Содержание
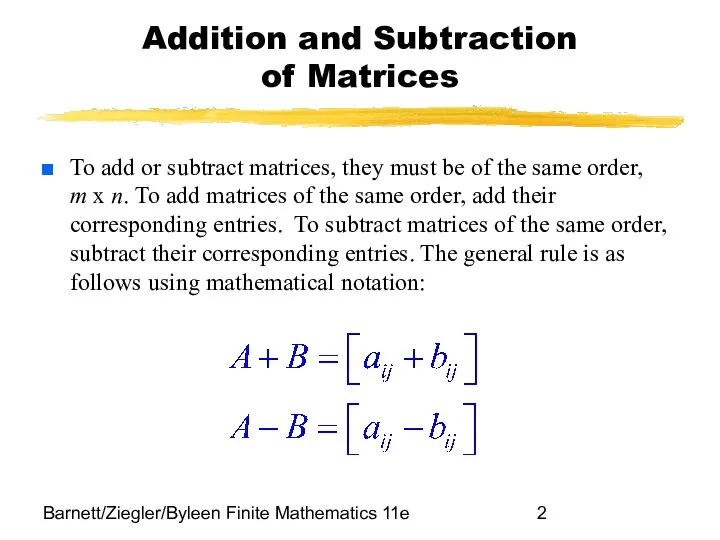
- 2. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Addition and Subtraction of Matrices To add or subtract matrices, they must
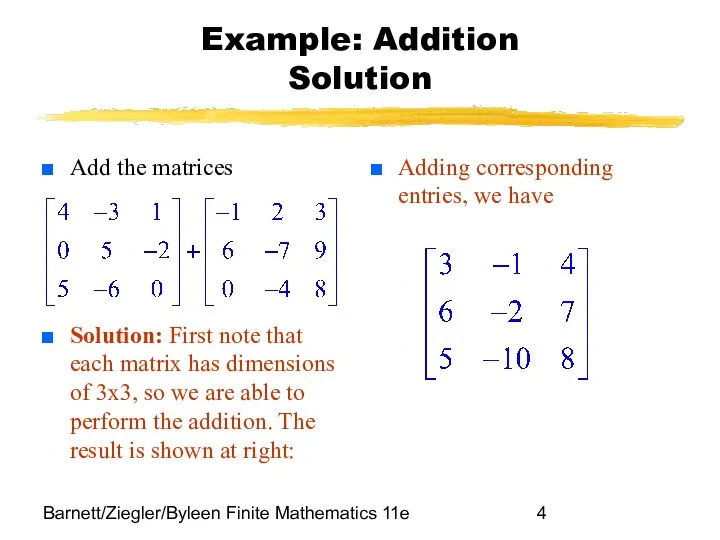
- 3. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Addition Add the matrices
- 4. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Addition Solution Add the matrices Solution: First note that each matrix
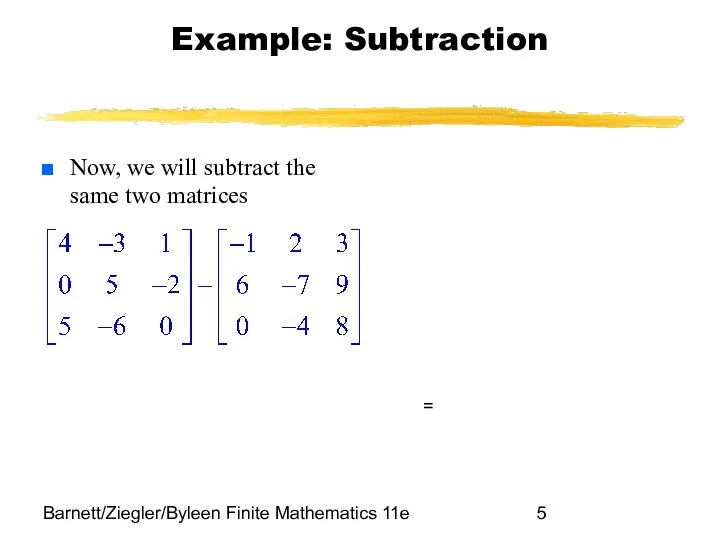
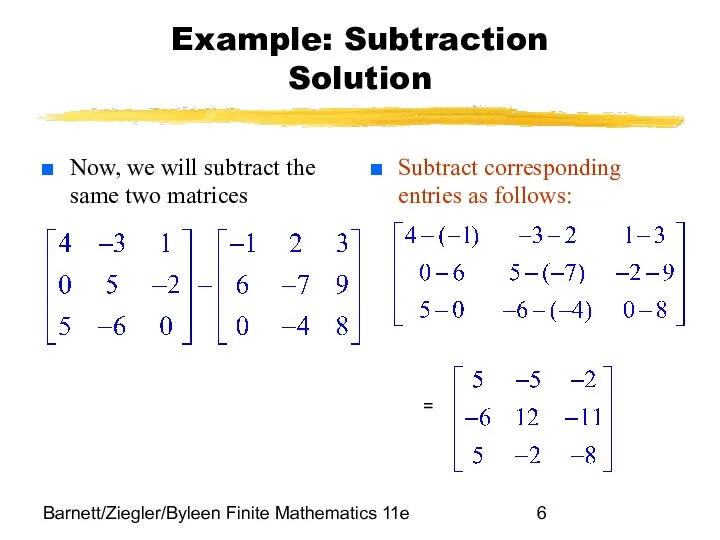
