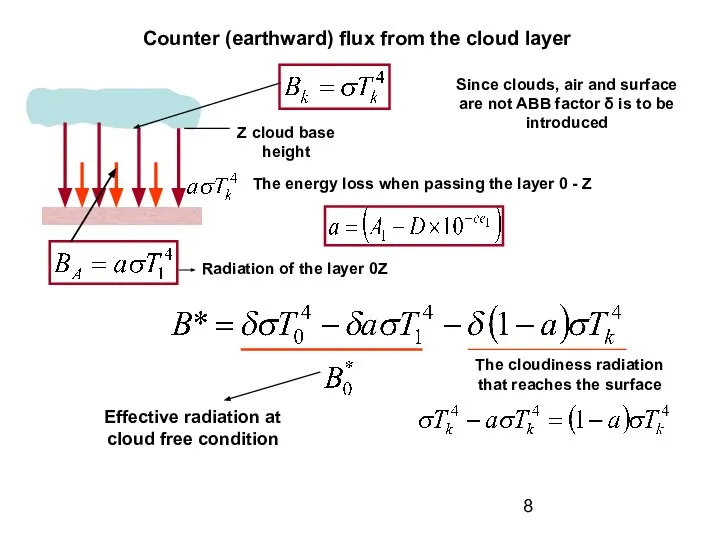
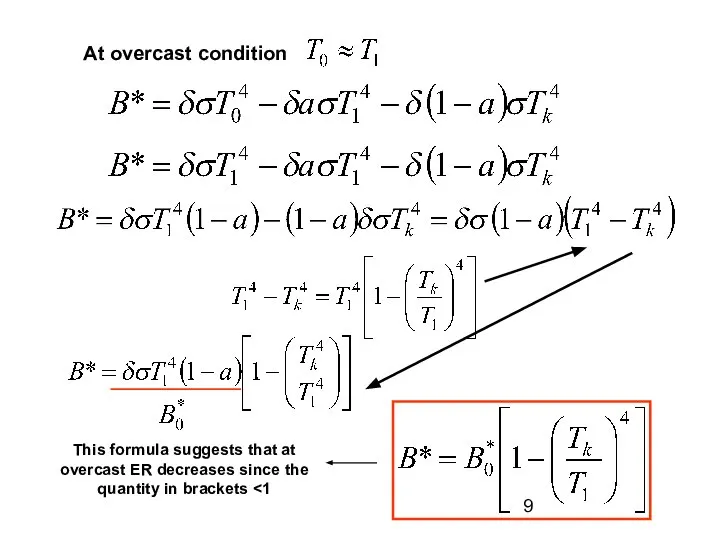
Effective radiation and water vapor in the atmosphere
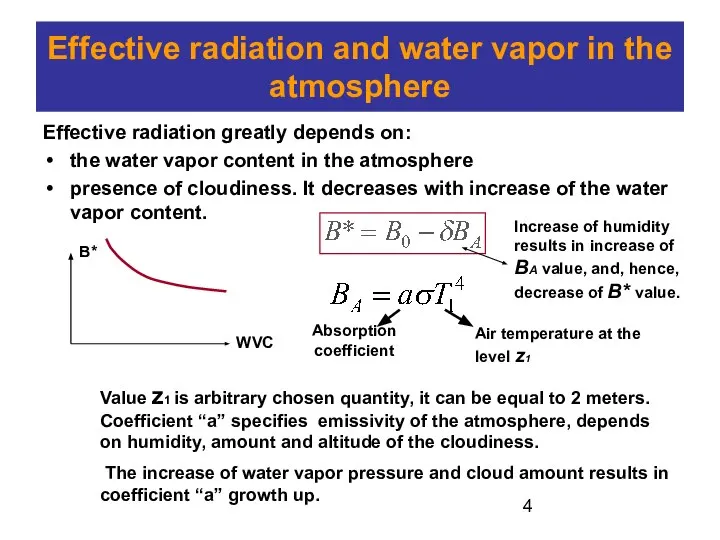
Effective radiation greatly depends
on:
the water vapor content in the atmosphere
presence of cloudiness. It decreases with increase of the water vapor content.
Increase of humidity results in increase of BA value, and, hence, decrease of B* value.
