Содержание
- 2. Objective Domain Matrix
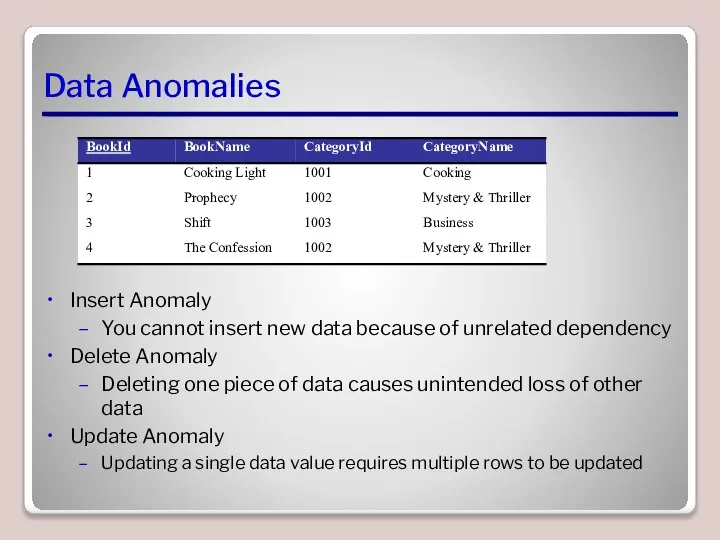
- 3. Data Anomalies Insert Anomaly You cannot insert new data because of unrelated dependency Delete Anomaly Deleting
- 4. Data Normalization The process of data normalization ensures that a database design is free of any
- 5. First Normal Form (1NF) In order for a table to be in the first normal form
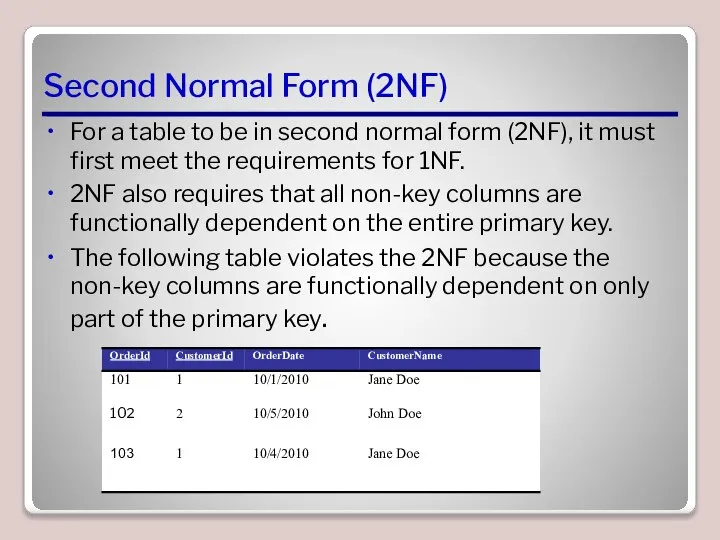
- 6. Second Normal Form (2NF) For a table to be in second normal form (2NF), it must
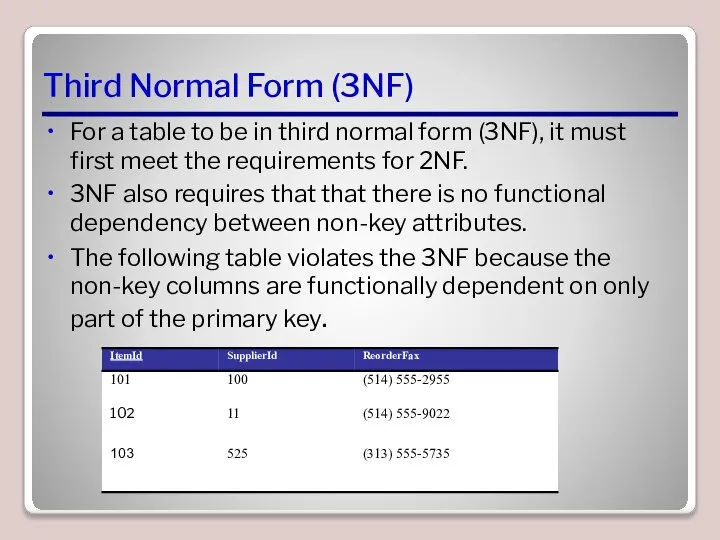
- 7. Third Normal Form (3NF) For a table to be in third normal form (3NF), it must
- 8. Structured Query Language (SQL) SQL is the language used by most database systems to manage the
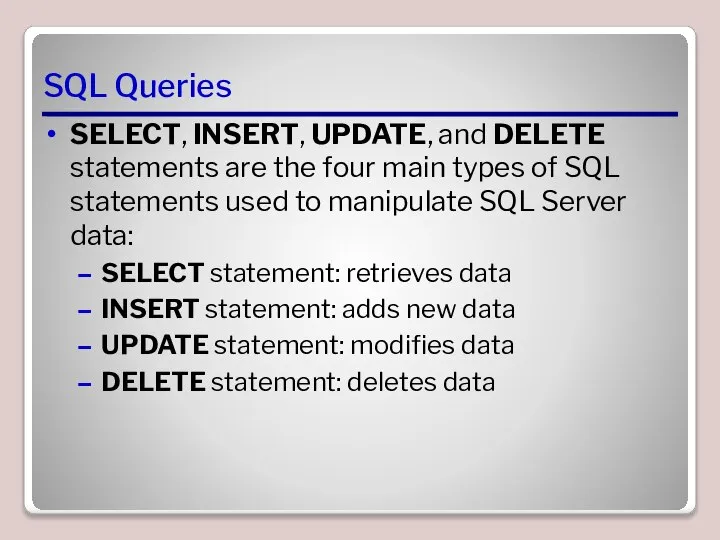
- 9. SQL Queries SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are the four main types of SQL statements
- 10. Running SQL Queries There are many way to communicate with SQL Server in order to run
- 11. Selecting Data The SELECT statement is used to retrieve data from one or more database tables.