- 5. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Subtraction Now, we will subtract the same two matrices =
- 6. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Subtraction Solution Now, we will subtract the same two matrices Subtract
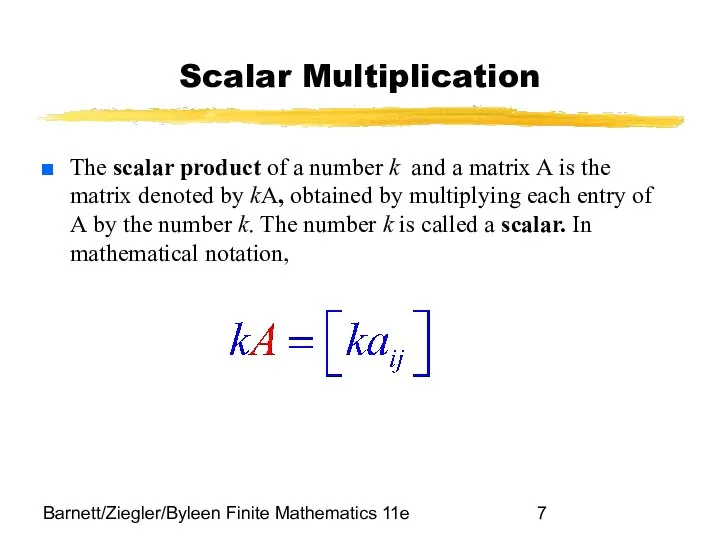
- 7. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Scalar Multiplication The scalar product of a number k and a matrix
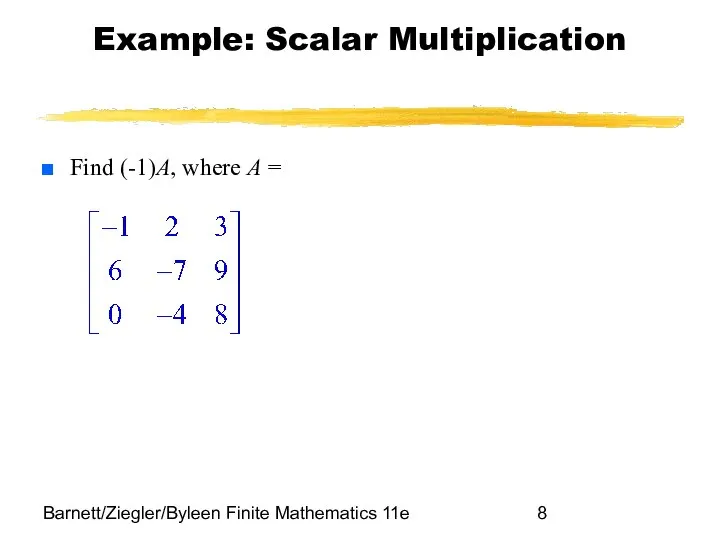
- 8. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Scalar Multiplication Find (-1)A, where A =
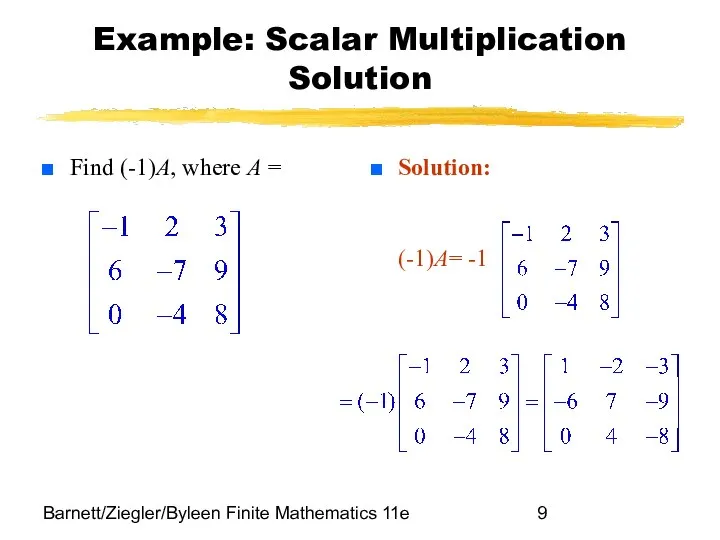
