Содержание
- 2. A cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the last link is wireless
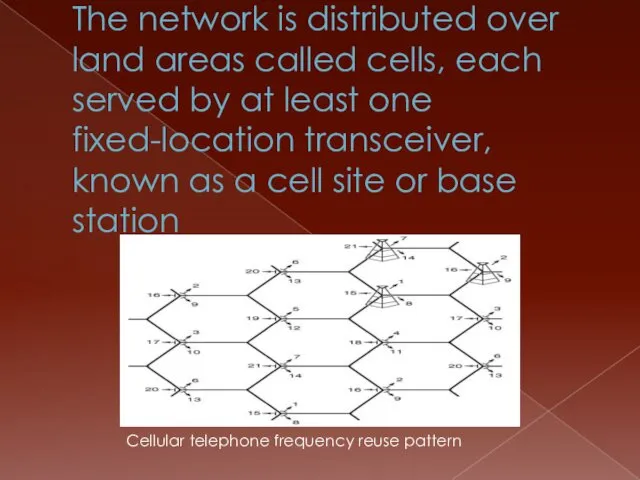
- 3. The network is distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location
- 4. Cellular networks offer a number of desirable features: More capacity than a single large transmitter, since
- 5. Cell signal encoding time division multiple access (TDMA) frequency division multiple access (FDMA) code division multiple
- 6. Mobile phone network The most common example of a cellular network is a mobile phone (cell
- 7. Structure of the mobile phone cellular network A network of radio base stations forming the base
- 8. Cellular frequency choice in mobile phone networks Low frequencies, such as 450 MHz NMT, serve very
- 9. Mobile phone services Voice call; The answering machine in mobile (service); Roaming; Caller ID (Caller Line
- 10. Cellular Communication in Kazakhstan Beeline Tele2 Kcell Altell
- 12. Скачать презентацию








 French cuisine
French cuisine  What is a gap year for? 9 класс
What is a gap year for? 9 класс Music in my life
Music in my life Презентация к уроку английского языка "The mature Middle Ages Gothic style XIII - XV centuries" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "The mature Middle Ages Gothic style XIII - XV centuries" - скачать  Olympic Games
Olympic Games  A tour around my home city Anzhero-Sudzhensk
A tour around my home city Anzhero-Sudzhensk Употребление артикля с существительными, обозначающими части суток, времена года
Употребление артикля с существительными, обозначающими части суток, времена года Неопределенный артикль
Неопределенный артикль Winter. Would YOU Rather?
Winter. Would YOU Rather? Digital watch
Digital watch  It is autumn
It is autumn  Economic policy
Economic policy Tyumen
Tyumen Презентация к уроку английского языка "First Lady of Song" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "First Lady of Song" - скачать бесплатно Exams in Ukraine
Exams in Ukraine  Can you skip (Vai tu proti pārlēkt)
Can you skip (Vai tu proti pārlēkt) Topic 2. Leadership structure
Topic 2. Leadership structure Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pirates of the caribbean" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pirates of the caribbean" - скачать  Past Simple Tense
Past Simple Tense Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I Презентация к уроку английского языка "Endangered animals" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Endangered animals" - скачать  ЖИВОТНЫХ ИЗУЧАЕМ ПО – АНГЛИЙСКИ ИХ НАЗЫВАЕМ. ( ВЕСЁЛЫЕ СТИХИ, ПОМОГАЮЩИЕ ЗАПОМНИТЬ АНГЛИЙСКОЕ СЛОВО) РЫЖИК
ЖИВОТНЫХ ИЗУЧАЕМ ПО – АНГЛИЙСКИ ИХ НАЗЫВАЕМ. ( ВЕСЁЛЫЕ СТИХИ, ПОМОГАЮЩИЕ ЗАПОМНИТЬ АНГЛИЙСКОЕ СЛОВО) РЫЖИК Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pointillism" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pointillism" - скачать  диалог
диалог Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous
Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous Добро Пожаловать! Welcome! Technical English Технический перевод
Добро Пожаловать! Welcome! Technical English Технический перевод Do you know Great Britain? Учитель английского языка МБОУ «СОШ № 28» г. Северодвинска Афанасьева Ольга Сергеевна
Do you know Great Britain? Учитель английского языка МБОУ «СОШ № 28» г. Северодвинска Афанасьева Ольга Сергеевна LONDON Piccadilly Circus
LONDON Piccadilly Circus