Содержание
- 2. Biography Naiqi Weng -- Autodesk Developer Network Education Bachelor of Computer Science Master of Computer Science
- 3. Dependency Graph
- 4. Agenda What is Dependency Graph (DG)? Concepts/Elements of DG Nodes Custom plug-in DG node with Maya
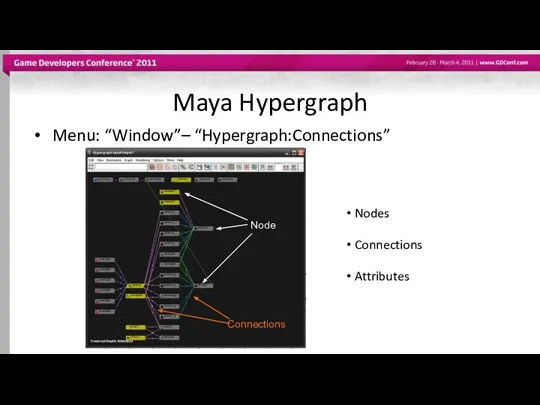
- 5. Maya Hypergraph Menu: “Window”– “Hypergraph:Connections” Nodes Node Connections Attributes Connections
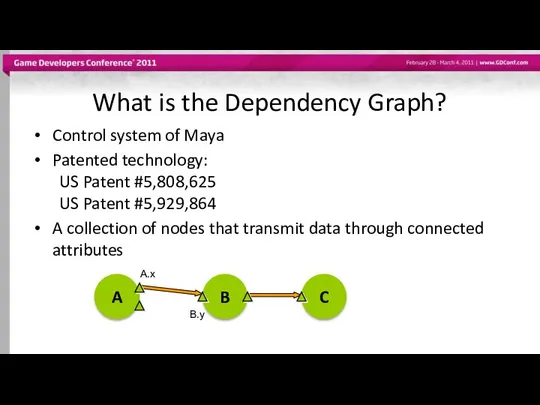
- 6. What is the Dependency Graph? Control system of Maya Patented technology: US Patent #5,808,625 US Patent
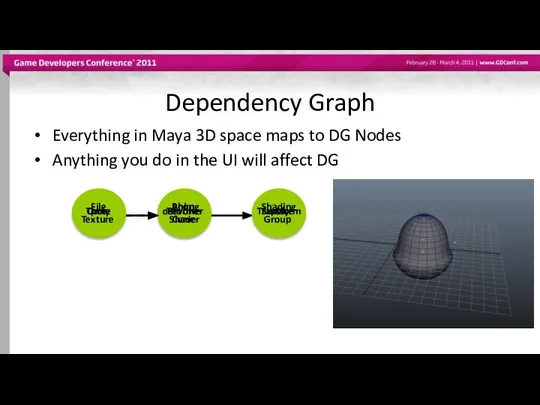
- 7. Dependency Graph Everything in Maya 3D space maps to DG Nodes Anything you do in the
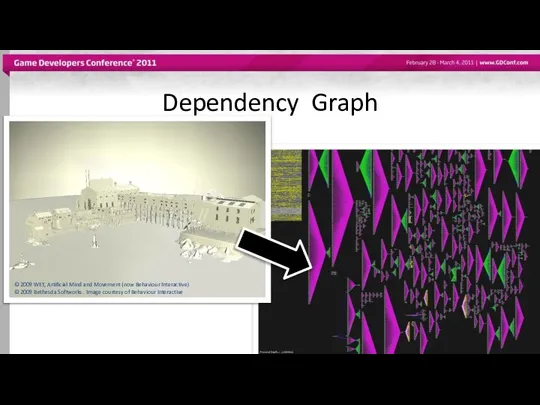
- 8. Dependency Graph © 2009 WET, Artificial Mind and Movement (now Behaviour Interactive) © 2009 Bethesda Softworks.