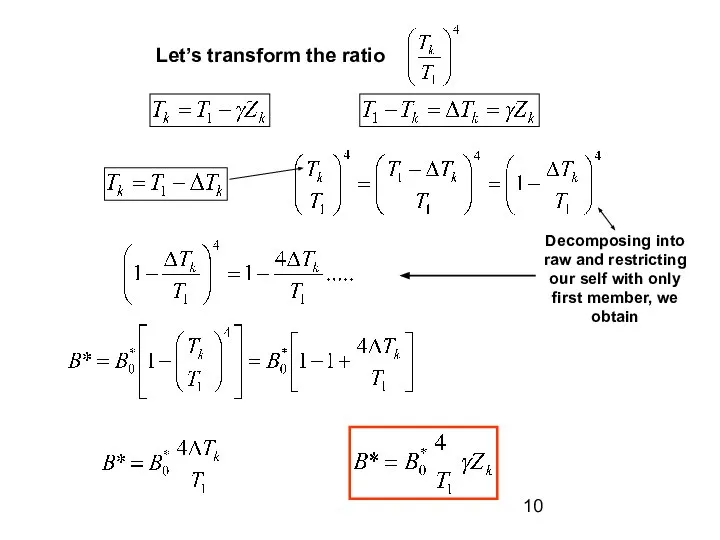
Air temperature at the level z1
Absorption coefficient
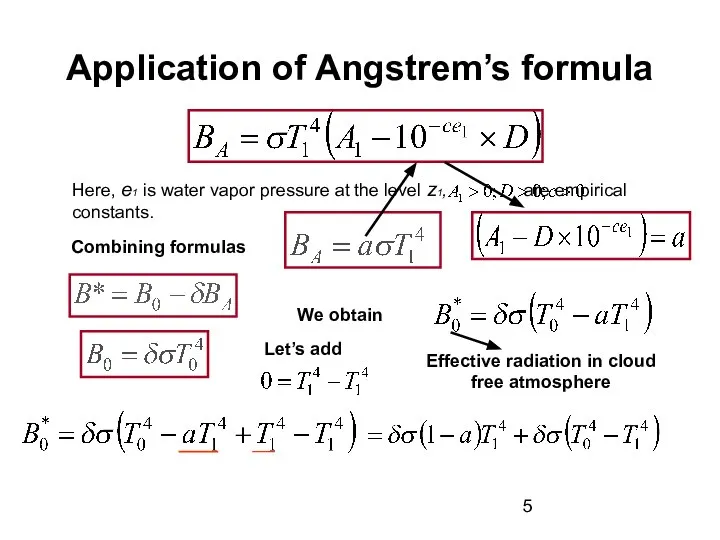
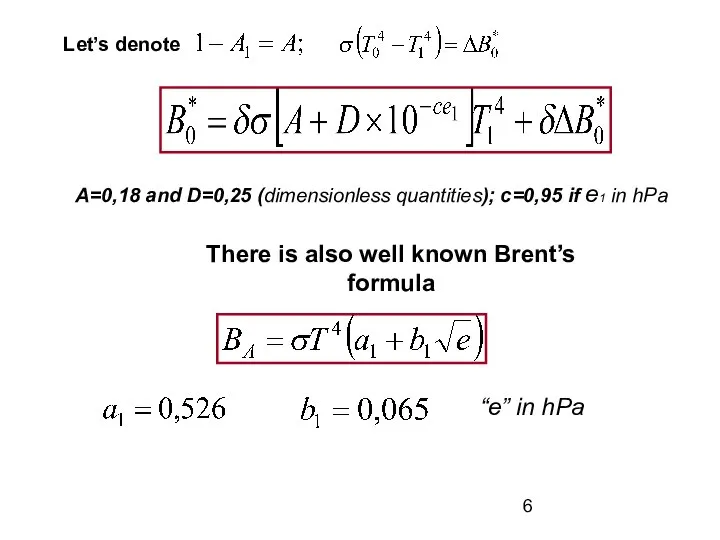
Value z1 is arbitrary chosen quantity, it can be equal to 2 meters. Coefficient “a” specifies emissivity of the atmosphere, depends on humidity, amount and altitude of the cloudiness.
The increase of water vapor pressure and cloud amount results in coefficient “a” growth up.


 Қазақша өрнектермен жасалған шақыру хаттар өндіру
Қазақша өрнектермен жасалған шақыру хаттар өндіру Россия – многонациональная культура
Россия – многонациональная культура Управленческий учет на предприятии
Управленческий учет на предприятии Специальные главы математики
Специальные главы математики Природа судебной бухгалтерии и ее место в системе научного знания
Природа судебной бухгалтерии и ее место в системе научного знания Привлечение в качестве обвиняемого
Привлечение в качестве обвиняемого Квентин Массейс Жизнь и творчество
Квентин Массейс Жизнь и творчество Рубежно – зачетная работа по системам компьютерной графики
Рубежно – зачетная работа по системам компьютерной графики  Диагностирование узлов и агрегатов
Диагностирование узлов и агрегатов Техногенные аварии: Взрыв на шахте «Северная
Техногенные аварии: Взрыв на шахте «Северная Глобализация. Характерные черты современного мира
Глобализация. Характерные черты современного мира Poznanie sposobu nagrywania makr i ich edycji w edytorze VBA
Poznanie sposobu nagrywania makr i ich edycji w edytorze VBA ВЫПУСКНАЯ КВАЛИФИКАЦИОННАЯ РАБОТА на высшую категорию Активизация мыслительной деятельности младших подростков средствами г
ВЫПУСКНАЯ КВАЛИФИКАЦИОННАЯ РАБОТА на высшую категорию Активизация мыслительной деятельности младших подростков средствами г экспертиза молочных консерв
экспертиза молочных консерв Ответственность за нарушение законодательства в области промышленной безопасности
Ответственность за нарушение законодательства в области промышленной безопасности Здоровый образ жизни Подготовила: студентка группы Э111б 2-го курса экономического факультета Лоскутова Виктория
Здоровый образ жизни Подготовила: студентка группы Э111б 2-го курса экономического факультета Лоскутова Виктория Деревянные узоры
Деревянные узоры Презентация по алгебре Неравенства и их решения
Презентация по алгебре Неравенства и их решения  Таинство Крещения
Таинство Крещения Навыки оценки санитарно-гигиенических требований к получению, транспортировке, хранению очищенной воды и воды для инъекций
Навыки оценки санитарно-гигиенических требований к получению, транспортировке, хранению очищенной воды и воды для инъекций Czarna Madonna
Czarna Madonna Нормативно-правовые документы по ультразвуковой диагностике
Нормативно-правовые документы по ультразвуковой диагностике Универсальный спортивный комплекс «Победа»
Универсальный спортивный комплекс «Победа» Невада-Семей қозғалысы
Невада-Семей қозғалысы Государственная политика в сфере формирования «электронного правительства»
Государственная политика в сфере формирования «электронного правительства» Механистическая картина мира
Механистическая картина мира Построение классификации для нормального распределения
Построение классификации для нормального распределения  Международная защита прав человека
Международная защита прав человека