Содержание
- 2. Physiology of Menstruation
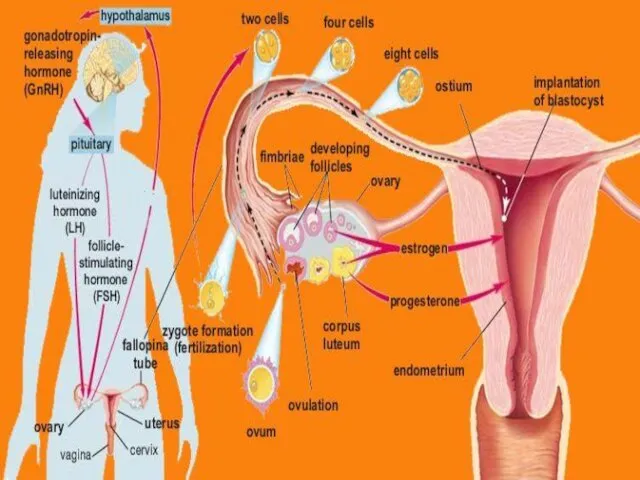
- 5. I- Onset of Puberty Due to hypothalamic maturation with insensitivity of hypothalamus to the inhibitory effect
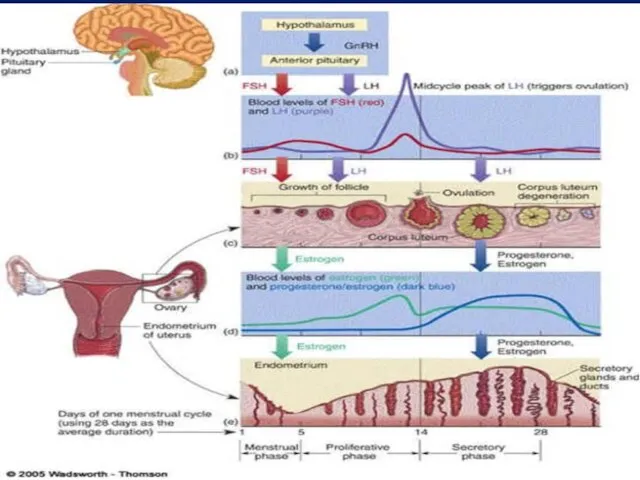
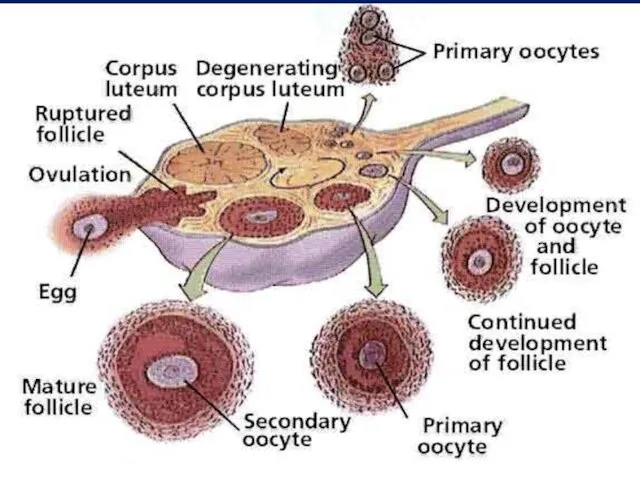
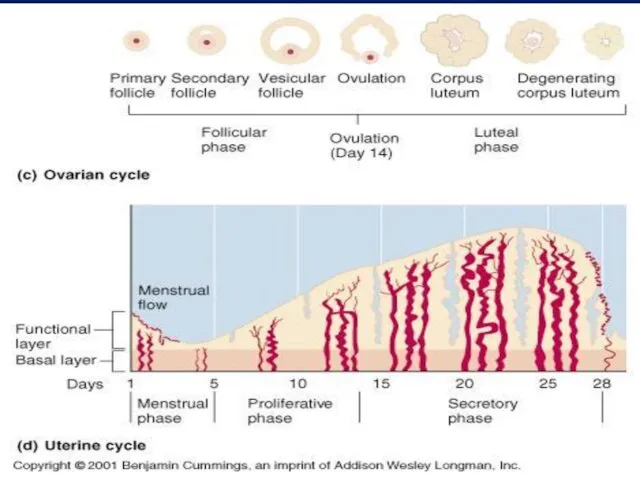
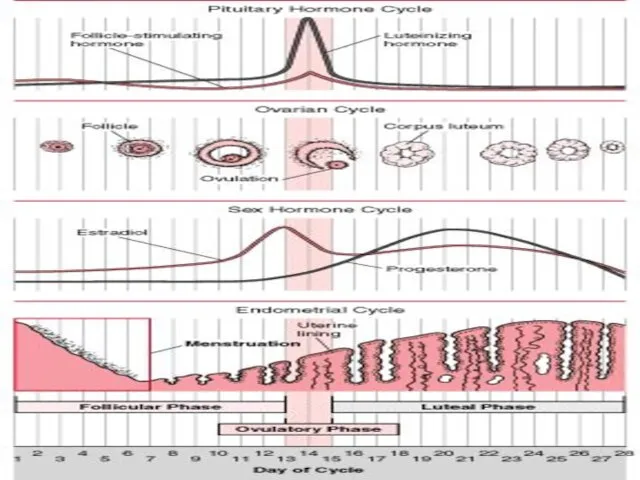
- 6. II- Ovarian Cycle 1- 1st half of the cycle (Follicular Phase): Under effect of FSH It
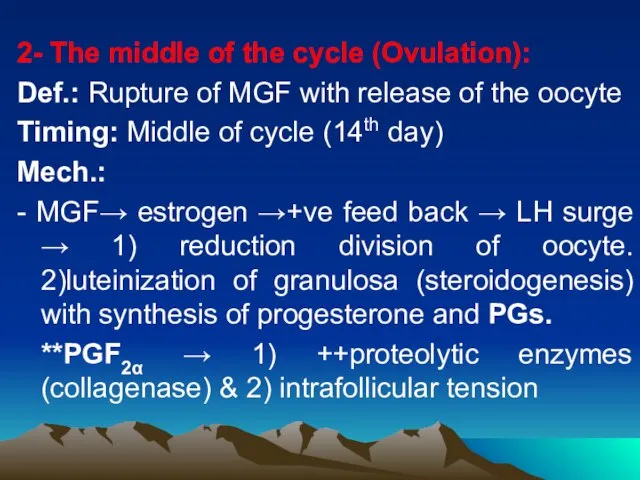
- 7. 2- The middle of the cycle (Ovulation): Def.: Rupture of MGF with release of the oocyte
- 8. 3- 2nd half of the cycle (Luteal Phase) Under effect of LH It includes: 1-Proliferation stage:
- 9. Fate of C.L.
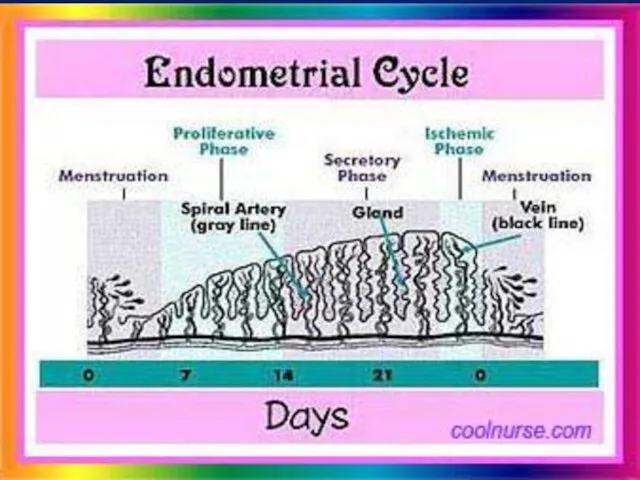
- 14. III- Changes in the endometrium
- 15. 3- Menstrual phase (Menstruation): Def.: cyclic shedding of compact and spongy endometrium Mech.: When NO pregnancy
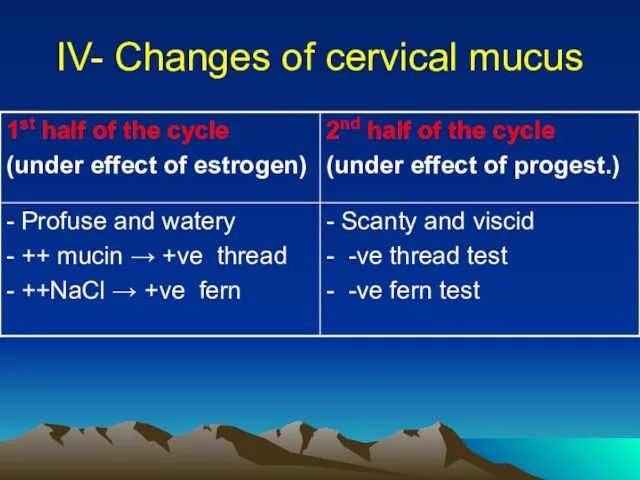
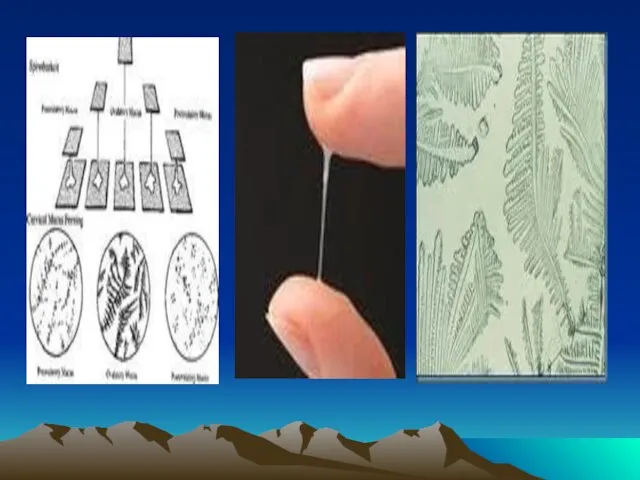
- 16. IV- Changes of cervical mucus
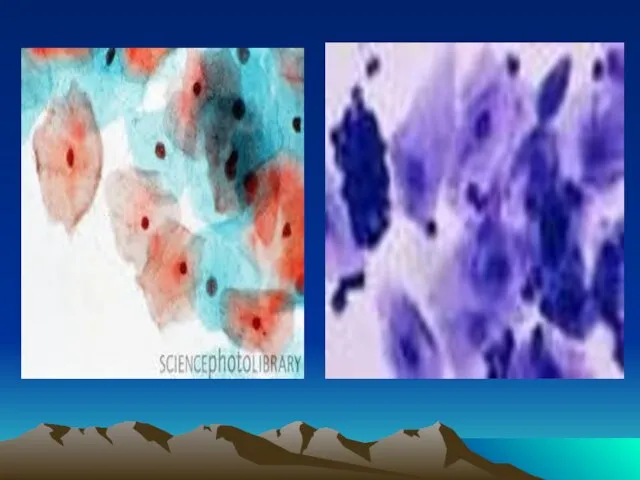
- 18. V- Changes in vaginal epithelium
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Особенности ведения больных с артериальной гипертензией в поликлинических условиях
Особенности ведения больных с артериальной гипертензией в поликлинических условиях Патологическая анатомия