- 9. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Scalar Multiplication Solution Find (-1)A, where A = Solution: (-1)A= -1
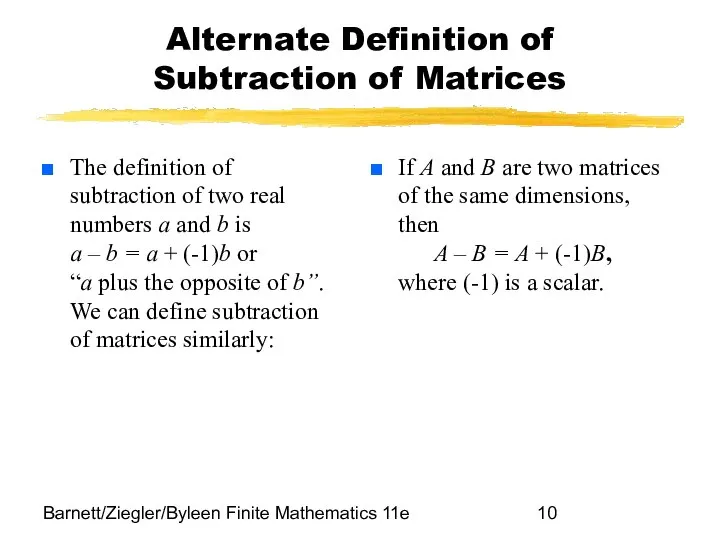
- 10. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Alternate Definition of Subtraction of Matrices The definition of subtraction of two
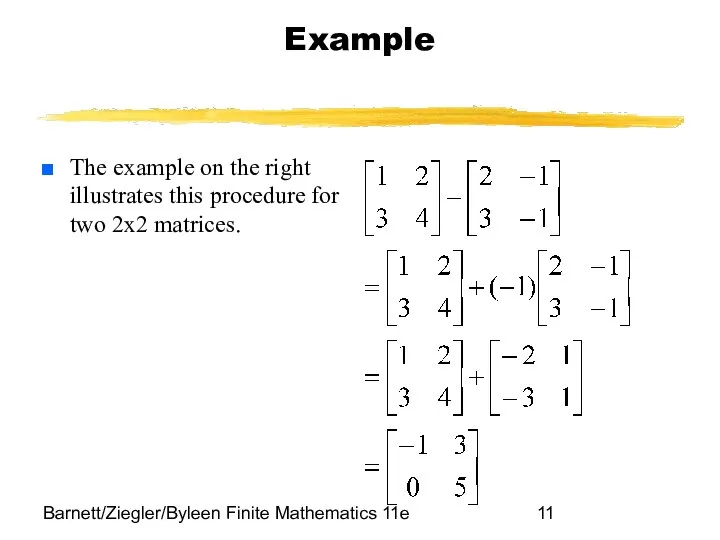
- 11. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example The example on the right illustrates this procedure for two 2x2
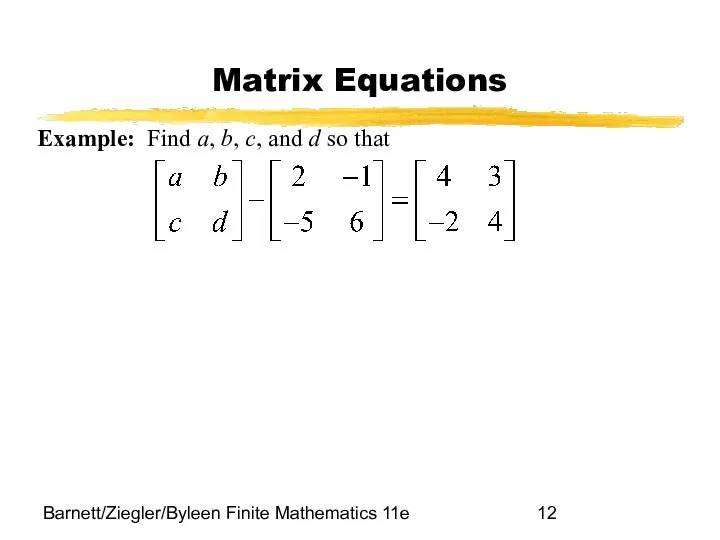
