Содержание
- 2. Words can be cut up into units called syllables. Syllable is a unit of spoken language
- 3. Determine how many syllables are in the following words: Emily Trevor Suzy Restroom Recess Book Environment
- 4. Syllables and their parts The parts are onset and rhyme; within the rhyme we find the
- 5. Onset (O) Onset: the beginning sounds of the syllable; the ones preceding the nucleus. These are
- 6. Rhyme (R) Rhyme (or rime): the rest of the syllable, after the onset (the underlined portions
- 7. Nucleus (N) is the core or essential part of a syllable. A nucleus must be present
- 8. [ l ] and the nasals [ m n ] become syllable nuclei when they follow
- 9. Coda (C) Coda is the ending sound of the syllable, the ones preceding the nucleus. These
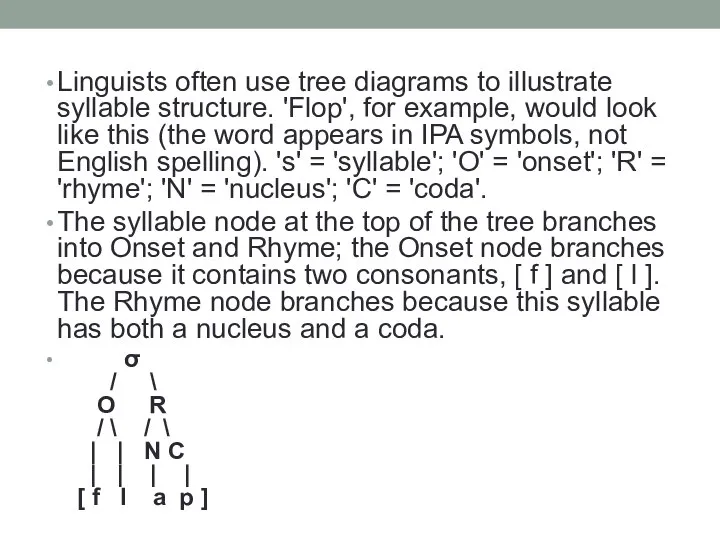
- 10. Linguists often use tree diagrams to illustrate syllable structure. 'Flop', for example, would look like this
- 11. Steps to determine the diagram: Determine the nucleus (N) Add Rhyme ( R ) on the
- 12. If a syllable has the coda, it is called as closed syllable Example : cap, sit,
- 13. Draw, the syllable structure of the following words: apron basic began begin depend even hotel
- 14. Syllables and Clusters A syllable must contain a vowel or a vowel-like sound. The most common
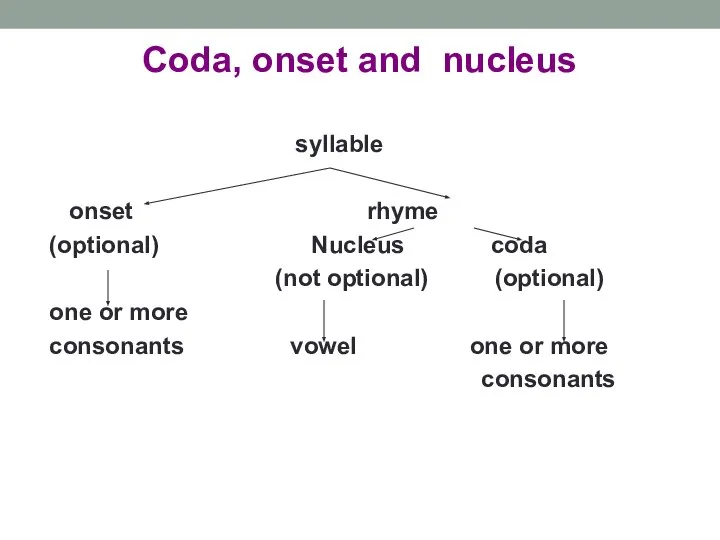
- 15. Coda, onset and nucleus syllable onset rhyme (optional) Nucleus coda (not optional) (optional) one or more
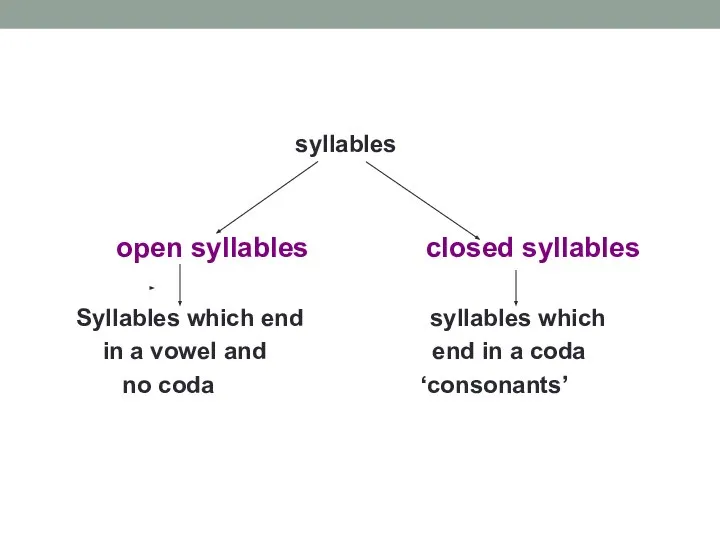
- 16. syllables open syllables closed syllables Syllables which end syllables which in a vowel and end in
- 17. Consonant clusters: both the onset and the coda can consist of more that one consonant e.g.