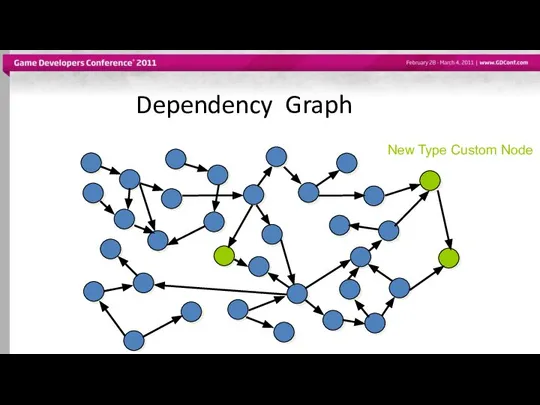
- 9. Dependency Graph New Type Custom Node
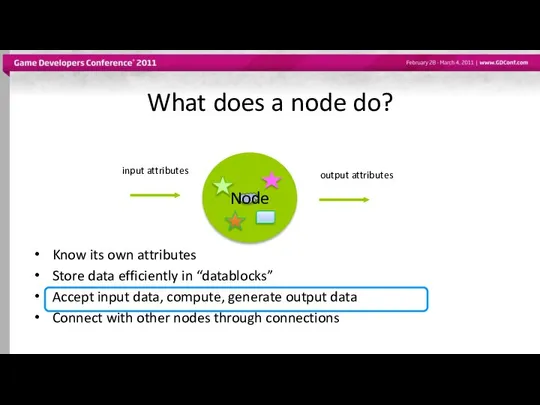
- 10. What does a node do? Know its own attributes Store data efficiently in “datablocks” Accept input
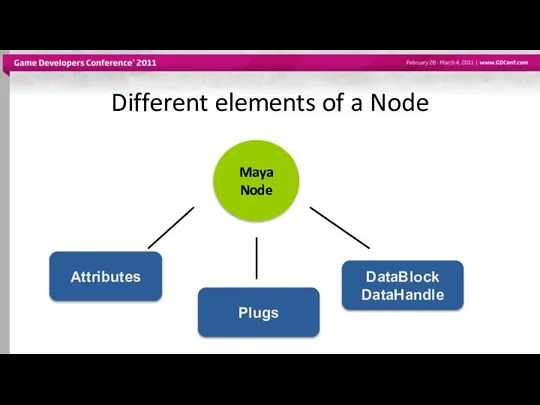
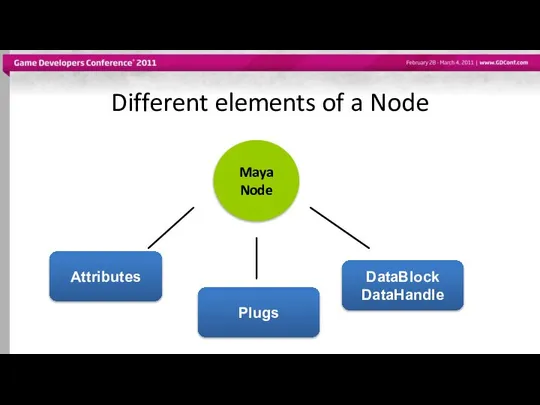
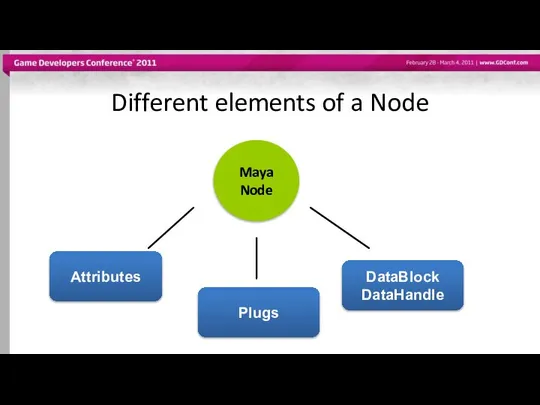
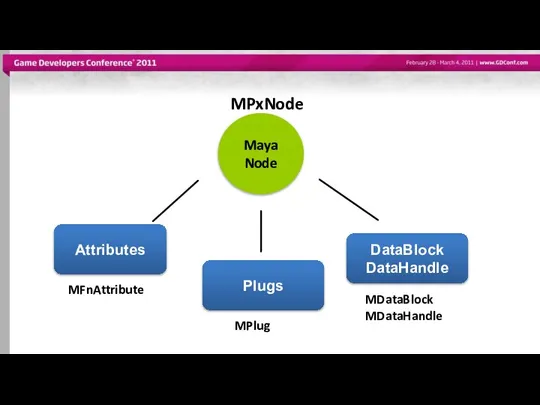
- 11. Different elements of a Node Maya Node Attributes Plugs DataBlock DataHandle
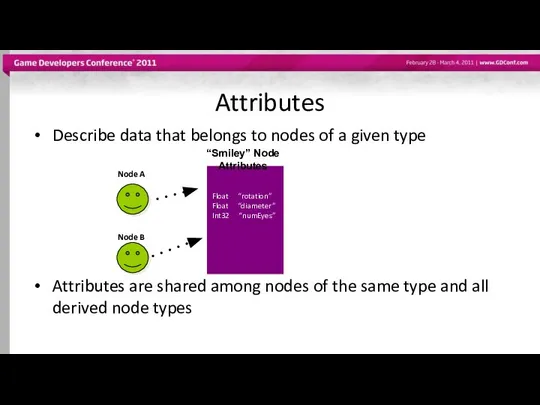
- 12. Attributes Describe data that belongs to nodes of a given type Attributes are shared among nodes
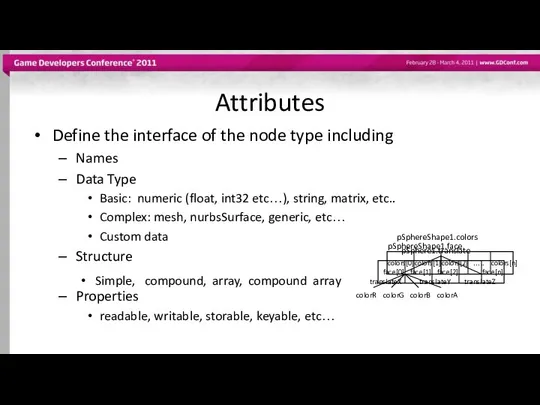
- 13. Attributes Define the interface of the node type including Names Data Type Basic: numeric (float, int32
- 14. API Classes for Attributes Base Class: MFnAttribute Takes care of all the common aspect of an
- 15. Different elements of a Node Maya Node Attributes Plugs DataBlock DataHandle
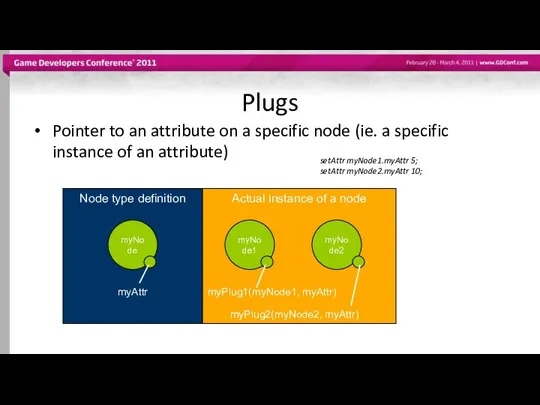
- 16. Plugs Pointer to an attribute on a specific node (ie. a specific instance of an attribute)