- 12. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Matrix Equations Example: Find a, b, c, and d so that
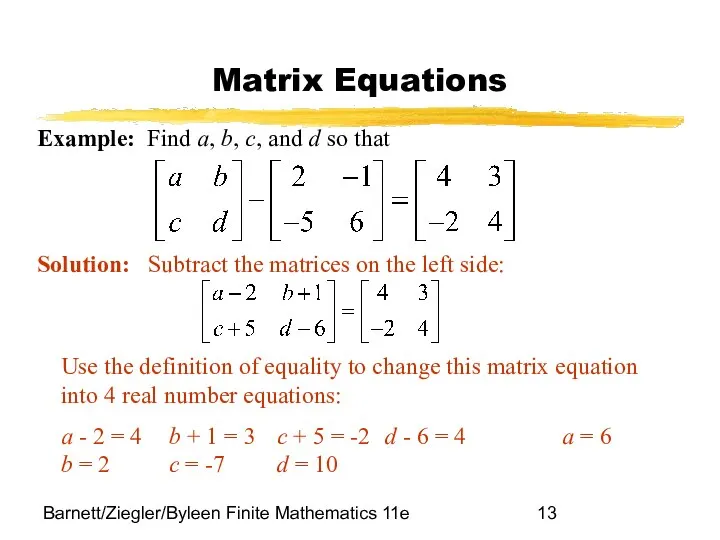
- 13. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Matrix Equations Example: Find a, b, c, and d so that Solution:
- 14. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Matrix Products The method of multiplication of matrices is not as intuitive
- 15. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Arthur Cayley 1821-1895 Introduced matrix multiplication
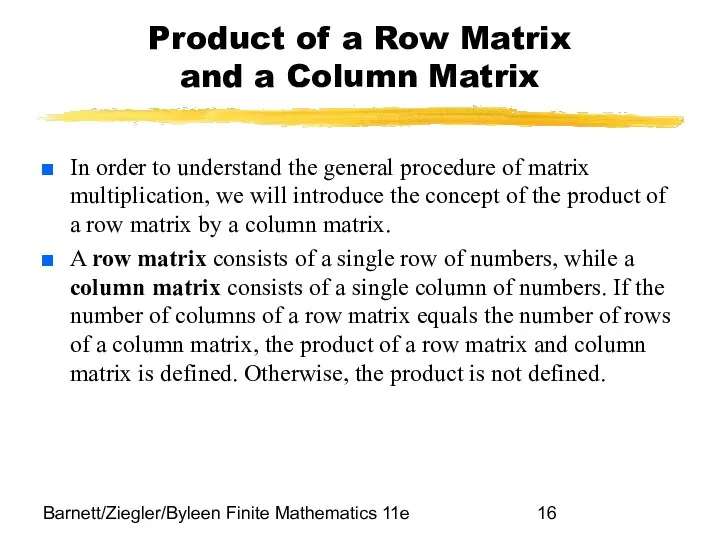
