Содержание
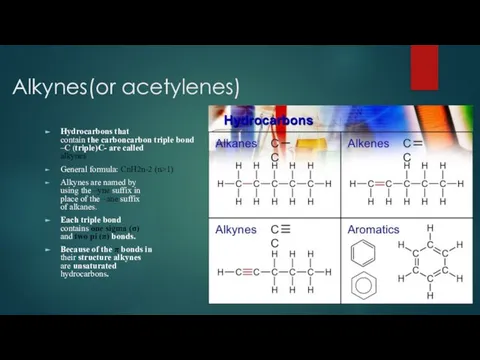
- 2. Alkynes(or acetylenes) Hydrocarbons that contain the carboncarbon triple bond –C (triple)C- are called alkynes General formula:
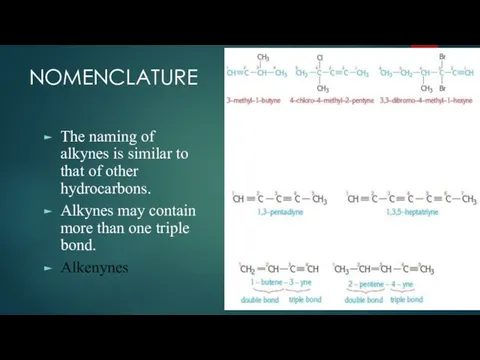
- 3. NOMENCLATURE The naming of alkynes is similar to that of other hydrocarbons. Alkynes may contain more
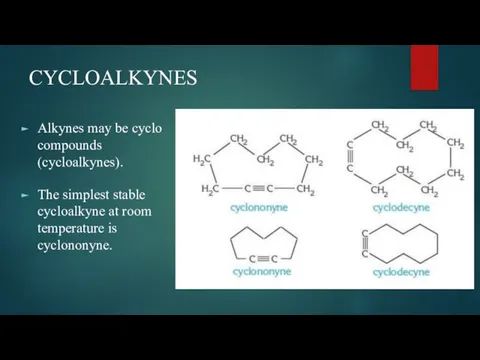
- 4. CYCLOALKYNES Alkynes may be cyclo compounds (cycloalkynes). The simplest stable cycloalkyne at room temperature is cyclononyne.
- 5. ISOMERISM The triple bond may be in different locations in an alkyne, so alkynes can exhibit
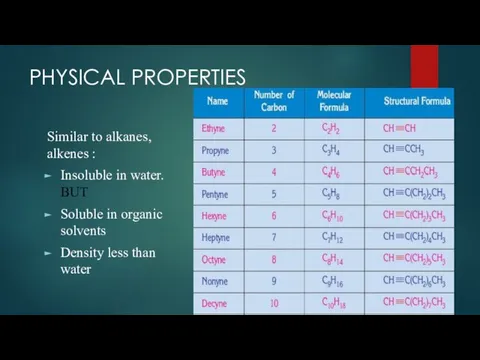
- 6. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Similar to alkanes, alkenes : Insoluble in water. BUT Soluble in organic solvents Density
- 7. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Alkynes are unsaturated compounds and their chemical properties are similar to alkenes. Alkynes undergo
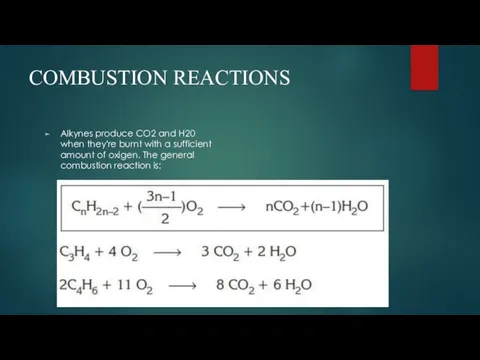
- 8. COMBUSTION REACTIONS Alkynes produce CO2 and H20 when they're burnt with a sufficient amount of oxigen.
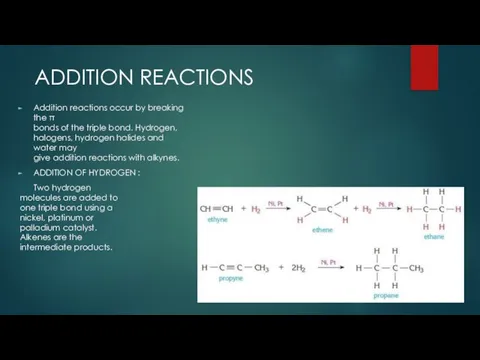
- 9. ADDITION REACTIONS Addition reactions occur by breaking the π bonds of the triple bond. Hydrogen, halogens,
- 10. PREPERATION OF ALKYNES Alkynes can be synthesized from metallic acetlylides and alkyl halides.
