Содержание
- 2. Memory flash ;) Please, give definitions to the following terms: Absolute humidity Specific humidity Surface layer
- 3. Non stop rotation of water in the atmosphere http://www.meted.ucar.edu/mesoprim/mesodefn/index.htm How much is the amount of water
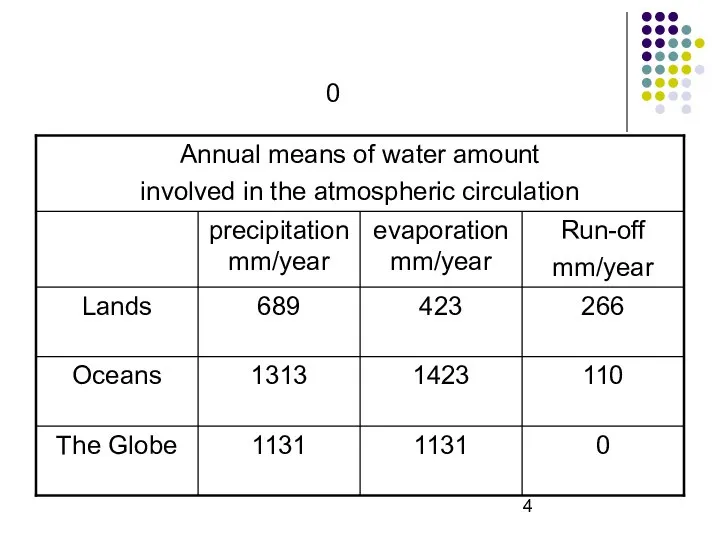
- 4. 0
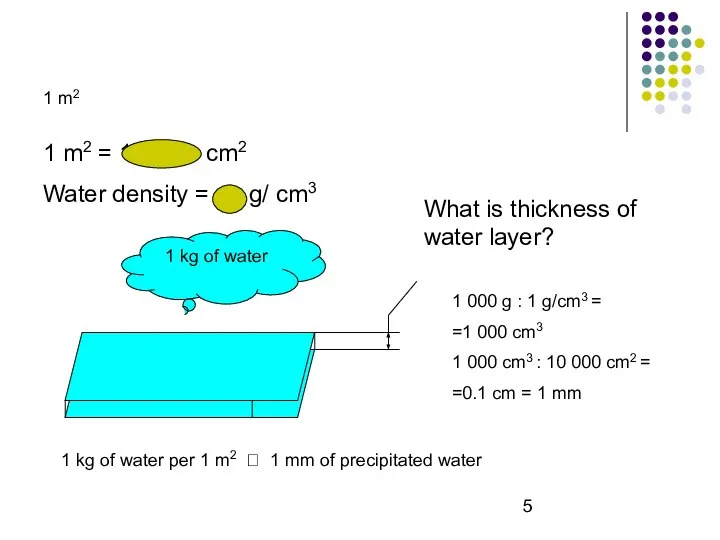
- 5. 1 m2 1 m2 1 m2 = 10 000 cm2 Water density = 1 g/ cm3
- 6. Annual amount of precipitation Spb 680 mm, Wien 300 mm, Amsterdam 1200 mm Tropics 680 mm/
- 7. 1131 / 25.5=45 times or every 8 days 1.29 *10 13 t of water in the
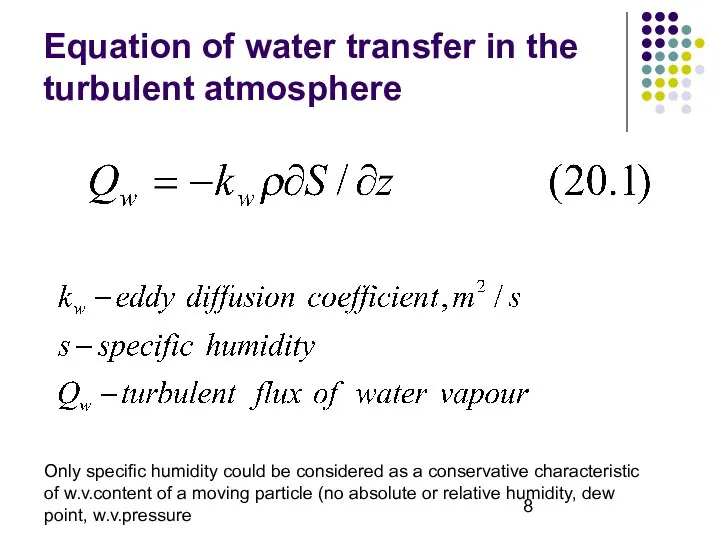
