Содержание
- 2. Diseases at which stem cells ineffective Diabetes of 1 type Cancer, oncology Cataract Glaucoma Menopause
- 3. Stem cell research in different countries: Countries colored in brown represent about 3.5 billion people, more
- 4. Interesting experiment For mice artificial appearance was cause a stroke, whereupon entered them own cells in
- 5. Advances in Stem Cell Research Mice testing have led scientists to develop an alternative way of
- 6. Stem Cells extracted from human bone marrow and then transplanted to diabetic mice has helped mice
- 8. Скачать презентацию





 Эндокринологическая аллея. Остановка Исторический музей
Эндокринологическая аллея. Остановка Исторический музей Репродуктивное здоровье – составляющая здоровья человека и общества
Репродуктивное здоровье – составляющая здоровья человека и общества Здоровый образ жизни – залог успешности специалиста
Здоровый образ жизни – залог успешности специалиста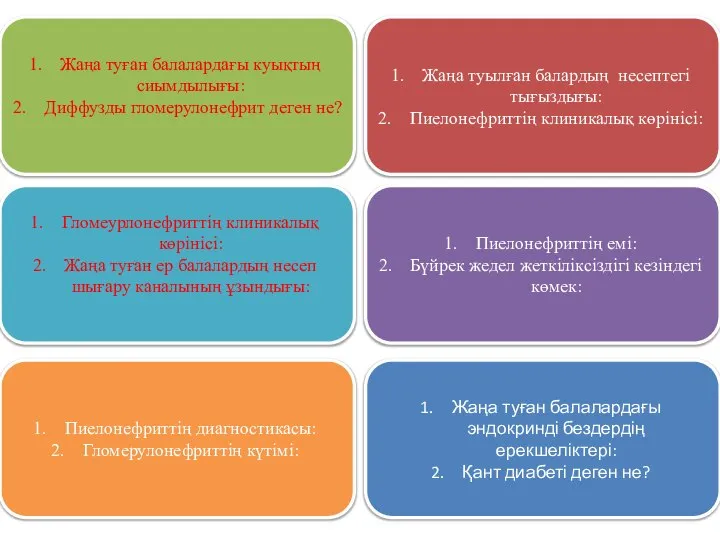 Педиатрия. Карточкалары
Педиатрия. Карточкалары Запальні захворювання органів малого тазу
Запальні захворювання органів малого тазу Туберкулез. Сепсис. Мерез
Туберкулез. Сепсис. Мерез Здоровая земля, здоровые растения и люди
Здоровая земля, здоровые растения и люди Ұрықтың туа біткен патологиясының алдын алу және ерте диагностикасы
Ұрықтың туа біткен патологиясының алдын алу және ерте диагностикасы Hendlings un zīdaiņa prasmes
Hendlings un zīdaiņa prasmes Усадка в стоматології
Усадка в стоматології Туа біткен жүрек ақаулары
Туа біткен жүрек ақаулары Организация ухода за больными кардиологического профиля
Организация ухода за больными кардиологического профиля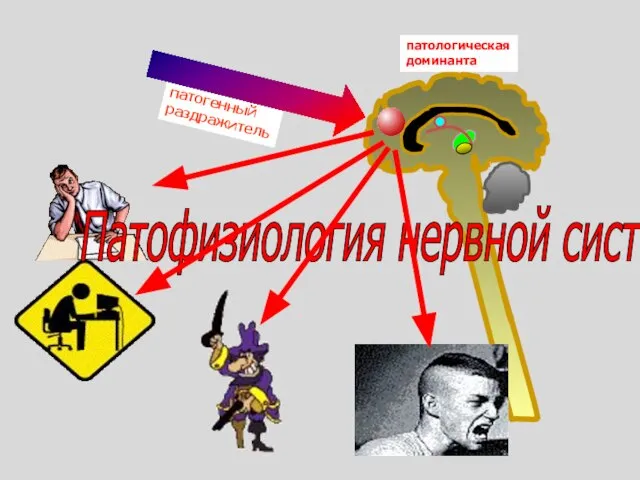 Патофизиология нервной системы
Патофизиология нервной системы Солнце, воздух и вода. Закаливание
Солнце, воздух и вода. Закаливание Роль общения в развитии личности
Роль общения в развитии личности Геморрагические лихорадки
Геморрагические лихорадки Болезнь Фабри-Андерсона: клиническая картина, диагностика, клинические наблюдения
Болезнь Фабри-Андерсона: клиническая картина, диагностика, клинические наблюдения Угрожающие тромбозы у детей
Угрожающие тромбозы у детей Влияние эмоционального стресса на здоровье полости рта
Влияние эмоционального стресса на здоровье полости рта Криза 3-х років
Криза 3-х років Ұршық буынының және санның зақымдалуы
Ұршық буынының және санның зақымдалуы Антибиотики. Классификация антибиотиков
Антибиотики. Классификация антибиотиков 3 период родов
3 период родов Передача возбуждения в холинергических синапсах
Передача возбуждения в холинергических синапсах Клинический случай острого респираторного заболевания у ребенка с некетотической гиперглицинемией
Клинический случай острого респираторного заболевания у ребенка с некетотической гиперглицинемией Клинические рекомендации по диагностике, профилактике и лечению тромбоза у детей и подростков
Клинические рекомендации по диагностике, профилактике и лечению тромбоза у детей и подростков Причины травматизма в школьном возрасте и пути их предотвращения
Причины травматизма в школьном возрасте и пути их предотвращения Понятие, признаки и виды вспомогательных репродуктивных технологий. Нормативно-правовое регулирование
Понятие, признаки и виды вспомогательных репродуктивных технологий. Нормативно-правовое регулирование