Содержание
- 2. Algorithms Algorithms derives from name of Central Asian scientist Al-Khorezmi. Algorithm is a step-by-step set of
- 3. Searching
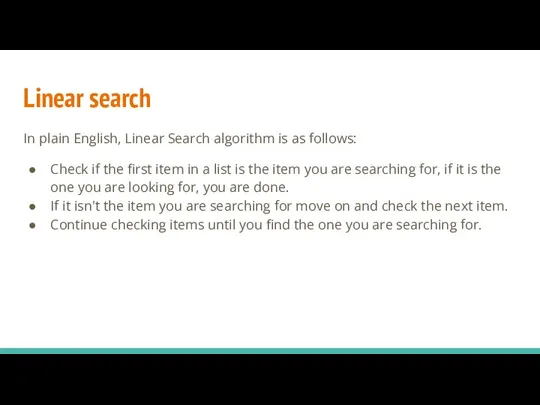
- 4. Linear search In plain English, Linear Search algorithm is as follows: Check if the first item
- 5. Binary search Binary Search is a very powerful algorithm. If you had 1000 presents to search
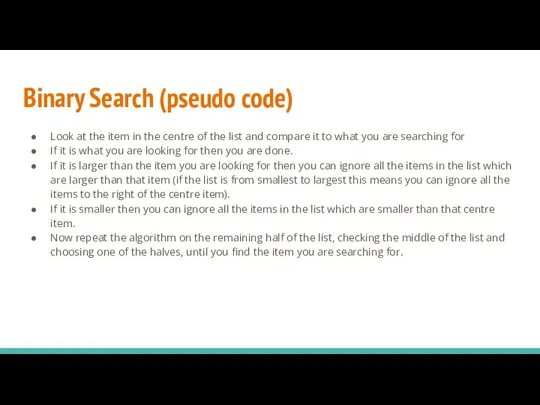
- 6. Binary Search (pseudo code) Look at the item in the centre of the list and compare
- 7. Binary Search vs Linear Search We have 1000 elements
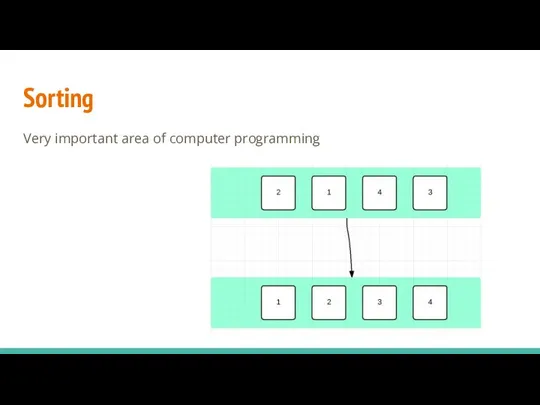
- 8. Sorting Very important area of computer programming
- 9. Bubble sort
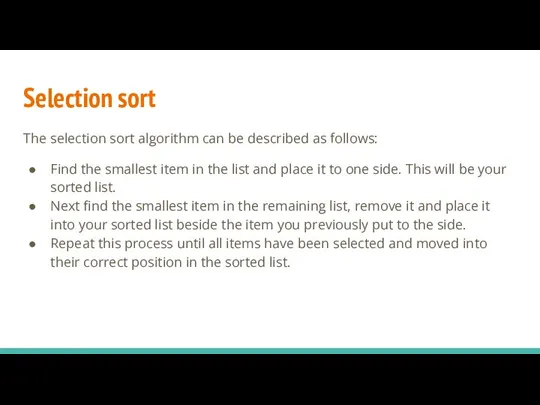
- 10. Selection sort The selection sort algorithm can be described as follows: Find the smallest item in
- 11. Insertion sort Insertion sort can be described with informal instructions as follows: Take an item from
- 12. Quicksort Quicksort can be described in the following way: Choose an item from the list and
- 13. Time and Space complexity Every algorithm uses some space and spends some time to solve problem
- 14. Best, worst and average Any algorithm has its own best, worst and average case For example:
- 15. Data structures We need to store some data, so that it can be: fastly find needed
- 16. Array or list Simplest data structure, saving it in memory sequence Finding n-th element is done
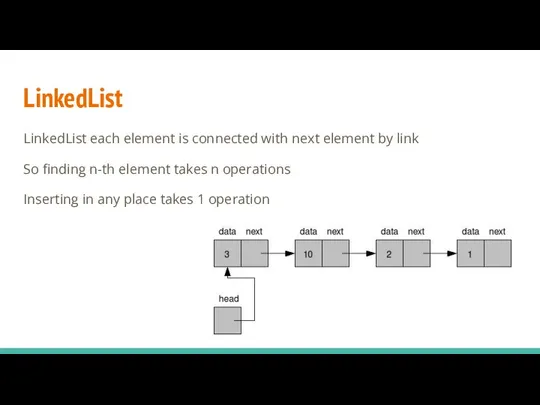
- 17. LinkedList LinkedList each element is connected with next element by link So finding n-th element takes
- 18. HashSet Searching by Hash takes 1 operation
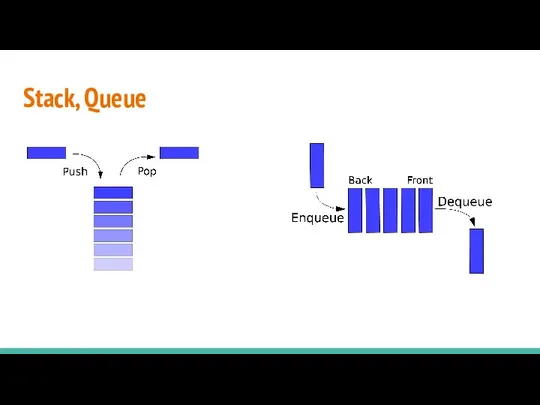
- 19. Stack, Queue
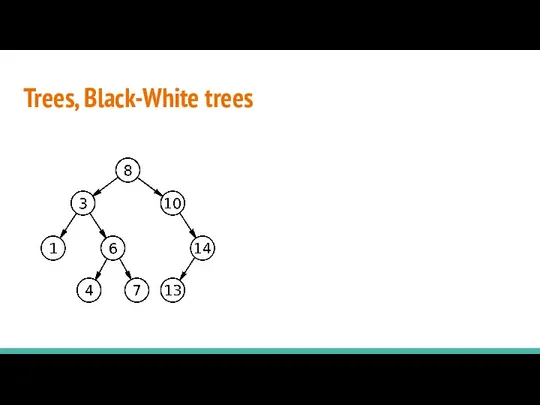
- 20. Trees, Black-White trees
- 21. HashSet and TreeSet
- 23. Скачать презентацию













 Презентация "Структурированные операторы Паскаля" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Структурированные операторы Паскаля" - скачать презентации по Информатике Работа в Microsoft Office Publisher Программа может широко использоваться для создания буклетов, издания школьной стенгазеты, приглашения и о
Работа в Microsoft Office Publisher Программа может широко использоваться для создания буклетов, издания школьной стенгазеты, приглашения и о Понятие алгоритма. Свойства алгоритмов
