Содержание
- 2. 1.The Purpose What are the foundations of the Korean companies? - Understanding some of the seeds
- 3. Contents Understanding the foundation of the Korean companies Confucianism Influence of Japan Influence of US Military
- 4. Public statement by Korean business leaders “My dream is to develop a company and contribute to
- 5. Public statement by Korean business leaders (cont.) “The incentive system is the greatest invention of the
- 6. The Foundations of Korean Capitalism & Companies Some of the foundations are.. - Confucianism - Influence
- 7. 1.Confucianism Confucianism is one aspect of Chinese culture and philosophy -Confucianism is the idea and Philosophy
- 8. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Five cardinal relationships - The relationship between farther & son - The relationship between monarch
- 9. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Confucianism emphasizes the strict observance of human relationships in order to maintain order and harmony
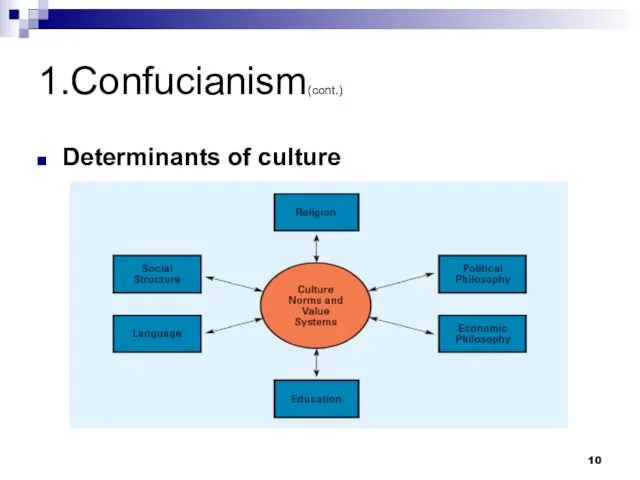
- 10. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Determinants of culture
- 11. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Dominant religions
- 12. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Religious & Ethical systems -Religion: a system of shared beliefs and rituals that are concerned
- 13. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Christianity & work ethics Christianity is the most widely practiced religion common throughout Europe, the
- 14. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Islam & work ethics Islam is an all-embracing way of life that governs one's being
- 15. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Islam & work ethics Question: What are the economic implications of Islam? Answer: Under Islam,
- 16. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Hinduism & work ethics Hinduism - focuses on the importance of achieving spiritual growth and
- 17. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Hinduism & work ethics Hinduism - focuses on the importance of achieving spiritual growth and
- 18. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Buddhism & work ethics Buddhists - stress spiritual growth and the afterlife, rather than achievement
- 19. 1.Confucianism(cont.) Confucianism & work ethics Confucianism - teaches the importance of attaining personal salvation through right
- 20. 1.Confucianism(cont.) - The importance of relative ages of individuals - Strong family orientation - Strong emphasis
- 22. Скачать презентацию


















 Feasibility Study & Business Plan for Commercial Implementation of The Short Intramedullary Nail in Armenia
Feasibility Study & Business Plan for Commercial Implementation of The Short Intramedullary Nail in Armenia Фреш-бар
Фреш-бар Регистрация нового предприятия
Регистрация нового предприятия Необычные предпринимательские идеи
Необычные предпринимательские идеи Структура показателей рейтинга
Структура показателей рейтинга SchoolDo-1. Команда Три кулачка
SchoolDo-1. Команда Три кулачка Мойка LUX. Бизнес план
Мойка LUX. Бизнес план Команда МКС: Electric step
Команда МКС: Electric step Марафон по созданию бизнеса на спортивных товарах - финал
Марафон по созданию бизнеса на спортивных товарах - финал Заведение общественного питания, в формате на вынос. Нут Тут - хумус, фалафель и турка
Заведение общественного питания, в формате на вынос. Нут Тут - хумус, фалафель и турка Юридическая сторона предпринимательства
Юридическая сторона предпринимательства Может ли бизнес быть миссией?
Может ли бизнес быть миссией? АО Ярославский завод опытных машин. Бизнес-план 2018
АО Ярославский завод опытных машин. Бизнес-план 2018 Увеличение доли продаж компенсаторов
Увеличение доли продаж компенсаторов Рынок биогаза в России и мире
Рынок биогаза в России и мире Описание клиентов
Описание клиентов Как разработать бизнес-модель
Как разработать бизнес-модель Экономика фирмы. Предпринимательство
Экономика фирмы. Предпринимательство Предпринимательство и его виды
Предпринимательство и его виды Определение продукта
Определение продукта Сбалансированная система показателей
Сбалансированная система показателей ООО Микадо
ООО Микадо Создание бизнес-плана торгового предприятия
Создание бизнес-плана торгового предприятия Сертификат за прохождение интенсива по включению в бизнес
Сертификат за прохождение интенсива по включению в бизнес Бизнес-план кальянной
Бизнес-план кальянной Ресторан: Ниагара
Ресторан: Ниагара Отели Sheraton
Отели Sheraton Бизнес - план Котокафе
Бизнес - план Котокафе