Содержание
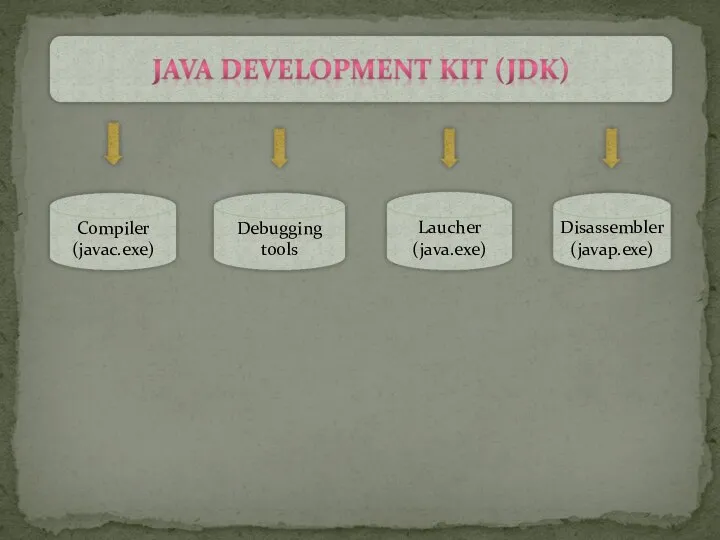
- 2. Java Developer Kit contains tools needed to develop the Java programs, and JRE to run the
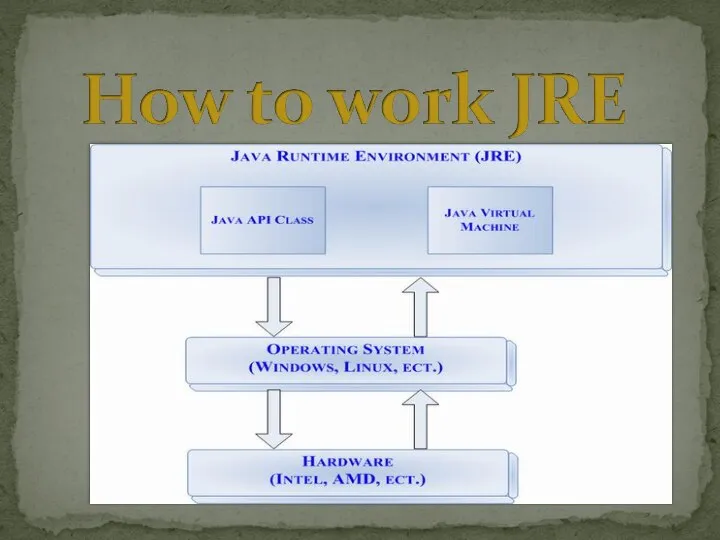
- 3. Java Runtime Environment contains JVM, class libraries, and other supporting files. It does not contain any
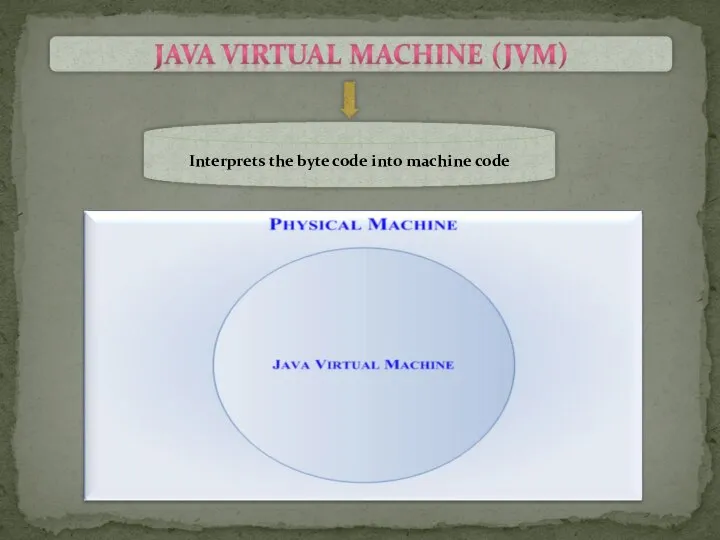
- 4. Java Virtual Machine interprets the byte code into the machine code depending upon the underlying operating
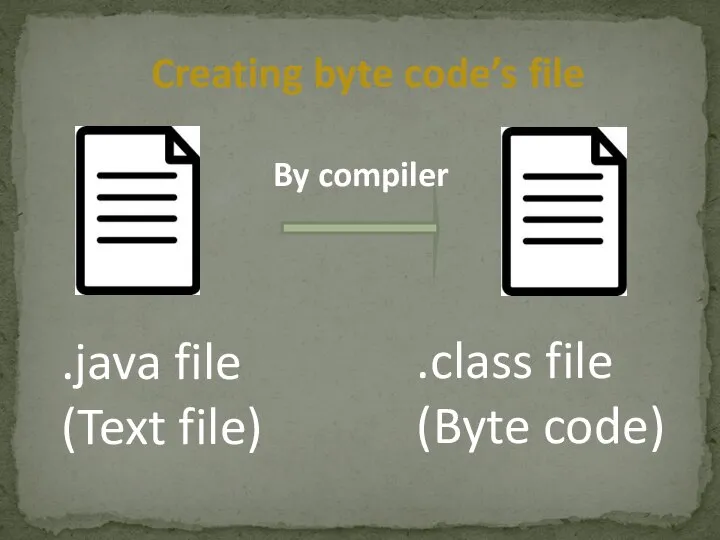
- 8. .java file (Text file) .class file (Byte code) By compiler Creating byte code’s file
- 9. int count; // create variable count Gets compiled to the following byte code: 0: iconst_0 //Push
- 11. Byte data type is an 8-bit signed two's complement integer. Minimum value is -128 (-2^7) Maximum
- 12. Short data type is a 16-bit signed two's complement integer. Minimum value is -32,768 (-2^15) Maximum
- 13. Int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer. Minimum value is - 2,147,483,648.(-2^31) Maximum
- 14. Long data type is a 64-bit signed two's complement integer. Minimum value is -9,223,372,036,854,775,808.(-2^63) Maximum value
- 15. Float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Minimum value is 3, 4
- 16. double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Minimum value is 1,7 *
- 17. boolean data type represents one bit of information. There are only two possible values: true and
- 19. Скачать презентацию












 Фотосинтез
Фотосинтез  Игрушки народов мира. Русская народная игрушка
Игрушки народов мира. Русская народная игрушка ГОСТ 2.305-2008. Изображения – виды, разрезы, сечения
ГОСТ 2.305-2008. Изображения – виды, разрезы, сечения Воображение и речь
Воображение и речь Инсей Лига Го
Инсей Лига Го Использование диаграмм Эйлера-Венна при решении логических задач
Использование диаграмм Эйлера-Венна при решении логических задач МЕНЕДЖМЕНТ И ОРГАНИЗАЦИОННАЯ ДЕМОКРАТИЯ