Патологическая анатомия Filling’s material: permanent & temporary
Filling’s material: permanent & temporary Ранняя диагностика рака головы и шеи
Ранняя диагностика рака головы и шеи Проведение флюорографических осмотров населения
Проведение флюорографических осмотров населения Повреждения таза и тазовых органов
Повреждения таза и тазовых органов Антигены
Антигены История развития психопатологии в России и зарубежных странах
История развития психопатологии в России и зарубежных странах Аффективные нарушения психики
Аффективные нарушения психики Нарушения опорно-двигательного аппарата
Нарушения опорно-двигательного аппарата Воссоздающее и творческое воображение
Воссоздающее и творческое воображение The medical aspects of psychic development and adaptive behavior in children
The medical aspects of psychic development and adaptive behavior in children Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки
Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки Пиелонефрит беременных
Пиелонефрит беременных Антисептика түрлері. Механикалық. Физикалық. Химиялық. Биологиялық
Антисептика түрлері. Механикалық. Физикалық. Химиялық. Биологиялық Медицинская информация
Медицинская информация Тромбоэмболия у ортопедо-травматологических больных
Тромбоэмболия у ортопедо-травматологических больных Задержка психического развития
Задержка психического развития Стратегия и механизмы перехода повышения квалификации врачей в систему непрерывного медицинского образования
Стратегия и механизмы перехода повышения квалификации врачей в систему непрерывного медицинского образования Захворювання сполучної тканини
Захворювання сполучної тканини Доклад о состоянии здоровья населения и организации здравоохранения по итогам деятельности органов исполнительной власти
Доклад о состоянии здоровья населения и организации здравоохранения по итогам деятельности органов исполнительной власти Бронх демікпесі дифференциалды диагностикасы
Бронх демікпесі дифференциалды диагностикасы Анализ локального рынка лекарственных препаратов группы цефалоспоринов
Анализ локального рынка лекарственных препаратов группы цефалоспоринов Сравнительня характеристика интратекального применения ропивакаина и бупивакаина при кесаревом сечении
Сравнительня характеристика интратекального применения ропивакаина и бупивакаина при кесаревом сечении Электрокардиография
Электрокардиография Сүйектердін сынүы
Сүйектердін сынүы Травмы грудной клетки. Задание к выполнению
Травмы грудной клетки. Задание к выполнению Аттестационная работа: Роль физических упражнений в формировании правильной осанки школьников
Аттестационная работа: Роль физических упражнений в формировании правильной осанки школьников