Содержание
- 2. Organic chemistry — chemistry of carbon containing compounds Elements Н, О, N, S, P – organigenic
- 3. Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (21 August 1816 – 19 August 1856). French chemist, known for his work
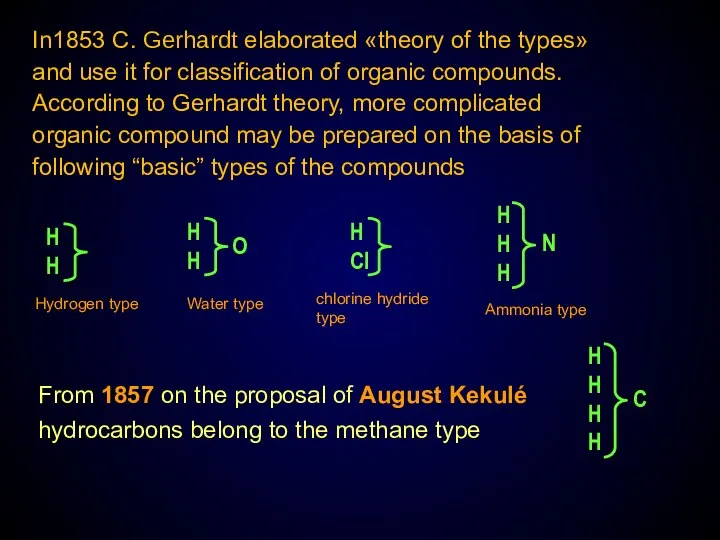
- 4. In1853 C. Gerhardt elaborated «theory of the types» and use it for classification of organic compounds.
- 5. Alexander Mikhaylovich Butlerov (September 15, 1828 – August 17, 1886) - a Russian chemist, one of
- 6. Basic statements of structure theory of organic compounds(1861) 1) In organic molecules atoms connected to each
- 7. 4) In organic molecules exists mutual effects between as bonded, so non-bonded atoms; 5) Chemical structure