- 8. Equation of water transfer in the turbulent atmosphere Only specific humidity could be considered as a
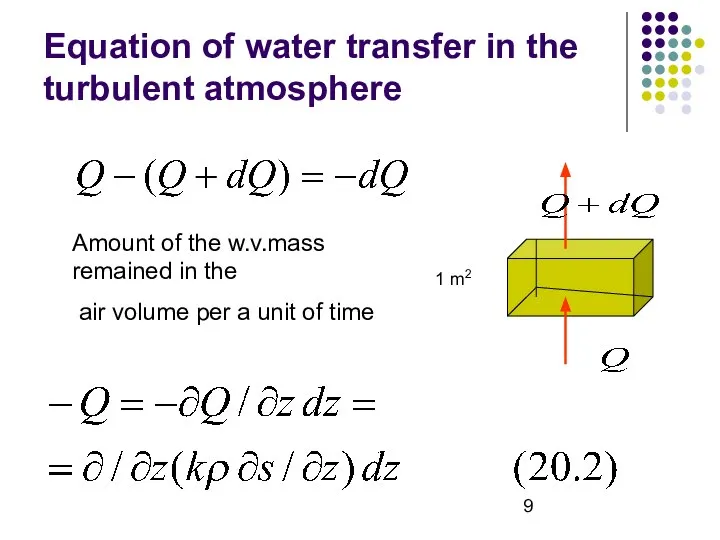
- 9. Equation of water transfer in the turbulent atmosphere 1 m2 Amount of the w.v.mass remained in
- 10. Advective terms could be neglected (too small) Advective terms could be neglected (too small)
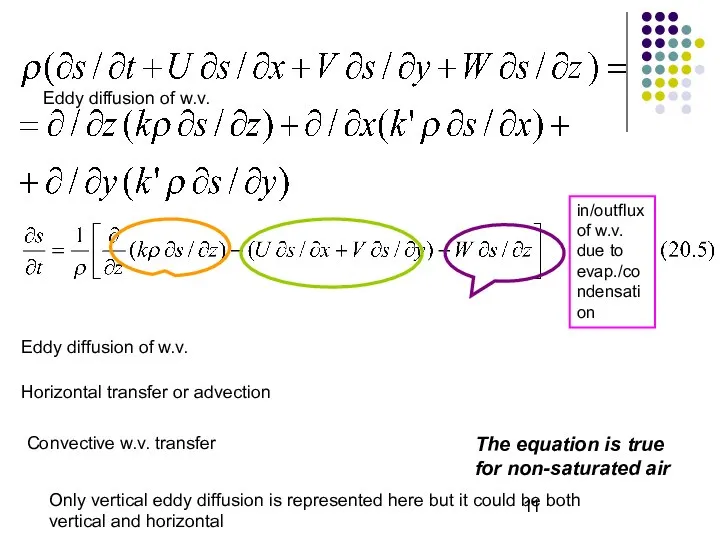
- 11. Eddy diffusion of w.v. Eddy diffusion of w.v. Horizontal transfer or advection Convective w.v. transfer Only
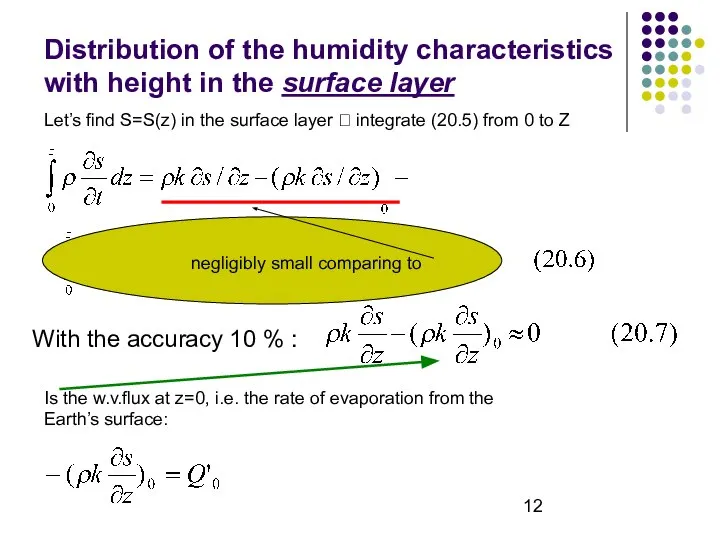
- 12. Distribution of the humidity characteristics with height in the surface layer Let’s find S=S(z) in the
