Содержание
- 2. Introduction https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tattoo_removal#Laser_removal http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1121212-overview#a4 WHY? Recent Break-up Change in Interests Maturity Career Poor Quality
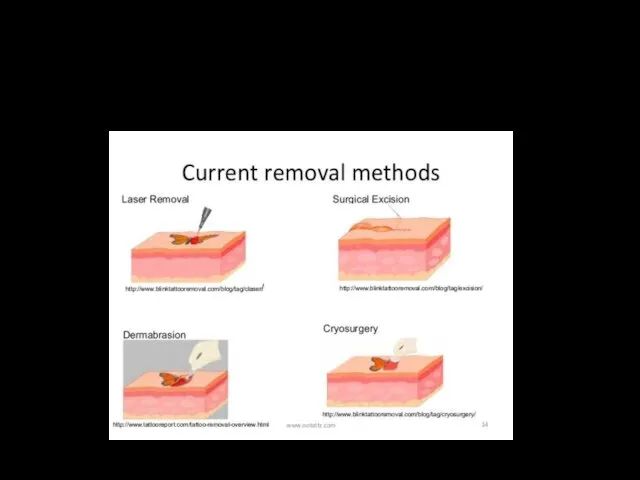
- 3. Tattoo removal Lasers have become the standard treatment for tattoo removal because they offer a bloodless,
- 4. Laser removal Laser treatment causes tattoo pigment particles to heat up and fragment into smaller pieces.
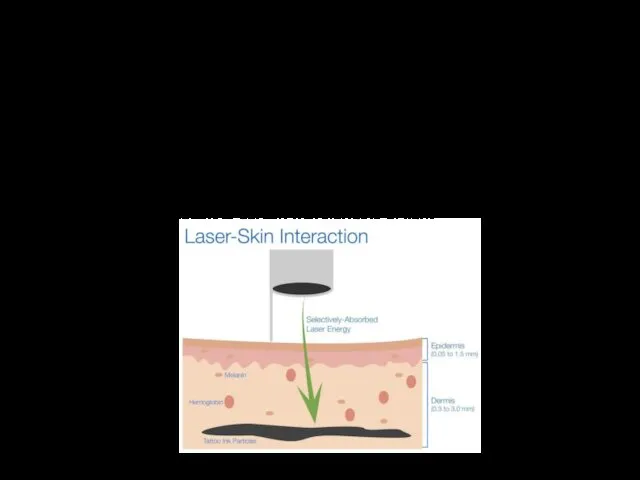
- 5. Laser-Skin-Ink interaction Properties deep ink placement melanin's ability to absorb light decreases with increasing wavelength tattoo-removing
- 6. Lasers Q-switched Frequency-doubled Nd:Yag: a green light which is highly absorbed by red and orange targets.
- 8. Скачать презентацию



 Внедрение дистанционного описания суточного мониторирования ЭКГ в Челябинской области
Внедрение дистанционного описания суточного мониторирования ЭКГ в Челябинской области Курация больных. История болезни
Курация больных. История болезни Ультразвук. Применение в медицине
Ультразвук. Применение в медицине Компьютерлік томогрфия
Компьютерлік томогрфия Ситуация по ВИЧ/СПИДу в Америке и Африке
Ситуация по ВИЧ/СПИДу в Америке и Африке Анализ приема противокашлевых и отхаркивающих средств при заболеваниях верхних дыхательных путей
Анализ приема противокашлевых и отхаркивающих средств при заболеваниях верхних дыхательных путей Мой профессиональный выбор
Мой профессиональный выбор Опухоли
Опухоли Приобретенные митральные пороки сердца
Приобретенные митральные пороки сердца Возрастные особенности психического и физического развития детей
Возрастные особенности психического и физического развития детей Интоксикация пестицидами
Интоксикация пестицидами Диагностика и лечение артериальной гипертензии. Клинические рекомендации
Диагностика и лечение артериальной гипертензии. Клинические рекомендации Виды судебно-психиатрических экспертиз
Виды судебно-психиатрических экспертиз Акушерство в средние века
Акушерство в средние века ПДБ (1) - орг. дыхания семиотика.pptx
ПДБ (1) - орг. дыхания семиотика.pptx Коронавирусная инфекция COVID-19
Коронавирусная инфекция COVID-19 ПМС. Дисменорея
ПМС. Дисменорея Курация пациентов с имплантированными кардиоустройствами: принципы и трудности
Курация пациентов с имплантированными кардиоустройствами: принципы и трудности Недоношенные дети. Сепсис новорожденных
Недоношенные дети. Сепсис новорожденных Індивідуальні зміни. Лекція 2
Індивідуальні зміни. Лекція 2 Доброкачественные и злокачественные опухоли эндокринной системы
Доброкачественные и злокачественные опухоли эндокринной системы Методическое пособие к лекциям и практическим занятиям по курсу: Морфология и анатомия человека
Методическое пособие к лекциям и практическим занятиям по курсу: Морфология и анатомия человека Дифференциальная диагностика алалии и других форм нарушений речи
Дифференциальная диагностика алалии и других форм нарушений речи Угрожающие тромбозы у детей
Угрожающие тромбозы у детей Патология почек
Патология почек Значение оптимального температурного режима как фактора профилактики заболеваний и повышения продуктивности животных
Значение оптимального температурного режима как фактора профилактики заболеваний и повышения продуктивности животных Оперативные вмешательства при внутричерепных гематомах
Оперативные вмешательства при внутричерепных гематомах Аномальды бүйректің гистоморфологиялық сипаттамасы
Аномальды бүйректің гистоморфологиялық сипаттамасы