- 16. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Product of a Row Matrix and a Column Matrix In order to
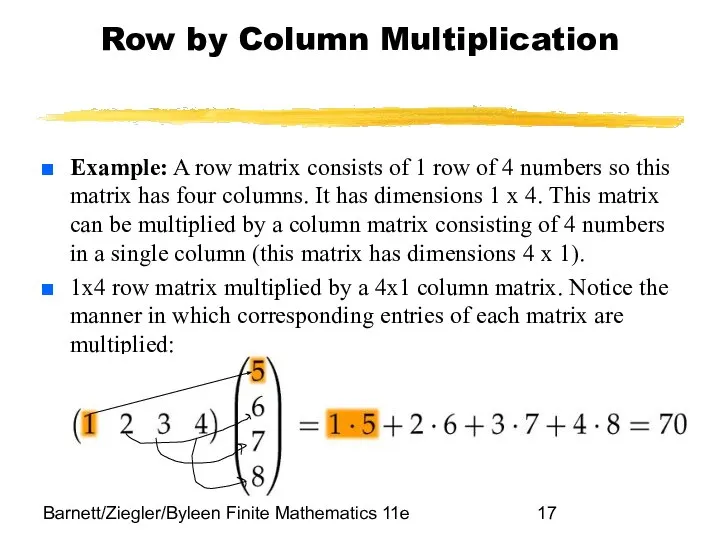
- 17. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Row by Column Multiplication Example: A row matrix consists of 1 row
- 18. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example: Revenue of a Car Dealer A car dealer sells four model
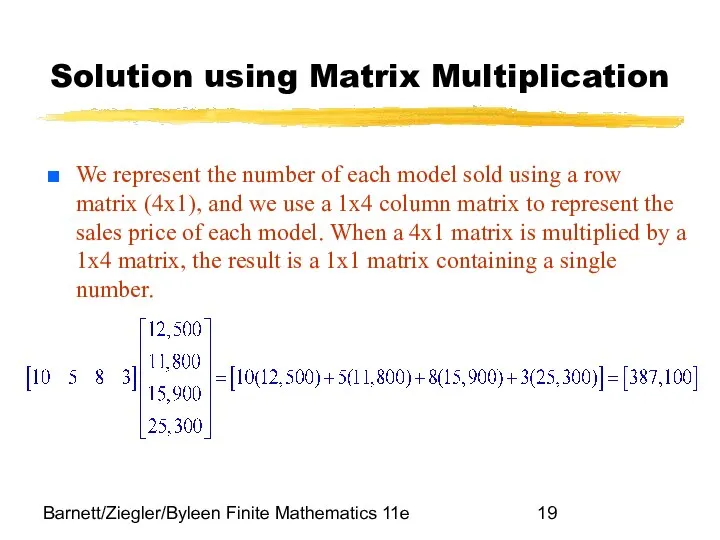
- 19. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Solution using Matrix Multiplication We represent the number of each model sold
