Содержание
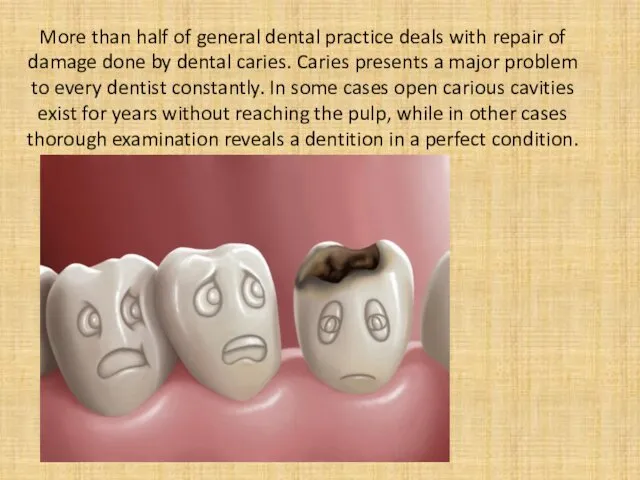
- 2. More than half of general dental practice deals with repair of damage done by dental caries.
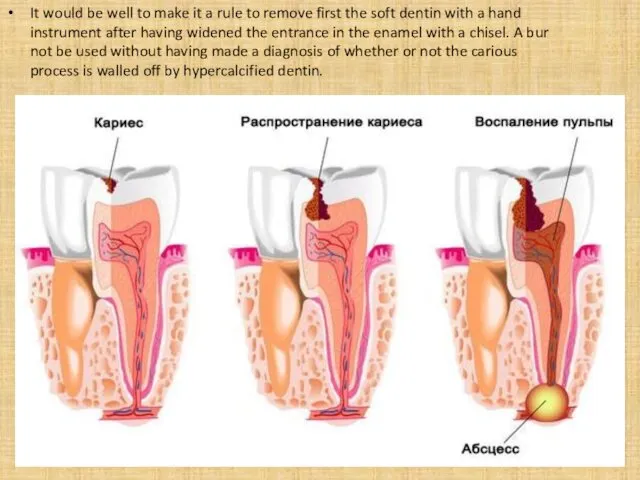
- 3. It would be well to make it a rule to remove first the soft dentin with
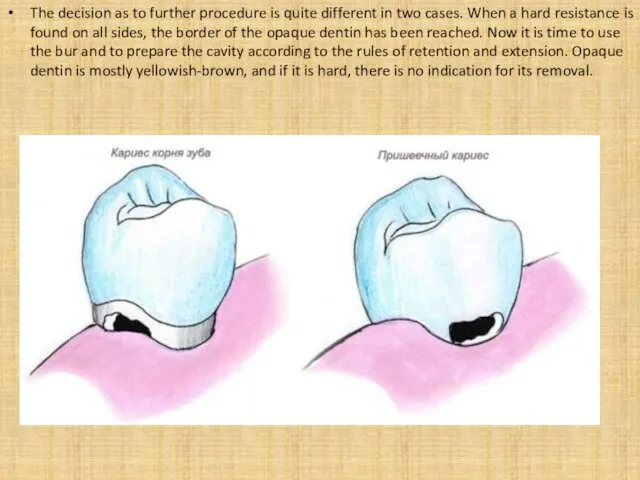
- 4. The decision as to further procedure is quite different in two cases. When a hard resistance
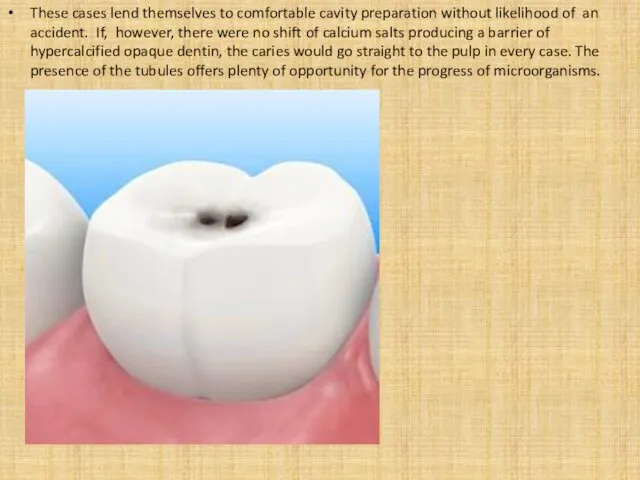
- 5. These cases lend themselves to comfortable cavity preparation without likelihood of an accident. If, however, there
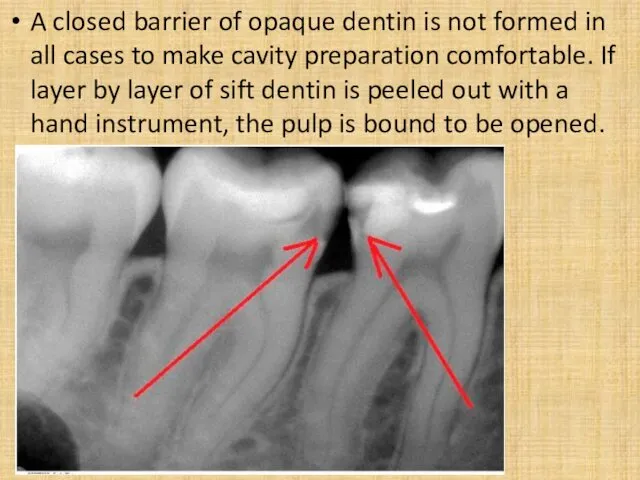