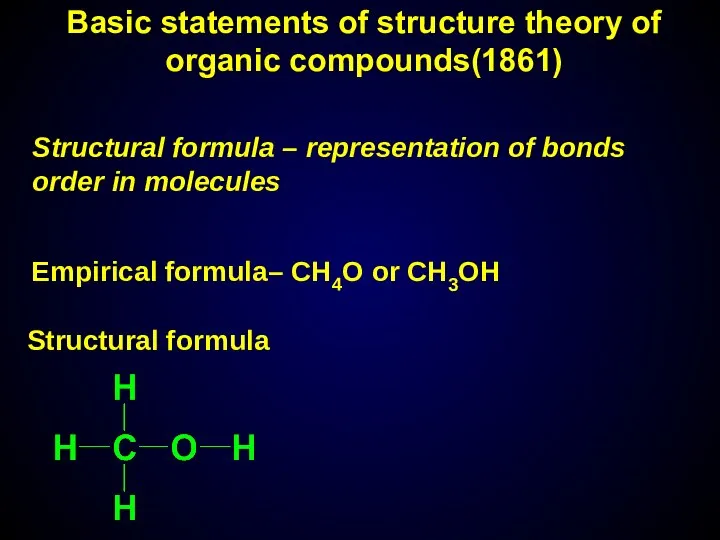
- 8. Structural formula – representation of bonds order in molecules Empirical formula– СН4О or CH3OH Structural formula
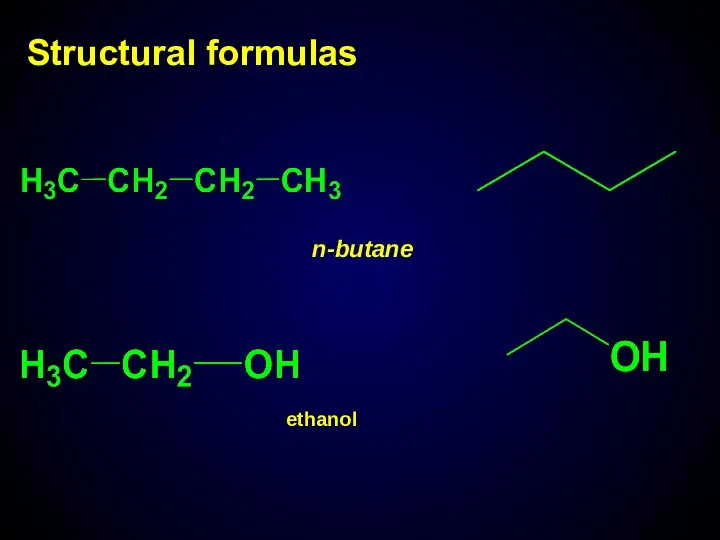
- 9. Structural formulas n-butane ethanol
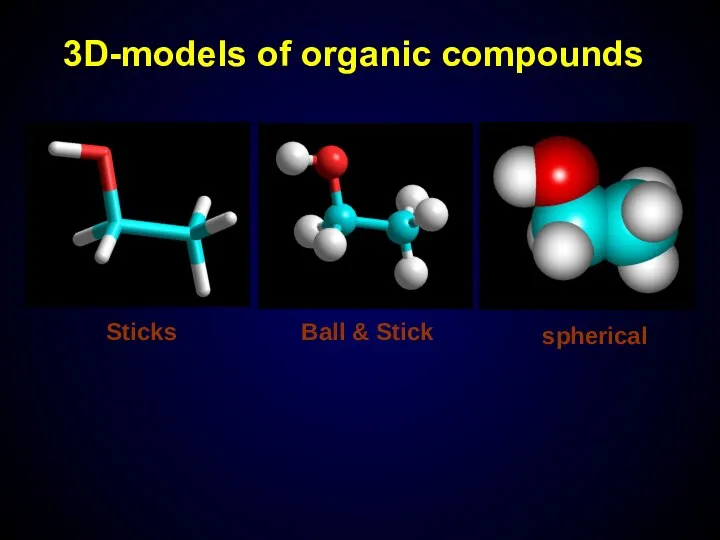
- 10. 3D-models of organic compounds Sticks Ball & Stick spherical
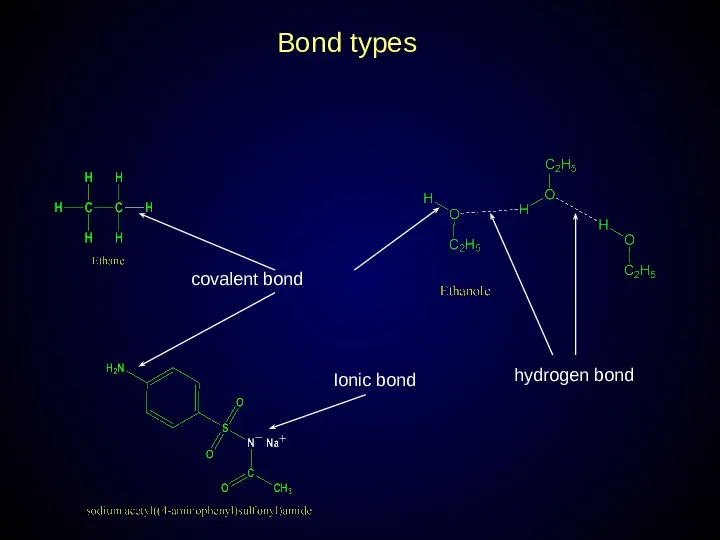
- 11. Bond types covalent bond hydrogen bond Ionic bond
- 12. Covalent bond in organic molecules: Polar Non-polar Single (σ-bond) Double or triple (σ-bond and π-bond) Hydrogen
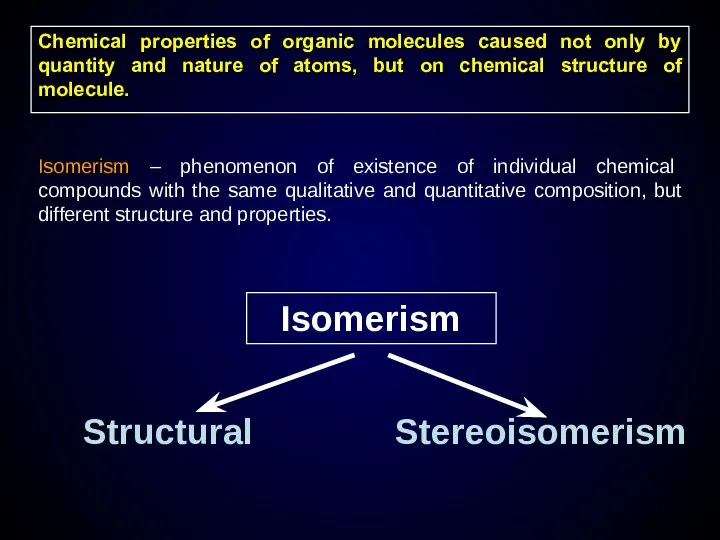
- 13. Chemical properties of organic molecules caused not only by quantity and nature of atoms, but on
