Сети связи следующего поколения
Сети связи следующего поколения Значение, строение, функционирование нервной системы.
Значение, строение, функционирование нервной системы.  Авторитаризм, как политический режим
Авторитаризм, как политический режим