Содержание
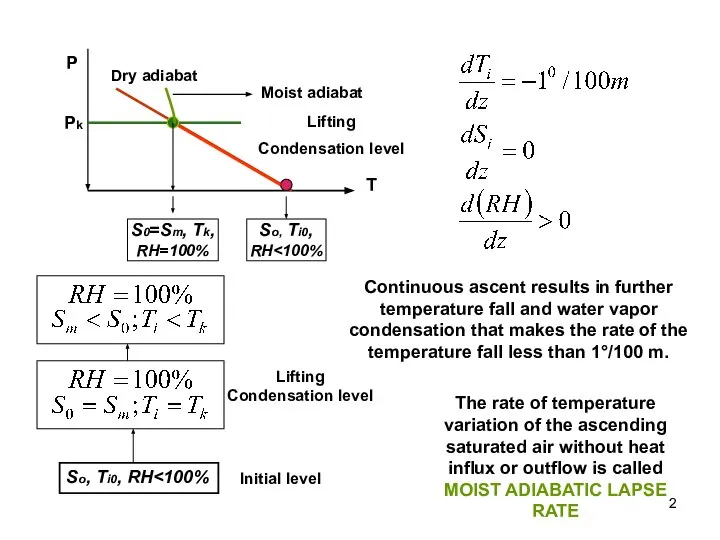
- 2. So, Ti0, RH S0=Sm, Tk, RH=100% Pk Lifting Condensation level Moist adiabat Continuous ascent results in
- 3. From the above reasoning it follows: Temperature of an ascending parcel of air decreases with height,
- 4. First law of thermodynamics for the moist, saturated air Suppose a parcel of the saturated air
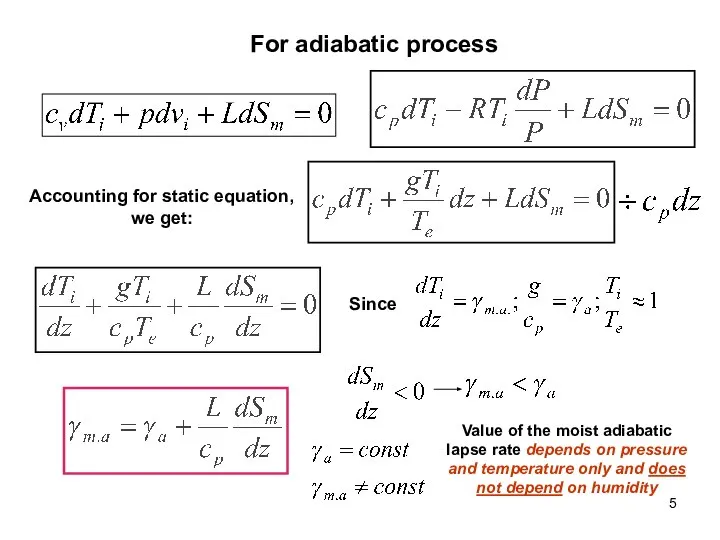
- 5. For adiabatic process Accounting for static equation, we get: Since Value of the moist adiabatic lapse
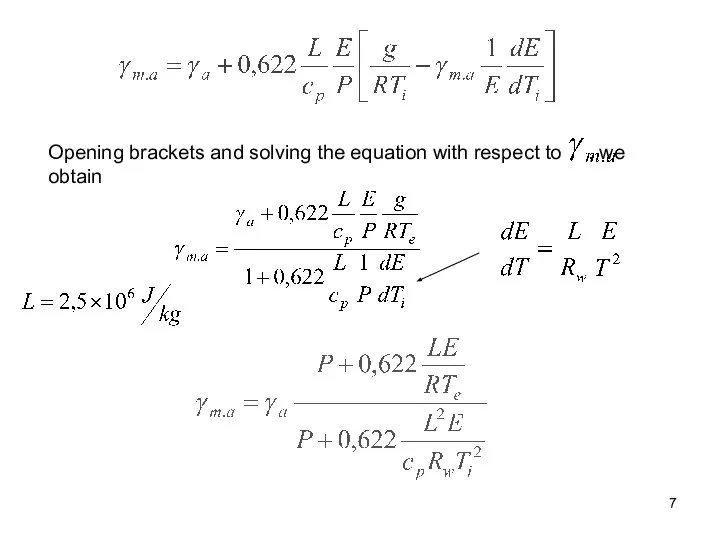
- 7. Opening brackets and solving the equation with respect to , we obtain
- 8. Values of the moist adiabatic lapse rate at different temperature and pressure
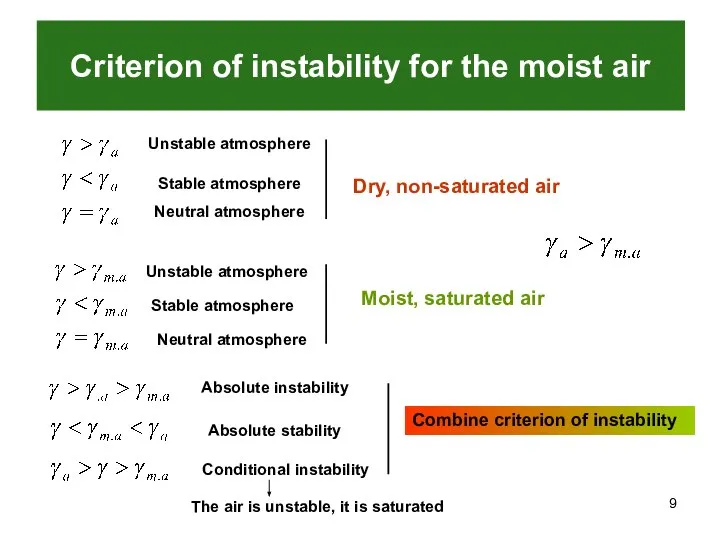
- 9. Criterion of instability for the moist air Unstable atmosphere Stable atmosphere Neutral atmosphere Dry, non-saturated air
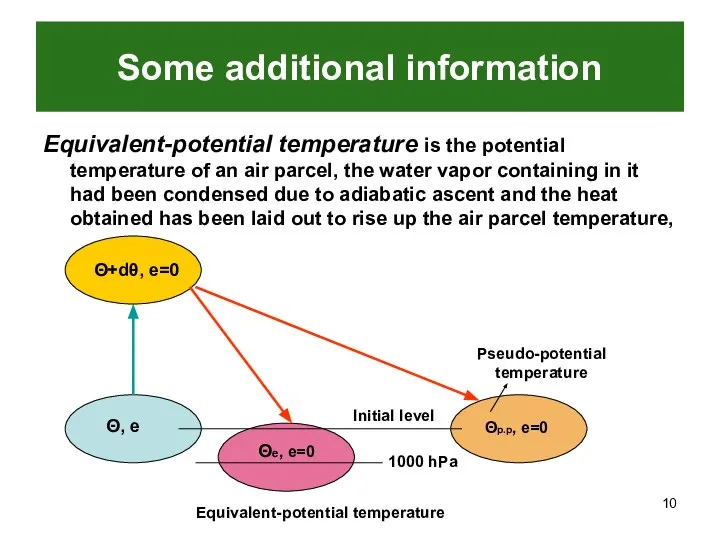
- 10. Some additional information Equivalent-potential temperature is the potential temperature of an air parcel, the water vapor
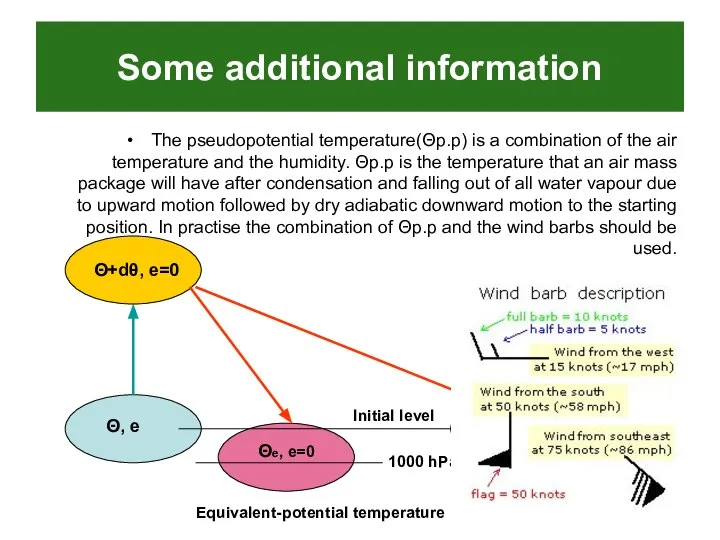
- 11. Some additional information The pseudopotential temperature(Θp.p) is a combination of the air temperature and the humidity.
- 13. Скачать презентацию




 Модульное программирование. (Лекция 15)
Модульное программирование. (Лекция 15) Новосибирский государственный краеведческий музей
Новосибирский государственный краеведческий музей Презентация "Кристоф Виллибальд Глюк" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Кристоф Виллибальд Глюк" - скачать презентации по МХК 432506