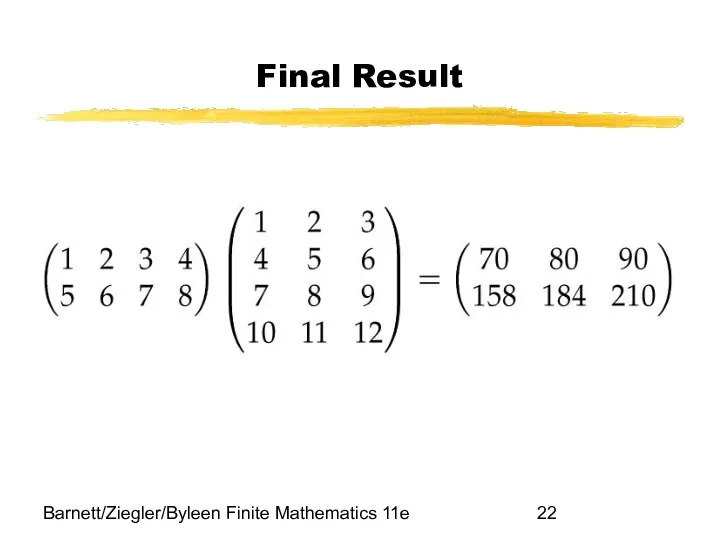
- 20. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Matrix Product If A is an m x p matrix and B
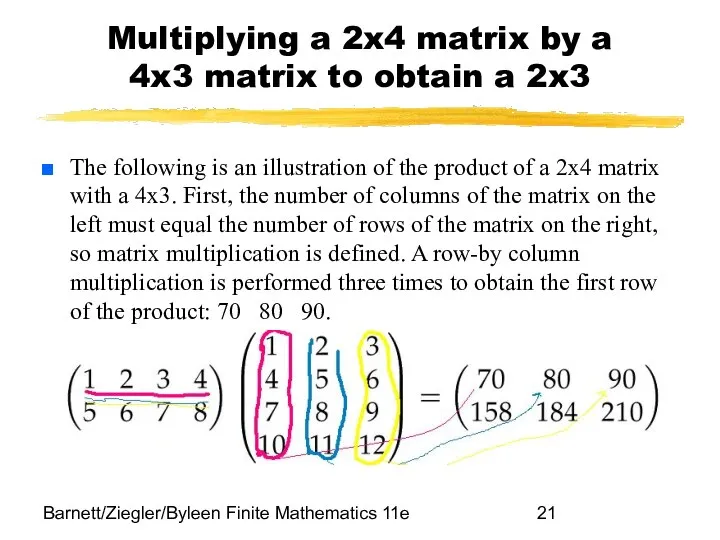
- 21. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Multiplying a 2x4 matrix by a 4x3 matrix to obtain a 2x3
- 22. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Final Result
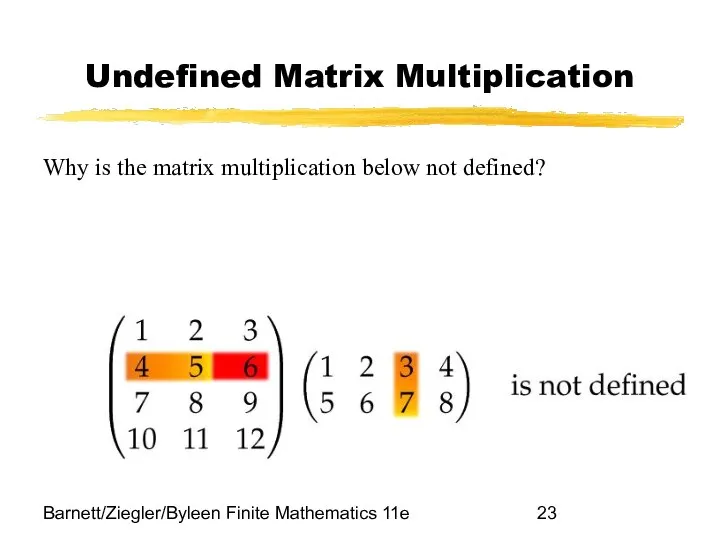
- 23. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Undefined Matrix Multiplication Why is the matrix multiplication below not defined?