- 17. Plugs Plugs can be used to: query / set a value create / remove /query a
- 18. Different elements of a Node Maya Node Attributes Plugs DataBlock DataHandle
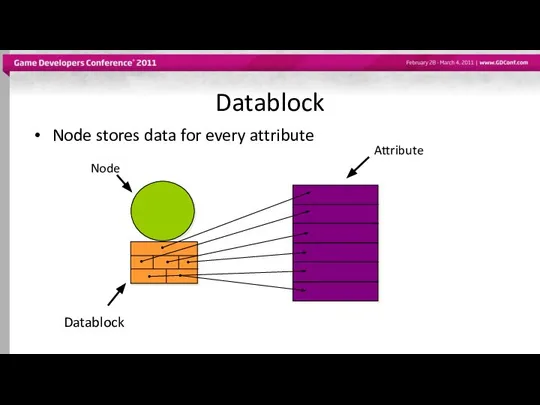
- 19. Datablock Node stores data for every attribute Datablock Node Attribute
- 20. Datablocks Datablock is the actual storage for the input and output data of a node For
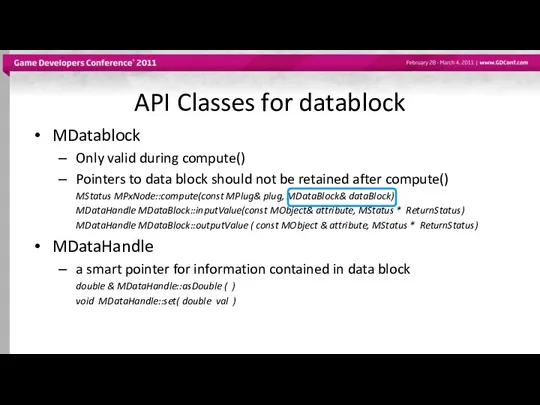
- 21. API Classes for datablock MDatablock Only valid during compute() Pointers to data block should not be
- 22. Maya Node Attributes Plugs DataBlock DataHandle MPxNode MFnAttribute MPlug MDataBlock MDataHandle
- 23. Custom Node Plug-in Implementation
- 24. Custom DG Node in Maya Entirely new operations MPxNode: base class for custom node implementation Extend
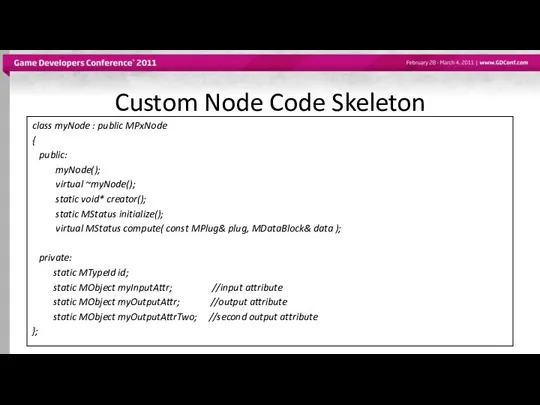
- 25. Custom Node Code Skeleton class myNode : public MPxNode { public: myNode(); virtual ~myNode(); static void*
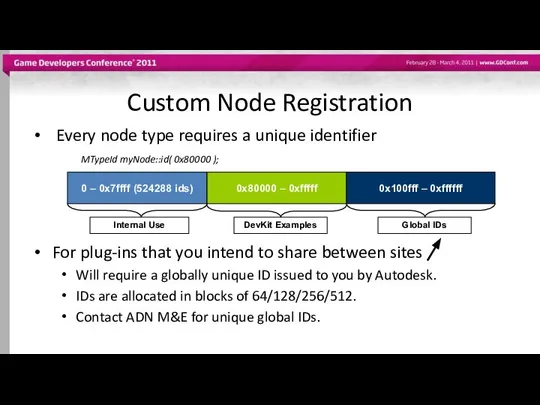