Понятие алгоритма. Свойства алгоритмов Жизненный цикл АИС. (Лекции 8-9)
Жизненный цикл АИС. (Лекции 8-9) Использование мультимедиа - курса «Мир информатики» на уроках по программе А.В.Горячева «Информатика в играх и задачах»
Использование мультимедиа - курса «Мир информатики» на уроках по программе А.В.Горячева «Информатика в играх и задачах» Запросы как приложения информационной системы
Запросы как приложения информационной системы Внешняя память
Внешняя память Эволюция игровых консолей
Эволюция игровых консолей Безопасное поведение школьников в сети Интернет
Безопасное поведение школьников в сети Интернет Нормальные алгоритмы Маркова
Нормальные алгоритмы Маркова Растровая и векторная графика
Растровая и векторная графика Способы привлечения трафика для арбитража
Способы привлечения трафика для арбитража О применении контрольно-кассовой техники
О применении контрольно-кассовой техники Всемирная паутина. Информация и информационные процессы
Всемирная паутина. Информация и информационные процессы Умный дом будущего
Умный дом будущего Игровые аспекты принятия решений
Игровые аспекты принятия решений Програмна система для тестування продуктивності сервера баз даних MySQL
Програмна система для тестування продуктивності сервера баз даних MySQL Проектирование и дизайн пользовательского интерфейса
Проектирование и дизайн пользовательского интерфейса Глубокое системное программирование
Глубокое системное программирование Раздел 14 Анализ отклика на случайное воздействие
Раздел 14 Анализ отклика на случайное воздействие  Перегрузка операций
Перегрузка операций Ёжик. Картинки
Ёжик. Картинки Приложение для регистрации обращений BPM-Client
Приложение для регистрации обращений BPM-Client 11 задание. ОГЭ 2022. Демоверсия
11 задание. ОГЭ 2022. Демоверсия Логические функции
Логические функции Особенности построения системы и организации обучения по профессиям рабочих по специальности: Оператор компьютерной графики
Особенности построения системы и организации обучения по профессиям рабочих по специальности: Оператор компьютерной графики Существенные свойства и принятие решения.
Существенные свойства и принятие решения. Текстовые редакторы. Основные понятия
Текстовые редакторы. Основные понятия