- 14. Structural isomerism caused by difference order and bonding type of atoms Chain isomerism Position isomerism Functional
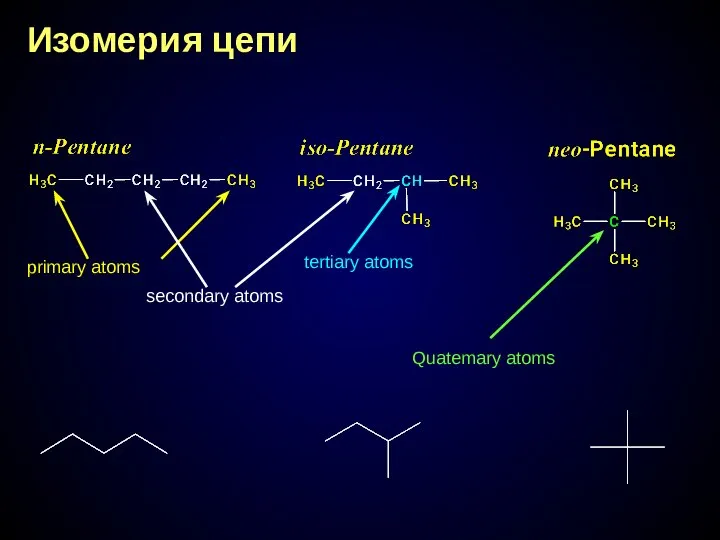
- 15. Изомерия цепи primary atoms secondary atoms tertiary atoms Quatemary atoms
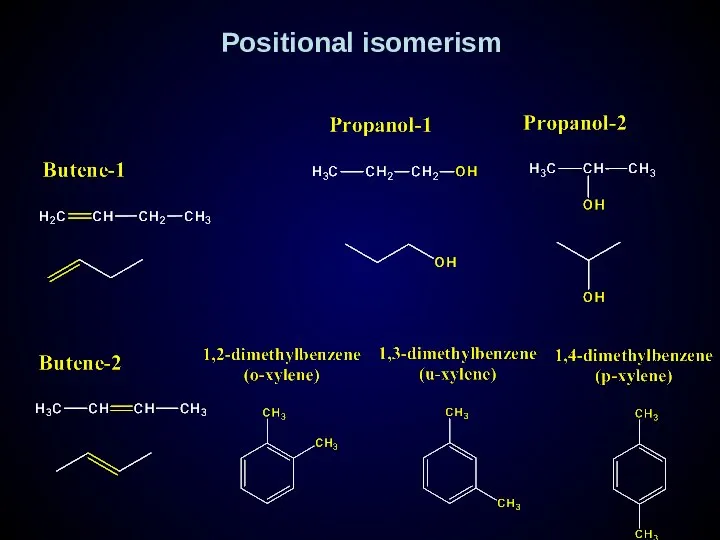
- 16. Positional isomerism
- 17. Functional group - atom or group of atom which contain elements differ from carbon and hydrogen
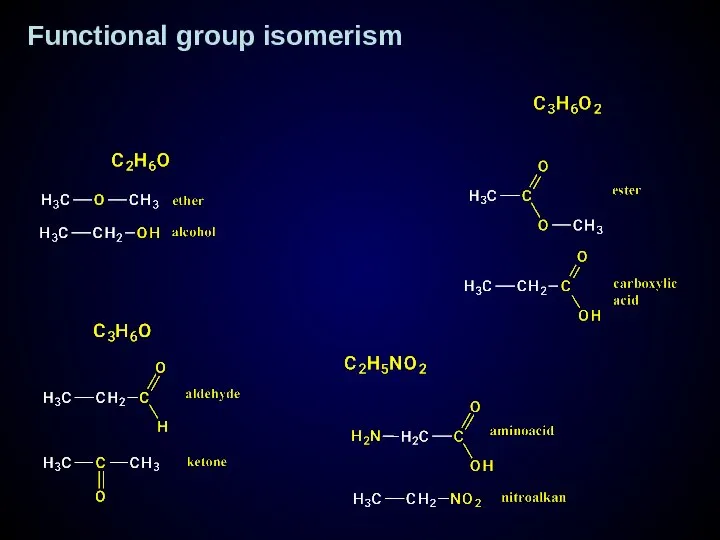
- 18. Functional group isomerism
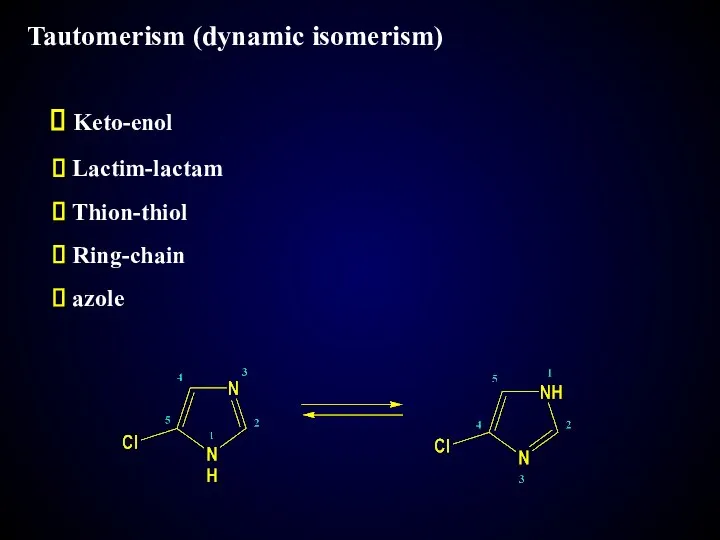
- 19. Tautomerism (dynamic isomerism) Keto-enol Lactim-lactam Thion-thiol Ring-chain azole
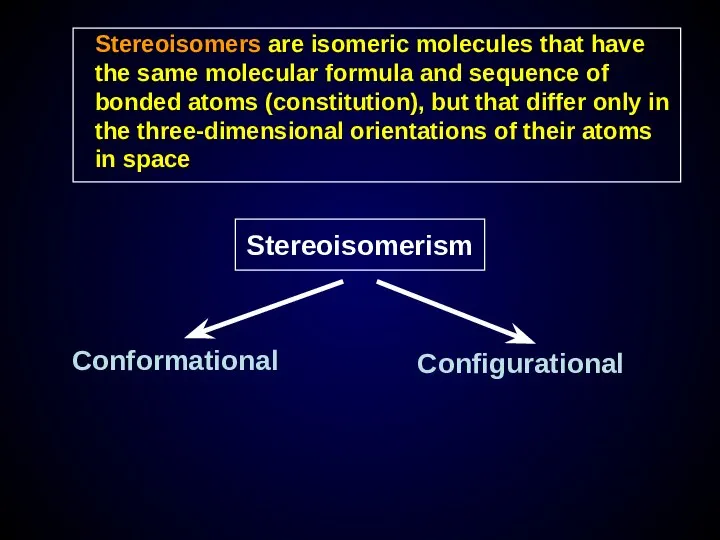
- 20. Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution),