432506 Презентация на тему "Педагогическое общение" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Педагогическое общение" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Mein Lieblingssänger heißt Mot
Mein Lieblingssänger heißt Mot Известные вирусы гепатита человека
Известные вирусы гепатита человека Алгоритмы обработки массивов
Алгоритмы обработки массивов Не демократические республики
Не демократические республики Сервистік қызмет көрсету логистикасы
Сервистік қызмет көрсету логистикасы Влияние стимуляторов роста на развитие и рост растений
Влияние стимуляторов роста на развитие и рост растений Оптимизация запросов
Оптимизация запросов Введение в проектирование по предметной области (DDD)
Введение в проектирование по предметной области (DDD) Синдром дыхательной недостаточности
Синдром дыхательной недостаточности Вір, душе, надійся
Вір, душе, надійся Отчёт-презентация. Прохождение практики ОАО «НПО «Квант»
Отчёт-презентация. Прохождение практики ОАО «НПО «Квант» Презентация Таможенная статистика и анализ
Презентация Таможенная статистика и анализ Платы и модули Arduino
Платы и модули Arduino Художественная культура Китая
Художественная культура Китая IBM电子商务解决 方案设计
IBM电子商务解决 方案设计 Презентация____
Презентация____ Основи програмування та алгоритмічні мови
Основи програмування та алгоритмічні мови Синтоизм - традиционная религия в Японии
Синтоизм - традиционная религия в Японии Спортивні ігри
Спортивні ігри Викторина. Пасха
Викторина. Пасха Развитие силовых способностей у школьников 10-11 классов во внеурочное время
Развитие силовых способностей у школьников 10-11 классов во внеурочное время Ионный обмен
Ионный обмен .9
.9