- 6. A closed barrier of opaque dentin is not formed in all cases to make cavity preparation
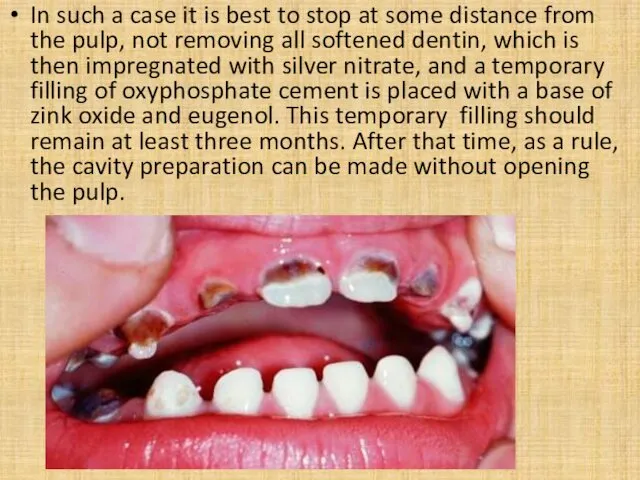
- 7. In such a case it is best to stop at some distance from the pulp, not
- 8. THE PRINCIPAL REASONS FOR RESTORING CARIOUS PRIMARY TEETH ARE: To eradicate disease and restore health. It
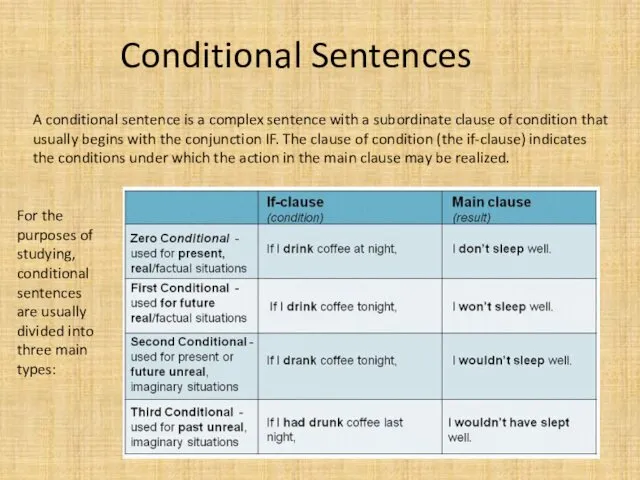
- 9. Conditional Sentences A conditional sentence is a complex sentence with a subordinate clause of condition that
- 10. First conditional Often called the "real" conditional because it is used for real or possible situations.