- 13. (20.8) shows that the w.v. eddy flux in the surface layer can be regarded as approximately
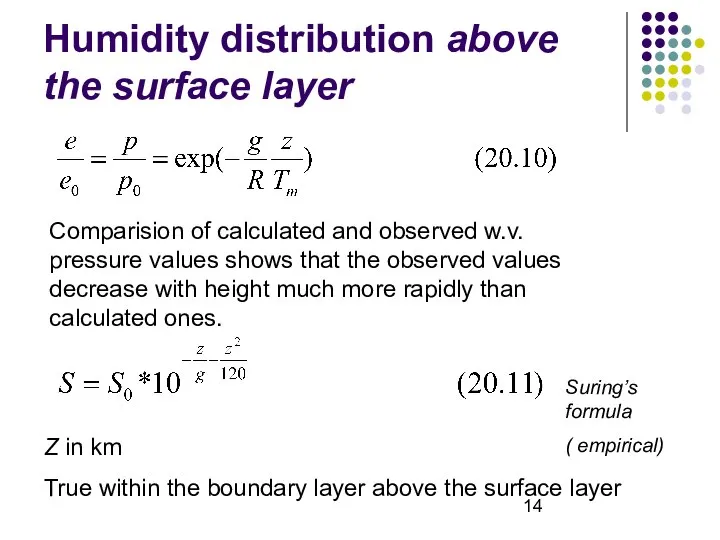
- 14. Humidity distribution above the surface layer Comparision of calculated and observed w.v. pressure values shows that
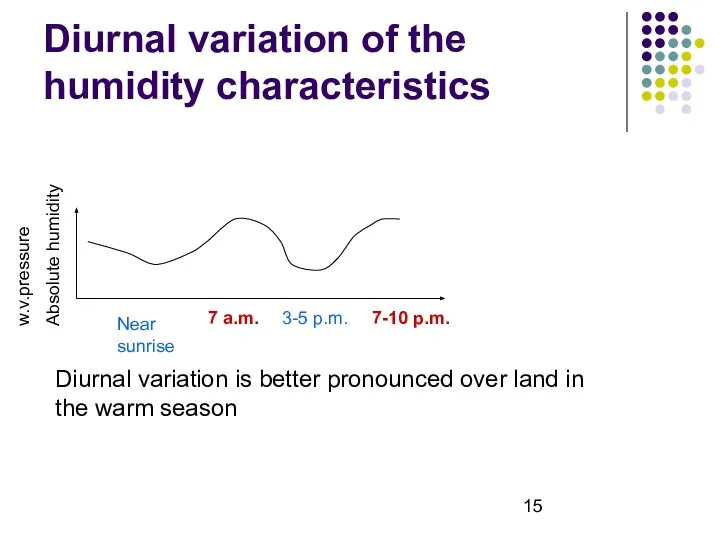
- 15. Diurnal variation of the humidity characteristics Near sunrise 7 a.m. 3-5 p.m. 7-10 p.m. Diurnal variation
- 17. Скачать презентацию






 Межнациональные особенности невербального общения Выполнила студентка группы Ю-104 Чуева Яна
Межнациональные особенности невербального общения Выполнила студентка группы Ю-104 Чуева Яна Основы общественного производства. Воспроизводство и его фазы.