- 26. Custom Node Registration Every node type requires a unique identifier MTypeId myNode::id( 0x80000 ); For plug-ins
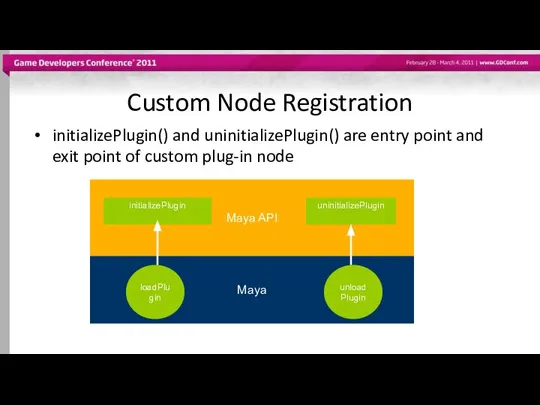
- 27. Custom Node Registration initializePlugin() and uninitializePlugin() are entry point and exit point of custom plug-in node
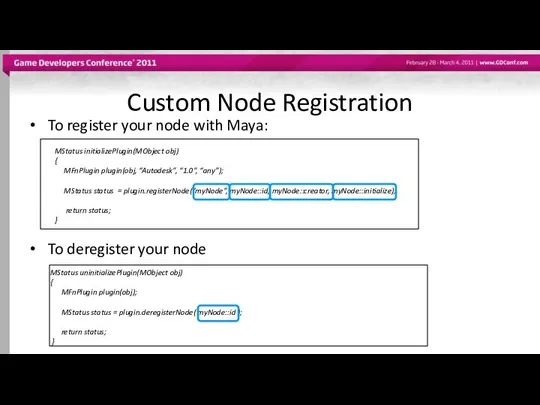
- 28. Custom Node Registration To register your node with Maya: To deregister your node MStatus initializePlugin(MObject obj)
- 29. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::creator() The creator method is called to return a new instance of
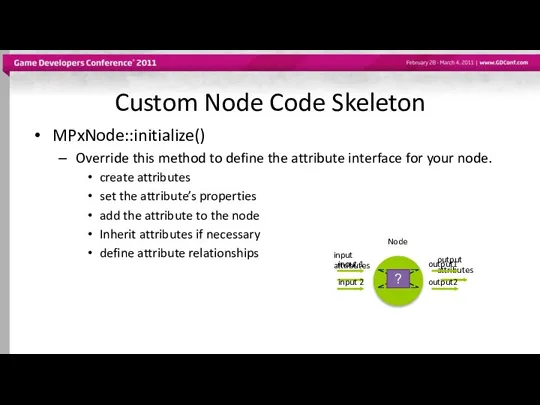
- 30. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::initialize() Override this method to define the attribute interface for your node.
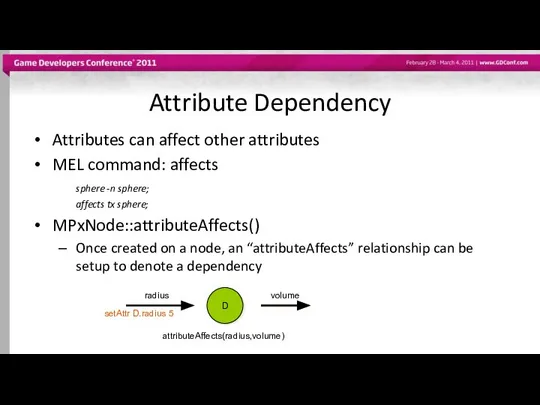
- 31. Attribute Dependency Attributes can affect other attributes MEL command: affects sphere -n sphere; affects tx sphere;
- 32. Custom Node Code Skeleton MStatus myNode::initialize() { MFnNumericAttribute nAttr; myInputAttr = nAttr.create(“myInput”, “mi”, MFnNumericData::kFloat, 1.0); nAttr.setStorable(true);