- 11. ACETYLENE Acetylene, the first member of the alkyne series, is one of the major chemicals used
- 12. ALKYNYL GROUP Alkynyl groups are formed from alkynes by removing one H atom. The most common
- 14. Скачать презентацию





 Презентация по Химии "Загальні способи добування металів" - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Загальні способи добування металів" - скачать смотреть бесплатно Химия өнеркәсібі
Химия өнеркәсібі Относительная атомная масса
Относительная атомная масса Коллоидные растворы поверхностно-активных веществ (ПАВ)
Коллоидные растворы поверхностно-активных веществ (ПАВ) Основания. Гидроксид натрия
Основания. Гидроксид натрия Закономерности протекания химических реакций. Основы химической термодинамики. Лекция 6
Закономерности протекания химических реакций. Основы химической термодинамики. Лекция 6 АТФ Аденозинтрифосфат
АТФ Аденозинтрифосфат Поверхностные явления
Поверхностные явления Алканы. Предельные углеводороды. Парафины. Насыщенные углеводороды
Алканы. Предельные углеводороды. Парафины. Насыщенные углеводороды Производство минеральных удобрений
Производство минеральных удобрений Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа внеурочной деятельности «Мир под микроскопом». (5 класс)
Аттестационная работа. Рабочая программа внеурочной деятельности «Мир под микроскопом». (5 класс) Отчет по ПП.03.01 «Лаборант химического анализа»
Отчет по ПП.03.01 «Лаборант химического анализа» Минералы. Свойства минералов
Минералы. Свойства минералов Периодический закон и периодическая система Д. И. Менделеева
Периодический закон и периодическая система Д. И. Менделеева обратимые и необратимые реакции, электролитическая диссоциация, сильные и слабые электролиты, определение кислот, солей, основан
обратимые и необратимые реакции, электролитическая диссоциация, сильные и слабые электролиты, определение кислот, солей, основан Маса та розміри атомів і молекул. Кількість речовини
Маса та розміри атомів і молекул. Кількість речовини Дисперсные
Дисперсные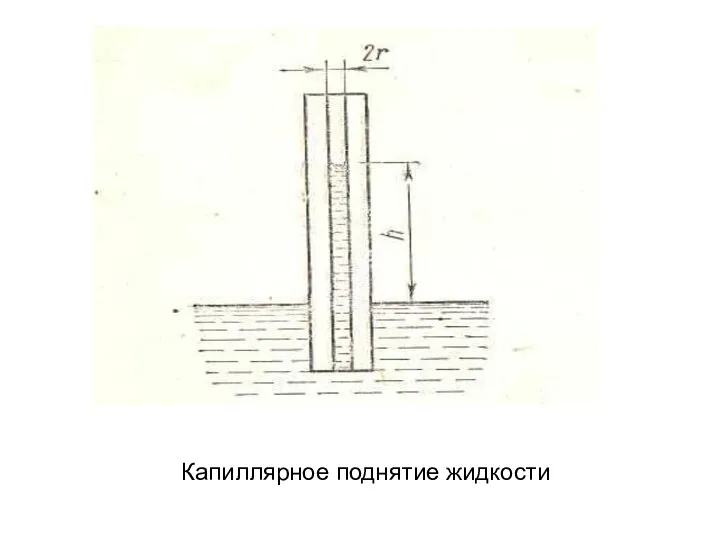 Капиллярное поднятие жидкости
Капиллярное поднятие жидкости Полезные свойства камней
Полезные свойства камней Гетерогенді химиялық реакциялар
Гетерогенді химиялық реакциялар Йод
Йод Презентация по Химии "Металлы. Общая характеристика металлов (нахождение в природе и физические свойства)" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Металлы. Общая характеристика металлов (нахождение в природе и физические свойства)" - скачать смотреть  Кислоты. Химические свойства кислот
Кислоты. Химические свойства кислот Презентация на тему: Хром
Презентация на тему: Хром Биохимия ферментов и кинетика
Биохимия ферментов и кинетика Презентация по Химии "Оцтова кислота" - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Оцтова кислота" - скачать смотреть бесплатно Презентация по Химии "Мило,та миючі засоби." - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Мило,та миючі засоби." - скачать смотреть бесплатно Геохимия редкоземельных элементов
Геохимия редкоземельных элементов