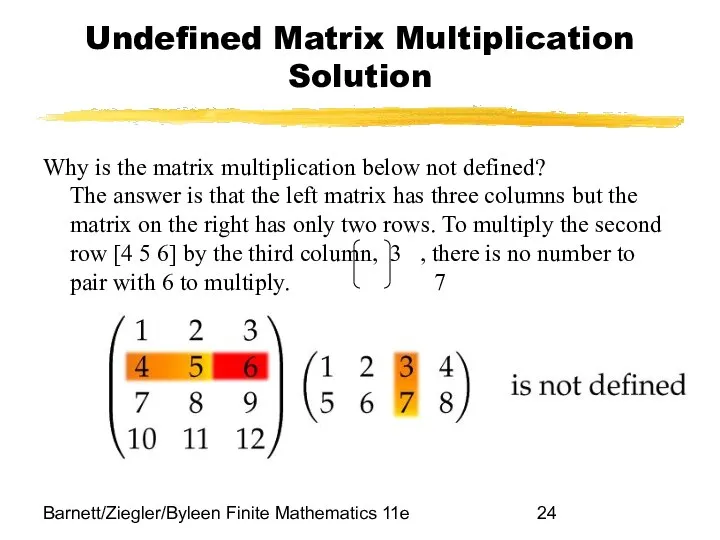
- 24. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Undefined Matrix Multiplication Solution Why is the matrix multiplication below not defined?
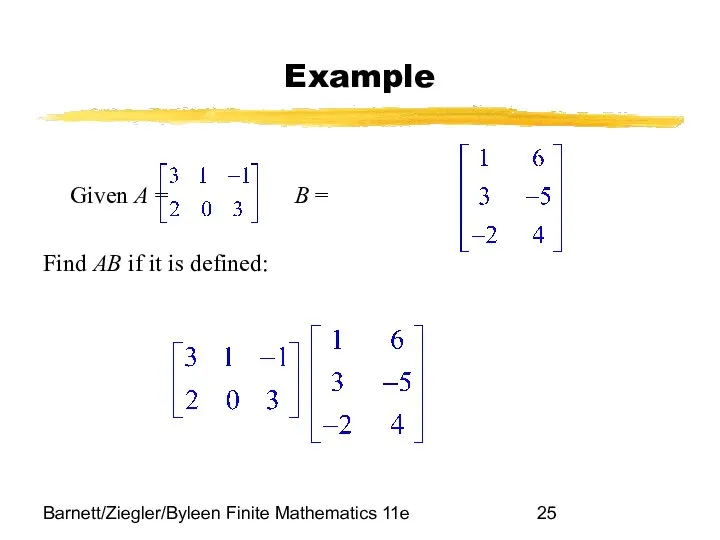
- 25. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Example Given A = B = Find AB if it is defined:
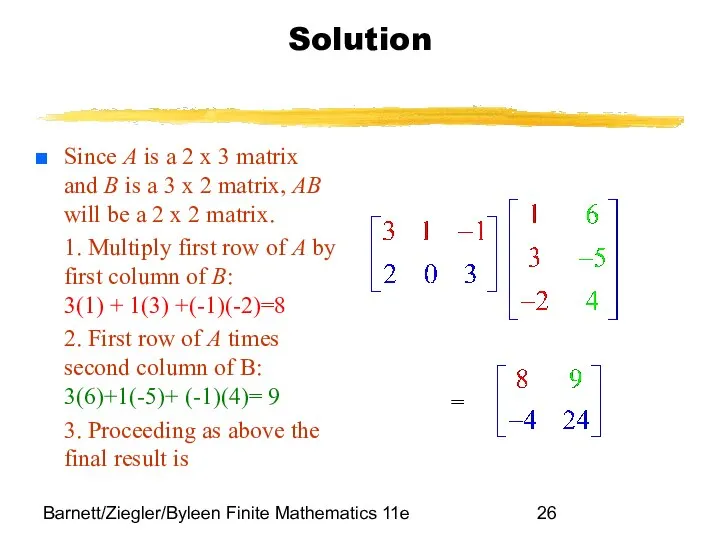
- 26. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Solution Since A is a 2 x 3 matrix and B is
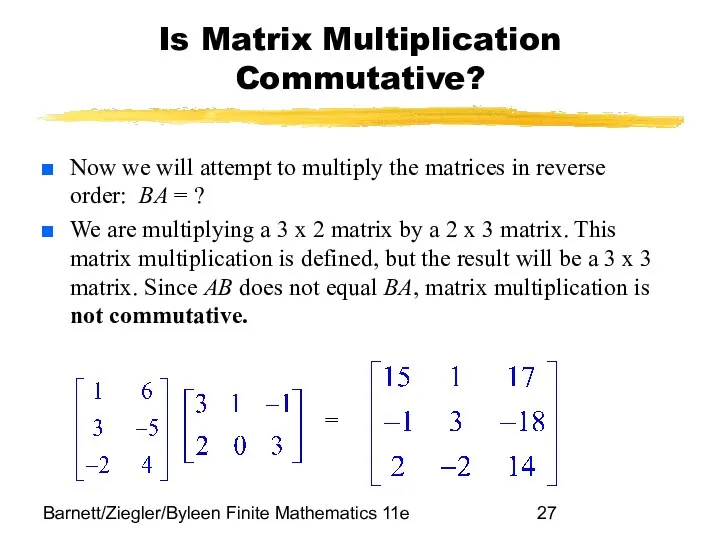
- 27. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Is Matrix Multiplication Commutative? Now we will attempt to multiply the matrices
- 28. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Finite Mathematics 11e Practical Application Suppose you a business owner and sell clothing. The following
- 30. Скачать презентацию





 Презентация на тему Второй и третий признаки подобия треугольников
Презентация на тему Второй и третий признаки подобия треугольников  ЦОР. Преобразование графиков функций
ЦОР. Преобразование графиков функций Показательные уравнения
Показательные уравнения Связь между координатами векторов и координатами точек
Связь между координатами векторов и координатами точек Деление десятичной дроби на натуральное число
Деление десятичной дроби на натуральное число Історія виникнення звичайних дробів
Історія виникнення звичайних дробів Сколько треугольников и четырехугольников изображено на картинке?
Сколько треугольников и четырехугольников изображено на картинке? Счетные множества
Счетные множества Лінійна функция, її графік
Лінійна функция, її графік Презентация по математике "Математическое образование в петровскую эпоху" - скачать
Презентация по математике "Математическое образование в петровскую эпоху" - скачать  Площадь многоугольника