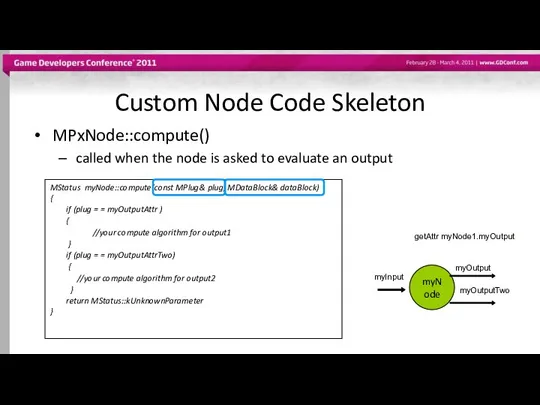
- 33. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::compute() called when the node is asked to evaluate an output MStatus
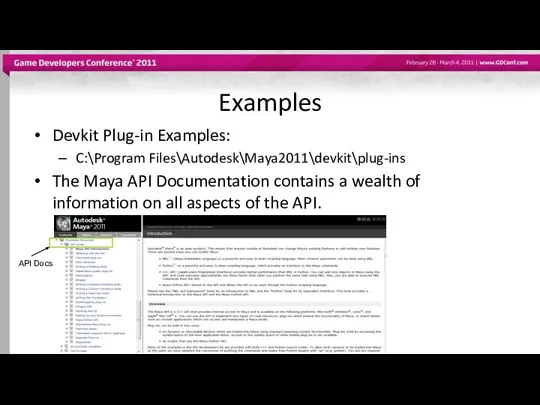
- 34. Examples Devkit Plug-in Examples: C:\Program Files\Autodesk\Maya2011\devkit\plug-ins The Maya API Documentation contains a wealth of information on
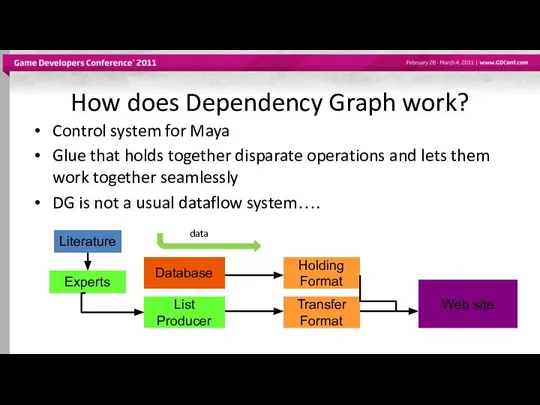
- 35. How does Dependency Graph work? Control system for Maya Glue that holds together disparate operations and
- 36. How does Dependency Graph Work? Two step Push-Pull mechanism: Dirty Propagation Evaluation
- 37. Dirty Propagation Maya DG caches values Uses dirty system to denote elements that require updating: Attributes
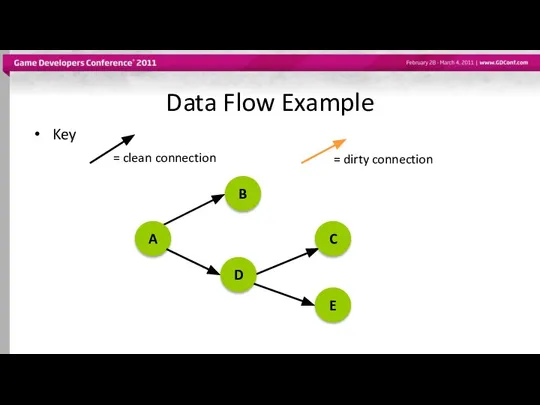
- 38. Data Flow Example Key = clean connection, = dirty connection A B D C E
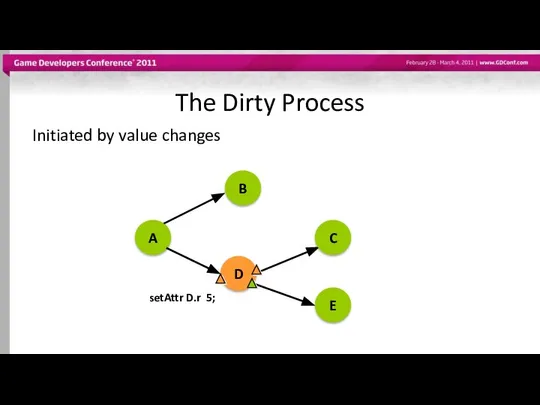
- 39. The Dirty Process Initiated by value changes setAttr D.r 5; A B D C E
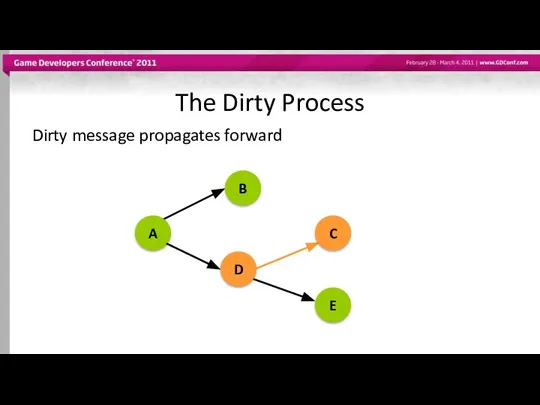