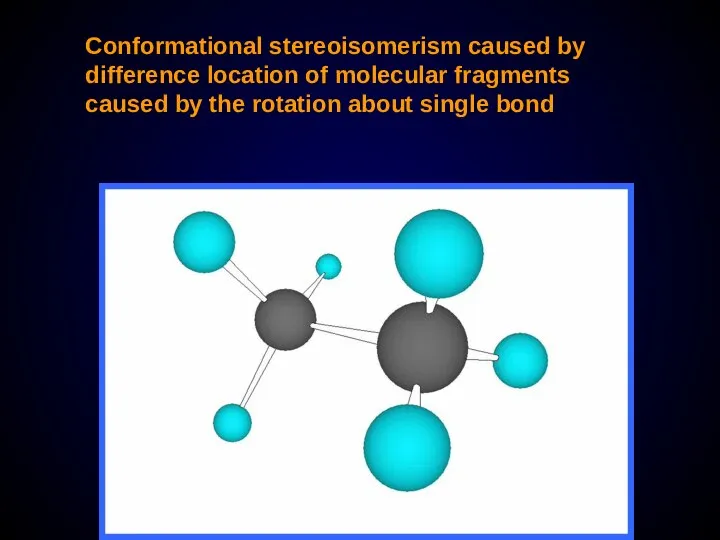
- 21. Conformational stereoisomerism caused by difference location of molecular fragments caused by the rotation about single bond
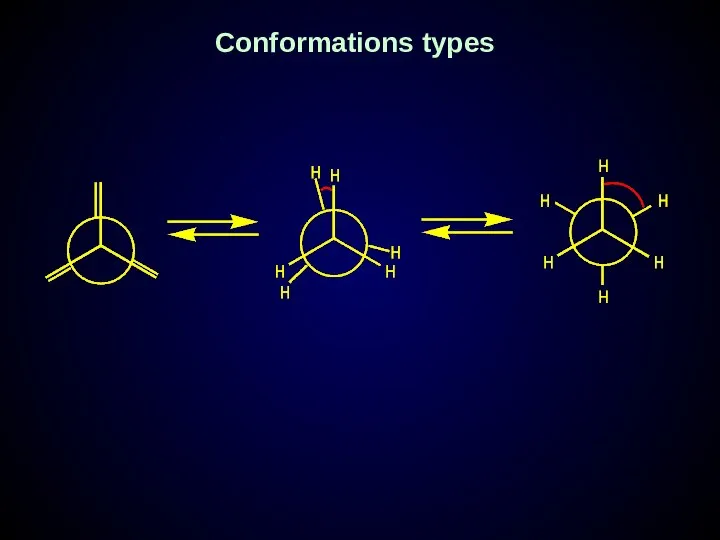
- 22. Conformations types
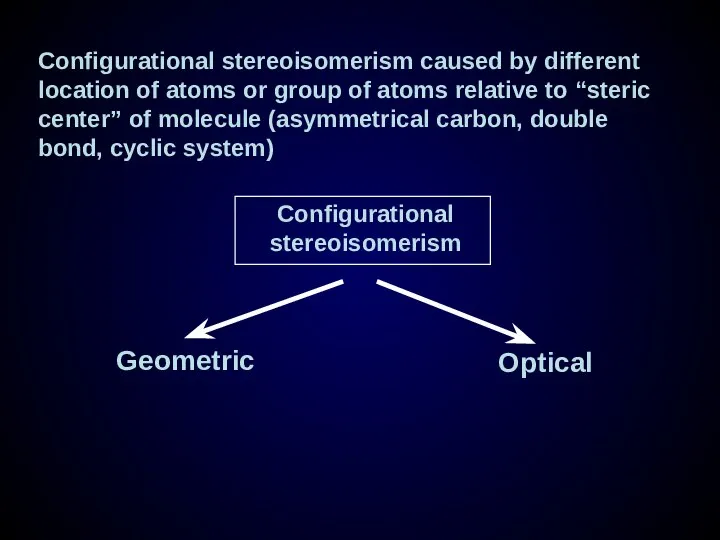
- 23. Configurational stereoisomerism caused by different location of atoms or group of atoms relative to “steric center”
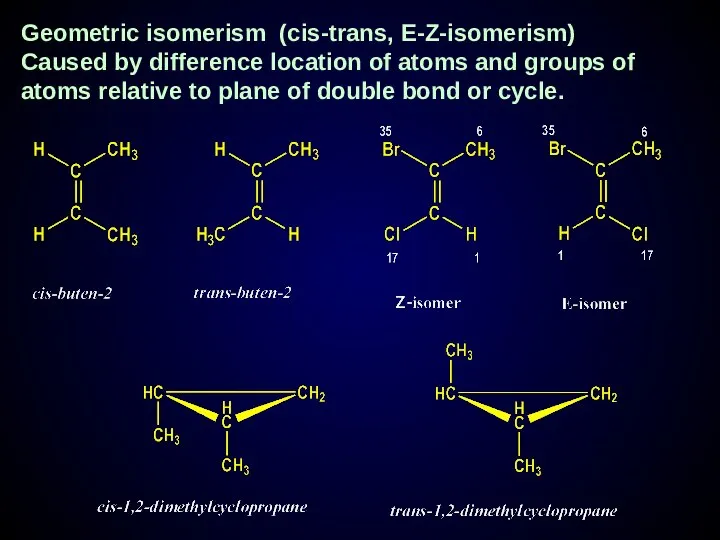
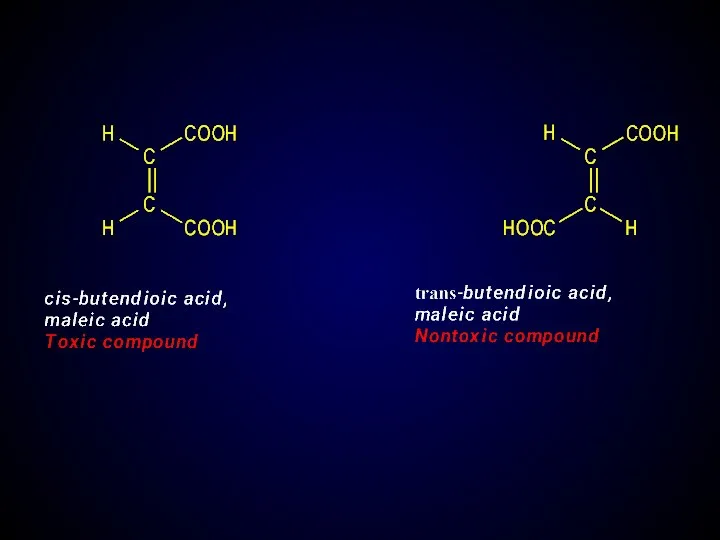
- 24. Geometric isomerism (cis-trans, E-Z-isomerism) Caused by difference location of atoms and groups of atoms relative to
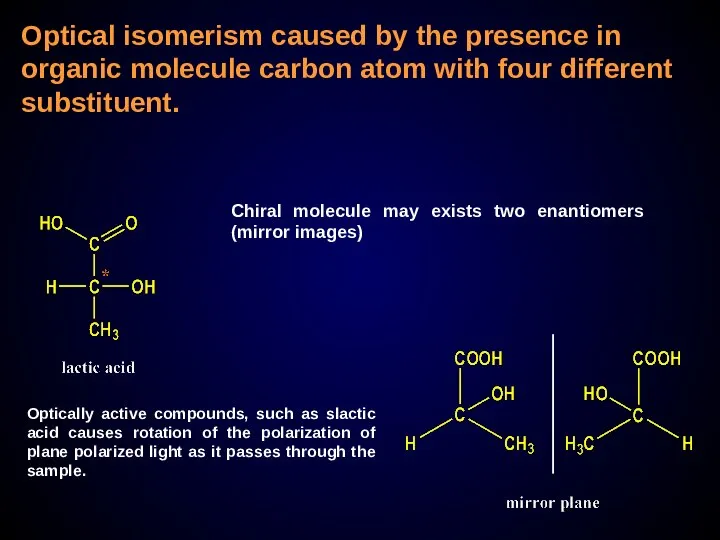
- 26. Optical isomerism caused by the presence in organic molecule carbon atom with four different substituent. Chiral