Основы общественного производства. Воспроизводство и его фазы. Образовательная технология «Портфолио»
Образовательная технология «Портфолио» Агбис
Агбис Движения земной коры
Движения земной коры Вербное воскресение. Неделя перед Пасхой
Вербное воскресение. Неделя перед Пасхой Презентация на тему "Инфекционная иммунология" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "Инфекционная иммунология" - скачать презентации по Медицине Четыре вида стиля интерьера: ампир, классический, модерн, Ар Деко
Четыре вида стиля интерьера: ампир, классический, модерн, Ар Деко Современное состояние системы подготовки спортивного резерва в Пермском крае
Современное состояние системы подготовки спортивного резерва в Пермском крае От фантазии к реализации
От фантазии к реализации Олимпийские игры в древней Греции: система обслуживания спортсменов и гостей
Олимпийские игры в древней Греции: система обслуживания спортсменов и гостей Зимующие птицы Автор презентации: Калмычкова Е.В., учитель начальных классов ГБОУ СОШ 1980 города Москвы.
Зимующие птицы Автор презентации: Калмычкова Е.В., учитель начальных классов ГБОУ СОШ 1980 города Москвы. Основные направления применения педагогических средств восстановления
Основные направления применения педагогических средств восстановления Шайхиева Надежда Ивановна, учитель изобразительного искусства МОБУ СОШ№3 им.Ю.Гагарина г. Таганрога Ростовской области
Шайхиева Надежда Ивановна, учитель изобразительного искусства МОБУ СОШ№3 им.Ю.Гагарина г. Таганрога Ростовской области Анализ переходных процессов классическим методом в цепях с одним реактивным элементом. (Лекция 3)
Анализ переходных процессов классическим методом в цепях с одним реактивным элементом. (Лекция 3) Презентация "Роль денег в регулировании экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Роль денег в регулировании экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике Презентация на тему "Использование метода проектов в начальной школе" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Использование метода проектов в начальной школе" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Разработка Web-технологий в сопровождении НОЦ
Разработка Web-технологий в сопровождении НОЦ Chesotka
Chesotka Организация транспортного обслуживания международных экономических связей
Организация транспортного обслуживания международных экономических связей Презентация____
Презентация____ Презентация на тему "Рефлекс. Рефлекторная дуга" - скачать презентации по Медицине
Презентация на тему "Рефлекс. Рефлекторная дуга" - скачать презентации по Медицине Виды и системы безопасности
Виды и системы безопасности  Основные понятия языка
Основные понятия языка Основы технологической культуры Технология трудовой деятельности Степанова Лариса Иосифовна, учитель технологии МОУ «ТСОШ №3»
Основы технологической культуры Технология трудовой деятельности Степанова Лариса Иосифовна, учитель технологии МОУ «ТСОШ №3» Презентация "Авторское кино в России" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Авторское кино в России" - скачать презентации по МХК ГРОСС ГАНС и его основные идеи в криминалистике и юридической психологии. Подготовила: Студентка 2 курса Группы Юб03/1303 Шестёр
ГРОСС ГАНС и его основные идеи в криминалистике и юридической психологии. Подготовила: Студентка 2 курса Группы Юб03/1303 Шестёр Глава 1 Принципы экономики 3. Рыночная система экономики
Глава 1 Принципы экономики 3. Рыночная система экономики