- 40. The Dirty Process Dirty message propagates forward A B D C E
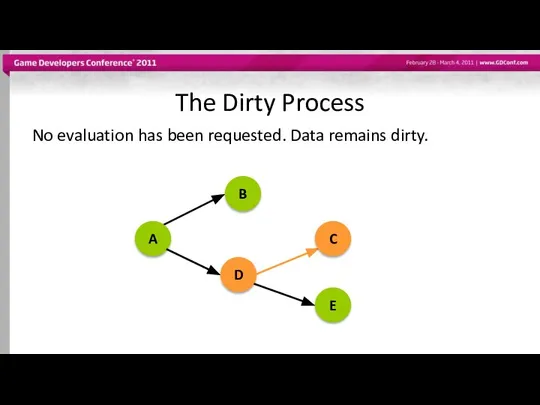
- 41. The Dirty Process No evaluation has been requested. Data remains dirty. A B D C E
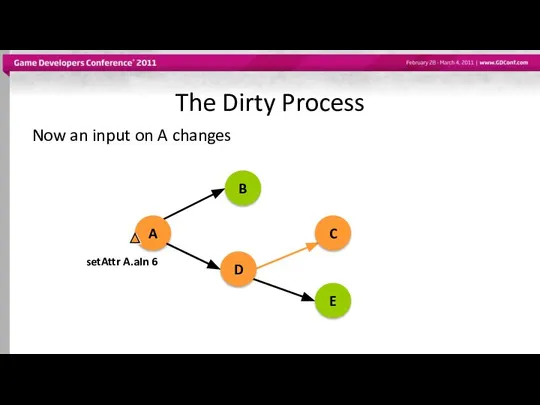
- 42. The Dirty Process Now an input on A changes setAttr A.aIn 6 A B D C
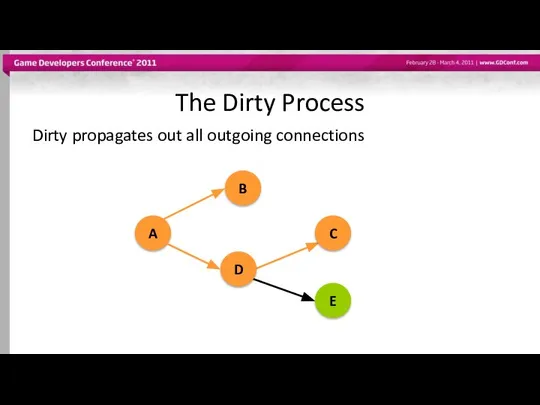
- 43. The Dirty Process Dirty propagates out all outgoing connections A B D C E
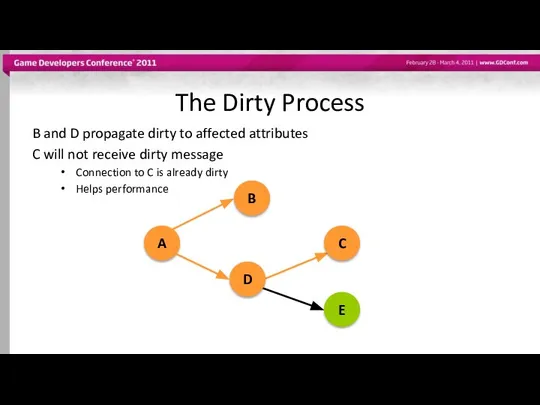
- 44. The Dirty Process B and D propagate dirty to affected attributes C will not receive dirty
- 45. The Evaluation Process Lazy Evaluation: On demand Evaluation is trigged when values are requested: Viewport refresh
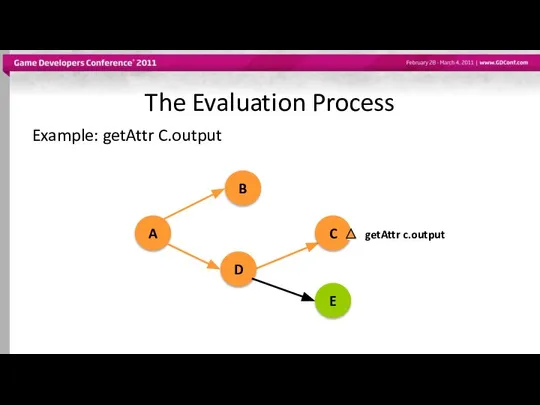
- 46. The Evaluation Process Example: getAttr C.output A B D C getAttr c.output E
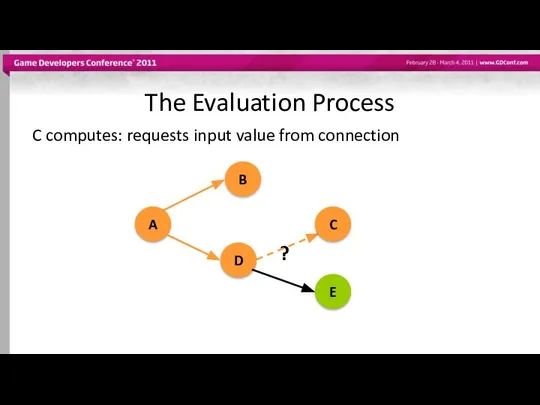
- 47. The Evaluation Process C computes: requests input value from connection ? A B D C E
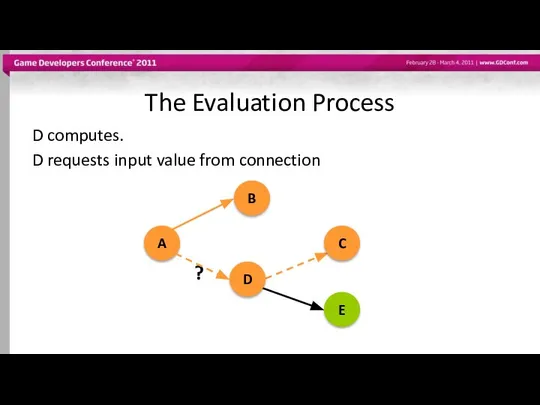
- 48. The Evaluation Process D computes. D requests input value from connection ? A B D C