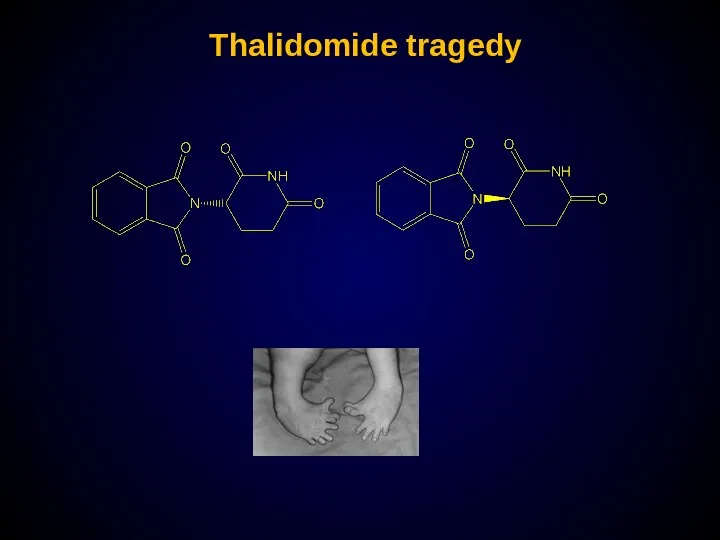
- 27. Thalidomide tragedy
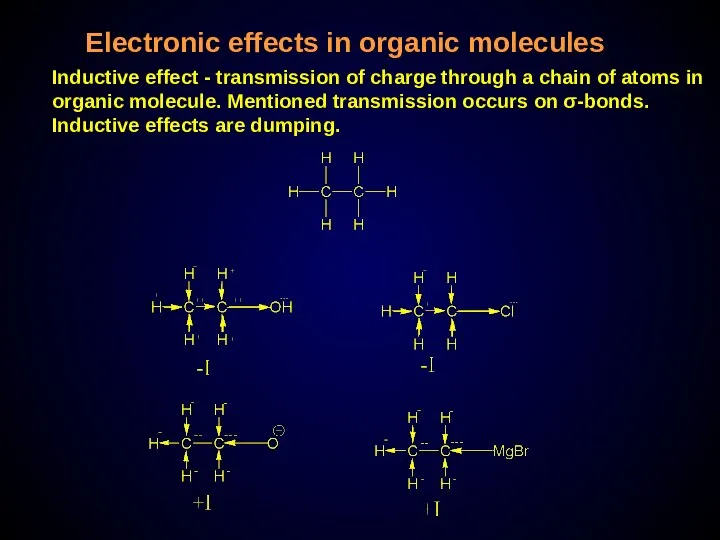
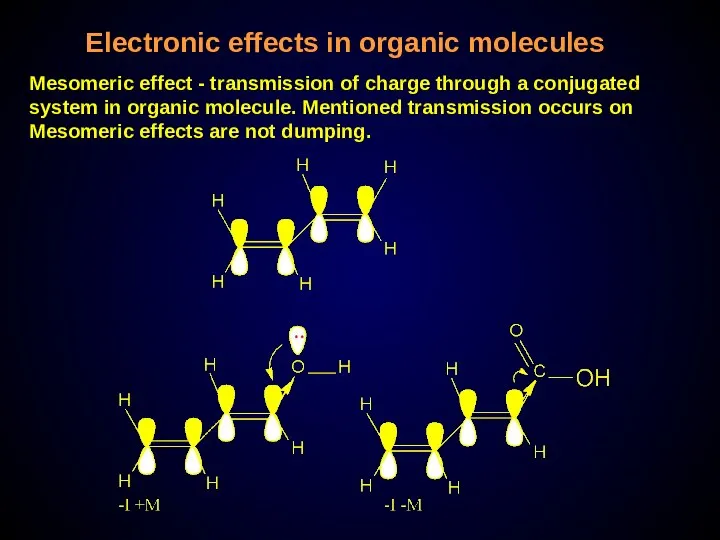
- 28. Electronic effects in organic molecules Inductive effect - transmission of charge through a chain of atoms
- 29. Electronic effects in organic molecules Mesomeric effect - transmission of charge through a conjugated system in
- 31. Скачать презентацию







 Гидроксилпроизводные углеводородов
Гидроксилпроизводные углеводородов Хімія у створенні нових матеріалів та побуті
Хімія у створенні нових матеріалів та побуті  Важнейшие классы неорганических соединений
Важнейшие классы неорганических соединений Симметрия, структура и свойства твердых тел – кристаллография и кристаллофизика
