Содержание
- 2. PHYSICAL VIEW A phoneme may be described roughly as a family of sounds consisting of an
- 3. A phoneme is a class of phonetically similar sounds, contrasting and mutually exclusive with all similar
- 4. Lena cleans a pool. [lʲi:nə klʲ˳i:nz ə pʰu:ɫ] lʲ, lʲ˳, ɫ - members of the “family”
- 5. CRITISIZING A phoneme is a mechanical sum of its allophones. This definition is vulgarly materialistic and
- 6. TO SUM UP A phoneme is a family of related speech sounds. Supporters: D. Jones, B.
- 7. FUNCTIONAL VIEW A phoneme is the minimal sound unit by which meanings may be differentiated without
- 8. R. JAKOBSON AND M. HALLE DISTINCTIVE FEATURE THEORY All features are privative (i.e. binary). There is
- 9. DISTINCTIVE FEATURES In 1956, Jakobson and Halle devised 12 distinctive features. E.g., the phoneme /m/ might
- 11. Скачать презентацию


![Lena cleans a pool. [lʲi:nə klʲ˳i:nz ə pʰu:ɫ] lʲ, lʲ˳, ɫ](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1308662/slide-3.jpg)





 Кафедра акушерства и гинекологии №1 Лектор: доцент Ш.М. Садуакасова
Кафедра акушерства и гинекологии №1 Лектор: доцент Ш.М. Садуакасова  Политический режим
Политический режим Благовещение Пресвятой Богородицы
Благовещение Пресвятой Богородицы Макроэкономика. Тема 5. Безработица Малышев Денис Перфильевич
Макроэкономика. Тема 5. Безработица Малышев Денис Перфильевич  Молитва
Молитва Иов Многострадальный
Иов Многострадальный Жизнь на уроке должна стать подлинной Полякова Наталья Петровна МОУ Комсомольская средняя общеобразовательная школа
Жизнь на уроке должна стать подлинной Полякова Наталья Петровна МОУ Комсомольская средняя общеобразовательная школа Заболеваемость, инвалидность населения. Общие положения регистрации
Заболеваемость, инвалидность населения. Общие положения регистрации И.А.Крылов «Чиж и голубь» 3 класс Учитель начальных классов МКОУ «ТШИ», п. Тазовский Беспалая Ирина Феликсовна
И.А.Крылов «Чиж и голубь» 3 класс Учитель начальных классов МКОУ «ТШИ», п. Тазовский Беспалая Ирина Феликсовна Тема: ПОВЫШЕНИЕ КАЧЕСТВА ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ В УСЛОВИЯХ СОЦИАЛЬНО-ГУМАНИТАРНОЙ НАПРАВЛЕННОСТИ УЧЕБНО-ВОСПИТАТЕЛЬНОГО ПРОЦЕССА
Тема: ПОВЫШЕНИЕ КАЧЕСТВА ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ В УСЛОВИЯХ СОЦИАЛЬНО-ГУМАНИТАРНОЙ НАПРАВЛЕННОСТИ УЧЕБНО-ВОСПИТАТЕЛЬНОГО ПРОЦЕССА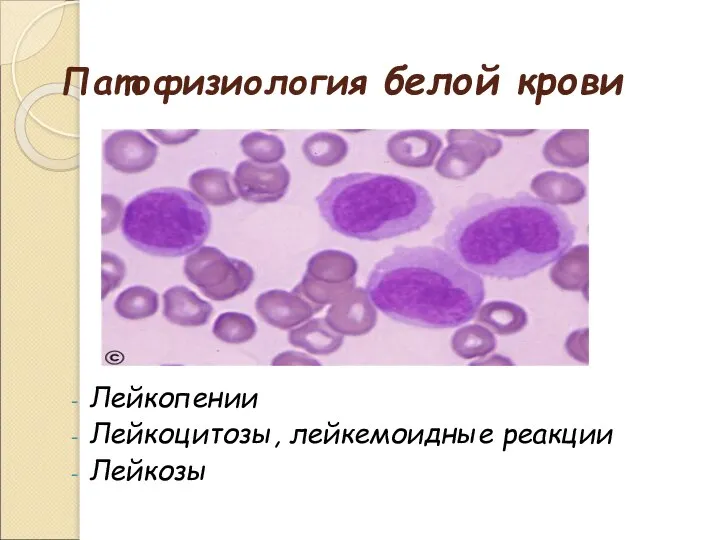 Патофизиология белой крови
Патофизиология белой крови Управление грошовими потоками
Управление грошовими потоками Николай Алексеевич Некрасов 1821-1877
Николай Алексеевич Некрасов 1821-1877 Основные международные НПА, с требованием которых необходимо соотносить семейное право России
Основные международные НПА, с требованием которых необходимо соотносить семейное право России Игра по философии О философия, вождь жизни!.. Ты породила города, ты созвала разрозненных людей в сообщество жизни
Игра по философии О философия, вождь жизни!.. Ты породила города, ты созвала разрозненных людей в сообщество жизни  Политическая система США
Политическая система США Имитатор электороакустических первичных преобразователей
Имитатор электороакустических первичных преобразователей Презентация на тему: Формы мышления
Презентация на тему: Формы мышления Методические рекомендации по оформлению ВКР
Методические рекомендации по оформлению ВКР EDU 6005 : cours 8. Introduction à la profession enseignante au primaire
EDU 6005 : cours 8. Introduction à la profession enseignante au primaire Deutscher Rap
Deutscher Rap Лучевая диагностика
Лучевая диагностика  Саяси режим және оның түрлері
Саяси режим және оның түрлері Финансовое право. Тема 6
Финансовое право. Тема 6 Repository and Unit of Work
Repository and Unit of Work Две забавные истории - презентация для начальной школы
Две забавные истории - презентация для начальной школы Основные свойства строительных материалов
Основные свойства строительных материалов Semyuel_Morze__telegraf_i_kod
Semyuel_Morze__telegraf_i_kod