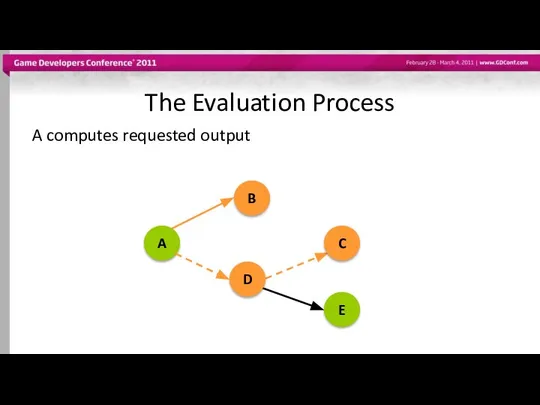
- 49. The Evaluation Process A computes requested output A B D C E
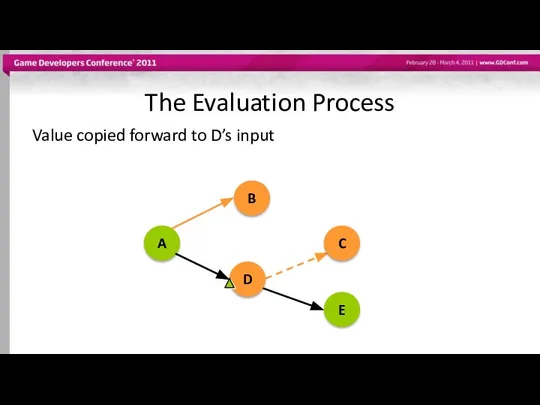
- 50. The Evaluation Process Value copied forward to D’s input A B D C E
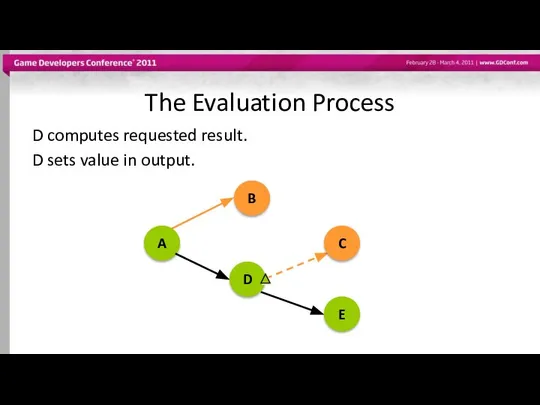
- 51. The Evaluation Process D computes requested result. D sets value in output. A B D C
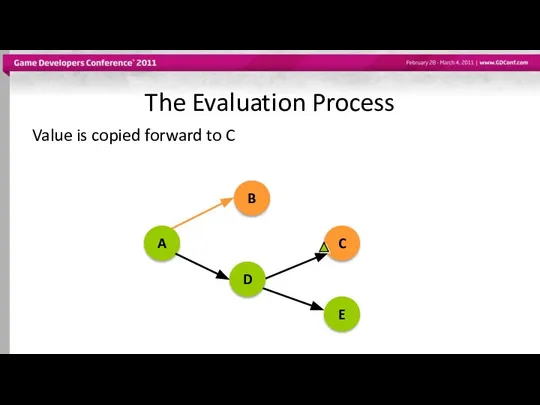
- 52. The Evaluation Process Value is copied forward to C A B D C E
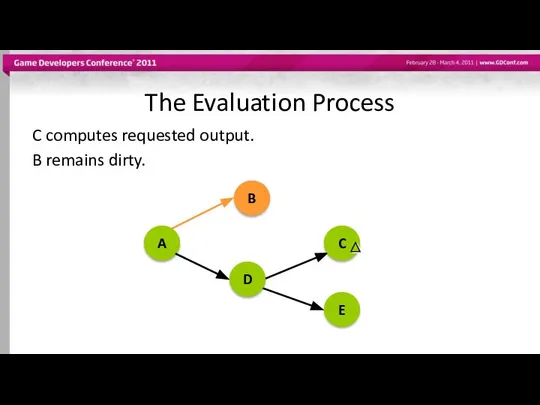
- 53. The Evaluation Process C computes requested output. B remains dirty. A B D C E
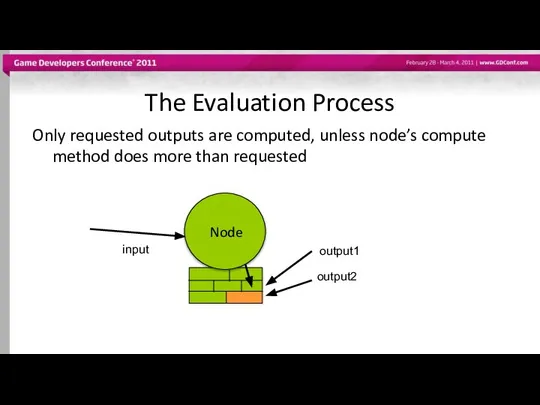
- 54. The Evaluation Process Only requested outputs are computed, unless node’s compute method does more than requested
- 55. Correct Coding with DG
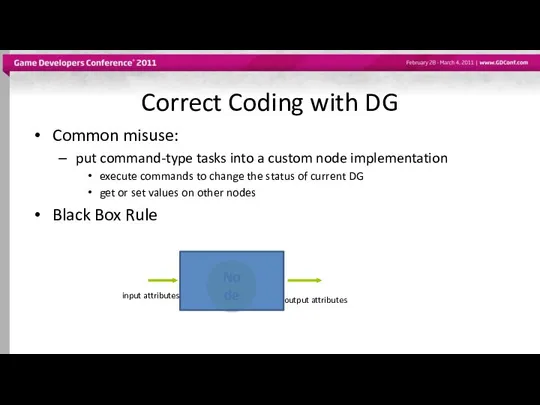
- 56. Correct Coding with DG Common misuse: put command-type tasks into a custom node implementation execute commands
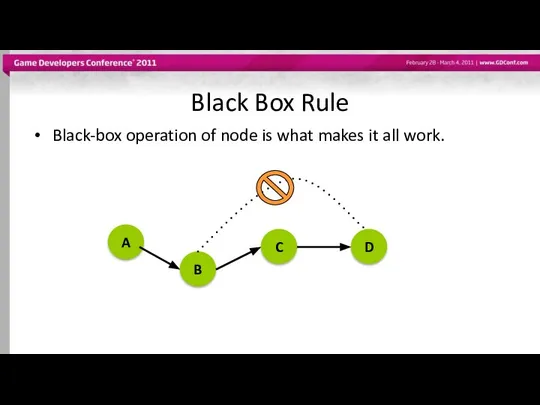
- 57. Black Box Rule Black-box operation of node is what makes it all work.