- 18. Syllabic consonants Sometimes when a vowel is elided a consonant can become a syllabic nucleus. Only
- 19. Syllables and stress Some syllables are more prominent than others. These are termed ‘stressed’ syllables. Stress
- 21. Скачать презентацию






![[ l ] and the nasals [ m n ] become](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1305522/slide-7.jpg)








 роль государственных финансов в социально-экономическом развитии общества Выполнила: Галибина Любовь Студентка 2 курса ФТД гр
роль государственных финансов в социально-экономическом развитии общества Выполнила: Галибина Любовь Студентка 2 курса ФТД гр ПРОИЗВОДСТВО ИНУЛИНА
ПРОИЗВОДСТВО ИНУЛИНА Масленица
Масленица Прилади спін-хвильової електроніки
Прилади спін-хвильової електроніки Jasnogórska Pani
Jasnogórska Pani Современная предпринимательсткая среда
Современная предпринимательсткая среда Перкуссия сердца
Перкуссия сердца Оценка потенциальных возможностей компании по освоению внешнего рынка
Оценка потенциальных возможностей компании по освоению внешнего рынка Культура и быт России в XVII веке
Культура и быт России в XVII веке Педагогический совет «Новые образовательные стандарты: программа духовно-нравственного развития» Использование социально-обра
Педагогический совет «Новые образовательные стандарты: программа духовно-нравственного развития» Использование социально-обра Проблемы связанные с оценкой и реализацией ИННОВАЦИОННЫХ ПРОЕКТОВ
Проблемы связанные с оценкой и реализацией ИННОВАЦИОННЫХ ПРОЕКТОВ  Венчурные инновационные предприятия
Венчурные инновационные предприятия  Презентация ИСТОРИЯ КОСТЮМА
Презентация ИСТОРИЯ КОСТЮМА  Презентация Пушно-меховые товары
Презентация Пушно-меховые товары Витамин А – Ретинол; 2. Витамин Е – Токоферол; 3. Витамин Д – Эргокальциферол
Витамин А – Ретинол; 2. Витамин Е – Токоферол; 3. Витамин Д – Эргокальциферол Що або хто це?
Що або хто це? Международные отношения на ближнем и среднем Востоке. Роль НАТО и её трансформация
Международные отношения на ближнем и среднем Востоке. Роль НАТО и её трансформация Классификация стен
Классификация стен Поздние гестозы
Поздние гестозы Антифизика в супергеройских фильмах
Антифизика в супергеройских фильмах Обувь с самоподтягивающимися шнурками. Бизнес-план
Обувь с самоподтягивающимися шнурками. Бизнес-план Тема: Платежный баланс как отражение международных валютно-кредитных операций страны
Тема: Платежный баланс как отражение международных валютно-кредитных операций страны  Принципы проектирования машин
Принципы проектирования машин Числовые последовательности Устинова Н.Г., лицей №1.
Числовые последовательности Устинова Н.Г., лицей №1. Особенности работы с объемными объектами дизайна
Особенности работы с объемными объектами дизайна Библиотека UTIL.LIB. Программный и аппаратный ШИМ регуляторы (на примере пакета CoDeSys)
Библиотека UTIL.LIB. Программный и аппаратный ШИМ регуляторы (на примере пакета CoDeSys) Залог в вузовских учебниках
Залог в вузовских учебниках Создание нового поколения перестраиваемых рентгеновских источников на основе мультичастотной рентгеновской трубки
Создание нового поколения перестраиваемых рентгеновских источников на основе мультичастотной рентгеновской трубки