- 12. SELECT Examples The following SELECT statement matches each order with corresponding customer: SELECT OrderID, Customers.CustomerId, ContactName
- 13. Updating Data The UPDATE statement is used to update information in database tables. The following statement
- 14. Inserting Data The INSERT statement is used to add one or more rows to a database
- 15. Deleting Data The DELETE statement is used to remove information from database tables. The following statement
- 16. Stored Procedures A stored procedure is a set of SQL statements that is stored in a
- 17. Creating Stored Procedures You use T-SQL’s CREATE PROCEDURE statement to create a stored procedure. The following
- 18. Parameterized Stored Procedures The following stored procedure, when executed, returns total sales for a given customer:
- 19. Working with Flat Files The data in a flat file can be plain text or binary.
- 20. Extensible Markup Language (XML) XML is a text-based format for representing structured data.
- 21. Working with XML The classes that work with XML data are organized in the System.Xml namespace:
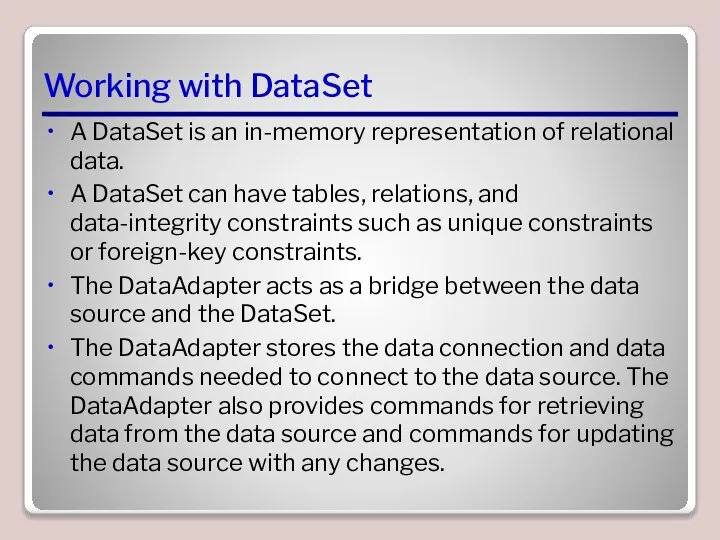
- 22. Working with DataSet A DataSet is an in-memory representation of relational data. A DataSet can have
- 24. Скачать презентацию















 Основы классификации (объектов)
Основы классификации (объектов) AppSec - хакерский путь. Анализ защищённости приложений
AppSec - хакерский путь. Анализ защищённости приложений Презентация "Создание школьного сайта" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Создание школьного сайта" - скачать презентации по Информатике Логические элементы
Логические элементы Администрирование Alfresco Community Edition
Администрирование Alfresco Community Edition Программирование. Введение в Java и С# (Тема 1)
Программирование. Введение в Java и С# (Тема 1) Эффективная работа с информационной системой
Эффективная работа с информационной системой Разработка урока в условиях дистанционного обучения
Разработка урока в условиях дистанционного обучения Создание виртуальных экскурсий по библиотеке
Создание виртуальных экскурсий по библиотеке Sissejuhatus informaatikasse. 11. Loeng
Sissejuhatus informaatikasse. 11. Loeng Мультимедийные среды и цифровые инструменты в междисциплинарной проектной деятельности в предметной области
Мультимедийные среды и цифровые инструменты в междисциплинарной проектной деятельности в предметной области Аппаратное и программное обеспечение ЭВМ и сетей
Аппаратное и программное обеспечение ЭВМ и сетей Облачные хранилища
Облачные хранилища Структура персонального компьютера
Структура персонального компьютера Моделирование как метод познания
Моделирование как метод познания Статья в научное издание. Структура статьи. Этапы работы
Статья в научное издание. Структура статьи. Этапы работы Создание базы данных
Создание базы данных Работа с файлами в Паскале
Работа с файлами в Паскале Презентация "Блок схемы" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Блок схемы" - скачать презентации по Информатике Электронные ресурсы библиотеки
Электронные ресурсы библиотеки Информационная безопасность Основные понятия Законодательство в сфере защиты информации
Информационная безопасность Основные понятия Законодательство в сфере защиты информации Обработка графической информации формирование изображения на экране монитора
Обработка графической информации формирование изображения на экране монитора Дистанційне навчання
Дистанційне навчання Емпірична інженерія програмного забезпечення. (Лекція 2)
Емпірична інженерія програмного забезпечення. (Лекція 2) Основные этапы решения задач на компьютере
Основные этапы решения задач на компьютере Основы языка программирования JAVA. Циклы
Основы языка программирования JAVA. Циклы Всероссийский конкурс прорывных проектов в области IT-технологий IT-прорыв
Всероссийский конкурс прорывных проектов в области IT-технологий IT-прорыв Обработка графической информации. § 28. Векторная графика
Обработка графической информации. § 28. Векторная графика