- 11. Second conditional Often called the "unreal" conditional because it is used for unreal impossible or improbable
- 13. Скачать презентацию



 Травма острыми предметами
Травма острыми предметами Введение в нематодологию. Диагностика неоаскариоза телят, аскариоза свиней, параскариоза лошадей
Введение в нематодологию. Диагностика неоаскариоза телят, аскариоза свиней, параскариоза лошадей Возбудители бактериальных кишечных инфекций
Возбудители бактериальных кишечных инфекций Сестринские манипуляции. Измерение и регистрация температуры тела в подмышечной области
Сестринские манипуляции. Измерение и регистрация температуры тела в подмышечной области Разработка устройства для аускультации внутренних органов
Разработка устройства для аускультации внутренних органов Теоретические основы общественного здоровья и здравоохранения
Теоретические основы общественного здоровья и здравоохранения Практика 6 Частная психопатология
Практика 6 Частная психопатология Нейропсихологическое обследование речи младших школьников
Нейропсихологическое обследование речи младших школьников Определение отеков
Определение отеков Роль медицинской сестры в соблюдении санитарно-противоэпидемического режима в условиях стационара
Роль медицинской сестры в соблюдении санитарно-противоэпидемического режима в условиях стационара Методика постановки диагноза. Основные врачебные ошибки
Методика постановки диагноза. Основные врачебные ошибки Сестринский уход за пациентами с хирургической инфекцией
Сестринский уход за пациентами с хирургической инфекцией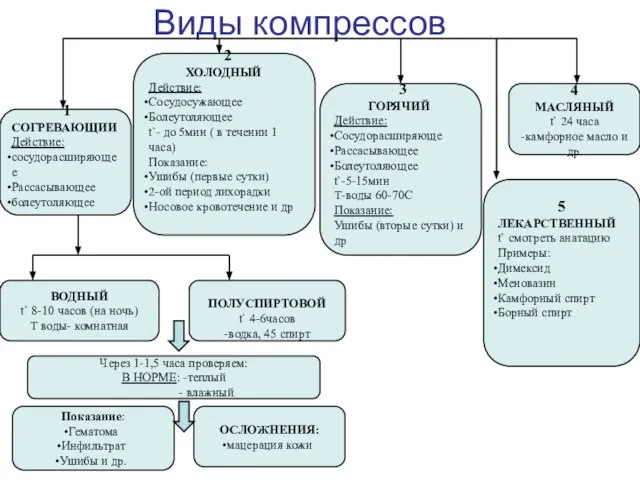 Виды компрессов
Виды компрессов Язвенный гингивит
Язвенный гингивит Травматические повреждения позвоночника
Травматические повреждения позвоночника Клинческая анестезиология
Клинческая анестезиология Лечение заболеваний крови у детей. Железодефицитная анемия. Лейкозы. Геморрагические диатезы
Лечение заболеваний крови у детей. Железодефицитная анемия. Лейкозы. Геморрагические диатезы Очищуючий крем-гель для дуже сухої, схильної до атопії шкіри
Очищуючий крем-гель для дуже сухої, схильної до атопії шкіри Гигиенический уход за кожными покровами
Гигиенический уход за кожными покровами Воспалительные заболевания гортани. Отек и стеноз гортани. (Лекция 14)
Воспалительные заболевания гортани. Отек и стеноз гортани. (Лекция 14) История развития психопатологии в России и зарубежных странах. Возникновение общей психопатологии
История развития психопатологии в России и зарубежных странах. Возникновение общей психопатологии Всё о гепатитах
Всё о гепатитах Подростковый возраст- период онтогенеза, занимающий положение между детством и юностью (от 11-12 до 15-16 лет)
Подростковый возраст- период онтогенеза, занимающий положение между детством и юностью (от 11-12 до 15-16 лет) Компьютерная томография
Компьютерная томография Аудіометрія
Аудіометрія Асқазан ішек жолдарының эрозивті жаралы зақымдануына әкелетін ықпал ететін тіс жақ аймағының аурулары
Асқазан ішек жолдарының эрозивті жаралы зақымдануына әкелетін ықпал ететін тіс жақ аймағының аурулары Заболевания склеры
Заболевания склеры Общая и частная психопатология
Общая и частная психопатология