Площадь многоугольника Множества. Основные понятия
Множества. Основные понятия George Boole
George Boole Определение производной
Определение производной Решение заданий по материалам ЕГЭ 2012 года. Математика (часть 3)
Решение заданий по материалам ЕГЭ 2012 года. Математика (часть 3) Аксиомы стереометрии
Аксиомы стереометрии Сумма углов треугольника
Сумма углов треугольника Презентация по математике "Задачи по математике для 4 класса" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Задачи по математике для 4 класса" - скачать бесплатно Презентация на тему Введение в логику
Презентация на тему Введение в логику  Равнобедренный треугольник
Равнобедренный треугольник Средства измерений. Классификация СИ. Метрологические характеристики средств измерений
Средства измерений. Классификация СИ. Метрологические характеристики средств измерений Соотношение между сторонами и углами прямоугольного треугольника
Соотношение между сторонами и углами прямоугольного треугольника Учебно-исследовательский проект «Логарифмы в ЕГЭ и не только…» ВЫПОЛНИЛА Николаева Анна УЧЕНИЦА 11А КЛАССА МАОУ СОШ П. ДЕМЯНСК, НОВГОРОДСКАЯ ОБЛ. УЧИТЕЛЬ МАТЕМАТИКИ
Учебно-исследовательский проект «Логарифмы в ЕГЭ и не только…» ВЫПОЛНИЛА Николаева Анна УЧЕНИЦА 11А КЛАССА МАОУ СОШ П. ДЕМЯНСК, НОВГОРОДСКАЯ ОБЛ. УЧИТЕЛЬ МАТЕМАТИКИ  Модуль числа. Противоположные числа
Модуль числа. Противоположные числа Единицы измерения длины Геометрические фигуры
Единицы измерения длины Геометрические фигуры Бифуркации динамических систем, катастрофы
Бифуркации динамических систем, катастрофы 5.Уравнение в полных дифференциалах. Интегрирующий множитель.
5.Уравнение в полных дифференциалах. Интегрирующий множитель.  Задачи на части
Задачи на части