МЕНЕДЖМЕНТ И ОРГАНИЗАЦИОННАЯ ДЕМОКРАТИЯ Актиномикозы
Актиномикозы  Презентация по ОБЖ Оползни, сели, обвалы, лавины.
Презентация по ОБЖ Оползни, сели, обвалы, лавины.  Потребности человека Потребности – это малоуправляемые побудители действий; состояние живого существа, выражающие зависимос
Потребности человека Потребности – это малоуправляемые побудители действий; состояние живого существа, выражающие зависимос Madonny
Madonny Музыкальные инструменты
Музыкальные инструменты Международный фестиваль юных дарований «Золотой мост. Рейс Москва – Прага»
Международный фестиваль юных дарований «Золотой мост. Рейс Москва – Прага» Туберкулинодиагностика
Туберкулинодиагностика  Нормы оценки знаний, умений и навыков
Нормы оценки знаний, умений и навыков Усадьба Остафьево
Усадьба Остафьево INFA
INFA Инструментальные программы
Инструментальные программы  Презентация на тему "Права человека класификация прав человека" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Права человека класификация прав человека" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Аналитическая геометрия на плоскости
Аналитическая геометрия на плоскости Система профилактики безнадзорности и правонарушений несовершеннолетних. Дом молодежи «Маяк». Взаимодействие
Система профилактики безнадзорности и правонарушений несовершеннолетних. Дом молодежи «Маяк». Взаимодействие Масленица. Картины русских художников
Масленица. Картины русских художников спектроск. методы. Атомная спектр.Л.7
спектроск. методы. Атомная спектр.Л.7 Болезни крови
Болезни крови Презентация Процесс управления маркетингом
Презентация Процесс управления маркетингом Арифметическая прогрессия 9 класс - презентация по Алгебре
Арифметическая прогрессия 9 класс - презентация по Алгебре Презентация Естественная монополия
Презентация Естественная монополия Классная работа. Пропорции.
Классная работа. Пропорции.