- 58. A Closer Look at MPxNode::compute() You can not control when compute() is getting called, Maya control
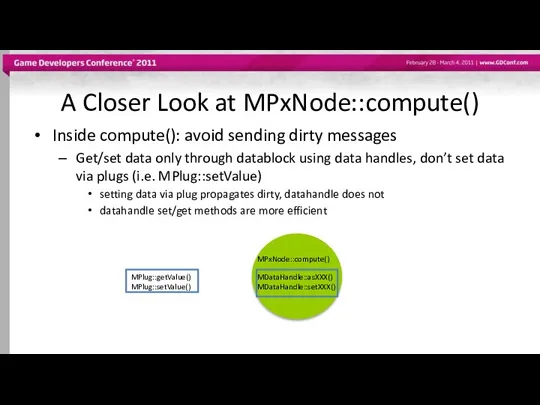
- 59. A Closer Look at MPxNode::compute() Inside compute(): avoid sending dirty messages Get/set data only through datablock
- 60. Learning Resources Maya Developer Center: http://www.autodesk.com/developmaya Questions and Problems: ADN http://www.autodesk.com/adn Maya API White Paper, DevTV,
- 61. Q & A
- 63. Скачать презентацию













 Порядок приема на работу. Порядок заключения и расторжения трудового договора
Порядок приема на работу. Порядок заключения и расторжения трудового договора ПРОГРАММА РАЗВИТИЯ ШКОЛЫ В ЛОГИКЕ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОЙ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЙ ИНИЦИАТИВЫ «НАША НОВАЯ ШКОЛА» РОССИЙСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ ПЕДАГ
ПРОГРАММА РАЗВИТИЯ ШКОЛЫ В ЛОГИКЕ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОЙ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЙ ИНИЦИАТИВЫ «НАША НОВАЯ ШКОЛА» РОССИЙСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ ПЕДАГ Изгибаемые элементы. Расчет прочности наклонных сечений железобетонных конструкций
Изгибаемые элементы. Расчет прочности наклонных сечений железобетонных конструкций О внесении изменений в Земельный кодекс Российской Федерации и отдельные законодательные акты Российской Федерации
О внесении изменений в Земельный кодекс Российской Федерации и отдельные законодательные акты Российской Федерации Мебель. Ассортимент
Мебель. Ассортимент Театр ХХ века Экспрессионизм (Германия) Футуризм (Италия) Конструктивизм (Россия) Сюрреализм (Франция)
Театр ХХ века Экспрессионизм (Германия) Футуризм (Италия) Конструктивизм (Россия) Сюрреализм (Франция) Параметры зубошевинговальных станков
Параметры зубошевинговальных станков Основные понятия. Механические характеристики материалов
Основные понятия. Механические характеристики материалов Ресвератрол – научный прорыв!
Ресвератрол – научный прорыв! Графическая информация и средства её обработки
Графическая информация и средства её обработки Внедрение информатики в УМК «Гармония», «Начальная школа 21 века» и «Школа 2000-2100» в начальной школе ,
Внедрение информатики в УМК «Гармония», «Начальная школа 21 века» и «Школа 2000-2100» в начальной школе , Политическая система России
Политическая система России Обучение охране труда
Обучение охране труда Минимализм
Минимализм Наладчики аппаратно-программного обеспечения. Области применения профессии
Наладчики аппаратно-программного обеспечения. Области применения профессии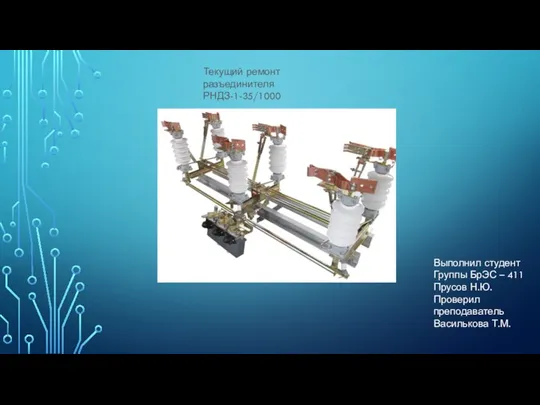 Текущий ремонт разъединителя РНДЗ-1-35/1000
Текущий ремонт разъединителя РНДЗ-1-35/1000 Viera Plasma Display. PC Board Recycling. Component Level Repair
Viera Plasma Display. PC Board Recycling. Component Level Repair Урок развития речи во 2 классе МОУ гимназии №9 Изложение по готовому плану учитель Сизонова Ирина Александровна
Урок развития речи во 2 классе МОУ гимназии №9 Изложение по готовому плану учитель Сизонова Ирина Александровна Политические партии и движения
Политические партии и движения Імпульсні модулятори (заняття № 3.1)
Імпульсні модулятори (заняття № 3.1) Иерархическая система многоуровневой организации ЭВМ
Иерархическая система многоуровневой организации ЭВМ Проектирование Последовательных схем
Проектирование Последовательных схем Презентация на тему "22" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "22" - скачать презентации по Медицине Кубок Love Radio по мини-футболу. Самый яркий праздник спорта и весны!
Кубок Love Radio по мини-футболу. Самый яркий праздник спорта и весны! Языки программирования
Языки программирования Платон и Аристотель об обществе и государстве.
Платон и Аристотель об обществе и государстве.  Средообразующая и рекреационная роль леса
Средообразующая и рекреационная роль леса Архітектура .NET. Основи C#
Архітектура .NET. Основи C#