Симметрия, структура и свойства твердых тел – кристаллография и кристаллофизика Значення хімії у житті людини
Значення хімії у житті людини Угольная кислота и ее производные. Сульфокислоты. (Лекция 12)
Угольная кислота и ее производные. Сульфокислоты. (Лекция 12) Обнаружение липидов с помощью качественной реакции
Обнаружение липидов с помощью качественной реакции Фармакология и токсикология этилового спирта
Фармакология и токсикология этилового спирта Химическое равновесие
Химическое равновесие Материаловедение и технологии конструкционных материалов
Материаловедение и технологии конструкционных материалов Презентация по Химии "Природные источники углеводородов" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Природные источники углеводородов" - скачать смотреть  Презентация по Химии "Биополимеры" - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Биополимеры" - скачать смотреть бесплатно Роль Химии в жизни общества
Роль Химии в жизни общества Сульфаттар және эфирсульфаттар
Сульфаттар және эфирсульфаттар Изомерия и номенклатура спиртов. Физические и химические свойства спиртов
Изомерия и номенклатура спиртов. Физические и химические свойства спиртов Минералы
Минералы Алмазы Индии Мультимедийный интегрированный проект
Алмазы Индии Мультимедийный интегрированный проект  Виконала Гаєвська Зоряна Учениця 10 класу
Виконала Гаєвська Зоряна Учениця 10 класу  Физикалық химия бағыты бойынша жеке бағдарланған индивидуалды ғылыми жұмыс
Физикалық химия бағыты бойынша жеке бағдарланған индивидуалды ғылыми жұмыс Пневмовакуум-формование
Пневмовакуум-формование Химия и биохимия игристых вин
Химия и биохимия игристых вин Карбоновые кислоты
Карбоновые кислоты Defect in solid
Defect in solid Обмен углеводов
Обмен углеводов Межмолекулярные силы (силы Ван дер Ваальса)
Межмолекулярные силы (силы Ван дер Ваальса) Полимеры. Высокомолекулярные соединения
Полимеры. Высокомолекулярные соединения Принципы создания полимерных конструкционных нанокомпозитов
Принципы создания полимерных конструкционных нанокомпозитов Введение в химию биологически активных веществ. (Тема 1)
Введение в химию биологически активных веществ. (Тема 1)